Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cluster Vs Distributed
Cluster Vs Distributed
Uploaded by
Shital JoshiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cluster Vs Distributed
Cluster Vs Distributed
Uploaded by
Shital JoshiCopyright:
Available Formats
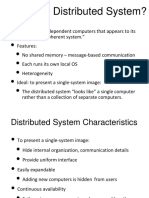
Clusters What is a distributed system (again)
§ “True” Distributed Operating System
u Loosely-coupled hardware
§ Distributed system def. Review
• No shared memory, but provides the “feel” of a single memory
§ Cluster definition
u Tightly-coupled software
§ Clusters vs. distributed systems • One single OS, or at least the feel of one
§ Cluster example 1 – reliable file service u Machines are somewhat, but not completely, autonomous
§ Cluster example 2 – fast web service
§ Classification of clusters
Disk1
M1 P1 M2 P2 M3 P3
Network
M4 P4 M5 P5
1 Printer4 Disk5 2
Clusters (C) vs. Distributed systems (D)
Clusters § structure
u [C] - homogeneous - purchased to perform a certain task
u [D] - heterogeneous - put together from the available hardware
§ A subclass of distributed systems § scale
§ a small scale (mostly) homogeneous (the same hardware and OS) u [C] - small scale - don’t have to make sure that the setup scales
array of computers (located usually in one site) dedicated to small
u [D] - medium/large - have to span (potentially) large number of machines
number of well defined tasks in solving of which the cluster acts as
one single whole. § task
u [C] - specialized - made to perform a small set of well-defined tasks
§ typical tasks for “classic” distributed systems:
u [D] - general - usually have to be general-user computing environments
u file services from/to distributed machines over (college) campus
u distributing workload of all machines on campus
§ price
u [C] - (relatively) cheap
§ typical tasks for a cluster:
u [D] - free(?)/expensive
u high-availability web-service/file service, other high-availability
applications § reliability
u [C] - as good as it needs to be
u computing “farms”.
u [D] - high/low?
§ security
3 u [C] - nodes trust each-other 4
u [D] - nodes do not trust each other
Cluster Cluster examples (cont.)
examples
§ active machine - serves files to the network of computers
§ standby machine -listens to network and updates it’s own copy of
pictures taken from “In Search of Clusters”, G.F. Pfister, 1998 files
§ branches get access to shared information even if one of § in case of machine failure - standby machine takes over file service 6
5
the links or computers fails transparent to users
Cluster examples (cont.)
Classification of clusters
§ Dispatcher (sprayer) machine - sends the web requests to server § By architecture:
machines and makes sure that the servers are evenly loaded
u with hardware additions - OpenVMS, Tandem Himalaya,
§ web service continues even if a server fails Parallel Syspex
u pure software - Beowulf, …
§ By task. There is no dividing line between clusters and true
distributed systems - as we add features the clusters start to
resemble D.S.
u availability
u batch processing
u database
u generic (scientific) computation
u full clusters (distributed systems) - single system image
7 8
You might also like
- Sun ClusterDocument87 pagesSun Clustersyedrahman75100% (1)
- Service ManualDocument116 pagesService Manualdocdogg100% (5)
- Cloud Computing NotesDocument3 pagesCloud Computing Notessarthakkulkarni235No ratings yet
- IntroDocument32 pagesIntroAnita Sofia KeyserNo ratings yet
- CS4513 Distributed Computer SystemsDocument23 pagesCS4513 Distributed Computer SystemsShahnaz ShakirNo ratings yet
- Drawbridge PDFDocument28 pagesDrawbridge PDFAlok H TripathiNo ratings yet
- ASECluster EditionDocument52 pagesASECluster EditionJairo CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Technology Applications For Business Session 3: IS StreamDocument22 pagesTechnology Applications For Business Session 3: IS StreamVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- CS 268: Lecture 20 Classic Distributed Systems: Bayou and BFTDocument29 pagesCS 268: Lecture 20 Classic Distributed Systems: Bayou and BFTRose GirlNo ratings yet
- Cluster 2Document26 pagesCluster 2parthsharma89No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 8 Mar 2022Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 8 Mar 2022luze asdNo ratings yet
- Distributed SystemsDocument14 pagesDistributed SystemsAero AmmarNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems IntroductionDocument21 pagesDistributed Systems IntroductionDerrickNo ratings yet
- 32karamel A System For Timely Provisioning Large-Scale Software Across IaaS CloudsDocument5 pages32karamel A System For Timely Provisioning Large-Scale Software Across IaaS CloudsDani VillalobosNo ratings yet
- BDS Session 2Document58 pagesBDS Session 2Sudeb DasNo ratings yet
- Introduction of DSDocument41 pagesIntroduction of DSHarsh NebhwaniNo ratings yet
- Cluster Computing: by Aakash Kumar SinghDocument26 pagesCluster Computing: by Aakash Kumar SinghJinal PanchalNo ratings yet
- A Cluster Computer and Its ArchitectureDocument3 pagesA Cluster Computer and Its ArchitecturePratik SharmaNo ratings yet
- En Crypt Ing Hard Disks With DM-Crypt LUKSDocument6 pagesEn Crypt Ing Hard Disks With DM-Crypt LUKSdocudeNo ratings yet
- TLE WorksheetDocument9 pagesTLE WorksheetBejiNo ratings yet
- 01 Cloud Computing Background Distributed SystemsDocument36 pages01 Cloud Computing Background Distributed SystemsKashfi ShormitaNo ratings yet
- Abstract TriadBased Architecture RdlabDocument4 pagesAbstract TriadBased Architecture RdlabifepostmfstcufhzboNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DCDocument21 pagesIntroduction To DCHillol DebNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud Computing ?Document2 pagesWhat Is Cloud Computing ?Ashraf MedNo ratings yet
- 2012 - Fail-Over ClusteringDocument34 pages2012 - Fail-Over ClusteringAbdul KasimNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument25 pagesIntroductionJonah K. MensonNo ratings yet
- Disconnected Operation in The Coda File SystemDocument23 pagesDisconnected Operation in The Coda File Systempravin_renold7435No ratings yet
- DockerTraining Nirmallya Day5Document33 pagesDockerTraining Nirmallya Day5Janaki sweetNo ratings yet
- The CAP Theorem and The Design of Large Scale Distributed Systems: Part IDocument44 pagesThe CAP Theorem and The Design of Large Scale Distributed Systems: Part IAnushriNo ratings yet
- DSECL ZG 522: Big Data Systems: Session 2: Parallel and Distributed SystemsDocument58 pagesDSECL ZG 522: Big Data Systems: Session 2: Parallel and Distributed SystemsSwati BhagavatulaNo ratings yet
- CSCE 613: Interlude: Distributed Shared MemoryDocument21 pagesCSCE 613: Interlude: Distributed Shared MemoryacercNo ratings yet
- Lec 03Document16 pagesLec 03youmnaxxeidNo ratings yet
- cloud computing الميدDocument2 pagescloud computing الميدDasha DeshoNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Scale Stretched Cluster Best PracticesDocument61 pagesSpectrum Scale Stretched Cluster Best PracticesAlexandre ReisNo ratings yet
- Flowvisor: A Network Virtualization LayerDocument15 pagesFlowvisor: A Network Virtualization LayerAlexandre B BritoNo ratings yet
- Paper PDFDocument52 pagesPaper PDFVengatraman PondicherryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Distributed Systems: Brian Nielsen Bnielsen@cs - Aau.dk Bnielsen@cs - Aau.dkDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Distributed Systems: Brian Nielsen Bnielsen@cs - Aau.dk Bnielsen@cs - Aau.dkIhab AmerNo ratings yet
- Apache Cassandra: by Chethan GowdaDocument12 pagesApache Cassandra: by Chethan GowdaChaithu GowdruNo ratings yet
- Adaptation For Mobile Data Access: (DM1 & PL1)Document40 pagesAdaptation For Mobile Data Access: (DM1 & PL1)Suraj ShahNo ratings yet
- Lecture1a DistSystDocument19 pagesLecture1a DistSystDeepesh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Eucalyptus Nimbus OpenNebulaDocument18 pagesEucalyptus Nimbus OpenNebulaAbhishek Nazare0% (1)
- SUSE HA Arch OverviewDocument26 pagesSUSE HA Arch Overviewpink blueNo ratings yet
- PDC 6 - Computer ClustersDocument16 pagesPDC 6 - Computer Clustersridz.ggsNo ratings yet
- Depspace: A Byzantine Fault-Tolerant Coordination ServiceDocument14 pagesDepspace: A Byzantine Fault-Tolerant Coordination Servicejoao.soares.diNo ratings yet
- Distributed SystemsDocument29 pagesDistributed Systemsproject122No ratings yet
- SystemdesignhandbookDocument39 pagesSystemdesignhandbookankur881120No ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document50 pagesChapter 02WilliamNo ratings yet
- Lecture#02 FileSystemAndDBDocument39 pagesLecture#02 FileSystemAndDBfarhan121921No ratings yet
- High Performance ComputingDocument61 pagesHigh Performance ComputingShrey Thakur100% (1)
- Amoeba: A Distributed Operating System For TheDocument10 pagesAmoeba: A Distributed Operating System For Thepou testeshitNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3 ... Part - 5Document21 pagesCh. 3 ... Part - 5ketan soniNo ratings yet
- A Mininet-Based Virtual Testbed For Distributed SDN DevelopmentDocument2 pagesA Mininet-Based Virtual Testbed For Distributed SDN DevelopmentRamadan GadahNo ratings yet
- Failover Clustering OverviewDocument2 pagesFailover Clustering OverviewDebashish RoyNo ratings yet
- Cache Coherence (Part 1)Document13 pagesCache Coherence (Part 1)mahmoudchawi100No ratings yet
- 3 Intro To CCDocument28 pages3 Intro To CC20010700No ratings yet
- Distributed SystemsDocument41 pagesDistributed Systemscomp.enginerNo ratings yet
- Virtualization Aware File Systems: Getting Beyond The Limitations of Virtual DisksDocument14 pagesVirtualization Aware File Systems: Getting Beyond The Limitations of Virtual DiskssushmsnNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Processes and Threads in DSDocument54 pagesChapter-2 Processes and Threads in DSGUTAMA KUSSE GELEGLONo ratings yet
- CCunit 1Document57 pagesCCunit 1Manish RoyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing with the Windows Azure PlatformFrom EverandCloud Computing with the Windows Azure PlatformRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- DRBD-Cookbook: How to create your own cluster solution, without SAN or NAS!From EverandDRBD-Cookbook: How to create your own cluster solution, without SAN or NAS!No ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Scheme For Clustering Protocol Prolonging The Lifetime of Heterogeneous Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument7 pagesEnergy Efficient Scheme For Clustering Protocol Prolonging The Lifetime of Heterogeneous Wireless Sensor NetworksShital JoshiNo ratings yet
- Design of A Distributed Energy-E Cient Clustering Algorithm For Heterogeneous Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument8 pagesDesign of A Distributed Energy-E Cient Clustering Algorithm For Heterogeneous Wireless Sensor NetworksShital JoshiNo ratings yet
- Power-Gated 9T SRAM Cell For Low-Energy OperationDocument5 pagesPower-Gated 9T SRAM Cell For Low-Energy OperationShital JoshiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6: September 20: 6.1.1 Processes Vs ThreadsDocument3 pagesLecture 6: September 20: 6.1.1 Processes Vs ThreadsShital JoshiNo ratings yet
- A Survey of IoT Authentication SchemesDocument43 pagesA Survey of IoT Authentication SchemesShital JoshiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 15 (Operating Systems An Overview)Document37 pagesCHAPTER - 15 (Operating Systems An Overview)Shital JoshiNo ratings yet
- CSS Tips & TricksDocument4 pagesCSS Tips & TricksShital JoshiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 16 (The User View of Operating Systems)Document32 pagesCHAPTER - 16 (The User View of Operating Systems)Shital JoshiNo ratings yet
- CS6411 Network Lab ManualDocument73 pagesCS6411 Network Lab ManualShital Joshi0% (1)
- Memristive Devices Fabrication, Characterization, and ModelingDocument125 pagesMemristive Devices Fabrication, Characterization, and ModelingShital JoshiNo ratings yet
- Adding Hyperlink To XML PublisherDocument2 pagesAdding Hyperlink To XML PublisherdonghoangnguNo ratings yet
- Sage300 GeneralLedger UsersGuideDocument280 pagesSage300 GeneralLedger UsersGuideAmani100% (1)
- RHUB3908 Hardware Maintenance GuideDocument22 pagesRHUB3908 Hardware Maintenance Guideapiruck sukjingNo ratings yet
- AC800F F2K Connect B1 6.2 CONFIGURATIONDocument43 pagesAC800F F2K Connect B1 6.2 CONFIGURATIONassessorNo ratings yet
- SanfoundryDocument3 pagesSanfoundryvaishnavi khilariNo ratings yet
- 5-M-BudgetDocument139 pages5-M-BudgetJohannes Gregorii LagueNo ratings yet
- RFC-1846 & Reply Code-521Document2 pagesRFC-1846 & Reply Code-521pandyakavi100% (1)
- Whats Notable and Different Oracle Analytics ServerDocument7 pagesWhats Notable and Different Oracle Analytics Serverquintas omondiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SMADocument35 pagesChapter 2 SMAandrinaNo ratings yet
- Food Delivery App BrochureDocument21 pagesFood Delivery App Brochurepatrickmengelwa9No ratings yet
- PHET Capacitor Internet LabDocument2 pagesPHET Capacitor Internet Labsobre1982No ratings yet
- GFST200Document7 pagesGFST200Arif andreas panjaitanNo ratings yet
- 1FK7063 2AF71 1RA1 Datasheet enDocument2 pages1FK7063 2AF71 1RA1 Datasheet enMd MansoorNo ratings yet
- Formato - Service Report - Motor Grader - KLTDDocument1 pageFormato - Service Report - Motor Grader - KLTDWILDERNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Nw-A30 1.1Document54 pagesService Manual Nw-A30 1.1alexandru ilieNo ratings yet
- Recommendation Letter From Team Lead For MS in CS PDFDocument3 pagesRecommendation Letter From Team Lead For MS in CS PDFgutsweNo ratings yet
- Basic PythonDocument40 pagesBasic PythonLearning Online Classes33% (3)
- AXWT-6 Manual PDFDocument14 pagesAXWT-6 Manual PDFNasser Youssouf MahamoudNo ratings yet
- Risk Leadership's Guide To The Second-Phase Impact of COVID-19Document3 pagesRisk Leadership's Guide To The Second-Phase Impact of COVID-19JMHRNo ratings yet
- Mobile Game NDA - Athar Ahmad MahmoodDocument3 pagesMobile Game NDA - Athar Ahmad MahmoodatharahmadmahmoodNo ratings yet
- 2) Memory and Storage Devices: Multimedia HardwareDocument4 pages2) Memory and Storage Devices: Multimedia HardwarekhananuNo ratings yet
- Machines Ece Class SamplesDocument3 pagesMachines Ece Class SamplesSonic HedgehogNo ratings yet
- WUSB600N V20 DS NC-web, 0Document2 pagesWUSB600N V20 DS NC-web, 0cavmfrNo ratings yet
- Exercices Corrigés D'algèbre Linéaire - Tome 2, Résumé de Cours Et Exercices Corrigés Broché - 12 Avril 2006 (PDFDrive)Document353 pagesExercices Corrigés D'algèbre Linéaire - Tome 2, Résumé de Cours Et Exercices Corrigés Broché - 12 Avril 2006 (PDFDrive)Med Raslene AlouiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument21 pagesUntitledBalderama ChickenNo ratings yet
- Anand Kumar LatestDocument1 pageAnand Kumar Latestapi-554643283No ratings yet
- Hasnain Yaseen: (Electrical Engineer)Document1 pageHasnain Yaseen: (Electrical Engineer)Syed Hasnain YaseenNo ratings yet
- 04 - Programming LayerDocument59 pages04 - Programming LayerLuân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Joining Form - C&a SystemsDocument2 pagesJoining Form - C&a SystemsVaibhav PrajapatiNo ratings yet