Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Psych
NCP Psych
Uploaded by
Scarlet0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views7 pagesThe patient was experiencing auditory hallucinations and delusional thoughts related to schizophrenia. Through nursing interventions like frequent contact, focusing on feelings rather than details of hallucinations, engaging in reality-based activities, and setting clear limits and structure, the goals were for the patient to be able to recognize sensory impairments and delusional thoughts, identify external stressors contributing to alterations, and eventually not respond to hallucinatory commands and experience a cessation of hallucinations. After initial interventions the patient was able to recognize impairments and modify some stressors, showing partial achievement of goals.
Original Description:
a
Original Title
NCP-psych
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe patient was experiencing auditory hallucinations and delusional thoughts related to schizophrenia. Through nursing interventions like frequent contact, focusing on feelings rather than details of hallucinations, engaging in reality-based activities, and setting clear limits and structure, the goals were for the patient to be able to recognize sensory impairments and delusional thoughts, identify external stressors contributing to alterations, and eventually not respond to hallucinatory commands and experience a cessation of hallucinations. After initial interventions the patient was able to recognize impairments and modify some stressors, showing partial achievement of goals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views7 pagesNCP Psych
NCP Psych
Uploaded by
ScarletThe patient was experiencing auditory hallucinations and delusional thoughts related to schizophrenia. Through nursing interventions like frequent contact, focusing on feelings rather than details of hallucinations, engaging in reality-based activities, and setting clear limits and structure, the goals were for the patient to be able to recognize sensory impairments and delusional thoughts, identify external stressors contributing to alterations, and eventually not respond to hallucinatory commands and experience a cessation of hallucinations. After initial interventions the patient was able to recognize impairments and modify some stressors, showing partial achievement of goals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
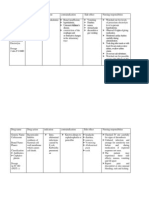
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term:
Disturbed auditory Although the etiology &
“Yun, may narinig sensory perception pathogenesis have not After 3 weeks of nursing - Help present and maintain Presenting reality is healthy Goal Fully Achieved
akong trials (but related to anxiety been fully determined, here intervention, the patient reality by frequent contact and for the client (1) After hour of nursing intervention,
actually no one said associated with multiple are some etiologies: will be able to communication with the client the client was able to recognize and
the word trials), stressors as evidenced Stressful life circumstances, 1.Recognize and correct/compensate for sensory
ganun na nga yun by auditory hallucination. genetic & biochemical correct/compensate for - Elicit description of The nurse’s understanding impairments.
kasi trials and defects, & brain damage in sensory impairments. hallucination to protect client of hallucination helps her Identify/modify 2/3 external factors
know how to calm or
challenges are just the fetus by prenatal 2. Identify/modify 2/3 and others. like stress and effects of
reassure the client (1)
the same.” as stated complications or viral external factors that medications, which contribute to
infection contribute to alterations alterations in sensory/perceptual
Close observation of the
Objective Data: in sensory/perceptual -Keep client in a safe, client with active abilities.
Reduced gray matter in the abilities. protected, restricted hallucinations in a secure
Diagnosed with temporal lobes environment. Avoid excessive environment is essential to Recommendation:
Paranoid activity and stimulation maintain safety of the client Terminate the Plan
Schizophrenia Abnormal cells in the & others. Excessive sensory
Auditory stimulation could overwhelm Discharge Outcome:
hippocampus (part of the
hallucination and agitate the client.
limbic system) Discharge Outcome:
Exaggerated
-Focus on the feelings about, Outcome Fully Achieved;
emotional Focusing on the client’s
responses Excessive dopamine After months or upon rather than details of, the feelings, which are real, Upon discharge, the client was able
Impaired secretions discharge, the client will hallucination. minimizes emphasis on the to not respond to hallucinatory
communication be able to 1. Not hallucination. commands, and hallucinations will
Poor concentration Enlarged third and lateral respond to hallucinatory subside. The client reported a
ventricles commands, and - Do not argue with the client Arguing with the client or decrease in, and eventually the total
hallucinations will about whether the expressing disbelief in the cessation of hallucinations. And the
subside. hallucinations are real; state, if hallucinations does not client was free from injury
Decreased blood flow to the 2. Be free form injury. asked, that you do not affect the client’s belief in
frontal lobes perceive the auditory stimuli the reality of the Recommendation:
that the client perceives. hallucination and can disrupt Terminate the Plan
trust & the therapeutic rel.
Abnormalities of neuro-
Expressing that you not hear
transmitters and neuro- the hallucinatory stimuli
endocrine systems. indirectly encourages him to
question the reality of the
Sensory overload and experience.
hyperarousal. Collaborative:
Auditory hallucination - Engage client in reality- To achieved maximal gains
based activities such as card in function and psychosocial
playing, occupational therapy, well-being
Reference: or listening to music.
Reference: (1) Psychiatric-
Pathophysiology for the Mental Health Nursing 5th
Health Professions 3rd Edition by Sheila L. Videbeck
Edition by Barbara E. Gould page 268
Page 588-589 (2) Psychiatric-Mental Health
Nursing by Mohr page 650
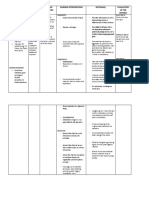
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term:
Disturbed thought Although the etiology &
“I really don’t process related to pathogenesis have not After 3 weeks of nursing - Be consistent in setting Clear, consistent limits Goal Partially Achieved
understand my father. presence of been fully determined, here intervention, the patient expectation, enforcing rules, provide a secure structure After hour of nursing intervention, the
Why can’t he psychological conflicts are some etiologies: will be able to and so forth for the client client was able to
understand me? Hindi (delusion of persecutory) Stressful life circumstances, 1. Verbalize recognition 1. Verbalize recognition of delusional
niya maappreciate as evidenced by impaired genetic & biochemical of delusional thoughts if - Do not make promises that Broken promises reinforce thoughts if they persist.
yung work ko. Is it ability to problem solve defects, & brain damage in they persist. you cannot keep. the client’s mistrust of other 2. Respond to reality-based
ingenuity or and disordered thought the fetus by prenatal 2. Respond to reality- interactions initiated by others; for
creativity? Dalawang sequencing. complications or viral based interactions - Recognize the client’s Recognizing the client’s example, verbally interact with staff
beses ako binaril ng infection initiated by others; for delusions as the client’s perception can help you for specified time period.
father ko.,” as stated example, verbally perception of the environment understand the feelings he
Reduced gray matter in the interact with staff for is experiencing
Objective Data: temporal lobes specified time period. Recommendation:
- Interact with the client on the Interacting with reality is Terminate the plan
Diagnosed with Abnormal cells in the basis of real things; do not healthy for the client
Paranoid hippocampus (part of the dwell on the delusional
Schizophrenia limbic system) material Discharge Outcome:
With a delusion to
his father (delusion Excessive dopamine - Never convey to the client Indicating belief in delusions Outcome Partially Achieved;
of persecutory) secretions Discharge Outcome: that you accept the delusions reinforces the delusion (and Upon discharge, the client was able to
Disordered thought are reality the client’s illness) free from delusions or demonstrate
sequencing or Enlarged third and lateral Upon discharge, the the ability to function without
Flight of ideas ventricles client will be able to be -Directly interject doubt As the client begins to trust responding to persistent delusional
Loose association free from delusions or regarding delusions as soon you, he may become willing thoughts.
Impaired ability to Decreased blood flow to the demonstrate the ability as the client seems ready to to doubt the delusion if you
problem solve frontal lobes to function without accept this. Do not argue but express your doubt. Recommendation:
responding to persistent present a factual account of Continue the Plan
Abnormalities of neuro- delusional thoughts. the situation as you see it.
transmitters and neuro-
endocrine systems. Collaborative:
-Engage the client in one-to-
With a delusion to his one activities at first, then A distrustful client can be
father (delusion of activities in small groups, and best deal with one person
persecutory) gradually activities in larger initially. Gradual introduction
Disordered thought groups of others as the client
sequencing or Flight of tolerate is less threatening.
ideas
Reference: Psychiatric-Mental
Health Nursing 5th Edition by
Reference: Sheila L. Videbeck page 264
Pathophysiology for the
Health Professions 3rd
Edition by Barbara E. Gould
Page 588-589
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term:
Impaired verbal Although the etiology &
“Ang pagkakaalam ko communication related to pathogenesis have not After 3 weeks of nursing - Reorient the client to person, Repeated presentation of Goal Partially Achieved
dahil ata nagdrawing loose associations and been fully determined, here intervention, the patient place, and time as indicated. reality is concrete After hour of nursing intervention, the
ako sa wall, uhm not flight of ideas as are some etiologies: will be able 1.Participate reinforcement for the client client was able to participate in
wall, it’s not also a evidenced by vague, Stressful life circumstances, in therapeutic therapeutic communication like using
table basta di ko alam diffuse, unfocused genetic & biochemical communication to get - Spend time with the client Your physical presence is silence, acceptance, reflecting and
tawag dun (seemed sequences of concepts defects, & brain damage in needs met and to reality. Allows client to think. active listening. Relate effectively with
confused then live it and switch of subjects the fetus by prenatal 2.Relate effectively with persons and his or her environment.
hanging and that are difficult to follow complications or viral persons and his or her - Encourage the client to talk Probing increases the Verbalize or indicate n understanding
continued to talk),” as the train of thought. infection environment. with you, but do not pry for client’s suspicion and of the communication difficulty but not
stated 3.Verbalize or indicate n information. interferes with the the plans for ways of handling.
Reduced gray matter in the understanding of the therapeutic relationship.
Objective Data: temporal lobes communication difficulty Recommendation:
Loose association and plans for ways of - When first communicating The client’s ability to Continue the Plan
of ideas Abnormal cells in the handling. with the client, use simple, perceive and respond to
Paranoid hippocampus (part of the direct sentences; avoid complex stimuli is impaired.
Schizophrenia limbic system) complex sentences or
Diagnosis directions. Discharge Outcome:
Flight of ideas Excessive dopamine
Difficulty in forming secretions - Use confrontation skills, To clarify discrepancies Outcome Partially Achieved;
words. when appropriate, within an between verbal and Upon discharge, the client was able to
Vague, diffuse, Enlarged third and lateral established nurse-client nonverbal cues. demonstrate congruent verbal and
Discharge Outcome: relationship nonverbal communication. He
unfocused ventricles
sequences of established partially method of
Upon discharge, the - Give positive feedback for communication in which needs can be
concepts Decreased blood flow to the Positive feedback for
client will be able to the client’s successes. expressed.
Switch of subjects frontal lobes
demonstrate congruent genuine success enhances
that are difficult to verbal and nonverbal the client’s sense of well-
follow the train of Abnormalities of neuro- being. Recommendation:
communication and 2. Continue the Plan
thought transmitters and neuro- Establish method of
endocrine systems. Collaborative:
communication in which
needs can be - Engage client in reality-
Flight of ideas expressed. based activities such as card To achieved maximal gains
Difficulty in forming playing, occupational therapy, in function and psychosocial
words. or listening to music. well-being
Vague, diffuse,
unfocused sequences of
concepts Reference: (1) Psychiatric-
Switch of subjects that Mental Health Nursing 5th
are difficult to follow the Edition by Sheila L. Videbeck
train of thought page 264 & 292
Reference:
Pathophysiology for the
Health Professions 3rd
Edition by Barbara E. Gould
Page 588-589
You might also like
- Specimen Question Paper Sec 3 Day 2Document2 pagesSpecimen Question Paper Sec 3 Day 2Saifur Rahman100% (1)
- Retreat Center ThesisDocument85 pagesRetreat Center ThesisScarletNo ratings yet
- Rle Worksheet Nursing ProcessDocument6 pagesRle Worksheet Nursing ProcessMARVIE JOY BALUMA CABIOCNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal MassDocument36 pagesLaryngeal MassJayson de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Otosclerosis Case StudyDocument3 pagesOtosclerosis Case StudySana Anwar0% (2)
- ARDS Care Respiratory Care Plan PDFDocument2 pagesARDS Care Respiratory Care Plan PDFeric parl0% (1)
- NCP PainDocument1 pageNCP PaindwightciderNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Purpose of Cystoclysis: 1. Closed Bladder Irrigation SystemDocument6 pages1.2 Purpose of Cystoclysis: 1. Closed Bladder Irrigation SystemKatleen Calang AlagNo ratings yet
- A Beautiful MindDocument4 pagesA Beautiful MindRahmaNo ratings yet
- MSEDocument20 pagesMSEJenny YenNo ratings yet
- Pontine BleedingDocument99 pagesPontine BleedingJeffrey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NeuralgiaDocument22 pagesTrigeminal NeuralgiaamandarestykbNo ratings yet
- Efficacy and Safety of For Treatment of Schizophrenia: LumateperoneDocument40 pagesEfficacy and Safety of For Treatment of Schizophrenia: LumateperoneReyadh JassemNo ratings yet
- Dulcolax Stool Softener Supp (Docusate Sodium)Document2 pagesDulcolax Stool Softener Supp (Docusate Sodium)ENo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic Douloureux) : Presented by MR - Mihir Patel, Nursing Tutor GCON, SiddhpurDocument15 pagesTrigeminal Neuralgia (Tic Douloureux) : Presented by MR - Mihir Patel, Nursing Tutor GCON, Siddhpurandreas kevinNo ratings yet
- Windshield Survey Document Assignment PDFDocument5 pagesWindshield Survey Document Assignment PDFmrikoputraNo ratings yet
- NCP Potts DiseaseDocument2 pagesNCP Potts Diseasearcitap0% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaria Fatima MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Anxiety NCPDocument2 pagesAnxiety NCPmitzi019No ratings yet
- Rle Module Rle Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Rle NCM 105 - Psychiatric NursingDocument5 pagesRle Module Rle Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Rle NCM 105 - Psychiatric NursingJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Clubfoot Written ReportDocument7 pagesClubfoot Written ReportAira Madel ArabaNo ratings yet
- Qi NCPDocument5 pagesQi NCPJesse Israel TadenaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain RT Surgical IncisionDocument1 pageAcute Pain RT Surgical Incisiondude06blumNo ratings yet
- NCP UreteroDocument1 pageNCP UreteroCerie Anne OlayNo ratings yet
- Team Abundance RBA CompleteDocument39 pagesTeam Abundance RBA CompleteDavrans GP100% (1)
- DiverticulosisDocument49 pagesDiverticulosisJewelyn Alafriz AngelesNo ratings yet
- Com/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewDocument2 pagesCom/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewCharles Belonio Dorado100% (1)
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument5 pagesNursing DiagnosisGeovanni Rai HermanoNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesMyasthenia Gravis PathophysiologyRyan Daet0% (1)
- Ca6 NCP Pain - NinaDocument6 pagesCa6 NCP Pain - NinaNinaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPmsinsanoNo ratings yet
- Beautiful MindDocument6 pagesBeautiful Mindapi-285003633No ratings yet
- Drug and NCPDocument15 pagesDrug and NCPgeelawlietNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4-Atty AliboghaDocument48 pagesCHAPTER 4-Atty AliboghaPaul EspinosaNo ratings yet
- CarePlan Psych TemplateDocument14 pagesCarePlan Psych TemplateSasha HayeNo ratings yet
- NCP Charm EditedDocument6 pagesNCP Charm EditedampogeNo ratings yet
- Process Recording 360Document9 pagesProcess Recording 360MarvinNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentAce Khiel PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Process RecordingDocument7 pagesProcess RecordingJohn Christian SayoNo ratings yet
- Brain Surgery Post Op NCPDocument6 pagesBrain Surgery Post Op NCPunnamed personNo ratings yet
- Fluoracil Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFluoracil Drug StudyNicole Louize CaloraNo ratings yet
- Name: Patient X Age: 14 Y/oDocument4 pagesName: Patient X Age: 14 Y/oRyan Jay Patacsil100% (1)
- Rle Module Rle Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Rle NCM 105 - Psychiatric NursingDocument6 pagesRle Module Rle Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Rle NCM 105 - Psychiatric NursingAllisson BeckersNo ratings yet
- Patient Discharge Assessment Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesPatient Discharge Assessment Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationVILLANUEVA ARASELNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPHuzzain PangcogaNo ratings yet
- Counselling LetterDocument1 pageCounselling LetterSeann LorescoNo ratings yet
- NCP Proper CholecystectomyDocument2 pagesNCP Proper CholecystectomyGail Lian SantosNo ratings yet
- X. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Goal MetDocument10 pagesX. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Goal MetAnonymous TpI3Lk50No ratings yet
- NF DR Concept Map Week 12Document4 pagesNF DR Concept Map Week 12Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPLuiji Amor TiamzonNo ratings yet
- NSG Care Plan SchizophreniaDocument1 pageNSG Care Plan SchizophreniaLisa LopezNo ratings yet
- Journal On DiabetesDocument8 pagesJournal On DiabetesMheaye Jheaa100% (1)
- NCP Hip FractureDocument5 pagesNCP Hip FractureCherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- X. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesX. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Neurologic DisordersDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Neurologic DisordersdanceNo ratings yet
- Moira Mae B. Balite BSN 2A: Post Partum Care DefinitionDocument5 pagesMoira Mae B. Balite BSN 2A: Post Partum Care DefinitionMoiraMaeBeridoBaliteNo ratings yet
- Assessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Imperforate Anus: Preoperative CareDocument2 pagesImperforate Anus: Preoperative CareLalisaM ActivityNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDeanne Carla DalilisNo ratings yet
- ARCOXIADocument22 pagesARCOXIATeresa JunioNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument6 pagesGoutNhoydaleen SandovalNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 4.1 ResortDocument4 pages4.1 ResortScarletNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Name: Kyla Marie G. Guadalquiver BS - Psychology GE6 (3152)Document5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Name: Kyla Marie G. Guadalquiver BS - Psychology GE6 (3152)ScarletNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Noli Me Tangere and El FilibusterismoDocument1 pageComparative Analysis of Noli Me Tangere and El FilibusterismoScarletNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Health Protocols Covid-19 Health ProtocolsDocument4 pagesGuidelines For Health Protocols Covid-19 Health ProtocolsScarletNo ratings yet
- Architecture The Importance To SocietyDocument2 pagesArchitecture The Importance To SocietyScarletNo ratings yet
- Personal Safety PracticesDocument2 pagesPersonal Safety PracticesScarletNo ratings yet
- Importance of ArchitectureDocument2 pagesImportance of ArchitectureScarletNo ratings yet
- Architecture The Importance To SocietyDocument2 pagesArchitecture The Importance To SocietyScarletNo ratings yet
- Personal Safety PracticesDocument2 pagesPersonal Safety PracticesScarletNo ratings yet
- English I C2Document10 pagesEnglish I C2José Sánchez100% (1)
- Caribbean Internet Café, CVP Analysis - Accurate EssaysDocument2 pagesCaribbean Internet Café, CVP Analysis - Accurate EssaysVishali ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- Odeona Grecian Urn: by John KeatsDocument10 pagesOdeona Grecian Urn: by John KeatsjayeNo ratings yet
- 1Document11 pages1Amjad PiroutiNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document15 pagesHW 5ottoporNo ratings yet
- NIT03 WAR Museurm PDFDocument78 pagesNIT03 WAR Museurm PDFDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Abhishek Jaiswal (14) Vikram Gupta (19) Gaurav Kumar (21) Ateet Gupta (28) Varun Yadav (47) Siddharth LohoDocument14 pagesPrepared By: Abhishek Jaiswal (14) Vikram Gupta (19) Gaurav Kumar (21) Ateet Gupta (28) Varun Yadav (47) Siddharth LohoateetiimNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab ManualDocument11 pagesBiochemistry Lab ManualShela MalubagNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Music LM 4Document47 pagesGrade 10 Music LM 4Tot Ching100% (9)
- LOUIS PASTEUR & First Year at HarrowDocument4 pagesLOUIS PASTEUR & First Year at HarrowSaif UllahNo ratings yet
- REINVENTING EDEN. The Fate of Nature in Western Culture. Carolyn Merchant, Second Edition (Updated With A New Foreword and Afterword), 2013Document334 pagesREINVENTING EDEN. The Fate of Nature in Western Culture. Carolyn Merchant, Second Edition (Updated With A New Foreword and Afterword), 2013Francis RijnaNo ratings yet
- EasterDocument32 pagesEasterNelson AnuncioNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateDocument3 pagesClinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateqselmmNo ratings yet
- Self Incompatibility: Dr. L.K.GangwarDocument38 pagesSelf Incompatibility: Dr. L.K.GangwarSiddhant Singh100% (1)
- Ind AS 115Document36 pagesInd AS 115yashNo ratings yet
- 3.6.b Relational Databases and NormalisationDocument10 pages3.6.b Relational Databases and Normalisationne002No ratings yet
- 10th Aug - 2022Document39 pages10th Aug - 2022Ranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- NetherlandsADULT STS Volume5457 PRINTDocument356 pagesNetherlandsADULT STS Volume5457 PRINTDan-Emmanuel AdedijiNo ratings yet
- Customs of The TagalogsDocument14 pagesCustoms of The TagalogsACIO, STEPHANY G.No ratings yet
- Crime and Punishment British English Teacher Ver2 BWDocument5 pagesCrime and Punishment British English Teacher Ver2 BWinaNo ratings yet
- Complete SAT Grammar RulesDocument13 pagesComplete SAT Grammar Rulesqingtnap50% (2)
- Yoga InvocationsDocument4 pagesYoga InvocationsJon DoughNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesBahasa InggrisAndy WirajayaNo ratings yet
- Music (G1)Document7 pagesMusic (G1)Bryan B. ArceNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Otago Exercise Dan Gaze Stability Exercise Terhadap Keseimbangan Pada Lanjut UsiaDocument10 pagesPengaruh Otago Exercise Dan Gaze Stability Exercise Terhadap Keseimbangan Pada Lanjut UsiaBimo AnggoroNo ratings yet
- A Study On Consumer Behaviour in Real Estate SectorDocument94 pagesA Study On Consumer Behaviour in Real Estate SectorNadeem khan100% (2)
- Details of Module and Its Structure: Ms. Kulwant KaurDocument14 pagesDetails of Module and Its Structure: Ms. Kulwant KaurAnkur TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Relational Attitude in Gestalt Therapy Theory and PracticeDocument15 pagesThe Relational Attitude in Gestalt Therapy Theory and PracticeAvtandilGogeshvili100% (1)
- General Studies Vision IasDocument12 pagesGeneral Studies Vision IasnitinjamesbondNo ratings yet