Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Voltagemultiplier 150406030541 Conversion Gate01
Voltagemultiplier 150406030541 Conversion Gate01
Uploaded by
Idris Jeffrey Manguera0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views15 pagesVoltage multipliers are AC-to-DC conversion devices made of diodes and capacitors that produce a higher DC voltage from a lower AC input. They operate in stages, with each stage containing a diode and capacitor. Common types include voltage doublers, triplers, and quadruplers, which produce outputs around twice, three times, and four times the input RMS voltage respectively. Voltage multipliers find use in applications requiring high voltage DC such as CRTs, lasers, x-rays, and electrostatic and vacuum tube systems.
Original Description:
voltage Multiplier
Original Title
Voltagemultiplier 150406030541 Conversion Gate01 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVoltage multipliers are AC-to-DC conversion devices made of diodes and capacitors that produce a higher DC voltage from a lower AC input. They operate in stages, with each stage containing a diode and capacitor. Common types include voltage doublers, triplers, and quadruplers, which produce outputs around twice, three times, and four times the input RMS voltage respectively. Voltage multipliers find use in applications requiring high voltage DC such as CRTs, lasers, x-rays, and electrostatic and vacuum tube systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views15 pagesVoltagemultiplier 150406030541 Conversion Gate01
Voltagemultiplier 150406030541 Conversion Gate01
Uploaded by
Idris Jeffrey MangueraVoltage multipliers are AC-to-DC conversion devices made of diodes and capacitors that produce a higher DC voltage from a lower AC input. They operate in stages, with each stage containing a diode and capacitor. Common types include voltage doublers, triplers, and quadruplers, which produce outputs around twice, three times, and four times the input RMS voltage respectively. Voltage multipliers find use in applications requiring high voltage DC such as CRTs, lasers, x-rays, and electrostatic and vacuum tube systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 15
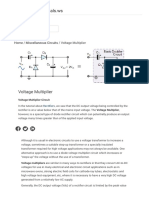
VOLTAGE MULTIPLIER
Introduction: What is a Multiplier?
• Voltage multipliers are AC-to-DC power
conversion devices, comprised of diodes and
capacitors, that produce a high potential DC
voltage from a lower voltage AC source.
Multipliers are made up of multiple stages.
Each stage is comprised of one diode and one
capacitor.
Types of voltage multiplier
Depending on the output voltage, multipliers
cajn be of different types
Voltage doublers
Voltage tipplers
Voltage quadrupler
Voltage doublers
A Voltage doubler produces a d.c. voltage
almost twice the rms value of the input a.c.
voltage.
Voltage doubler can be of two types;
Half wave voltage doubler
Full wave voltage doubler
Half wave voltage doubler
The circuit for a half wave voltage doubler.
During the positive half cycle of the secondary
voltage diode D1 conducts and D2 is cut off.
Now capacitor C1 charges to the peak
rectified voltage Vm, with polarity shown in
the figure. During the negative half cycle, the
secondary voltage comes in series with
voltage across the capacitor C1.
Contd…
Thus C2 will try to charge towards 2Vm(Vm of
the input and Vm of the capacitor C1. After
few cycles the voltage across the capacitor C2
will be equal to 2Vm Since diode D2 acts as a
short during the negative half-cycle (and
diode D1 is open), we can sum the voltages
around the outside loop. i.e;
−𝑉𝑉 − 𝑉𝑉1−𝑉𝑉2=0 (or) −𝑉𝑉 − 𝑉𝑉 −𝑉𝑉2=0
from which, 𝑉𝑉2=2𝑉𝑉
Circuit Diagram
Contd….
In the circuit capacitor C1 will discharge in the
negative half cycle. Again in the positive half
cycle, it starts charging. Thus the half wave
voltage doubler supplies the voltage to the
load in one half cycles. Therefore regulation of
the half wave voltage doubler is poor.
Full wave voltage doubler
Another voltage doubler circuit called full wave voltage
doubler is shown in fig. During the positive half cycle of
the secondary voltage diode D1conducts, charging the
capacitor the capacitor C1to the peak voltage Vm. At
this time diode D2 is non-conducting. During negative
half cycle diode D2conducts, charging capacitor C2to
Vm, with polarity as marked, while diode D2is non-
conducting. Since both capacitors C1and C2are in
series, the final output voltage is approximately 2Vm.
This circuit is called full wave voltage doubler because
one of the output capacitor is being charged during
each half cycle of the input voltage
Circuit diagram
Voltage tripler
• The voltage tripler arrangement adds another
diode/capacitor set.
• + half-cycle: C1 charges to Vp through D1,
• - half-cycle: C2 charges to 2Vp through C2,
• Next + half-cycle: C3 charges to 2Vp through
C3.
• Output is across C1 & C3.
Circuit diagram
Voltage Quadruplers
• The voltage tripler arrangement adds another
diode/capacitor set.
• + half-cycle: C1 charges to Vp through D1,
• - half-cycle: C2 charges to 2Vp through C2,
• Next + half-cycle: C3 charges to 2Vp through
C3.
• Next - half-cycle: C4 charges to 2Vp through C4
• Quadruple Output is across C2 & C4.
Circuit diagram
Common Multiplier Applications
Originally used for television CRT's, voltage
multipliers are now used for lasers, x-ray
systems, traveling wave tubes (TWT's),
photomultiplier tubes, ion pumps,
electrostatic systems, copy machines, and
many other applications that utilizehigh
voltage DC.
You might also like
- Module 6 - Communications CircuitsDocument26 pagesModule 6 - Communications CircuitsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Two-Way Power Source Chicken Egg IncubatorDocument35 pagesTwo-Way Power Source Chicken Egg IncubatorIdris Jeffrey Manguera100% (4)
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument8 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifierArun Jyothi82% (11)
- Voltagemultiplier 150406030541 Conversion Gate01Document15 pagesVoltagemultiplier 150406030541 Conversion Gate01rahabar azizNo ratings yet
- ABSTRAC1 MinDocument10 pagesABSTRAC1 MinGUMMADISANI RISHITHA 193T1A0417No ratings yet
- In Voltage Multiplier Circuit Two or More Peak Rectifiers Are Cascaded To Produce A DDocument3 pagesIn Voltage Multiplier Circuit Two or More Peak Rectifiers Are Cascaded To Produce A DAmit GargNo ratings yet
- Doubler, TriplerDocument3 pagesDoubler, TriplerARUNNo ratings yet
- Voltage Multipliers PDFDocument3 pagesVoltage Multipliers PDFlaltu adgiriNo ratings yet
- Voltage MultiplierDocument7 pagesVoltage Multiplierswarupa.23iseNo ratings yet
- Voltagemultiplier AMOSDocument3 pagesVoltagemultiplier AMOSAbhilash OSNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Voltage MultiplierDocument5 pagesLab 6 - Voltage MultiplierUmar Ali BaigNo ratings yet
- Clampers, VTG MultplrDocument7 pagesClampers, VTG MultplrTinotenda Malvern ChitenguNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document17 pagesLec 2mezo4326No ratings yet
- Voltage Multipler: Half Wave Voltage DoublerDocument3 pagesVoltage Multipler: Half Wave Voltage DoublerAshik AhmedNo ratings yet
- Voltage Multiplier and Voltage Doubler CircuitDocument8 pagesVoltage Multiplier and Voltage Doubler CircuitShashank PandeyNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Voltage Multiplier: Voltage Multipliers Are Similar in Many Ways To Rectifiers in That They ConvertDocument5 pagesFull Wave Voltage Multiplier: Voltage Multipliers Are Similar in Many Ways To Rectifiers in That They ConvertRex Albert Tejadilla100% (2)
- High Voltage Engineering: Chapter 4 Generation of High VoltagesDocument75 pagesHigh Voltage Engineering: Chapter 4 Generation of High VoltagesSunny ModiNo ratings yet
- Voltage Multipliers: Half-Wave Voltage DoublerDocument5 pagesVoltage Multipliers: Half-Wave Voltage DoublerKade Ben100% (1)
- Voltage Multiplier: Basic Electronics Dr. S.K. WijayasekaraDocument19 pagesVoltage Multiplier: Basic Electronics Dr. S.K. WijayasekaraNidushan NethsaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Clippers, Clampers & Voltage MultipliersDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Clippers, Clampers & Voltage MultipliersTarisai DoroNo ratings yet
- T3 TugasDocument15 pagesT3 TugasSri rahayuNo ratings yet
- Presentation 7Document12 pagesPresentation 7dmn 2000No ratings yet
- UNIT 1-DC Power SupplyDocument30 pagesUNIT 1-DC Power SupplyMuizz ZainolNo ratings yet
- Voltage Multiplier CircuitDocument4 pagesVoltage Multiplier Circuitnobody126100% (1)
- Unit2 HveDocument15 pagesUnit2 HveShivani ReddamNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment - 4Document16 pagesLab Report Experiment - 4Debjit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument6 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifierBilal KhanNo ratings yet
- Generation of High D.C. Voltages: Unit-IvDocument18 pagesGeneration of High D.C. Voltages: Unit-IvsrilakshmisiriNo ratings yet
- 663 - Cockcroft-Walton GeneratorDocument27 pages663 - Cockcroft-Walton GeneratorcassioalvarengaNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Votage Multilpier CircuitsDocument6 pagesLab 5 - Votage Multilpier CircuitseyobNo ratings yet
- Clipper Clamper Voltage MultiplierDocument27 pagesClipper Clamper Voltage Multiplierdeepakkapeed67% (3)
- Direct Test Voltage: - Ripple FactorDocument9 pagesDirect Test Voltage: - Ripple Factorسرحان سويد عيسىNo ratings yet
- Clipper and ClamperDocument11 pagesClipper and ClamperPoorni Jayaraman100% (1)
- Cliping & Clamping of DiodesDocument19 pagesCliping & Clamping of DiodesashutoshvashistNo ratings yet
- Full-Wave Rectifiers (Full-Wave Rectification)Document13 pagesFull-Wave Rectifiers (Full-Wave Rectification)مصطفى عدنان احمدNo ratings yet
- 6 Measurement of Ripple Factor of RectifiersDocument5 pages6 Measurement of Ripple Factor of Rectifierskarthiksubramanian940% (1)
- 1 DC Power SupplyDocument33 pages1 DC Power Supplyapolloroka33% (3)
- Voltage Tripler and Quadruples: Date: AIM: Calculate Voltage at Various Points at Voltage Multiplier Circuit. TheoryDocument2 pagesVoltage Tripler and Quadruples: Date: AIM: Calculate Voltage at Various Points at Voltage Multiplier Circuit. TheoryDharmistha VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Voltage Doubler: Navigation Search AC DC Voltage Multiplier Diodes CapacitorsDocument10 pagesVoltage Doubler: Navigation Search AC DC Voltage Multiplier Diodes CapacitorsReyne Col-iteng Reyl100% (1)
- Clamping CircuitsDocument9 pagesClamping Circuitsnikola CHECNo ratings yet
- Generation of High Voltage Using Cockcroft-Walton Voltage Multiplier CircuitDocument18 pagesGeneration of High Voltage Using Cockcroft-Walton Voltage Multiplier Circuitroute2rahulNo ratings yet
- Generation of High Voltages & CurrentsDocument79 pagesGeneration of High Voltages & CurrentshamzaNo ratings yet
- To Design A Clamper Circuit Design.: Components RequiredDocument10 pagesTo Design A Clamper Circuit Design.: Components RequiredSyed Ali Raza ShahNo ratings yet
- HV Ee20m084 PowerlabDocument10 pagesHV Ee20m084 Powerlabpallavharshvardhan27No ratings yet
- High Voltage Pspice Manual PDFDocument35 pagesHigh Voltage Pspice Manual PDFMuhammad Ahtisham AsifNo ratings yet
- Voltage MultiplierDocument3 pagesVoltage MultiplierabhishekNo ratings yet
- Voltage MultipliersDocument7 pagesVoltage MultipliersBuriro HayatNo ratings yet
- Parallel Capacitor Inverter With Feedback DiodesDocument9 pagesParallel Capacitor Inverter With Feedback DiodesJayant Kirpekar100% (1)
- Smps 1Document23 pagesSmps 1Tewodros ShegawNo ratings yet
- 2 Power Supply (Voltage Regulator) - 2Document78 pages2 Power Supply (Voltage Regulator) - 2Winter NaiNo ratings yet
- Ac Fundamnetals ManualDocument12 pagesAc Fundamnetals ManualRaj Mehra MeharNo ratings yet
- Unit II RectifiersDocument37 pagesUnit II Rectifiersdawa penjorNo ratings yet
- Diode ApplicationsDocument33 pagesDiode Applicationspransdom10No ratings yet
- EDC Lab 4Document10 pagesEDC Lab 4Z S PlaysNo ratings yet
- Module - 1 Elec NotesDocument29 pagesModule - 1 Elec Notesswarupa.23iseNo ratings yet
- Application of Diodes: RectifiersDocument16 pagesApplication of Diodes: RectifiersBangla TweaksNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Generation: S. VenkateshDocument26 pagesHigh Voltage Generation: S. Venkateshumesh0% (1)
- Astable Multivibrator Using TransistorsDocument10 pagesAstable Multivibrator Using TransistorsGangireddy SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Dual Transistor Multivariate Circuit.Document3 pagesDual Transistor Multivariate Circuit.sbpatel123No ratings yet
- Unit Iv Wave Shaping CircuitsDocument42 pagesUnit Iv Wave Shaping Circuitsyuktha venkatesanNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- ECEP 353 Quiz # 1Document1 pageECEP 353 Quiz # 1Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP353 SyllabusDocument2 pagesECEP353 SyllabusIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A243 Final Examination 2BDocument1 pageA243 Final Examination 2BIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECE313 Quiz 1 Ece 3 FDocument2 pagesECE313 Quiz 1 Ece 3 FIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A 243 MT Exam 20202021 CDocument1 pageA 243 MT Exam 20202021 CIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- 61 ECEP433 Communications 3 - Transmission Media and Antenna SystemsDocument3 pages61 ECEP433 Communications 3 - Transmission Media and Antenna SystemsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A243 Midterm ExaminationDocument1 pageA243 Midterm ExaminationIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECE313 Quiz 1 Ee 3 eDocument2 pagesECE313 Quiz 1 Ee 3 eIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- The Electronics Engineering ProfessionDocument41 pagesThe Electronics Engineering ProfessionIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A353q1 Set ADocument2 pagesA353q1 Set AIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP433 Activity 2Document1 pageECEP433 Activity 2Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP353 (Signals, Spectra, Signal Processing) Midterm ExaminationDocument1 pageECEP353 (Signals, Spectra, Signal Processing) Midterm ExaminationIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Course Code Course Title Date Effective: Date Revised: Prepared By: Approved By: Page No.Document3 pagesCourse Code Course Title Date Effective: Date Revised: Prepared By: Approved By: Page No.Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A353 (Fundamentals of Electronic Communications) Midterm ExaminationDocument1 pageA353 (Fundamentals of Electronic Communications) Midterm ExaminationIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP351L Activity 2Document1 pageECEP351L Activity 2Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- M113 Quiz 1Document1 pageM113 Quiz 1Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A353q1 Set BDocument2 pagesA353q1 Set BIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Principles of CommunicationsDocument174 pagesLecture Notes in Principles of CommunicationsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Y N X (N: ECEP 353 Quiz # 2Document1 pageY N X (N: ECEP 353 Quiz # 2Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Inertial Navigation Systems 1Document176 pagesAircraft Inertial Navigation Systems 1azarodeenNo ratings yet
- SMT Lab ManualDocument4 pagesSMT Lab Manualsurendra yadavNo ratings yet
- Datasheet - GO 8105M 5GE UVDocument2 pagesDatasheet - GO 8105M 5GE UVCaio F.No ratings yet
- Pfisterer Electrical Safety CatalogueDocument104 pagesPfisterer Electrical Safety CatalogueCorey PorterNo ratings yet
- Jumpstarter: Tire InflatorDocument32 pagesJumpstarter: Tire InflatorGio RatnaclaNo ratings yet
- Best Collection of Mouse Types - Hafeez Center Online StoreDocument3 pagesBest Collection of Mouse Types - Hafeez Center Online StoreRichardNo ratings yet
- Fusibles NH FEDERALDocument11 pagesFusibles NH FEDERALantonioNo ratings yet
- SIMS-201: What Is Bandwidth and How It Is UsedDocument25 pagesSIMS-201: What Is Bandwidth and How It Is UsedElena PocketNo ratings yet
- l2. Zen Mini 3000Document1 pagel2. Zen Mini 3000Luis AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Electrical QuantitiesDocument79 pagesElectrical QuantitiesTasnim Tabassum Promee 2031150649No ratings yet
- VW ManualDocument28 pagesVW ManualImanol SantsNo ratings yet
- IR Sensor Interfacing With ArduinoDocument9 pagesIR Sensor Interfacing With ArduinoÅň ÄñYå Ř100% (1)
- Data Sheet Transistor 2n3906Document7 pagesData Sheet Transistor 2n3906Raul EsparzaNo ratings yet
- 2 SD 716Document1 page2 SD 716Bawantha Prasad MihirangaNo ratings yet
- PCS-9705 - X - Instruction Manual - EN - Overseas General - X - R2.01 - (EN - CKZZ5395.0086.0006)Document252 pagesPCS-9705 - X - Instruction Manual - EN - Overseas General - X - R2.01 - (EN - CKZZ5395.0086.0006)Farid Hakiki100% (1)
- LP-G Surface 380 Ground Floor 80 100: Lighting Lighting Lighting SocketDocument1 pageLP-G Surface 380 Ground Floor 80 100: Lighting Lighting Lighting SocketSobhy NadaNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature of Home Security SystemDocument6 pagesReview of Related Literature of Home Security SystemafdtfgkbvNo ratings yet
- Chap 27 Advanced Machining PPT MFG Chapter27 FinalDocument42 pagesChap 27 Advanced Machining PPT MFG Chapter27 FinalnguyenhoanNo ratings yet
- Description Mechanical Dimensions: 350 Ma High Voltage Microwave Oven RectifiersDocument2 pagesDescription Mechanical Dimensions: 350 Ma High Voltage Microwave Oven Rectifierscarlos duranNo ratings yet
- Ba WNB en D10329 PDFDocument20 pagesBa WNB en D10329 PDFAmiribrahimbio AmirNo ratings yet
- Rme Pec Module 4 - Sept 2015Document2 pagesRme Pec Module 4 - Sept 2015Bianca SañezNo ratings yet
- Gaby Lau Gel55 Mae 3780 Individual Final Report Fall 2021 2Document14 pagesGaby Lau Gel55 Mae 3780 Individual Final Report Fall 2021 2api-581695353No ratings yet
- SPF-47236 A1Document6 pagesSPF-47236 A1정현우No ratings yet
- eWON COSY 141 - Installation GuideDocument20 pageseWON COSY 141 - Installation GuideSergeyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Effects 1 QPDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Effects 1 QPnssNo ratings yet
- Section 260526 - Grounding and Bonding For Electrical SystemsDocument6 pagesSection 260526 - Grounding and Bonding For Electrical SystemsVCNo ratings yet
- GCE O/L ICT Source01Document5 pagesGCE O/L ICT Source01Mohamaad SihatthNo ratings yet
- Wiring Diagram Jeep ZJ 1998Document488 pagesWiring Diagram Jeep ZJ 1998sunthron somchaiNo ratings yet
- Onn6engmanual Rdn1010321fczpfinalDocument40 pagesOnn6engmanual Rdn1010321fczpfinalsecundwonnNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide VIO 50/100 C: Necessary Operating StepsDocument2 pagesQuick Guide VIO 50/100 C: Necessary Operating StepsVu HieuNo ratings yet