Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Med Template
Med Template
Uploaded by
AnbarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Med Template
Med Template
Uploaded by
AnbarCopyright:
Available Formats
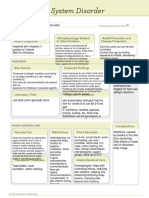
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: Medication
Anbar Yaqoob
STUDENT NAME______________________________________
Calcium Gluconate
MEDICATION___________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER__58
__________
CATEGORY CLASS__Antidotes, Other; Calcium Salts
_____________________________________________________________________
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic Use
Maintain cell membrane and capillary Replacement of calcium for deficiencies.
permeability. Helps in transmission of nerve Treatment of hyperkalemia, hyper-magnesia, and
impulses and contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and adjunct in cardiac arrest or calcium channel
smooth muscle. Essential for bone formation and blocking agent toxicity
blood coagulation.
Complications Medication Administration
Little or no urination, swelling, rapid weight gain, Calcium Gluconate should be
lightheadedness, slow or irregular heartbeats, nausea, vomiting, administered intravenously either
constipation, increased thirst or urination, muscle weakness, directly or by infusion. Adults: 500
bone pain, confusion, lack of energy, and feeling tired mg - 2 grams (5-20 mL). Children:
200-500 mg (2-5 mL). Infants: not
more than 200 mg (not more than 2
mL)
Contraindications/Precautions
Hypercalcemia, renal calculi, ventricular fibrillation, severe
respiratory insufficiency patients, renal disease, cardiac
Nursing Interventions
disease,
Monitor ECG and BP frequently.
Administer infusion slowly. Monitor
vital signs throughout infusion. If
patient experiences side effects,
halt infusion and resume slowly
Interactions once symptoms stop
Calcium can decrease the absorption of other drugs such as
bisphosphonates (for example, alendronate), tetracycline
antibiotics (such as doxycycline, minocycline), estramustine,
levothyroxine, and quinolone antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin,
levofloxacin). Certain foods (cereals, spinach) may decrease
absorption
Client Education
Do not take any OTC
medication without
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness consulting physician. Maintain diet with
adequate calcium levels. Separate
Increase in serum calcium levels. Decrease in the signs and other medications as recommended by
symptoms of hypocalcemia. Decrease in the signs and physician with calcium supplements.
symptoms of magnesium toxcity. Muscular issues resolved Avoid alcohol and smoking. Watch for
signs of drug interactions or
hyper/hypocalcemia and report to
physician immediately
Source: ATI Medication Book and
https://www.rxlist.com/consumer_calcium_gluconate_gluconate_ca/drugs-condition.htm#what_other_drugs_interact
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES Therapeutic Procedure A7
You might also like
- System Do CopdDocument1 pageSystem Do CopdMarissa Hamby100% (1)
- Ati Medication Template KetorolacDocument1 pageAti Medication Template KetorolacSharee HaywoodNo ratings yet
- Name of Student: - InstructionDocument31 pagesName of Student: - InstructionPaul Jackson50% (2)
- Ati Medication Template HydrocortisoneDocument1 pageAti Medication Template HydrocortisoneSharee HaywoodNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Case 1: Jackson Weber (Core) : Guided Reflection QuestionsDocument3 pagesPediatric Case 1: Jackson Weber (Core) : Guided Reflection QuestionsDai Nguyen100% (1)
- System Disorder GHDDocument1 pageSystem Disorder GHDSariahNo ratings yet
- Medication - ALT-Template - Albuterol Sulfate PDFDocument1 pageMedication - ALT-Template - Albuterol Sulfate PDFNancyAmissah100% (1)
- Ams 11Document702 pagesAms 11CrazyNo ratings yet
- System Disorder: Renal CalculiDocument1 pageSystem Disorder: Renal CalculiHolly DeckelmanNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Maternity Case 5: Fatime SanogoDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Maternity Case 5: Fatime SanogoNicole AngelNo ratings yet
- Ati Medication Template CodeineDocument1 pageAti Medication Template CodeineSharee HaywoodNo ratings yet
- Final Evaluation - With CommentsDocument19 pagesFinal Evaluation - With Commentsapi-313720439No ratings yet
- A Beautiful MindDocument7 pagesA Beautiful Mindapi-308731198No ratings yet
- Acetaminophen PDFDocument1 pageAcetaminophen PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- N 313 Pediatric Nursing Syllabus Fall 2011 Part 1Document12 pagesN 313 Pediatric Nursing Syllabus Fall 2011 Part 1bmccsnresourcesNo ratings yet
- Ocne Competencies Updated 3 11 15Document8 pagesOcne Competencies Updated 3 11 15api-255767391No ratings yet
- OB MIdterm ExamDocument31 pagesOB MIdterm Examkatiana louisNo ratings yet
- SERVAID Internship ReportDocument25 pagesSERVAID Internship ReportHafsa Ahmed100% (1)
- Cun Dell Objectionable Microorganism Sept 2015Document36 pagesCun Dell Objectionable Microorganism Sept 2015KuldeepNo ratings yet
- ATI Medication Template RanitidineDocument1 pageATI Medication Template RanitidineSharee HaywoodNo ratings yet
- Waiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Focused ReviewDocument6 pagesFocused ReviewGina GiammalvoNo ratings yet
- MedSurg Nursing Clinical-Concept Map-2Document3 pagesMedSurg Nursing Clinical-Concept Map-2adaezeNo ratings yet
- Medication - ALT-Template - Enoxaparin SodiumDocument1 pageMedication - ALT-Template - Enoxaparin SodiumNancyAmissahNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test Psychiatric NursingDocument17 pagesPre-Test Psychiatric NursingDefensor Pison Gringgo100% (1)
- Concept Map TemplateDocument16 pagesConcept Map Templatenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Nursing PhilosophyDocument1 pageNursing PhilosophyNene DikeNo ratings yet
- System Disorder ADDocument1 pageSystem Disorder ADSariahNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin Med InfoDocument1 pageAmpicillin Med InfoJan McgovernNo ratings yet
- Health PromotionDocument5 pagesHealth Promotionapi-433917537No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan #1 Mental HealthDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan #1 Mental HealthNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis TemplateDocument6 pagesNursing Diagnosis Templatesdk6972No ratings yet
- Community Mental Health NursingDocument16 pagesCommunity Mental Health NursingsrinivasanaNo ratings yet
- Draft: Jurisprudence Learning Module & ExaminationDocument45 pagesDraft: Jurisprudence Learning Module & ExaminationDeepanshi RajputNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - The Nursing ProcessDocument10 pagesWeek 4 - The Nursing ProcessMiss VinaNo ratings yet
- GI Notes For Exam 3Document4 pagesGI Notes For Exam 3cathyNo ratings yet
- NFDN 2005 Professional PortfolioDocument2 pagesNFDN 2005 Professional PortfolioTiffany MartellsNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic Usekelly fullingimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Concept MapDocument2 pagesNursing Concept MapMary Mann100% (1)
- A00-212 Braindumps SAS Institute SAS Institute Systems CertificationDocument6 pagesA00-212 Braindumps SAS Institute SAS Institute Systems Certificationdhiraj_nilangeNo ratings yet
- Spices ToolDocument2 pagesSpices ToolTrisha Fae Loyola BalagotNo ratings yet
- Individual Performance Profile PN Mental Health 2011 Form BDocument4 pagesIndividual Performance Profile PN Mental Health 2011 Form BStan TanNo ratings yet
- History and Evolution of NursingDocument45 pagesHistory and Evolution of NursingStephany Zamoras100% (1)
- Question PsychDocument23 pagesQuestion PsychChucky VergaraNo ratings yet
- Basic Nursing Fundamentals EliminationDocument35 pagesBasic Nursing Fundamentals Eliminationlisa100% (1)
- Quotes NursingDocument14 pagesQuotes NursingFreddy ÁlvaroNo ratings yet
- Nur411 Syllabus Part 1 Fall 2011Document21 pagesNur411 Syllabus Part 1 Fall 2011bmccsnresources0% (1)
- Neurologic System: Carolyn Jarvis Physical Examination and Health Assessment Fourth EditionDocument37 pagesNeurologic System: Carolyn Jarvis Physical Examination and Health Assessment Fourth Edition03152788100% (1)
- ATI RN Mental Health Online Practice BDocument38 pagesATI RN Mental Health Online Practice Bseansdrew2No ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument1 pagePeptic Ulcer DiseaseEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Vsim Nursing Assignment #1: Toua Xiong 501 Pathophysiology and Pharmacology Gelsey Jian University of Maryland School of Nursing 9/14/18Document7 pagesVsim Nursing Assignment #1: Toua Xiong 501 Pathophysiology and Pharmacology Gelsey Jian University of Maryland School of Nursing 9/14/18Gelsey Gelsinator JianNo ratings yet
- Guide Mse For Vsim Sharon ColeDocument3 pagesGuide Mse For Vsim Sharon Cole002No ratings yet
- Clinical Case Study - Online Discussion Form Fall 2020-1Document14 pagesClinical Case Study - Online Discussion Form Fall 2020-1Sabrina Odies100% (1)
- Nursing Pharmacology HandoutsDocument10 pagesNursing Pharmacology HandoutsMICHAELA TIMBOLNo ratings yet
- Pyschiatric Nursing SummarizeDocument39 pagesPyschiatric Nursing SummarizeKyssel Seyer100% (1)
- Concept Map COPDDocument2 pagesConcept Map COPDnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Porfolio NFDN 2005Document2 pagesPorfolio NFDN 2005api-318906225100% (1)
- Med Surg Week 6Document11 pagesMed Surg Week 6Eunice Cortés100% (1)
- Health Assessment - in ProgressDocument50 pagesHealth Assessment - in ProgressCindy MaharajNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing Bullets Neurotransmission TheoryDocument4 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Bullets Neurotransmission TheoryDefensor Pison Gringgo100% (1)
- Meds - KaplanDocument3 pagesMeds - KaplanJodi BairNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Ha SL PrelimsDocument11 pagesHa SL PrelimsEthel May GranilNo ratings yet
- Midodrine For Post-Operative Hypotension - 094 - 2021-02Document3 pagesMidodrine For Post-Operative Hypotension - 094 - 2021-02Miad HabibiNo ratings yet
- A Critical Analysis of The UGC-approved List of Journals' List of Verified JournalsDocument54 pagesA Critical Analysis of The UGC-approved List of Journals' List of Verified JournalsHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Case 1 Health PlusDocument2 pagesCase 1 Health PlusCia SevillaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.1 Department of Health Area Program-Based Health PlanningDocument7 pagesWorksheet 1.1 Department of Health Area Program-Based Health PlanningNik Rose ElNo ratings yet
- Flazol®: Metronidazole Tablets I Ora SuspensionDocument1 pageFlazol®: Metronidazole Tablets I Ora Suspensionahmad albadryNo ratings yet
- Promethazine (Phenergan)Document1 pagePromethazine (Phenergan)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacovigilance Responsibilities of Medicine Sponsors: Australian Recommendations and RequirementsDocument44 pagesPharmacovigilance Responsibilities of Medicine Sponsors: Australian Recommendations and RequirementsAnne LethbridgeNo ratings yet
- 2012-Iadc Isp Qa Book2Document30 pages2012-Iadc Isp Qa Book2Teodor Ioan Ghinet Ghinet DorinaNo ratings yet
- National Pharmaceutical Master PlanDocument13 pagesNational Pharmaceutical Master PlanNitu AhmadNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument21 pagesSeminar ReportGurdev SinghNo ratings yet
- The Medication Order Unit 11Document10 pagesThe Medication Order Unit 11novie100% (2)
- Consent Form Male To Female.Document10 pagesConsent Form Male To Female.Vivian LuxonNo ratings yet
- Policies of Pharmacy and Therapeutic CommitteeDocument36 pagesPolicies of Pharmacy and Therapeutic CommitteeSamson Raj100% (6)
- Mid-April 2021Document20 pagesMid-April 2021John M100% (1)
- Substance Impairment PolicyDocument4 pagesSubstance Impairment PolicyryanmackintoshNo ratings yet
- Rights: THE of Our Patients, and TheirDocument3 pagesRights: THE of Our Patients, and TheirAccreditation ConsultantNo ratings yet
- AstraZeneca ARA 09Document212 pagesAstraZeneca ARA 09Jordan BarnesNo ratings yet
- Almanacs, Handbooks, FactbooksDocument28 pagesAlmanacs, Handbooks, FactbooksIbrahimh504No ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument8 pagesStrategic ManagementAlbert Katabarwa100% (1)
- Catalogo Tecnico 2018Document26 pagesCatalogo Tecnico 2018rene david villacis orqueraNo ratings yet
- International: The Year of COVID: Top 20 COVID-19 Care & Treatment Milestones of 2020Document28 pagesInternational: The Year of COVID: Top 20 COVID-19 Care & Treatment Milestones of 2020Anonymous 58LGc3No ratings yet
- AESGP Regulatory Conference, Conference ReportDocument4 pagesAESGP Regulatory Conference, Conference ReportaesgpNo ratings yet
- The Water CureDocument10 pagesThe Water Curemaro108No ratings yet
- Quality Control Analysis of Chlorpheniramine Maleate Marketed in NigeriaDocument7 pagesQuality Control Analysis of Chlorpheniramine Maleate Marketed in Nigeriaحمزة الفنينيNo ratings yet
- Pharma CO VigilanceDocument33 pagesPharma CO VigilanceSravani ReddyNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument6 pagesPDFKoko “urya” No NekoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients Receiving ChemotherapyDocument28 pagesNursing Care of Patients Receiving Chemotherapyradhagiri79% (19)