Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. Dungca
Hypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. Dungca
Uploaded by
JAMES ROD MARINDUQUEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. Dungca
Hypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. Dungca
Uploaded by
JAMES ROD MARINDUQUECopyright:
Available Formats
HYPOTHERMIA
By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. Dungca
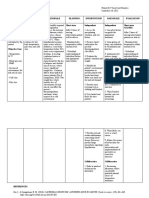
Nursing Nursing Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Assessment Diagnosis
Objective: Ineffective After 4 hours Independent: After 4 hours of
Pale, weak thermoregulation: of nursing 1. Note patient’s age To impart the proper nursing
looking and hypothermia intervention, 2. Determine if present medication intervention, the
cold clammy related to the patient will illness or condition Causative factors guide the patient will have a
skin excessive have a body appropriate treatment. body temperature
results from exposure
Blood loss bleeding. temperature within normal
to environmental
estimated more within normal limits as
limits as factors, trauma, or manifested by an
than 500 mL as
evidenced of manifested by infection increase of
3. Note and monitor For alert patients, oral
profusely an increase of temperature is regarded as
temperature from
bleeding temperature patient’s more reliable than tympanic or 35.3 C to 36.5 C.
Hypothermia from 35.3 C to temperature. axillary. For hypothermic
* Temp: 35.3 36.5 C. patients, core temperature can GOAL: MET
* BP: 130/90 be monitored using a
* SP02: 94℅ temperature-sensitive
* BPM: 110 pulmonary artery catheter or
bladder catheter.
4. Regulate the These methods provide for a
environment more gradual warming of the
temperature or body. Rapid warming can
relocate the patient to induce ventricular fibrillation.
Moisture promotes
a warmer setting. evaporative heat loss.
Keep the patient and
linens dry.
5. Let the patient The more we understand how
verbalize risk and protective factors
interact, the better prepared we
understanding of will be to develop appropriate
individual risk factor. interventions.
6. Demonstrate
Patient is able to monitor and
behaviors for maintain temperature with
monitoring and herself.
maintaining
appropriate body
temperature
7. Provide extra heat
These measures raise the core
source: temperature and improve
Heat lamp, circulation. Core warming is
radiant warmer indicated when body
Warming pads, temperature is below 30 °C
mattress, or (86 °F).
blankets
Submersion in a
warm bath
Heated,
moisturized
oxygen
Warmed
intravenous
fluids or lavage
fluids
Collaborative:
1. Monitor fluid intake Decreased output may indicate
and urine output dehydration or poor renal
(and/or central perfusion. Avoid fluid
overload to prevent pulmonary
venous pressure).
edema, pneumonia, and taxing
2. Check for electrolytes, an already compromised
arterial blood gases, and cardiac and renal status.
oxygen saturation by
pulse oximetry.
Acidosis may emerge from
hypoventilation and hypoxia.
You might also like
- NCP FeverDocument3 pagesNCP Feversinister1785% (48)
- Flocare Infinity Pump Troubleshooting GuideDocument6 pagesFlocare Infinity Pump Troubleshooting GuideLorena GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nurse Practitioner Board ReviewFrom EverandNurse Practitioner Board ReviewRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 057608komatsu Hydraulic Oil HO 46-HMDocument5 pages057608komatsu Hydraulic Oil HO 46-HMrolex21No ratings yet
- Fever NCPDocument5 pagesFever NCPNikael Patun-ogNo ratings yet
- NCP LeptospirosisDocument2 pagesNCP LeptospirosisLouise Anne Asuncion OclimaNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLODocument4 pagesHyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLOMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Gender: FemaleDocument9 pagesGender: FemaleNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPTroy MirandaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Chicken PoxDocument4 pagesNCP - Chicken Poxhanna_lim0% (1)
- Dnrle Influenza NCPDocument3 pagesDnrle Influenza NCPEna RodasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationAlyssa Moutrie Dulay Arabe100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentKristine Young67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Soure: Marilyn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr "Nursespocket Guide."14th Ed.p.784Document30 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Soure: Marilyn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr "Nursespocket Guide."14th Ed.p.784Jesil MarolinaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentMoi Valdoz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationWinnie AriolaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanAnnahNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentKasandra Dawn Moquia Beriso100% (1)
- NCP Hyperthermia Related To Underlying InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP Hyperthermia Related To Underlying InfectionNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia (Hipertermia)Document5 pagesHyperthermia (Hipertermia)Eki MegaraniNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument3 pagesHyperthermia NCPkaylejordan_29100% (2)
- Nursing InterventionsDocument37 pagesNursing InterventionsRajalakshmi100% (1)
- NCP Case PresDocument2 pagesNCP Case PresAnton QueralNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationChristian ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Case Agent RookieDocument2 pagesActivity 1 - Case Agent RookieChristian ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMichelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument7 pagesVital SignsEmeroot RootNo ratings yet
- CHN RleDocument3 pagesCHN RleCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesChicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- NCM 101B - NCP - Miguel, Roenth Rhene D - BSN 1DDocument2 pagesNCM 101B - NCP - Miguel, Roenth Rhene D - BSN 1DRiri MiguelNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Need Objective Interventions Evaluation Subjective Data: C O G N I T I V E - P E R C E P T U A L Goal MetDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Need Objective Interventions Evaluation Subjective Data: C O G N I T I V E - P E R C E P T U A L Goal MetAngel Mikaela CilladoNo ratings yet
- Weygan NCPDocument5 pagesWeygan NCPKate WeyganNo ratings yet
- SNU49Document2 pagesSNU49Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- SNU49Document2 pagesSNU49Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment: Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Goal: Nursing Intervention: Rationale: EvaluationDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment: Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Goal: Nursing Intervention: Rationale: Evaluationeliza luisNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis - Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesToxoplasmosis - Nursing Care PlanJulia Trisha MasukolNo ratings yet
- Influenza PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument3 pagesInfluenza PATHOPHYSIOLOGYElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention RationaleDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationalekimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAkiraMamoNo ratings yet
- NCP Sample 1Document9 pagesNCP Sample 1Vincent BarcenillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan PediaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan PediaNat B. AntipoloNo ratings yet
- NCP No. 2Document2 pagesNCP No. 2Lorraine Tuesday BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- HYPOTHERMIADocument3 pagesHYPOTHERMIARyll Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- TASk 2 DS NCPDocument3 pagesTASk 2 DS NCPCHRISTIAN CALAMBANo ratings yet
- NCP For Swine FluDocument3 pagesNCP For Swine FluGiana CalloNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument8 pagesHyperthermiaAzizah Widyawati RahmahNo ratings yet
- NCP PediaDocument9 pagesNCP Pediajuworski1No ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument2 pagesHyperthermia NCPmahangin85% (20)
- HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesHyperthermiaSäbïná D. GabätöNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: FeverDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: FeverOlive Claire T. ManlambusNo ratings yet
- VI. Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesVI. Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationJenny AjocNo ratings yet
- The Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseFrom EverandThe Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Hypothermia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypothermia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Guillain Barre Syndrome A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandGuillain Barre Syndrome A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Flu: A Guide for Prevention and TreatmentFrom EverandThe Flu: A Guide for Prevention and TreatmentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Critical CareDocument22 pagesCritical CareJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Marinduque CS InstrumentsDocument6 pagesMarinduque CS InstrumentsJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- EnemaDocument33 pagesEnemaJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument16 pagesPulmonary EmbolismJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- New Ballard ScoreDocument39 pagesNew Ballard ScoreJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Family Nursing ProcessDocument25 pagesFamily Nursing ProcessJAMES ROD MARINDUQUE100% (1)
- 19th Century Philippines As RizalDocument3 pages19th Century Philippines As RizalJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (Imci)Document6 pagesLesson 2 Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (Imci)JAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- SKILL: Providing Perineal - Genital Care: Preparations 0 1 2 CommentsDocument4 pagesSKILL: Providing Perineal - Genital Care: Preparations 0 1 2 CommentsJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- High-Risk Labor & Delivery Client & Her FamilyDocument68 pagesHigh-Risk Labor & Delivery Client & Her FamilyJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Note PediaDocument4 pagesNote PediaJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance-NCPDocument5 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance-NCPJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Enteral Nutriton TherapyDocument5 pagesEnteral Nutriton TherapyJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Caesarean SectionDocument42 pagesCaesarean SectionJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument2 pagesAnesthesiaJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument14 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Introduction& History of Microbiology For FB PDFDocument96 pagesIntroduction& History of Microbiology For FB PDFJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation MedicaleDocument458 pagesRehabilitation MedicaleactoneNo ratings yet
- Ultrarunning MagDocument60 pagesUltrarunning MagLynseyNo ratings yet
- Betz Rebecca ResumeDocument2 pagesBetz Rebecca Resumeapi-316054946No ratings yet
- OPD and OT Days of Doctors of Clinical Department of Guru Gobind Singh Medical HospitalDocument4 pagesOPD and OT Days of Doctors of Clinical Department of Guru Gobind Singh Medical HospitalBohar singh Brar BrarNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Nutritional Changes in Food During ExtrusionDocument30 pagesChemical and Nutritional Changes in Food During ExtrusionZubi BaigNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument10 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseSusana Soto López100% (2)
- CSQ Nap4 FullDocument219 pagesCSQ Nap4 FullJeisson FarroNo ratings yet
- Emergency Animal Hospital in Clifton Veterinary Emergency GroupDocument1 pageEmergency Animal Hospital in Clifton Veterinary Emergency Group6kqznycbyzNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Vaccination Microplan Date - (06-05-2021) District: Kanpur NagarDocument4 pagesCovid-19 Vaccination Microplan Date - (06-05-2021) District: Kanpur NagarAditi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Kiran Raju - Techversant PayslipDocument3 pagesKiran Raju - Techversant PayslipCap RJNo ratings yet
- Clinical AssignmentDocument9 pagesClinical AssignmentkomalNo ratings yet
- Soal D3 Bidan HermanDocument2 pagesSoal D3 Bidan HermanMidwifeDeviFadhaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat %pareto Dan Ven 15Document200 pagesDaftar Obat %pareto Dan Ven 15sofia nofiantiNo ratings yet
- Central HypotoniaDocument5 pagesCentral HypotoniaayunisallehNo ratings yet
- Medicare Enrollment TipsDocument34 pagesMedicare Enrollment TipsdaringdreuNo ratings yet
- Anthropometry For ElderlyDocument20 pagesAnthropometry For ElderlyjarvantaraNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Medicine For Bhutansha RasaDocument6 pagesAyurvedic Medicine For Bhutansha RasaKolluri RajeshNo ratings yet
- Cheung2020 PDFDocument15 pagesCheung2020 PDFSandra Milena Cortes SotoNo ratings yet
- MSPG Infographic 2Document9 pagesMSPG Infographic 2Norzaherawati Aryani Md TahirNo ratings yet
- SynopsisDocument8 pagesSynopsisarunNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Centre: Assignment - 3Document12 pagesDialysis Centre: Assignment - 3grvoneandonlyNo ratings yet
- Brain Workshop - a Dual N-Back game - نسخةDocument4 pagesBrain Workshop - a Dual N-Back game - نسخةBTQNo ratings yet
- College of Criminal Justice Education Block Schedule of CoursesDocument12 pagesCollege of Criminal Justice Education Block Schedule of CoursesKristel Ann ManlangitNo ratings yet
- Practice 9-10-11Document12 pagesPractice 9-10-11cheplit123No ratings yet
- 3) Z. 10.1016@j.jcrc.2020.06.005 (Alexis Tabah)Document18 pages3) Z. 10.1016@j.jcrc.2020.06.005 (Alexis Tabah)Mastifa HanasitaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Penerapan Metode Activity Based Costing (ABC) Dalam Menentukan Tarif Jasa Rawat Inap Di RSUD Kota PrabumulihDocument12 pagesAnalisis Penerapan Metode Activity Based Costing (ABC) Dalam Menentukan Tarif Jasa Rawat Inap Di RSUD Kota PrabumulihAffira AfriNo ratings yet
- Admission: Athia Fidian, M.PDDocument6 pagesAdmission: Athia Fidian, M.PDAthiaNo ratings yet
- ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 Edition - Ning PDFDocument112 pagesACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 Edition - Ning PDFbasuthker raviNo ratings yet