Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7FABM 1 Module Accounting Equation
7FABM 1 Module Accounting Equation
Uploaded by
Kristhine DarvinCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Financial Accounting, 7e by Pfeiffer, Hanlon, Magee 2023, Test BankDocument32 pagesFinancial Accounting, 7e by Pfeiffer, Hanlon, Magee 2023, Test BankTest bank World0% (1)
- Book Principles of AccountingDocument268 pagesBook Principles of AccountingMohammad Salim Hossain88% (17)
- Chapter 3 Review Problems With SolutionsDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Review Problems With Solutionsaby251188No ratings yet
- Recording Transactions Under PERPETUAL INVENTORY SYSTEMDocument6 pagesRecording Transactions Under PERPETUAL INVENTORY SYSTEMJalieca Lumbria Gadong0% (1)
- Fa2 BPP Kit 2016Document218 pagesFa2 BPP Kit 2016Hameed Ullah75% (4)
- Acctg 111 Assign3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesAcctg 111 Assign3 ReviewerChris Jay LatibanNo ratings yet
- 2 CHAPTER Lesson 2 1 AssetsDocument6 pages2 CHAPTER Lesson 2 1 AssetsRegine BaterisnaNo ratings yet
- Exercises - 5 Cs of CreditDocument1 pageExercises - 5 Cs of Creditmarissa casareno almueteNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 Leah GarciaDocument12 pagesExercise 3 Leah GarciaMa Sophia Mikaela EreceNo ratings yet
- Canvas Activity - Journalizing - Oct - 29 PDFDocument2 pagesCanvas Activity - Journalizing - Oct - 29 PDFJian Francisco100% (2)
- PeriodicDocument23 pagesPeriodicalmorsNo ratings yet
- Enclosure 1. Teacher-Made Learner's Home Task (Week 3)Document7 pagesEnclosure 1. Teacher-Made Learner's Home Task (Week 3)Kim FloresNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1 MabalaDocument5 pagesACTIVITY 1 MabalaJulie mabuyoNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 PPTDocument65 pagesFabm1 PPTBenjie Galicia AngelesNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Common Business TransactionsDocument18 pagesAnalysis of Common Business TransactionsClarisse RosalNo ratings yet
- General Journal CholoDocument9 pagesGeneral Journal CholokrylNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 Completing The Accounting CycleDocument16 pagesFabm1 Completing The Accounting CycleVenice100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 1Document19 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 1Shiellai Mae Polintang0% (1)
- Bart M ManuelDocument27 pagesBart M ManuelBea TiuNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship 2nd Q.exam OktcindyDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurship 2nd Q.exam OktcindyDaryl MacatbagNo ratings yet
- Fabm2 Q2 M4 - 4 CsefDocument20 pagesFabm2 Q2 M4 - 4 CsefZeus MalicdemNo ratings yet
- LUYONG - 3rd Periodical - FABM1Document4 pagesLUYONG - 3rd Periodical - FABM1Jonavi Luyong100% (2)
- Business Math - Interest QuizDocument1 pageBusiness Math - Interest QuizAi ReenNo ratings yet
- Integrated Accounting Learning Module Attachment (Do Not Copy)Document15 pagesIntegrated Accounting Learning Module Attachment (Do Not Copy)Jasper PelicanoNo ratings yet
- Name of Examinee: - : Prepare The FollowingDocument15 pagesName of Examinee: - : Prepare The FollowingNoel CarpioNo ratings yet
- Answer Keys - Test Bank - Fabm2Document10 pagesAnswer Keys - Test Bank - Fabm2Kevin Pereña GuinsisanaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 Activity 1Document5 pagesMODULE 3 Activity 1Nermeen C. Alapa100% (1)
- Adjusting Journal EntriesDocument8 pagesAdjusting Journal EntriesChaaaNo ratings yet
- Rovelyn E. Forcadas ABM-11 Activity #9-BDocument2 pagesRovelyn E. Forcadas ABM-11 Activity #9-BRovelyn E. ForcadasNo ratings yet
- Week 7-8Document8 pagesWeek 7-8Kim Albero Cubel0% (1)
- ACTIVITY. On February 1, 20A4, Mira Delamar Opened A Store That SellsDocument1 pageACTIVITY. On February 1, 20A4, Mira Delamar Opened A Store That SellsMiguel Lulab100% (1)
- Pages 178Document7 pagesPages 178Krestyl Ann GabaldaNo ratings yet
- 1Q BM 3rd Module A.Y. 2021 - 2022Document20 pages1Q BM 3rd Module A.Y. 2021 - 2022Jewel RamosNo ratings yet
- Fabm Nites PrintDocument3 pagesFabm Nites Printwiz wizNo ratings yet
- ABM FABM1 AIRs LM Q3 W5 M5Document20 pagesABM FABM1 AIRs LM Q3 W5 M5Trisha Mae DuatNo ratings yet
- Trucking and StorageDocument2 pagesTrucking and StorageMichael San Luis100% (1)
- Example: Manang Rosie's Famous Barbeques: Assets Liabilities + EquityDocument2 pagesExample: Manang Rosie's Famous Barbeques: Assets Liabilities + EquityKezia Gwyneth Bofill OrisNo ratings yet
- Businessfinance12 - q3 - Mod6.2 - Basic Long Term Financial Concepts - Loan AmortizationDocument22 pagesBusinessfinance12 - q3 - Mod6.2 - Basic Long Term Financial Concepts - Loan AmortizationBernadette MendozaNo ratings yet
- FABM 1.module 2Document21 pagesFABM 1.module 2SHIERY MAE FALCONITINNo ratings yet
- Journal, T Accounts, Worksheet and PostingDocument29 pagesJournal, T Accounts, Worksheet and Postingkenneth coronelNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choice: Read and Analyze Each Item. Circle The Letter of The Best Answer. 1Document3 pagesI. Multiple Choice: Read and Analyze Each Item. Circle The Letter of The Best Answer. 1HLeigh Nietes-GabutanNo ratings yet
- FABM REVIEWER 2nd QUARTERDocument5 pagesFABM REVIEWER 2nd QUARTERMikaella Adriana GoNo ratings yet
- JOURNALIZINGDocument2 pagesJOURNALIZINGArneld SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 2nd ActivityDocument2 pages2nd ActivityResaa100% (1)
- Fabm2 Module Week 1Document8 pagesFabm2 Module Week 1Mylene Santiago100% (1)
- Q1WK2-accounting 1Document6 pagesQ1WK2-accounting 1Brian Reyes GangcaNo ratings yet
- FABM2 Module-1Document18 pagesFABM2 Module-1Jean Carlo Delizo CacheroNo ratings yet
- FAR Chapter4 FinalDocument43 pagesFAR Chapter4 FinalPATRICIA COLINANo ratings yet
- Business Finance: Mrs. Leah O. RualesDocument28 pagesBusiness Finance: Mrs. Leah O. RualesCleofe Sobiaco100% (1)
- Handout No. 1 in Fundamentals of Accounting, Business, and Management 2Document8 pagesHandout No. 1 in Fundamentals of Accounting, Business, and Management 2Stephanie DecidaNo ratings yet
- Final Accounting Part 1Document1 pageFinal Accounting Part 1Joaquin Jeanne Marie B.0% (2)
- Accounting 101Document17 pagesAccounting 101Jenne Santiago BabantoNo ratings yet
- Fabm 1-PTDocument10 pagesFabm 1-PTClay MaaliwNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 1 New Module 1Document22 pagesCbmec 1 New Module 1Calabia, Angelica MerelosNo ratings yet
- Fabm2 - Se (2) Answer KeyDocument2 pagesFabm2 - Se (2) Answer Keyl m100% (1)
- General Journal: Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit Posting ReferenceDocument9 pagesGeneral Journal: Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit Posting ReferenceCherrie Mae BanaagNo ratings yet
- Las-Business-Finance-Q1 Week 1Document16 pagesLas-Business-Finance-Q1 Week 1Kinn Jay100% (1)
- Fabm Note 6Document12 pagesFabm Note 6Angelica ManahanNo ratings yet
- Certified Bookkeeper Program: January 12, 19, 26 and February 2, 2007 ADB Ave. OrtigasDocument63 pagesCertified Bookkeeper Program: January 12, 19, 26 and February 2, 2007 ADB Ave. OrtigasAllen CarlNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis: Mr. Christopher B. CauanDocument63 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis: Mr. Christopher B. CauanChristopher Beltran CauanNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: Net Present Value MethodDocument12 pagesBusiness Finance: Net Present Value MethodAngelica ParasNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing GRADE 12/week 3 & 4Document6 pagesPrinciples of Marketing GRADE 12/week 3 & 4Master NistroNo ratings yet
- 77 FDocument3 pages77 FJohn CalvinNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 Lesson 7 The Accounting EquationDocument19 pagesFABM 1 Lesson 7 The Accounting EquationTiffany Ceniza100% (1)
- What Are The Basic Accounting TheoriesDocument5 pagesWhat Are The Basic Accounting TheoriesSandra MagnoNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Chapter 3Document60 pagesAnswer Key Chapter 3HectorNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Concepts: The Income Statement: Changes From Eleventh EditionDocument19 pagesBasic Accounting Concepts: The Income Statement: Changes From Eleventh EditionDhiwakar SbNo ratings yet
- Notes in Accounting Made SimpleDocument1 pageNotes in Accounting Made SimplemarvieelumbaringNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 9th Edition Spiceland Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesIntermediate Accounting 9th Edition Spiceland Solutions ManualGregoryVasqueztkbn100% (55)
- Principle of AccountingDocument23 pagesPrinciple of Accountingdaood abdullahNo ratings yet
- Transaction AnalysisDocument33 pagesTransaction AnalysisIzzeah RamosNo ratings yet
- Accounting BasicsDocument119 pagesAccounting Basicsjunlab0807100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Eshaal FatimaNo ratings yet
- Accounting EquationDocument11 pagesAccounting EquationZaheer Ahmed SwatiNo ratings yet
- The Accounting EquationDocument13 pagesThe Accounting EquationJooneel Vlogs100% (1)
- LA 2 - Chapters 2 & 3 (Class Notes 1)Document33 pagesLA 2 - Chapters 2 & 3 (Class Notes 1)u22639684No ratings yet
- Orig. ACC 111 SIM SLO DDocument14 pagesOrig. ACC 111 SIM SLO DAnthony CanamanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Analysis of Business TransactionsDocument27 pagesModule 2 Analysis of Business TransactionsjilliantrcieNo ratings yet
- Exercises Chapter 1 & 2Document4 pagesExercises Chapter 1 & 2Kiko Doragon Inoue TsubasaNo ratings yet
- 2 Accounting Equestion and Double Entry UDDocument10 pages2 Accounting Equestion and Double Entry UDERICK MLINGWANo ratings yet
- Frank Wood's Principle of Accounts For HK Book1 CH2Document3 pagesFrank Wood's Principle of Accounts For HK Book1 CH2CHRISTINA LEENo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Small Business Management Creating A Sustainable Competitive Advantage 7th Edition Timothy S Hatten DownloadDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Small Business Management Creating A Sustainable Competitive Advantage 7th Edition Timothy S Hatten DownloadBenjaminWilsongaco100% (19)
- Accounting Equation Lesson 1.1Document23 pagesAccounting Equation Lesson 1.1Renz RaphNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Remedial Handout 1Document5 pagesYear 11 Remedial Handout 1Janice BaltorNo ratings yet
- Learning Resource - Accounting and The Business EnvironmentDocument109 pagesLearning Resource - Accounting and The Business EnvironmentCrystal Castor LabragueNo ratings yet
- Apple Academy Exams Trainers: Monday 19th July, 2021 Principles of Accounts Summer ClassesDocument10 pagesApple Academy Exams Trainers: Monday 19th July, 2021 Principles of Accounts Summer ClassesAnthony JulesNo ratings yet
- CER3054 T1.1 - Accounting TerminologyDocument31 pagesCER3054 T1.1 - Accounting TerminologyCharlene MontebelloNo ratings yet
- Accounting Basics MCQs - Accountancy KnowledgeDocument15 pagesAccounting Basics MCQs - Accountancy KnowledgeMuhammad KashifNo ratings yet
- PPT Week 1 OkDocument27 pagesPPT Week 1 OkDelwiena AgnelNo ratings yet
7FABM 1 Module Accounting Equation
7FABM 1 Module Accounting Equation
Uploaded by
Kristhine DarvinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7FABM 1 Module Accounting Equation
7FABM 1 Module Accounting Equation
Uploaded by
Kristhine DarvinCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management 1
Accounting Equation
Content Standards
The learners demonstrate an understanding of the accounting equation.
Performance Standards
The learners shall be able to solve problems by applying the accounting equation.
Learning Competencies
The learners shall be able to illustrate the accounting equation; perform operations involving
simple cases with the use of the accounting equation
Specific Learning Objectives
At the end of this lesson, the learners will be able to equate assets with liabilities and equity
solve problems using the accounting equation
INTRODUCTION
Accounting equation is Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Assets are resources owned by the business.
Liabilities are obligations by the business.
Equity is the residual interest of the owner of the business.
Four elements that affect equity:
(1) Investment;
(2) Withdrawal;
(3) Revenue, and;
(4) Expenses.
MOTIVATION
For every transaction the accounting equation should always balance.
INSTRUCTION
Assets invested by the owner
July 1 - Paolo Reyes started a delivery service on July 1,2020. The following transactions
occurred during the month of July. He invested PHP800,000 cash and Cars amounting to
PHP200,000
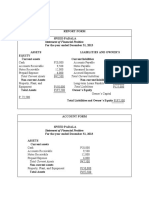
ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
1-Jul Cash 800,000.00 Reyes, Capital 1,000,000.00
Cars 200,000.00
Borrowings from the bank
July 2 – Reyes borrowed PHP100,000 cash from PNB for use in his business.
ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
2-Jul Cash 100,000.00 Loans Payable 100,000.00
BALANCES ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash 900,000.00 Loans Payable 100,000.00 Reyes, Capital 1,000,000.00
Cars 200,000.00
Asset purchased for cash
July 7 – Bought tables and chairs from Orocan and paid PHP45,000 cash
ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
7-Jul Furnitures 45,000.00
Cash (45,000.00)
BALANCES ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash 855,000.00 Loans Payable 100,000.00 Reyes, Capital 1,000,000.00
Cars 200,000.00
Furnitures 45,000.00
Assets purchased on account
July 15 – Various equipment were purchased on account from Fortune for PHP55,000
15-Jul ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Equipment 55,000.00 Accounts Payable 55,000.00
BALANCES ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash 855,000.00 Loans Payable 100,000.00 Reyes, Capital 1,000,000.00
Cars 200,000.00 Accounts Payable 55,000.00
Furnitures 45,000.00
Equipment 55,000.00
Cash withdrawal by the owner
July 18 – Reyes made a cash withdrawal of PHP5,000 for personal use
18-Jul ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash (5,000.00) Reyes, Drawing (5,000.00)
BALANCES ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash 850,000.00 Loans Payable 100,000.00 Reyes, Capital 1,000,000.00
Cars 200,000.00 Accounts Payable 55,000.00 Reyes, Drawing (5,000.00)
Furnitures 45,000.00
Equipment 55,000.00
Payment of liability
July 20 – The account due to Fortune was paid in cash
20-Jul ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash (55,000.00) Accounts Payable (55,000.00)
BALANCES ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash 795,000.00 Loans Payable 100,000.00 Reyes, Capital 1,000,000.00
Cars 200,000.00 Reyes, Drawing (5,000.00)
Furnitures 45,000.00
Equipment 55,000.00
The following table summarizes the effects of these transactions on the accounting equation
Date ASSETS LIABILITIES OWNERS' EQUITY
Loans Accounts Reyes, Reyes,
July Cash Cars Furnitures Equipment
Payable Payable Drawings Capital
1 800,000 200,000 1,000,000
2 100,000 100,000
Balances 900,000 200,000 - - 100,000 - - 1,000,000
7 (45,000) 45,000
Balances 855,000 200,000 45,000 - 100,000 - - 1,000,000
15 55,000 55,000
Balances 855,000 200,000 45,000 55,000 100,000 55,000 - 1,000,000
18 (5,000) (5,000)
Balances 850,000 200,000 45,000 55,000 100,000 55,000 (5,000) 1,000,000
20 (55,000) (55,000)
Balances 795,000 200,000 45,000 55,000 100,000 - (5,000) 1,000,000
1,095,000 1,095,000
Determining profit through operation
• Accrual basis of accounting vs Cash basis of accounting – accrual basis recognizes
revenue when earned and recognizes expenses when incurred
• Under the expense recognition principle, expenses can be recognized either as: (1)
matching; (2) systematic allocation, or; (3) direct association.
• Profit measures the performance of the company. If the revenue exceeds expenses,
then it is a net profit; otherwise, it is a net loss.
Received cash for revenue earned
July 21 – A customer hired the services of Reyes. Cash of PHP15,000 was received from the
customers.
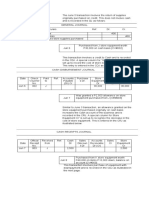
21-Jul ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash 15,000.00 Service Revenue 15,000.00
Paid cash for expenses incurred
July 22 – Cash was paid for the following: gas and oil, PHP500 and car repairs, PHP1,000.
22-Jul ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash (1,500.00) Gas and Oil (500.00)
Repair Expense (1,000.00)
Revenue rendered on account
July 24 – Another customer hired the services of Reyes and promised to pay PHP16,000 on July
31.
24-Jul ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Accounts Receivables 16,000.00 Service Revenue 16,000.00
Paid for expenses incurred
July 25 – Paid PHP500 for telephone bill.
25-Jul ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash (500.00) Telephone Expense (500.00)
Revenue earned with a downpayment, balance on account
July 27 – Another customer hired the services of Reyes. A bill was issued to them for
PHP20,000, 50% of which was collected
27-Jul ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash 10,000.00 Service Revenue 20,000.00
Accounts Receivables 10,000.00
Customer’s account collected in cash
July 30 – The customer on July 24 paid 50% of his account in cash.
30-Jul ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash 8,000.00
Accounts Receivables (8,000.00)
Paid cash for expenses incurred
July 31 – Paid PHP10,000 for rental of office space, and salaries of PHP9,000
31-Jul ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash (19,000.00) Rent Expense 10,000.00
Salaries Expense (9,000.00)
PRACTICE
Concept check. Use the following question set for practice.
For each transaction, tell whether the assets, liabilities and equity will increase (I), decrease (D)
or is not affected (NE).
Asset Liabilities Equity
1 The owner invests personal cash in the business
2 The owner withdraws business assets for personal
use
3 The company receives cash from a bank loan
4 The company repays the bank that has lent money
5 The company purchases equipment with its cash
6 The owner contributes her personal truck to the
business
7 The company purchases supplies on credit
8 The company purchases land by paying half in cash
and signing a note
9 The owner withdraws cash for personal use
10 The company repays the suppliers
ENRICHMENT
The activity below is in reverse. Describe the given transaction.
Date ASSETS LIABILITIES OWNER'S EQUITY
Cash Supplies Equipment
Balances 60,000 7,500 300,000 75,000 292,500
1 150,000 150,000
2 (20,000) 20,000
3 (112,500) (112,500)
4 5,000 5,000
5 (15,000) (15,000)
6 (53,000) (53,000)
7 (8,000) (8,000)
EVALUATION
Give the following questions as their assignment
Aug. 1 Garcia invested PHP48,000 cash in the business.
Aug. 1 Rented office space and paid PHP800 cash for the August rent.
Aug. 3 Purchased exploration equipment for PHP22,000 by paying PHP12,000 cash and
agreeing to pay the balance in 3 months.
Aug. 5 Purchased office supplies by paying PHP1,500 cash.
Aug. 6 Completed exploration work and immediately collected PHP420 cash for the
work.
Aug. 8 Purchased PHP1,350 of office equipment on credit.
Aug. 15 Completed exploration work on credit in the amount of PHP8,000.
Aug. 18 Purchased PHP700 of office supplies on credit.
Aug. 20 Paid cash for the office equipment purchased on August 8.
Aug. 24 Billed a client PHP2,400 for work completed; the balance is due in 30 days.
Aug. 28 Received PHP5,000 cash for the work completed on August 15.
Aug. 30 Paid the assistant’s salary of PHP1,100 cash for this month.
Aug. 30 Paid PHP340 cash for this month’s utility bill.
Aug. 30 Garcia withdrew PHP1,050 cash from the business for personal use.
Required
1. Arrange the following asset, liability, and equity titles in a table: Cash; Accounts
Receivable; Office Supplies; Office Equipment; Exploration Equipment; Accounts
Payable; Jerome Garcia, Capital; Jerome Garcia, Withdrawals; Revenues; and Expenses.
2. Use additions and subtractions to show the effects of each transaction on the accounts
in the accounting equation. Show new balances after each transaction.
You might also like
- Financial Accounting, 7e by Pfeiffer, Hanlon, Magee 2023, Test BankDocument32 pagesFinancial Accounting, 7e by Pfeiffer, Hanlon, Magee 2023, Test BankTest bank World0% (1)
- Book Principles of AccountingDocument268 pagesBook Principles of AccountingMohammad Salim Hossain88% (17)
- Chapter 3 Review Problems With SolutionsDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Review Problems With Solutionsaby251188No ratings yet
- Recording Transactions Under PERPETUAL INVENTORY SYSTEMDocument6 pagesRecording Transactions Under PERPETUAL INVENTORY SYSTEMJalieca Lumbria Gadong0% (1)
- Fa2 BPP Kit 2016Document218 pagesFa2 BPP Kit 2016Hameed Ullah75% (4)
- Acctg 111 Assign3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesAcctg 111 Assign3 ReviewerChris Jay LatibanNo ratings yet
- 2 CHAPTER Lesson 2 1 AssetsDocument6 pages2 CHAPTER Lesson 2 1 AssetsRegine BaterisnaNo ratings yet
- Exercises - 5 Cs of CreditDocument1 pageExercises - 5 Cs of Creditmarissa casareno almueteNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 Leah GarciaDocument12 pagesExercise 3 Leah GarciaMa Sophia Mikaela EreceNo ratings yet
- Canvas Activity - Journalizing - Oct - 29 PDFDocument2 pagesCanvas Activity - Journalizing - Oct - 29 PDFJian Francisco100% (2)
- PeriodicDocument23 pagesPeriodicalmorsNo ratings yet
- Enclosure 1. Teacher-Made Learner's Home Task (Week 3)Document7 pagesEnclosure 1. Teacher-Made Learner's Home Task (Week 3)Kim FloresNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1 MabalaDocument5 pagesACTIVITY 1 MabalaJulie mabuyoNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 PPTDocument65 pagesFabm1 PPTBenjie Galicia AngelesNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Common Business TransactionsDocument18 pagesAnalysis of Common Business TransactionsClarisse RosalNo ratings yet
- General Journal CholoDocument9 pagesGeneral Journal CholokrylNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 Completing The Accounting CycleDocument16 pagesFabm1 Completing The Accounting CycleVenice100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 1Document19 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 1Shiellai Mae Polintang0% (1)
- Bart M ManuelDocument27 pagesBart M ManuelBea TiuNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship 2nd Q.exam OktcindyDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurship 2nd Q.exam OktcindyDaryl MacatbagNo ratings yet
- Fabm2 Q2 M4 - 4 CsefDocument20 pagesFabm2 Q2 M4 - 4 CsefZeus MalicdemNo ratings yet
- LUYONG - 3rd Periodical - FABM1Document4 pagesLUYONG - 3rd Periodical - FABM1Jonavi Luyong100% (2)
- Business Math - Interest QuizDocument1 pageBusiness Math - Interest QuizAi ReenNo ratings yet
- Integrated Accounting Learning Module Attachment (Do Not Copy)Document15 pagesIntegrated Accounting Learning Module Attachment (Do Not Copy)Jasper PelicanoNo ratings yet
- Name of Examinee: - : Prepare The FollowingDocument15 pagesName of Examinee: - : Prepare The FollowingNoel CarpioNo ratings yet
- Answer Keys - Test Bank - Fabm2Document10 pagesAnswer Keys - Test Bank - Fabm2Kevin Pereña GuinsisanaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 Activity 1Document5 pagesMODULE 3 Activity 1Nermeen C. Alapa100% (1)
- Adjusting Journal EntriesDocument8 pagesAdjusting Journal EntriesChaaaNo ratings yet
- Rovelyn E. Forcadas ABM-11 Activity #9-BDocument2 pagesRovelyn E. Forcadas ABM-11 Activity #9-BRovelyn E. ForcadasNo ratings yet
- Week 7-8Document8 pagesWeek 7-8Kim Albero Cubel0% (1)
- ACTIVITY. On February 1, 20A4, Mira Delamar Opened A Store That SellsDocument1 pageACTIVITY. On February 1, 20A4, Mira Delamar Opened A Store That SellsMiguel Lulab100% (1)
- Pages 178Document7 pagesPages 178Krestyl Ann GabaldaNo ratings yet
- 1Q BM 3rd Module A.Y. 2021 - 2022Document20 pages1Q BM 3rd Module A.Y. 2021 - 2022Jewel RamosNo ratings yet
- Fabm Nites PrintDocument3 pagesFabm Nites Printwiz wizNo ratings yet
- ABM FABM1 AIRs LM Q3 W5 M5Document20 pagesABM FABM1 AIRs LM Q3 W5 M5Trisha Mae DuatNo ratings yet
- Trucking and StorageDocument2 pagesTrucking and StorageMichael San Luis100% (1)
- Example: Manang Rosie's Famous Barbeques: Assets Liabilities + EquityDocument2 pagesExample: Manang Rosie's Famous Barbeques: Assets Liabilities + EquityKezia Gwyneth Bofill OrisNo ratings yet
- Businessfinance12 - q3 - Mod6.2 - Basic Long Term Financial Concepts - Loan AmortizationDocument22 pagesBusinessfinance12 - q3 - Mod6.2 - Basic Long Term Financial Concepts - Loan AmortizationBernadette MendozaNo ratings yet
- FABM 1.module 2Document21 pagesFABM 1.module 2SHIERY MAE FALCONITINNo ratings yet
- Journal, T Accounts, Worksheet and PostingDocument29 pagesJournal, T Accounts, Worksheet and Postingkenneth coronelNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choice: Read and Analyze Each Item. Circle The Letter of The Best Answer. 1Document3 pagesI. Multiple Choice: Read and Analyze Each Item. Circle The Letter of The Best Answer. 1HLeigh Nietes-GabutanNo ratings yet
- FABM REVIEWER 2nd QUARTERDocument5 pagesFABM REVIEWER 2nd QUARTERMikaella Adriana GoNo ratings yet
- JOURNALIZINGDocument2 pagesJOURNALIZINGArneld SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 2nd ActivityDocument2 pages2nd ActivityResaa100% (1)
- Fabm2 Module Week 1Document8 pagesFabm2 Module Week 1Mylene Santiago100% (1)
- Q1WK2-accounting 1Document6 pagesQ1WK2-accounting 1Brian Reyes GangcaNo ratings yet
- FABM2 Module-1Document18 pagesFABM2 Module-1Jean Carlo Delizo CacheroNo ratings yet
- FAR Chapter4 FinalDocument43 pagesFAR Chapter4 FinalPATRICIA COLINANo ratings yet
- Business Finance: Mrs. Leah O. RualesDocument28 pagesBusiness Finance: Mrs. Leah O. RualesCleofe Sobiaco100% (1)
- Handout No. 1 in Fundamentals of Accounting, Business, and Management 2Document8 pagesHandout No. 1 in Fundamentals of Accounting, Business, and Management 2Stephanie DecidaNo ratings yet
- Final Accounting Part 1Document1 pageFinal Accounting Part 1Joaquin Jeanne Marie B.0% (2)
- Accounting 101Document17 pagesAccounting 101Jenne Santiago BabantoNo ratings yet
- Fabm 1-PTDocument10 pagesFabm 1-PTClay MaaliwNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 1 New Module 1Document22 pagesCbmec 1 New Module 1Calabia, Angelica MerelosNo ratings yet
- Fabm2 - Se (2) Answer KeyDocument2 pagesFabm2 - Se (2) Answer Keyl m100% (1)
- General Journal: Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit Posting ReferenceDocument9 pagesGeneral Journal: Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit Posting ReferenceCherrie Mae BanaagNo ratings yet
- Las-Business-Finance-Q1 Week 1Document16 pagesLas-Business-Finance-Q1 Week 1Kinn Jay100% (1)
- Fabm Note 6Document12 pagesFabm Note 6Angelica ManahanNo ratings yet
- Certified Bookkeeper Program: January 12, 19, 26 and February 2, 2007 ADB Ave. OrtigasDocument63 pagesCertified Bookkeeper Program: January 12, 19, 26 and February 2, 2007 ADB Ave. OrtigasAllen CarlNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis: Mr. Christopher B. CauanDocument63 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis: Mr. Christopher B. CauanChristopher Beltran CauanNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: Net Present Value MethodDocument12 pagesBusiness Finance: Net Present Value MethodAngelica ParasNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing GRADE 12/week 3 & 4Document6 pagesPrinciples of Marketing GRADE 12/week 3 & 4Master NistroNo ratings yet
- 77 FDocument3 pages77 FJohn CalvinNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 Lesson 7 The Accounting EquationDocument19 pagesFABM 1 Lesson 7 The Accounting EquationTiffany Ceniza100% (1)
- What Are The Basic Accounting TheoriesDocument5 pagesWhat Are The Basic Accounting TheoriesSandra MagnoNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Chapter 3Document60 pagesAnswer Key Chapter 3HectorNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Concepts: The Income Statement: Changes From Eleventh EditionDocument19 pagesBasic Accounting Concepts: The Income Statement: Changes From Eleventh EditionDhiwakar SbNo ratings yet
- Notes in Accounting Made SimpleDocument1 pageNotes in Accounting Made SimplemarvieelumbaringNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 9th Edition Spiceland Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesIntermediate Accounting 9th Edition Spiceland Solutions ManualGregoryVasqueztkbn100% (55)
- Principle of AccountingDocument23 pagesPrinciple of Accountingdaood abdullahNo ratings yet
- Transaction AnalysisDocument33 pagesTransaction AnalysisIzzeah RamosNo ratings yet
- Accounting BasicsDocument119 pagesAccounting Basicsjunlab0807100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Eshaal FatimaNo ratings yet
- Accounting EquationDocument11 pagesAccounting EquationZaheer Ahmed SwatiNo ratings yet
- The Accounting EquationDocument13 pagesThe Accounting EquationJooneel Vlogs100% (1)
- LA 2 - Chapters 2 & 3 (Class Notes 1)Document33 pagesLA 2 - Chapters 2 & 3 (Class Notes 1)u22639684No ratings yet
- Orig. ACC 111 SIM SLO DDocument14 pagesOrig. ACC 111 SIM SLO DAnthony CanamanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Analysis of Business TransactionsDocument27 pagesModule 2 Analysis of Business TransactionsjilliantrcieNo ratings yet
- Exercises Chapter 1 & 2Document4 pagesExercises Chapter 1 & 2Kiko Doragon Inoue TsubasaNo ratings yet
- 2 Accounting Equestion and Double Entry UDDocument10 pages2 Accounting Equestion and Double Entry UDERICK MLINGWANo ratings yet
- Frank Wood's Principle of Accounts For HK Book1 CH2Document3 pagesFrank Wood's Principle of Accounts For HK Book1 CH2CHRISTINA LEENo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Small Business Management Creating A Sustainable Competitive Advantage 7th Edition Timothy S Hatten DownloadDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Small Business Management Creating A Sustainable Competitive Advantage 7th Edition Timothy S Hatten DownloadBenjaminWilsongaco100% (19)
- Accounting Equation Lesson 1.1Document23 pagesAccounting Equation Lesson 1.1Renz RaphNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Remedial Handout 1Document5 pagesYear 11 Remedial Handout 1Janice BaltorNo ratings yet
- Learning Resource - Accounting and The Business EnvironmentDocument109 pagesLearning Resource - Accounting and The Business EnvironmentCrystal Castor LabragueNo ratings yet
- Apple Academy Exams Trainers: Monday 19th July, 2021 Principles of Accounts Summer ClassesDocument10 pagesApple Academy Exams Trainers: Monday 19th July, 2021 Principles of Accounts Summer ClassesAnthony JulesNo ratings yet
- CER3054 T1.1 - Accounting TerminologyDocument31 pagesCER3054 T1.1 - Accounting TerminologyCharlene MontebelloNo ratings yet
- Accounting Basics MCQs - Accountancy KnowledgeDocument15 pagesAccounting Basics MCQs - Accountancy KnowledgeMuhammad KashifNo ratings yet
- PPT Week 1 OkDocument27 pagesPPT Week 1 OkDelwiena AgnelNo ratings yet