Professional Documents
Culture Documents
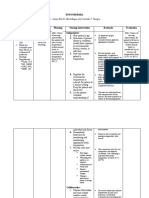
Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan
Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Julianne B. Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Deadly Deception - Robert WillnerDocument303 pagesDeadly Deception - Robert Willnerleocarvalho001_60197100% (6)
- Department of Molecular Virology: COVID-19 (Corona) VirusDocument1 pageDepartment of Molecular Virology: COVID-19 (Corona) VirusMuhammad AreebNo ratings yet
- NCP FeverDocument3 pagesNCP Feversinister1785% (48)
- NCP HypothermiaDocument2 pagesNCP HypothermiaJohn Paolo Ocampo100% (3)
- Nurse Practitioner Board ReviewFrom EverandNurse Practitioner Board ReviewRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Essential Intrapartum and Newborn Care (EINC)Document26 pagesEssential Intrapartum and Newborn Care (EINC)Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Intellectual RevolutionsDocument2 pagesIntellectual RevolutionsJulianne B. Dela Cruz89% (19)
- Fever NCPDocument5 pagesFever NCPNikael Patun-ogNo ratings yet
- NCP LeptospirosisDocument2 pagesNCP LeptospirosisLouise Anne Asuncion OclimaNo ratings yet
- Low Birth WeightDocument22 pagesLow Birth Weightエド パジャロン100% (4)
- Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Home VisitDocument5 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Home VisitJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Clinic VisitDocument6 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Clinic VisitJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Cumitech 41 - Detection and Prevention of Clinical Microbiology Laboratory-Associated ErrorsDocument16 pagesCumitech 41 - Detection and Prevention of Clinical Microbiology Laboratory-Associated ErrorsAnjali MohanNo ratings yet
- Case Pres (NCP-Hyperthermia)Document2 pagesCase Pres (NCP-Hyperthermia)Trixia DiazNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesHyperthermiapamgee100% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentKristine Young67% (3)
- Toxoplasmosis - Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesToxoplasmosis - Nursing Care PlanJulia Trisha MasukolNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument2 pagesHyperthermia NCPmahangin85% (20)
- Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal & Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal & Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationLP BenozaNo ratings yet
- Chona NCP 2Document3 pagesChona NCP 2Jan Mark SotoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationAlyssa Moutrie Dulay Arabe100% (1)
- NCP - NewbornDocument4 pagesNCP - NewbornVinzii DrtNo ratings yet
- Case Study Ii Nursing Assessment of Patients and FamiliesDocument3 pagesCase Study Ii Nursing Assessment of Patients and FamiliesEti JuniaNo ratings yet
- Gender: FemaleDocument9 pagesGender: FemaleNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLODocument4 pagesHyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLOMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAkiraMamoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPTroy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentMoi Valdoz100% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Askep Bahasa Inggris Pnemonia 2Document6 pagesAskep Bahasa Inggris Pnemonia 2Ni Putu AngelinaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- NCP For Swine FluDocument3 pagesNCP For Swine FluGiana CalloNo ratings yet
- B NCP On and Off Fever 2b ImproveddocxDocument6 pagesB NCP On and Off Fever 2b ImproveddocxKylie CatralNo ratings yet
- Herpes NCPDocument3 pagesHerpes NCPSanny L Asim Jr.No ratings yet
- NCP Sugaton HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNCP Sugaton HyperthermiaPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Hypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. DungcaDocument2 pagesHypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. DungcaJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Child Nursing CareDocument3 pagesChild Nursing Carelina solihanNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCP ActualDocument3 pagesCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNo ratings yet
- NCP Sample 1Document9 pagesNCP Sample 1Vincent BarcenillaNo ratings yet
- Garcia Jomari A. BSN 2h Kawa-NcpDocument6 pagesGarcia Jomari A. BSN 2h Kawa-NcpRaid GarciaNo ratings yet
- Subjective: DX:: Case: Systemic InfectionDocument2 pagesSubjective: DX:: Case: Systemic InfectionMheaye JheaaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationWinnie AriolaNo ratings yet
- NCP Neonatal HypothermiaDocument2 pagesNCP Neonatal HypothermiaMarjorie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia Related To Dengue Fever As Evidenced by Temperature Above The Normal RangeDocument2 pagesHyperthermia Related To Dengue Fever As Evidenced by Temperature Above The Normal RangeAlyssa marieNo ratings yet
- NCP - Chicken PoxDocument4 pagesNCP - Chicken Poxhanna_lim0% (1)
- SNU49Document2 pagesSNU49Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- Ncp. HyperDocument2 pagesNcp. HyperZmiaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Inggris Askep - Ririsudaeni23Document7 pagesTugas Inggris Askep - Ririsudaeni23Riris Udaeni RNo ratings yet
- Nicu NCPDocument2 pagesNicu NCPYette Polillo Conde100% (1)
- NCP Fever FinalDocument3 pagesNCP Fever FinalAllyssa Jane PragadosNo ratings yet
- Physio ThermoregulationDocument9 pagesPhysio ThermoregulationStd DlshsiNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP 1 HyperthermiaBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanChriss Una PacamalanNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 Elevated Boy TempDocument2 pagesNCP 1 Elevated Boy TempDudong SasakiNo ratings yet
- FNP Prelims Reviewer PDFDocument29 pagesFNP Prelims Reviewer PDFJOSHUA TORRICERNo ratings yet
- SNU49Document2 pagesSNU49Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- Lung CenterDocument4 pagesLung CenterNylia AtibiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan On HyperthermiaAleah JayaganNo ratings yet
- NCP 3Document2 pagesNCP 3FitzLucario QueNo ratings yet
- The Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseFrom EverandThe Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Living Systems Information Therapy LSIT: Introduction to Quantum MedicineFrom EverandLiving Systems Information Therapy LSIT: Introduction to Quantum MedicineNo ratings yet
- Hypothermia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypothermia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Soak It In: Hydrotherapy Treatments In 20 Minutes or Less for Health and BeautyFrom EverandSoak It In: Hydrotherapy Treatments In 20 Minutes or Less for Health and BeautyNo ratings yet
- Thermometer TechniqueDocument6 pagesThermometer TechniqueJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Bag Technique: Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1Document5 pagesBag Technique: Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Food AdvertisementDocument1 pageFood AdvertisementJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument12 pagesNursing Care During LaborJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Basketball: Vision: Mission: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesBasketball: Vision: Mission: ObjectivesJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MMDST FormDocument3 pagesMMDST FormJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Notions of Development That May Evolve Into ScientismDocument2 pagesNotions of Development That May Evolve Into ScientismJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Administering Opthalmic MedicationsDocument6 pagesAdministering Opthalmic MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Historical Antecedents in The Course of Science and TechnologyDocument1 pageHistorical Antecedents in The Course of Science and TechnologyJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Administering Intradermal MedicationsDocument4 pagesAdministering Intradermal MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument1 pageHealth Teaching PlanJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument10 pagesNursing Care During LaborAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Patient P / Room No. 415 - 1Document3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Patient P / Room No. 415 - 1Julianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument12 pagesNursing Care During LaborJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Partograph UseDocument8 pagesPartograph UseJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (2)
- APGAR Scoring and Ballard's Assessment ToolDocument2 pagesAPGAR Scoring and Ballard's Assessment ToolJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of Systems: Involuntarily Blinking Pink ConjunctivaDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of Systems: Involuntarily Blinking Pink ConjunctivaJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1 Endorsement NotesDocument1 page1 Endorsement NotesJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument9 pagesHealth Teaching PlanJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Histolytica) Vaginalis) Brucei) Donovani)Document2 pagesHistolytica) Vaginalis) Brucei) Donovani)Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Administering Opthalmic MedicationsDocument6 pagesAdministering Opthalmic MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PDF TextDocument1 pagePDF TextSarthak ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Ocular Mycoses CMRDocument69 pagesOcular Mycoses CMRDewi Masyithah DarlanNo ratings yet
- TQ For 1st Quarter Practical Research 1Document3 pagesTQ For 1st Quarter Practical Research 1Kee Jay Pondoc100% (1)
- Fix PPT Penyakit Kambing DombaDocument52 pagesFix PPT Penyakit Kambing DombaGaluh EnggarNo ratings yet
- IATA-Infectious Substance ClassificationDocument5 pagesIATA-Infectious Substance ClassificationMor NgomNo ratings yet
- Caregiving 9 - Maintain A Clean and Hygienic EnvironmentDocument24 pagesCaregiving 9 - Maintain A Clean and Hygienic EnvironmentKATHRYN ALFONSONo ratings yet
- Betta Fish Diseases and Care TipsDocument33 pagesBetta Fish Diseases and Care TipsAna Irina CrînganuNo ratings yet
- MHA Syllabus CorrectedDocument69 pagesMHA Syllabus Correctedமாணிக்கவாசகம் பூஜாNo ratings yet
- PMWeb SlideShowDocument74 pagesPMWeb SlideShowLuther BlissettNo ratings yet
- The Big Six PathogensDocument3 pagesThe Big Six PathogensJennifer CollinsNo ratings yet
- Essay-Use of ForceDocument3 pagesEssay-Use of ForceChinmaya MadanNo ratings yet
- Bacte Sample QuestionDocument45 pagesBacte Sample QuestionpikachuNo ratings yet
- 14 Amazing Natural Antibiotics Mechanisms & Side EffectsDocument26 pages14 Amazing Natural Antibiotics Mechanisms & Side EffectsGuillermoNo ratings yet
- Replacement Study On The Potency Test of Anti-Rabies Immunoglobulin in ChinaDocument7 pagesReplacement Study On The Potency Test of Anti-Rabies Immunoglobulin in ChinaGhanta Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- The Dynamics of Staphylococcus Epidermis Biofilm Formation in Relation To Nutrition, Temperature, and TimeDocument6 pagesThe Dynamics of Staphylococcus Epidermis Biofilm Formation in Relation To Nutrition, Temperature, and TimeMohamed Amine MekniNo ratings yet
- 542-Shredder or Grinder Maintenance Checks - SOP-finalDocument11 pages542-Shredder or Grinder Maintenance Checks - SOP-finalphuyangNo ratings yet
- Breaking Bad NewsDocument26 pagesBreaking Bad News8625g8xmbpNo ratings yet
- Covid EssayDocument2 pagesCovid EssayThant Htet SintNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Pts Bahasa Inggris Kelas X Semester GenapDocument8 pagesLatihan Soal Pts Bahasa Inggris Kelas X Semester GenapAllisa MasithaNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography Graphic OrganizerDocument4 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Graphic Organizerapi-348035481No ratings yet
- MeaslesDocument1 pageMeaslesDavid HylandNo ratings yet
- Biofilm in OtorhinolaryngologyDocument10 pagesBiofilm in OtorhinolaryngologyMohammed SahibNo ratings yet
- Counselling For Lifelong DiseasesDocument111 pagesCounselling For Lifelong Diseasesersavenu249No ratings yet
- NcpsDocument10 pagesNcpskotoirNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Mikroorganisme Dengan SanitasiDocument31 pagesHubungan Mikroorganisme Dengan SanitasiAlbar PervectNo ratings yet
- Didier Montet, R.C. Ray - Aquaculture Microbiology and Biotechnology, Vol. 1 (2009, Science Publishers) PDFDocument274 pagesDidier Montet, R.C. Ray - Aquaculture Microbiology and Biotechnology, Vol. 1 (2009, Science Publishers) PDFMst Pany100% (1)
- Measles: The New Red Scare: by Oman YstrianykDocument20 pagesMeasles: The New Red Scare: by Oman YstrianykManuel AlbaNo ratings yet
Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan
Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Julianne B. Dela CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan
Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Julianne B. Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
NURSING CARE PLAN
Identified Problem: Decreased body temperature
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for hypothermia related to immaturity of newborn’s temperature regulatory system
CUES OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Short term objectives: Short term:
No data available 1. Establish rapport 1. To promote cooperation
Within 8 hours of providing 2. Provide therapeutic environment 2. To provide comfort After 8 hours of providing nursing
nursing care, patient’s body interventions, patient’s body
temperature will rise from 3. Monitor patient’s vital signs every hour 3. To establish baseline data temperature has started to rise.
36.3°C above STO is partially met
4. Regulate the environment temperature 4. To provide comfort to
or relocate the patient to a warmer patient
setting.
5. Keep patient dry and wrapped in blanket; 5. To prevent heat loss
Objective: keep the head covered with a cap
V/S taken as follows: 6. Control the heat source according to the 6. Body temperature should
T:36.3°C, patient’s physical response be raised no more than a
PR: 153 bpm, few degrees per hour.
SPO2 95% with 02 Vasodilation occurs as the
RR: 60 cpm patient’s core temperature
Long term objectives: increases leading to a Long term:
Cool skin decrease in BP.
Within 1 day of providing Hypotension, metabolic After 1 day of providing nursing
Anthropometric Measurements: nursing care, the patient’s core acidosis, and dysrhythmias interventions, the patient’s core
Height: 54cm body temperature will rise to are complications of body temperature is above
36.5°C but not higher than rewarming. 36.5°C but not higher than 37.5°C
HC: 34 cm
37.5°C 7. Explain procedures to patient’s SO or 7. To understand the LTO is met
CC: 32 cm
mother interventions done to the
AC: 30cm patient and to avoid
MAC:13 cm confusion
8. Encourage mother to hold baby for skin 8. Ways to stabilize the
to skin contact newborns body
temperature include placing
the infant directly on the
mother’s abdomen
Collaborative: Collaborative:
1. Restore/maintain core temperature 1. Client may require
within client’s normal range. May refer to interventions to treat
NDs Hypothermia hypothermia
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 1
NURSING CARE PLAN
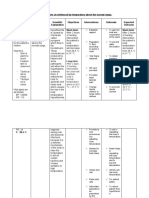
Identified Problem: Risk for Infection
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Infection related to neonatal immune system
CUES OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 2
Subjective: Short term objectives: Independent: Short term:
No data available
1. Establish rapport 1. To promote cooperation
Within an hour, patient will After an hour, patient has
demonstrate a 2. Provide therapeutic environment 2. To provide comfort demonstrated a meticulous hand
meticulous hand washing technique. STO is met
washing technique. 3. Monitor for signs and symptoms of 3. Signs and symptoms of
infection infection vary according to
the body area involved.
4. Ensure that any articles used are 4. This reduces or eliminates
properly disinfected or sterilized before germs.
Objective: use
-Pt’s Mother did not have any
prenatal check-ups. 5. Wash hands or perform hand hygiene 5. Friction and running water
-Skin is cracking pale with rare before having contact with the patient. effectively remove
veins Also impart these duties to the patient microorganisms from
-vital signs taken as follows: and their significant others. Know the hands. Washing between
T:36.3C instances when to perform hand hygiene procedures reduces the
PR: 153 bpm or “5 moments for hand hygiene”: risk of transmitting
RR: 60 cpm pathogens from one area of
SPO2 95% with 02 Before touching a patient the body to another. Wash
Long term objectives: Before clean or aseptic hands with antiseptic soap Long term:
procedure (wound dressing, and water for at least 15
Patient will remain free of starting an IV, etc) seconds followed by Patient remains free of infection,
infection After body fluid exposure alcohol-based hand rub. If as evidenced by normal vital
After touching a patient hands were not in contact signs and absence of signs and
After touching the patiend’s with anyone or anything in symptoms of infection. LTO is met
surroundings the room, use an alcohol-
based hand rub and rub
until dry. Plain soap is good
at reducing bacterial counts
but antimicrobial soap is
better, and alcohol-based
hand rubs are the best.
6. Educate clients and SO about 6. Knowledge of ways to
appropriate methods for cleaning, reduce or eliminate germs
disinfecting, and sterilizing items reduces the likelihood of
transmission.
7. Perform measures to break the chain of 7. The following methods help
infection and prevent infection break the chain of infection,
and prevent conditions that
may be suitable for
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 3
microbial growth:
1. Change dressing and
bandages that are soiled or
wet.
2. Assist clients in carrying
out appropriate skin and
oral hygiene.
3. Dispose of soiled linens
properly.
4. Ensure all fluid
containers are covered or
capped.
5. Avoid talking, coughing,
or sneezing over open
wounds or sterile fields.
6. Wear gloves when
handling patient secretions.
7. Instruct clients to
perform hand hygiene
when handling food or
eating.
8. Limit visitors 8. Restricting visitation
reduces the transmission of
pathogens.
9. Provide surgical masks to visitors who 9. Educating visitors on the
are coughing and provide rationale to importance of preventing
enforce usage. Instruct visitors to cover droplet transmission from
mouth and nose (by using the elbows to themselves to others
cover) during coughing or sneezing; use reduces the risk of
of tissues to contain respiratory infection.
secretions with immediate disposal to a
no-touch receptacle; perform hand
hygiene afterward.
10. Place the patient in protective isolation if 10. Protective isolation is set
the patient is at high risk of infection. when the WBC indicates
neutropenia.
11. Teach the importance of avoiding 11. Other people can spread
contact with individuals who have infections or colds to a
infections or colds. Teach the importance susceptible patient (e.g.,
of physical distancing. immunocompromised)
through direct contact,
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 4
contaminated objects, or
through air currents.
Dependent:
12. Crede's prophylaxis (Tetracyline 1%, 12. represented a tremendous
Erythromycin 0.5%) ointment OU step forward in the
prevention of inflammatory
eye disease in newborns in
the late 19th century.
13. Vitamin K (Phytonadione) 0.1ml (10mg) 13. Low levels of vitamin K can
IM at vastus lateralis, right lead to
dangerous bleeding in
newborns and infants. The
vitamin K given at birth
provides protection
against bleeding that could
occur because of low levels
of this essential vitamin.
14. Hepatitis B Vaccine 0.5 ml IM @ vastus 14. They will be protected as
lateralis, left early as possible from any
exposure to the hepatitis
B virus
15. BCG Vaccine (dose: 0.05 ml) ID @ R 15. Helps your child’s immune
deltoid system fight the germs that
cause TB and helps stop
them from getting serious
TB disease.
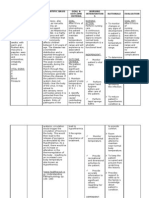
Identified Problem: Ineffective Infant Breastfeeding
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective infant breastfeeding related to poor sucking reflex of the patient
CUES OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 5
Subjective: Short term objectives: Independent Short term:
“Gasakit akoang tahi kung Within 8 hours of providing 1. Established rapport 1. To promote cooperation After 8 hours of providing
mangihi ko” nursing care, the patient nursing care, the patient was
will able: 2. Provide privacy 2. Breastfeeding needs to take able to improve his suckling
“Dili ko kamao mutambal sa -To improve his sucking reflex place in a setting where the reflex and intake breast milk
akoang samad” as verbalized during breastfeeding. mother of the infant is able to properly due to improved
by the patient. freely feed her baby. breastfeeding practices and
-To improve the mother and techniques.
infant’s breastfeeding 3. Explain to the mother the process and 3. It will let the mother to have a
practices and techniques. importance of breastfeeding. Include the better understanding on the
. health benefits to both mother and her benefits of breastfeeding. It will
child motivate them to achieve their
goal.
4. It will let the mother and baby to
Objective: 4. Explain the correct positioning of the have a successful breastfeeding Long term:
mother and infant during breastfeeding through correct positioning. This
Inability of the patient Long term objectives: by demonstrating the proper technique. will prevent disruption of the After 3 days of providing
to suck/swallow process. nursing care, the patient was
effectively is noted Within 7 days of providing able to intake adequate
nursing care, the patient will 5. Proper positioning of the infant breast milk and gain proper
Poor sucking with his be able to manifests signs of 5. Check the infant’s ability to grasp the during breastfeeding aids in the nutrition as evidenced by
mom’s breast cries adequate improvement in his areola of the breast with his lips, tongue success of the infant to patient’s steady weight gain,
immediately and breast milk intake and gain and jaw. breastfeed form his mother. pass more urine several
looked uncomfortable proper nutrition. times a day, color of his stool
with the position. 6. To aid the infant in maintaining a is converted to dark yellow,
successful breastfeeding. sleeping peacefully for a
6. Check the infant’s ability to suck breast longer duration
milk 7. This will prevent disruption of the
breastfeeding process and
promote successful infant
Vital Signs: 7. Promote relaxation and comfort during feeding.
T: 36.3C breastfeeding process. Provide a calm,
PR: 153bpm quiet and non-stimulating environment
RR: 60cpm while feeding.
SPO2 95% with O2
8. Reinforces that feeding time is
pleasurable and enhances
8. Recommend for infant sucking on a digestion.
regular basis
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 6
Collaborative 9. It will prevent interference with
proper feeding pattern and so as
1. Refer the mother and new born to the to maintain infant’s proper
attending physician if there is an unusual nutrition.
symptom during breastfeeding.
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 7
You might also like
- Deadly Deception - Robert WillnerDocument303 pagesDeadly Deception - Robert Willnerleocarvalho001_60197100% (6)
- Department of Molecular Virology: COVID-19 (Corona) VirusDocument1 pageDepartment of Molecular Virology: COVID-19 (Corona) VirusMuhammad AreebNo ratings yet
- NCP FeverDocument3 pagesNCP Feversinister1785% (48)
- NCP HypothermiaDocument2 pagesNCP HypothermiaJohn Paolo Ocampo100% (3)
- Nurse Practitioner Board ReviewFrom EverandNurse Practitioner Board ReviewRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Essential Intrapartum and Newborn Care (EINC)Document26 pagesEssential Intrapartum and Newborn Care (EINC)Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Intellectual RevolutionsDocument2 pagesIntellectual RevolutionsJulianne B. Dela Cruz89% (19)
- Fever NCPDocument5 pagesFever NCPNikael Patun-ogNo ratings yet
- NCP LeptospirosisDocument2 pagesNCP LeptospirosisLouise Anne Asuncion OclimaNo ratings yet
- Low Birth WeightDocument22 pagesLow Birth Weightエド パジャロン100% (4)
- Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Home VisitDocument5 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Home VisitJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Clinic VisitDocument6 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Clinic VisitJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Cumitech 41 - Detection and Prevention of Clinical Microbiology Laboratory-Associated ErrorsDocument16 pagesCumitech 41 - Detection and Prevention of Clinical Microbiology Laboratory-Associated ErrorsAnjali MohanNo ratings yet
- Case Pres (NCP-Hyperthermia)Document2 pagesCase Pres (NCP-Hyperthermia)Trixia DiazNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesHyperthermiapamgee100% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentKristine Young67% (3)
- Toxoplasmosis - Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesToxoplasmosis - Nursing Care PlanJulia Trisha MasukolNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument2 pagesHyperthermia NCPmahangin85% (20)
- Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal & Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal & Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationLP BenozaNo ratings yet
- Chona NCP 2Document3 pagesChona NCP 2Jan Mark SotoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationAlyssa Moutrie Dulay Arabe100% (1)
- NCP - NewbornDocument4 pagesNCP - NewbornVinzii DrtNo ratings yet
- Case Study Ii Nursing Assessment of Patients and FamiliesDocument3 pagesCase Study Ii Nursing Assessment of Patients and FamiliesEti JuniaNo ratings yet
- Gender: FemaleDocument9 pagesGender: FemaleNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLODocument4 pagesHyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLOMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAkiraMamoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPTroy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentMoi Valdoz100% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Askep Bahasa Inggris Pnemonia 2Document6 pagesAskep Bahasa Inggris Pnemonia 2Ni Putu AngelinaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- NCP For Swine FluDocument3 pagesNCP For Swine FluGiana CalloNo ratings yet
- B NCP On and Off Fever 2b ImproveddocxDocument6 pagesB NCP On and Off Fever 2b ImproveddocxKylie CatralNo ratings yet
- Herpes NCPDocument3 pagesHerpes NCPSanny L Asim Jr.No ratings yet
- NCP Sugaton HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNCP Sugaton HyperthermiaPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Hypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. DungcaDocument2 pagesHypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. DungcaJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Child Nursing CareDocument3 pagesChild Nursing Carelina solihanNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCP ActualDocument3 pagesCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNo ratings yet
- NCP Sample 1Document9 pagesNCP Sample 1Vincent BarcenillaNo ratings yet
- Garcia Jomari A. BSN 2h Kawa-NcpDocument6 pagesGarcia Jomari A. BSN 2h Kawa-NcpRaid GarciaNo ratings yet
- Subjective: DX:: Case: Systemic InfectionDocument2 pagesSubjective: DX:: Case: Systemic InfectionMheaye JheaaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationWinnie AriolaNo ratings yet
- NCP Neonatal HypothermiaDocument2 pagesNCP Neonatal HypothermiaMarjorie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia Related To Dengue Fever As Evidenced by Temperature Above The Normal RangeDocument2 pagesHyperthermia Related To Dengue Fever As Evidenced by Temperature Above The Normal RangeAlyssa marieNo ratings yet
- NCP - Chicken PoxDocument4 pagesNCP - Chicken Poxhanna_lim0% (1)
- SNU49Document2 pagesSNU49Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- Ncp. HyperDocument2 pagesNcp. HyperZmiaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Inggris Askep - Ririsudaeni23Document7 pagesTugas Inggris Askep - Ririsudaeni23Riris Udaeni RNo ratings yet
- Nicu NCPDocument2 pagesNicu NCPYette Polillo Conde100% (1)
- NCP Fever FinalDocument3 pagesNCP Fever FinalAllyssa Jane PragadosNo ratings yet
- Physio ThermoregulationDocument9 pagesPhysio ThermoregulationStd DlshsiNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP 1 HyperthermiaBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanChriss Una PacamalanNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 Elevated Boy TempDocument2 pagesNCP 1 Elevated Boy TempDudong SasakiNo ratings yet
- FNP Prelims Reviewer PDFDocument29 pagesFNP Prelims Reviewer PDFJOSHUA TORRICERNo ratings yet
- SNU49Document2 pagesSNU49Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- Lung CenterDocument4 pagesLung CenterNylia AtibiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan On HyperthermiaAleah JayaganNo ratings yet
- NCP 3Document2 pagesNCP 3FitzLucario QueNo ratings yet
- The Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseFrom EverandThe Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Living Systems Information Therapy LSIT: Introduction to Quantum MedicineFrom EverandLiving Systems Information Therapy LSIT: Introduction to Quantum MedicineNo ratings yet
- Hypothermia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypothermia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Soak It In: Hydrotherapy Treatments In 20 Minutes or Less for Health and BeautyFrom EverandSoak It In: Hydrotherapy Treatments In 20 Minutes or Less for Health and BeautyNo ratings yet
- Thermometer TechniqueDocument6 pagesThermometer TechniqueJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Bag Technique: Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1Document5 pagesBag Technique: Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Food AdvertisementDocument1 pageFood AdvertisementJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument12 pagesNursing Care During LaborJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Basketball: Vision: Mission: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesBasketball: Vision: Mission: ObjectivesJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MMDST FormDocument3 pagesMMDST FormJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Notions of Development That May Evolve Into ScientismDocument2 pagesNotions of Development That May Evolve Into ScientismJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Administering Opthalmic MedicationsDocument6 pagesAdministering Opthalmic MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Historical Antecedents in The Course of Science and TechnologyDocument1 pageHistorical Antecedents in The Course of Science and TechnologyJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Administering Intradermal MedicationsDocument4 pagesAdministering Intradermal MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument1 pageHealth Teaching PlanJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument10 pagesNursing Care During LaborAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Patient P / Room No. 415 - 1Document3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Patient P / Room No. 415 - 1Julianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument12 pagesNursing Care During LaborJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Partograph UseDocument8 pagesPartograph UseJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (2)
- APGAR Scoring and Ballard's Assessment ToolDocument2 pagesAPGAR Scoring and Ballard's Assessment ToolJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of Systems: Involuntarily Blinking Pink ConjunctivaDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of Systems: Involuntarily Blinking Pink ConjunctivaJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1 Endorsement NotesDocument1 page1 Endorsement NotesJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument9 pagesHealth Teaching PlanJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Histolytica) Vaginalis) Brucei) Donovani)Document2 pagesHistolytica) Vaginalis) Brucei) Donovani)Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Administering Opthalmic MedicationsDocument6 pagesAdministering Opthalmic MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PDF TextDocument1 pagePDF TextSarthak ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Ocular Mycoses CMRDocument69 pagesOcular Mycoses CMRDewi Masyithah DarlanNo ratings yet
- TQ For 1st Quarter Practical Research 1Document3 pagesTQ For 1st Quarter Practical Research 1Kee Jay Pondoc100% (1)
- Fix PPT Penyakit Kambing DombaDocument52 pagesFix PPT Penyakit Kambing DombaGaluh EnggarNo ratings yet
- IATA-Infectious Substance ClassificationDocument5 pagesIATA-Infectious Substance ClassificationMor NgomNo ratings yet
- Caregiving 9 - Maintain A Clean and Hygienic EnvironmentDocument24 pagesCaregiving 9 - Maintain A Clean and Hygienic EnvironmentKATHRYN ALFONSONo ratings yet
- Betta Fish Diseases and Care TipsDocument33 pagesBetta Fish Diseases and Care TipsAna Irina CrînganuNo ratings yet
- MHA Syllabus CorrectedDocument69 pagesMHA Syllabus Correctedமாணிக்கவாசகம் பூஜாNo ratings yet
- PMWeb SlideShowDocument74 pagesPMWeb SlideShowLuther BlissettNo ratings yet
- The Big Six PathogensDocument3 pagesThe Big Six PathogensJennifer CollinsNo ratings yet
- Essay-Use of ForceDocument3 pagesEssay-Use of ForceChinmaya MadanNo ratings yet
- Bacte Sample QuestionDocument45 pagesBacte Sample QuestionpikachuNo ratings yet
- 14 Amazing Natural Antibiotics Mechanisms & Side EffectsDocument26 pages14 Amazing Natural Antibiotics Mechanisms & Side EffectsGuillermoNo ratings yet
- Replacement Study On The Potency Test of Anti-Rabies Immunoglobulin in ChinaDocument7 pagesReplacement Study On The Potency Test of Anti-Rabies Immunoglobulin in ChinaGhanta Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- The Dynamics of Staphylococcus Epidermis Biofilm Formation in Relation To Nutrition, Temperature, and TimeDocument6 pagesThe Dynamics of Staphylococcus Epidermis Biofilm Formation in Relation To Nutrition, Temperature, and TimeMohamed Amine MekniNo ratings yet
- 542-Shredder or Grinder Maintenance Checks - SOP-finalDocument11 pages542-Shredder or Grinder Maintenance Checks - SOP-finalphuyangNo ratings yet
- Breaking Bad NewsDocument26 pagesBreaking Bad News8625g8xmbpNo ratings yet
- Covid EssayDocument2 pagesCovid EssayThant Htet SintNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Pts Bahasa Inggris Kelas X Semester GenapDocument8 pagesLatihan Soal Pts Bahasa Inggris Kelas X Semester GenapAllisa MasithaNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography Graphic OrganizerDocument4 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Graphic Organizerapi-348035481No ratings yet
- MeaslesDocument1 pageMeaslesDavid HylandNo ratings yet
- Biofilm in OtorhinolaryngologyDocument10 pagesBiofilm in OtorhinolaryngologyMohammed SahibNo ratings yet
- Counselling For Lifelong DiseasesDocument111 pagesCounselling For Lifelong Diseasesersavenu249No ratings yet
- NcpsDocument10 pagesNcpskotoirNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Mikroorganisme Dengan SanitasiDocument31 pagesHubungan Mikroorganisme Dengan SanitasiAlbar PervectNo ratings yet
- Didier Montet, R.C. Ray - Aquaculture Microbiology and Biotechnology, Vol. 1 (2009, Science Publishers) PDFDocument274 pagesDidier Montet, R.C. Ray - Aquaculture Microbiology and Biotechnology, Vol. 1 (2009, Science Publishers) PDFMst Pany100% (1)
- Measles: The New Red Scare: by Oman YstrianykDocument20 pagesMeasles: The New Red Scare: by Oman YstrianykManuel AlbaNo ratings yet