Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 02: 100km/hr and V
ENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 02: 100km/hr and V
Uploaded by
manoliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 02: 100km/hr and V
ENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 02: 100km/hr and V
Uploaded by
manoliCopyright:
Available Formats
ENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 02
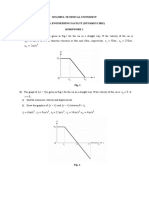
1. A roller coaster carriage starts from rest at A and moves along the rails ABCD.
The carriage has a uniform acceleration of 6m/s2 as it moves down sections AB
and CD and its velocity is constant between B and C. If the velocity of the
carriage at D is 30m/s, then determine: (a) The distance d between C and D. (b)
The total time lapsed for the carriage to reach D. (c) The initial carriage speed if
the same conditions apply, however, it now reaches C in 4.5 seconds. (d = 45m, t
= 7.64s, vA = 8.18m/s).
2. Two cars A and B are approaching each other in adjacent highway lanes. At t = 0,
A and B are 1 km apart with speeds of vA = 100km/hr and vB = 70km/hr. If A
passes the point where B was at t = 0 in 44sec and B passes the point where A was
at t = 0 in 40 seconds, determine (a) the uniform accelerations of vehicles A and B,
(b) when the vehicles pass each other and (c) the speed of B at that time.
(aA = -0.229m/s2, aB = 0.277m/s2, t = 20.9s, vB = 25.24m/s).
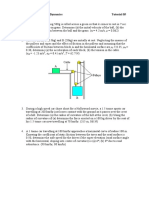
3. Blocks A and B are connected over a series of pulleys by an inextensible cable as
shown. Block B starts from rest and moves downwards with a constant
acceleration. Knowing that after slider block A has moved 600mm its velocity is
6m/s, determine (a) the accelerations of A and B, (b) the velocity and change in
position of B after 1 second and (c) the velocity of A after 1 second. (aA = 30m/s2,
aB = 10m/s2, vB = 10m/s, xB = 5m, vA = 30m/s).
You might also like
- Rectilinear Motion: Variable AccelerationDocument11 pagesRectilinear Motion: Variable AccelerationKavita DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3, From N-T Upto ConstrainedDocument4 pagesWorksheet 3, From N-T Upto Constrainedhemengebeyehu862No ratings yet
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 1 (Chapter 1)Document3 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 1 (Chapter 1)Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document5 pagesTutorial 2Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (Chapter 11a)Document2 pagesTutorial 1 (Chapter 11a)EcoliNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document3 pagesHomework 1sara MartinezNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 DynamicsDocument2 pagesProblem Set 2 DynamicsKent Edve Neil Rabe0% (2)
- Numericals Class - IX TMHDocument80 pagesNumericals Class - IX TMHSohan Yadav69% (29)
- Assignment 1 PDFDocument10 pagesAssignment 1 PDFYoussef AbdelhamidNo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Physics - Motion in A Straight LineDocument23 pagesClass 11 - Physics - Motion in A Straight LineM KumarNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument3 pagesHomeworkUriel CadenaNo ratings yet
- Final Mech 2 2015-2016Document2 pagesFinal Mech 2 2015-2016Saleh KettanNo ratings yet
- IX Phy Kinematics QB Gaurav Kukreja FinalDocument11 pagesIX Phy Kinematics QB Gaurav Kukreja FinalAditya ParuiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 SolutionDocument10 pagesTutorial 1 SolutionSu YiNo ratings yet
- Crash Class Xi Test No. 3Document2 pagesCrash Class Xi Test No. 3Kamran AliNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 1Document5 pagesKinematics 1deepaknitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - WorksheetDocument11 pagesChapter 2 - WorksheetHenokNo ratings yet
- 20202021-01 Test 1 QuestionsDocument3 pages20202021-01 Test 1 QuestionsParamoda TriangleNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight LineDocument20 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight LineDhananjay JoshiNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument4 pagesProblem SetJULLIANA VILORIANo ratings yet
- Kinematics P ME KNM 04 08Document3 pagesKinematics P ME KNM 04 08Raghav MishraNo ratings yet
- 11th DPP 1D Kinematic-1Document5 pages11th DPP 1D Kinematic-1SaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- CE222 Problem Set 1Document6 pagesCE222 Problem Set 1Mehmet ArasNo ratings yet
- 1 Unit DynamicsDocument4 pages1 Unit DynamicsmanojNo ratings yet
- Emch 212 Final Exam SP 2020 Typed - M - CDocument7 pagesEmch 212 Final Exam SP 2020 Typed - M - CRajib BaruaNo ratings yet
- Emch 212 Final Exam SP 2020 Typed - MDocument7 pagesEmch 212 Final Exam SP 2020 Typed - MRajib BaruaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Motion in Straight LineDocument21 pagesCH 3 Motion in Straight LineZeel ShahNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 Dynamics Acceleration Velocity PDFDocument2 pagesProblem Set 2 Dynamics Acceleration Velocity PDFJershey MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Problems On Trains-FormulaeDocument2 pagesProblems On Trains-Formulaesai pranayNo ratings yet
- Mech PsetDocument7 pagesMech PsetJomel JazminNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument10 pagesDynamics of Rigid BodiesJohn Michael SalasNo ratings yet
- Motion in Straight Line Level 1Document3 pagesMotion in Straight Line Level 1cimfam2008No ratings yet
- DPP 2Document5 pagesDPP 2RAJ RUPALINo ratings yet
- MCHE-213 Assignment IDocument8 pagesMCHE-213 Assignment IAbed BaalbakiNo ratings yet
- Practice Test. MotionDocument3 pagesPractice Test. MotionsatyamheykarNo ratings yet
- Important Formulas For Train Problem AptitudesDocument3 pagesImportant Formulas For Train Problem AptitudesAsok KumarNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: 1. B. 2s 2. A. 3km/h 3. B. Zero 4. D. 6sDocument7 pagesAnswer Key: 1. B. 2s 2. A. 3km/h 3. B. Zero 4. D. 6sRakeshNo ratings yet
- Prob Set 2Document2 pagesProb Set 2salvadortobitoNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 ME31003 SolutionDocument10 pagesAssignment1 ME31003 Solution吳心No ratings yet
- X KM/HR XX 5: Points To RememberDocument15 pagesX KM/HR XX 5: Points To Rememberkiran_y2No ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument17 pagesUnit IImansikakaniNo ratings yet
- Problems On Trains For CLAT 2013: Important FormulasDocument5 pagesProblems On Trains For CLAT 2013: Important FormulasAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 ExerciceMechanics Part1 QuestionDocument8 pagesUSTH B1 ExerciceMechanics Part1 QuestionCó Tên KhôngNo ratings yet
- NCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 03 Motion in A Straight LineDocument26 pagesNCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 03 Motion in A Straight LineBhagyaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics - Question PaperDocument10 pagesKinematics - Question PaperRishi GargNo ratings yet
- TES - Basic SUVAT QuestionsDocument1 pageTES - Basic SUVAT QuestionsDataDen Pro Account 2No ratings yet
- Class Exercise: Page 1 of 7Document7 pagesClass Exercise: Page 1 of 7Tanishq BarejaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet I - Kinematics of ParticlesDocument7 pagesWorksheet I - Kinematics of ParticlesAdnan ShafiNo ratings yet
- Physics WorksheetDocument15 pagesPhysics Worksheetrosh naNo ratings yet
- Problem Set2 DynamicsDocument2 pagesProblem Set2 DynamicsSonrim JunioNo ratings yet
- ENGN 37 HomeworkDocument25 pagesENGN 37 HomeworkLucia AntoniusNo ratings yet
- Problems On TrainDocument3 pagesProblems On Trainvj kumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document5 pagesTutorial 1lokezhengyan22No ratings yet
- Tarea 1 de DinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 1 de DinamicaMelany Elizabeth BarriosNo ratings yet
- Beacon Actvi 3rd Chapter Addition of VectorsDocument8 pagesBeacon Actvi 3rd Chapter Addition of VectorsshoaibNo ratings yet
- Numericals On Equations of MotionDocument3 pagesNumericals On Equations of MotionDiya sashiniNo ratings yet
- Numericals Class IX TMHDocument80 pagesNumericals Class IX TMHMr. JocularNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersFrom EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Tutorial - AS1684 - Using - Span - Tables - 7 - 14Document37 pagesTopic 2 - Tutorial - AS1684 - Using - Span - Tables - 7 - 14manoliNo ratings yet
- ENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 05Document1 pageENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 05manoliNo ratings yet
- ENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 04: be θ = (2n+1) π, n = 0, 1, 2…)Document1 pageENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 04: be θ = (2n+1) π, n = 0, 1, 2…)manoliNo ratings yet
- + 6t - 5t - 3t + 10, Where T Is In: ENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 01Document1 page+ 6t - 5t - 3t + 10, Where T Is In: ENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 01manoliNo ratings yet
- ENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 03Document1 pageENG105 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial 03manoliNo ratings yet