Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
178 viewsMedication Template Prednisone
Medication Template Prednisone
Uploaded by
Judith MeranvilThe document discusses the medication prednisone, including its expected pharmacological actions in decreasing inflammation and suppressing the immune system. It is used for long-term management of chronic asthma and short-term management of post-exacerbation symptoms. The document outlines potential complications, administration, contraindications, nursing interventions, and patient education related to prednisone therapy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter 24-Asepsis and Infection Control Case Study - 2Document3 pagesChapter 24-Asepsis and Infection Control Case Study - 2Judith MeranvilNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Diclofenac KDocument3 pagesDrug Study Diclofenac KCarl Julienne Masangcay100% (1)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Thailand's Basic Education Core Curriculum 2551 (English Version)Document308 pagesThailand's Basic Education Core Curriculum 2551 (English Version)fatensia80% (5)
- A Drug Study On PrednisoneDocument5 pagesA Drug Study On PrednisonePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Drug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineDocument6 pagesDrug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineJelly Ong 王金玉No ratings yet
- Nursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeDocument5 pagesNursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeSophia limNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- NLM MedicatingDocument11 pagesNLM MedicatingQuimberly ModequilloNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone DrugStudyDocument8 pagesDexamethasone DrugStudySophia IbuyanNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDexamethasoneMits Valencia Karlsson0% (2)
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsElisa Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyAlexander Chavez Alto100% (1)
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 pagesCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Stan Drug StudyDocument10 pagesStan Drug StudyIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizNo ratings yet
- Group-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Document31 pagesGroup-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Hanna CarsanoNo ratings yet
- Ward6 Drug StudyDocument6 pagesWard6 Drug StudyMichael Lloyd T. SabijonNo ratings yet
- Prednisone, ZN S04Document3 pagesPrednisone, ZN S04Francesca Reyes0% (1)
- A Drug Study On: Monaliza J. Lee, RN, MNDocument6 pagesA Drug Study On: Monaliza J. Lee, RN, MNJeah Bearl AbellarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRyan BancoloNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument6 pagesDexamethasoneapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykamirure02No ratings yet
- DrugmedsDocument52 pagesDrugmedsshirleyNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsmidskiescreamzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PrednisoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study PrednisoneAMIN BARINo ratings yet
- Drug Study NRMFDocument11 pagesDrug Study NRMFKristine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNo ratings yet
- SinacDocument2 pagesSinacENo ratings yet
- Chapter 06.inddDocument23 pagesChapter 06.inddRohit AnthuliaNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument6 pagesGeneric Namewilfred_prontoNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCiprofloxacin Drug StudyRosalie Delfin90% (10)
- CiprofloxacinDocument1 pageCiprofloxacinMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- CortisoneDocument2 pagesCortisoneJulioNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument8 pagesGeneric Namemel aquinoNo ratings yet
- Pediaward NotesDocument4 pagesPediaward NotesChristie TirolNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLDocument6 pagesA Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Drug Data Generic Name: 0.5% Sodium Chloride Brand Name: Plain Natural Saline SolutionDocument10 pagesDrug Data Generic Name: 0.5% Sodium Chloride Brand Name: Plain Natural Saline SolutionHayashi Breads MaaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudysarahtotNo ratings yet
- Domperidone Uses:: Nausea and Vomiting BreastDocument6 pagesDomperidone Uses:: Nausea and Vomiting BreastAnna Charissa Arcales HoraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (GBS)Document16 pagesDrug Study (GBS)Mary Rose Verzosa LuisNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyPrincess CavestaniNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument3 pagesPrednisoneShaira TanNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy of Helminth Infections: DR - Rathnakar U.PDocument39 pagesChemotherapy of Helminth Infections: DR - Rathnakar U.PDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyjeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument7 pagesDrugs Studymcmac24No ratings yet
- MG Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMG Drug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Document40 pagesAntibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Moses MberwaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsClarence Lyndyll ToldingNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaDocument10 pagesName of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaVictor BiñasNo ratings yet
- Brand NameDocument8 pagesBrand NameChristine Joy CamachoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyLarah Mae AndogNo ratings yet
- CaseStudy DengueDocument16 pagesCaseStudy DenguexxandraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyRhanne Bolante100% (1)
- Medication Template BaclofenDocument2 pagesMedication Template BaclofenJudith MeranvilNo ratings yet
- Medication Template AntispasmoticsDocument2 pagesMedication Template AntispasmoticsJudith MeranvilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32 - Skin Integrity and Wound Care Case Study - 2Document2 pagesChapter 32 - Skin Integrity and Wound Care Case Study - 2Judith Meranvil100% (1)
- ST. KABIR SCHOOL 2020-21: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesST. KABIR SCHOOL 2020-21: Multiple Choice Questionspratyush parekhNo ratings yet
- Mavericks of The Mind - John LillyDocument14 pagesMavericks of The Mind - John LillyAmigoNo ratings yet
- Dumont Mathieu2005Document10 pagesDumont Mathieu2005Jose Alonso Aguilar ValeraNo ratings yet
- DSM 5 Update 2015 PDFDocument30 pagesDSM 5 Update 2015 PDFMilla N. HassanaNo ratings yet
- StranglesDocument30 pagesStranglesSagar KrNo ratings yet
- Chronic Hepatitis BDocument5 pagesChronic Hepatitis BMurat HessesNo ratings yet
- What Is Gene Therapy?Document2 pagesWhat Is Gene Therapy?Alister KingNo ratings yet
- Venipuncture and Health Check Vocabulary Lesson 2019Document9 pagesVenipuncture and Health Check Vocabulary Lesson 2019Bythia LouzounNo ratings yet
- G.O 395-Jun 13, 2021Document2 pagesG.O 395-Jun 13, 2021Deiva MaganNo ratings yet
- PSCPBC Infographic v8Document2 pagesPSCPBC Infographic v8PGold Goodboy Golden RupNo ratings yet
- Exploring Female Sexual Violence in GangsDocument22 pagesExploring Female Sexual Violence in GangsSamantha BakerNo ratings yet
- DICE Roadmap Colorectal Cancer Europe FINALDocument53 pagesDICE Roadmap Colorectal Cancer Europe FINALHuy Trần ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Cariotipo X Fragil y 47, XXX PDFDocument6 pagesCariotipo X Fragil y 47, XXX PDFLìzeth RamìrezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiologysushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Crypt Orchid Is MDocument29 pagesCrypt Orchid Is Mzackypradana95No ratings yet
- 24 Periop Hemodynamic Instability, Consensus, APSFDocument12 pages24 Periop Hemodynamic Instability, Consensus, APSFabsenrifkyjamalNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Analyzing A Long Dream Series What Can We Learn About How Dreaming Works 1St Edition Michael Schredl PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter Analyzing A Long Dream Series What Can We Learn About How Dreaming Works 1St Edition Michael Schredl PDFlorena.ballard933100% (5)
- M.K.Jayaraj ReportDocument176 pagesM.K.Jayaraj ReportMas Thulan100% (5)
- Discharge Planning ProjectDocument5 pagesDischarge Planning Projectapi-325271731No ratings yet
- Law Relating To Healthcare (Law570)Document5 pagesLaw Relating To Healthcare (Law570)Serena JamesNo ratings yet
- Anemia Hemolitica Congenita y Adq Ped in ReviewDocument14 pagesAnemia Hemolitica Congenita y Adq Ped in ReviewEliana LopezNo ratings yet
- NCM103L Skills Lab Unoccupied BedDocument8 pagesNCM103L Skills Lab Unoccupied BedKyla RamosNo ratings yet
- Treatment For Neurodegenerative DiseaseDocument13 pagesTreatment For Neurodegenerative Diseaseapi-250013896No ratings yet
- Home Health Education Service: Image Title Description PriceDocument18 pagesHome Health Education Service: Image Title Description PriceK. Banteilang NonglangNo ratings yet
- Prescribing, Recording and Reporting Photon Beam Therapy (Report 62)Document62 pagesPrescribing, Recording and Reporting Photon Beam Therapy (Report 62)Fang PreyNo ratings yet
- NCM 103: Skills Laboratory: LiftingDocument74 pagesNCM 103: Skills Laboratory: LiftingLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- 10 Respiratory System 2Document120 pages10 Respiratory System 2rosalyn gaboniNo ratings yet
- Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in HivDocument37 pagesImmune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Hivpokhara gharipatanNo ratings yet
- Changing Trends in Hospital CareDocument23 pagesChanging Trends in Hospital CareArchana67% (3)
Medication Template Prednisone
Medication Template Prednisone
Uploaded by
Judith Meranvil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
178 views5 pagesThe document discusses the medication prednisone, including its expected pharmacological actions in decreasing inflammation and suppressing the immune system. It is used for long-term management of chronic asthma and short-term management of post-exacerbation symptoms. The document outlines potential complications, administration, contraindications, nursing interventions, and patient education related to prednisone therapy.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the medication prednisone, including its expected pharmacological actions in decreasing inflammation and suppressing the immune system. It is used for long-term management of chronic asthma and short-term management of post-exacerbation symptoms. The document outlines potential complications, administration, contraindications, nursing interventions, and patient education related to prednisone therapy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
178 views5 pagesMedication Template Prednisone
Medication Template Prednisone
Uploaded by
Judith MeranvilThe document discusses the medication prednisone, including its expected pharmacological actions in decreasing inflammation and suppressing the immune system. It is used for long-term management of chronic asthma and short-term management of post-exacerbation symptoms. The document outlines potential complications, administration, contraindications, nursing interventions, and patient education related to prednisone therapy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
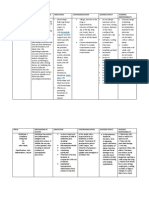
Student: Judith Meranvil
Date: 2/23/21
To be presented in Clinical
MEDICATION Prednisone
(Brand & Generic)
Expected Decreases inflammation via suppression of the migration of
Pharmacological polymorphonuclear leukocytes and reversing increased
capillary permeability. It also suppresses the immune system by
Action
reducing the activity and the volume of the immune system.
Therapeutic Use Long-term management of chronic asthma
Short-term management of post-exacerbation symptoms
(oral)
Complications Inhaled: Oral candidiasis
Oral: Suppression of adrenal function
Bone demineralization, muscle wasting
Hyperglycemia
Peptic ulcer disease
Infection
Fluid and electrolyte imbalances
Nasal: Dry mucous membranes, epistaxis, sore throat
Headache
Medication Oral:
Administration
Use oral therapy twice daily for 5 to 10 days.
For long-term use (10 days or more), take once daily using
alternate-day dosing.
Taper the dose slowly when symptoms are controlled to
establish the lowest possible oral dose.
Take supplemental doses as needed in times of stress (illness,
surgery).
Contraindications Recent live virus immunization
Systemic fungal infection
Oral candidiasis
Nursing Provide/prescribe a spacer.
Interventions
Initiate antifungal therapy as needed.
Observe for suppression of adrenal function.
Monitor plasma drug levels.
Recommend alternate-day dosing.
Monitor for signs of bone demineralization, muscle
wasting.
Recommend the lowest possible effective dose and
alternate-day dosing.
Monitor blood glucose levels, especially for clients who
have diabetes mellitus.
Recommend adjustment of dosages of
insulin/hypoglycemic drugs accordingly.
Observe for gastrointestinal bleeding (bloody vomitus;
black, tarry stools).
Implement gastric protective measures.
Give drug with food or meals.
Recommend analgesic substitute if NSAID is
prescribed.
Observe for signs of infection that may not include
fever or inflammation (sore throat, fatigue, tachycardia,
and discharge from a wound).
Recommend initiation of appropriate antimicrobial
therapy.
Monitor for weight gain or edema (hypernatremia).
Monitor for generalized weakness (hypokalemia).
Recommend initiation of appropriate fluid and
electrolyte replacement therapy.
Provide client with water and hard candy or throat
lozenges to suck on.
Provide humidified air for epistaxis and sore throat.
Administer non-NSAID analgesic such as
acetaminophen.
Client Education Use a spacer (on most glucocorticoid metered-dose
inhalers) to deposit less drug in the oropharynx.
Rinse the mouth and/or gargle after using the
glucocorticoid inhaler to prevent candidiasis.
Explain the schedule of alternate-day therapy.
Taper the dose before discontinuing it. NEVER stop
abruptly.
Take the drug on alternate days.
Perform weight-bearing exercise daily.
Consume adequate calcium and vitamin D.
Avoid taking NSAIDs.
Take the drug with food or meals.
Use a humidifier during sleep.
Increase fluid intake.
Suck on hard candy or lozenges.
Take over-the-counter, non-NSAID analgesics as
needed.
Report any of the following conditions immediately:
Polyphagia, polydipsia, and polyuria
Indigestion or bloody vomitus as well as black,
tarry stools
Signs of infection, such as a sore throat, that
may not be accompanied by fever or
inflammation
Painful mucous membranes with white patches
Weight gain or edema
Weakness
You might also like
- Chapter 24-Asepsis and Infection Control Case Study - 2Document3 pagesChapter 24-Asepsis and Infection Control Case Study - 2Judith MeranvilNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Diclofenac KDocument3 pagesDrug Study Diclofenac KCarl Julienne Masangcay100% (1)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Thailand's Basic Education Core Curriculum 2551 (English Version)Document308 pagesThailand's Basic Education Core Curriculum 2551 (English Version)fatensia80% (5)
- A Drug Study On PrednisoneDocument5 pagesA Drug Study On PrednisonePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Drug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineDocument6 pagesDrug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineJelly Ong 王金玉No ratings yet
- Nursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeDocument5 pagesNursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeSophia limNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- NLM MedicatingDocument11 pagesNLM MedicatingQuimberly ModequilloNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone DrugStudyDocument8 pagesDexamethasone DrugStudySophia IbuyanNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDexamethasoneMits Valencia Karlsson0% (2)
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsElisa Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyAlexander Chavez Alto100% (1)
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 pagesCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Stan Drug StudyDocument10 pagesStan Drug StudyIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizNo ratings yet
- Group-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Document31 pagesGroup-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Hanna CarsanoNo ratings yet
- Ward6 Drug StudyDocument6 pagesWard6 Drug StudyMichael Lloyd T. SabijonNo ratings yet
- Prednisone, ZN S04Document3 pagesPrednisone, ZN S04Francesca Reyes0% (1)
- A Drug Study On: Monaliza J. Lee, RN, MNDocument6 pagesA Drug Study On: Monaliza J. Lee, RN, MNJeah Bearl AbellarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRyan BancoloNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument6 pagesDexamethasoneapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykamirure02No ratings yet
- DrugmedsDocument52 pagesDrugmedsshirleyNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsmidskiescreamzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PrednisoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study PrednisoneAMIN BARINo ratings yet
- Drug Study NRMFDocument11 pagesDrug Study NRMFKristine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNo ratings yet
- SinacDocument2 pagesSinacENo ratings yet
- Chapter 06.inddDocument23 pagesChapter 06.inddRohit AnthuliaNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument6 pagesGeneric Namewilfred_prontoNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCiprofloxacin Drug StudyRosalie Delfin90% (10)
- CiprofloxacinDocument1 pageCiprofloxacinMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- CortisoneDocument2 pagesCortisoneJulioNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument8 pagesGeneric Namemel aquinoNo ratings yet
- Pediaward NotesDocument4 pagesPediaward NotesChristie TirolNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLDocument6 pagesA Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Drug Data Generic Name: 0.5% Sodium Chloride Brand Name: Plain Natural Saline SolutionDocument10 pagesDrug Data Generic Name: 0.5% Sodium Chloride Brand Name: Plain Natural Saline SolutionHayashi Breads MaaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudysarahtotNo ratings yet
- Domperidone Uses:: Nausea and Vomiting BreastDocument6 pagesDomperidone Uses:: Nausea and Vomiting BreastAnna Charissa Arcales HoraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (GBS)Document16 pagesDrug Study (GBS)Mary Rose Verzosa LuisNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyPrincess CavestaniNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument3 pagesPrednisoneShaira TanNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy of Helminth Infections: DR - Rathnakar U.PDocument39 pagesChemotherapy of Helminth Infections: DR - Rathnakar U.PDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyjeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument7 pagesDrugs Studymcmac24No ratings yet
- MG Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMG Drug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Document40 pagesAntibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Moses MberwaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsClarence Lyndyll ToldingNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaDocument10 pagesName of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaVictor BiñasNo ratings yet
- Brand NameDocument8 pagesBrand NameChristine Joy CamachoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyLarah Mae AndogNo ratings yet
- CaseStudy DengueDocument16 pagesCaseStudy DenguexxandraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyRhanne Bolante100% (1)
- Medication Template BaclofenDocument2 pagesMedication Template BaclofenJudith MeranvilNo ratings yet
- Medication Template AntispasmoticsDocument2 pagesMedication Template AntispasmoticsJudith MeranvilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32 - Skin Integrity and Wound Care Case Study - 2Document2 pagesChapter 32 - Skin Integrity and Wound Care Case Study - 2Judith Meranvil100% (1)
- ST. KABIR SCHOOL 2020-21: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesST. KABIR SCHOOL 2020-21: Multiple Choice Questionspratyush parekhNo ratings yet
- Mavericks of The Mind - John LillyDocument14 pagesMavericks of The Mind - John LillyAmigoNo ratings yet
- Dumont Mathieu2005Document10 pagesDumont Mathieu2005Jose Alonso Aguilar ValeraNo ratings yet
- DSM 5 Update 2015 PDFDocument30 pagesDSM 5 Update 2015 PDFMilla N. HassanaNo ratings yet
- StranglesDocument30 pagesStranglesSagar KrNo ratings yet
- Chronic Hepatitis BDocument5 pagesChronic Hepatitis BMurat HessesNo ratings yet
- What Is Gene Therapy?Document2 pagesWhat Is Gene Therapy?Alister KingNo ratings yet
- Venipuncture and Health Check Vocabulary Lesson 2019Document9 pagesVenipuncture and Health Check Vocabulary Lesson 2019Bythia LouzounNo ratings yet
- G.O 395-Jun 13, 2021Document2 pagesG.O 395-Jun 13, 2021Deiva MaganNo ratings yet
- PSCPBC Infographic v8Document2 pagesPSCPBC Infographic v8PGold Goodboy Golden RupNo ratings yet
- Exploring Female Sexual Violence in GangsDocument22 pagesExploring Female Sexual Violence in GangsSamantha BakerNo ratings yet
- DICE Roadmap Colorectal Cancer Europe FINALDocument53 pagesDICE Roadmap Colorectal Cancer Europe FINALHuy Trần ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Cariotipo X Fragil y 47, XXX PDFDocument6 pagesCariotipo X Fragil y 47, XXX PDFLìzeth RamìrezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiologysushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Crypt Orchid Is MDocument29 pagesCrypt Orchid Is Mzackypradana95No ratings yet
- 24 Periop Hemodynamic Instability, Consensus, APSFDocument12 pages24 Periop Hemodynamic Instability, Consensus, APSFabsenrifkyjamalNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Analyzing A Long Dream Series What Can We Learn About How Dreaming Works 1St Edition Michael Schredl PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter Analyzing A Long Dream Series What Can We Learn About How Dreaming Works 1St Edition Michael Schredl PDFlorena.ballard933100% (5)
- M.K.Jayaraj ReportDocument176 pagesM.K.Jayaraj ReportMas Thulan100% (5)
- Discharge Planning ProjectDocument5 pagesDischarge Planning Projectapi-325271731No ratings yet
- Law Relating To Healthcare (Law570)Document5 pagesLaw Relating To Healthcare (Law570)Serena JamesNo ratings yet
- Anemia Hemolitica Congenita y Adq Ped in ReviewDocument14 pagesAnemia Hemolitica Congenita y Adq Ped in ReviewEliana LopezNo ratings yet
- NCM103L Skills Lab Unoccupied BedDocument8 pagesNCM103L Skills Lab Unoccupied BedKyla RamosNo ratings yet
- Treatment For Neurodegenerative DiseaseDocument13 pagesTreatment For Neurodegenerative Diseaseapi-250013896No ratings yet
- Home Health Education Service: Image Title Description PriceDocument18 pagesHome Health Education Service: Image Title Description PriceK. Banteilang NonglangNo ratings yet
- Prescribing, Recording and Reporting Photon Beam Therapy (Report 62)Document62 pagesPrescribing, Recording and Reporting Photon Beam Therapy (Report 62)Fang PreyNo ratings yet
- NCM 103: Skills Laboratory: LiftingDocument74 pagesNCM 103: Skills Laboratory: LiftingLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- 10 Respiratory System 2Document120 pages10 Respiratory System 2rosalyn gaboniNo ratings yet
- Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in HivDocument37 pagesImmune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Hivpokhara gharipatanNo ratings yet
- Changing Trends in Hospital CareDocument23 pagesChanging Trends in Hospital CareArchana67% (3)