Professional Documents
Culture Documents
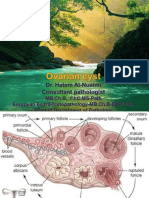
Ovarian Cyst
Ovarian Cyst
Uploaded by
Loriene LopezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ovarian Cyst
Ovarian Cyst
Uploaded by
Loriene LopezCopyright:
Available Formats
Ovarian Cyst 4.
Maternal gonadotropins
5. Cigarette Smoking
a sac filled with fluid or a semisolid material that forms on or
6. Tubal Ligation
within one of the ovaries. Complications
Most ovarian cysts occur as part of the normal workings of the Ovarian torsion: all ovarian cysts have the potential to twist on
ovaries. These cysts are generally harmless and disappear their axes or "torse," occluding vascular supply. Larger cysts
without treatment in a few months (over 6 cm) are more likely to torse. Ovarian torsion is a surgical
Cysts caused by abnormal cell growth and aren’t related to the emergency as the ovary must be promptly untwisted to restore
menstrual cycle. They can develop before and after menopause perfusion and preserve ovarian tissue. Ultrasound with Doppler
Ovaries can identify lack of blood flow to the ovary.
small organs in the pelvis that make female hormones and hold Cyst rupture: all cyst types can potentially rupture, spilling fluid
egg cells. into the pelvis, which is often painful. If the contents are from a
Types of Cysts dermoid or abscess, surgical lavage may be indicated.
Functional Cysts Hemorrhagic Cysts Hemorrhage: In the case of hemorrhagic cysts, the management
Cysts that develop as part of The granulosa layer of the of hemorrhage depends on the hemodynamic stability of the
the menstrual cycle and are ovary remains avascular until
usually harmless and the time of ovulation. After patient, but is most often expectantly managed.
short-lived ovulation occurs, the granulosa
Diagnosis and Tests
Most common type of Ovarian layer quickly becomes
cyst;usually asymptomatic vascularized by thin-walled A pelvic exam: During this exam, the doctor uses an instrument
generally shrink over time, vessels, which rupture easily,
usually within 60 days, without giving rise to a hemorrhagic to widen the vagina, which allows the doctor to examine the
specific treatment. cyst
Follicular Cyst internal hemorrhage occurs into vagina, cervix and uterus. The doctor also feels the reproductive
results when the follicle does functional cysts of the ovary organs for any lumps or changes.
not release an egg
fluid in the follicle remains and Blood tests: These tests are used to measure the levels of
forms a cyst
usually harmless and go away certain hormones in the blood.
on their own in time.
Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to create images of the
Corpus Luteum Cyst
develops when a follicle seals body's internal organs. It can be used to detect cysts on the
after releasing an egg.
Fluid builds up in the follicle and ovaries.
forms a cyst
can grow quite large and Laparoscopy: This is a procedure, performed in an operating
become several inches in size room, in which the doctor inserts a small device through an
It may rupture and bleed
The fertility drug clomiphene incision (cut) in the abdomen. He or she views the reproductive
citrate increases the risk of
developing a corpus luteum organs and pelvic cavity using the device. If a cyst is diagnosed
cyst.
at this time, it can be removed.
A corpus luteum cyst does not
harm or threaten a pregnancy. Medical history and physical findings: large cysts may be
palpable on abdominal examination.
Dermoid Cysts Endometriomas
Mature Cystic Teratomas a type of cyst that is filled with
Pregnancy Test: a positive result may suggest the patient has a
a saclike growth that is present menstrual blood and Corpus Luteum Cyst
at birth. endometrial tissue.
contain mature tissue of arise either via retrograde Medical Treatment
ectodermal (eg, skin, hair), menstruation from the uterus or
mesodermal (eg, muscle, bleeding from an endometriotic Functional ovarian cysts generally go away without treatment.
urinary), and endodermal (eg, implant itself. Watchful waiting (observation): An Ultrasound scan will be
gastrointestinal, lung) origin
are almost always benign but carried out about a month or so later to check it, and to see
have the potential to rupture,
spilling sebum, or torse whether it has gone
Birth Control Pills: to reduce the risk of new cysts developing in
Signs and Symptoms future menstrual cycles, doctor may recommend this. Oral
An ovarian cyst may or may not produce symptoms. Larger cysts may contraceptives also reduce the risk of developing ovarian cancer
cause the following symptoms: Analgesic (Pain Relievers): such as nonsteroidal
1. Pelvic pain or a dull ache in your back. anti-inflammatory drugs, opiod analgesic
2. A feeling of fullness (bloating) in your lower belly.
3. Pain during intercourse. Surgical treatment:
4. Painful periods. Laparoscopy: This is a procedure in which the doctor inserts
5. Breast tenderness
6. Nausea and vomiting a small device through a small incision in the abdomen. He or
Some prolonged symptoms may be associated with a condition she views the reproductive organs and pelvic cavity using the
called polycystic ovary syndrome. device. The doctor can remove the cyst through tiny incisions.
When a cyst ruptures from the ovary, there may be: Laparotomy: This procedure uses a bigger incision to remove
1. Severe or sharp pelvic pain in lower abdomen in one side the cyst. The cyst will be tested for cancer. If it is cancer, the
2. Fever
3. Faintness or dizziness doctor may need to remove one or both ovaries, the uterus, a
4. Rapid breathing fold of fatty tissue called the omentum and some lymph nodes.
Risk Factors
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures found
1. Infertility Treatment
2. Pregnancy throughout the body that produce and store infection-fighting
3. Hypothyroidism cells, but may contain cancer cells.
You might also like
- Germ Cell Tumor Ovary PDFDocument70 pagesGerm Cell Tumor Ovary PDFmelysaNo ratings yet
- Neuro 2 AnsDocument14 pagesNeuro 2 AnsSantiago AldayNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CystDocument26 pagesOvarian CystAlmyr RimandoNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Document11 pagesCP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease - A Case StudyDocument13 pagesCongenital Heart Disease - A Case Studydna2life0% (1)
- Urolithiasis PowerpointDocument41 pagesUrolithiasis PowerpointPinkrose Chiong FabellaNo ratings yet
- HEMOTHORAXDocument7 pagesHEMOTHORAXVanessa Kate Rosalejos JailaniNo ratings yet
- Case Study GonorrheaDocument37 pagesCase Study GonorrheaAnge MinguitoNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument5 pagesMalariaMiguel Cuevas Dolot100% (1)
- MiscarriageDocument42 pagesMiscarriageAnonymous pJfAvl100% (3)
- Acute PeritonitisDocument4 pagesAcute PeritonitisSatrio Tri HadmokoNo ratings yet
- Complete Intestinal ObstructionDocument8 pagesComplete Intestinal ObstructionThuganamix100% (2)
- Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument12 pagesAcute Lymphocytic Leukemiajustin_saneNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesDischarge PlanPaul Loujin LeeNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Dumaguete College of NursingDocument15 pagesSt. Paul University Dumaguete College of NursingaltianNo ratings yet
- AnencephalyDocument10 pagesAnencephalyRm LavariasNo ratings yet
- Dilation and Curettage Janelle ReforDocument4 pagesDilation and Curettage Janelle ReforCjay HernandezNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument3 pagesAbruptio Placentachichilovesyou100% (1)
- Acute Cholecystitis: Pableo, Rachel MDocument47 pagesAcute Cholecystitis: Pableo, Rachel MLd Rachel PableoNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhoea FactsheetDocument4 pagesGonorrhoea FactsheetWilhelmus Wincent WijayaNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument33 pagesBreast Canceredenpearlcastillo67% (3)
- Wilms TumorDocument12 pagesWilms TumorKath CamachoNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument37 pagesSystemic Lupus ErythematosusFirman Ichlasul AmalNo ratings yet
- Uterine CancerDocument20 pagesUterine CancerAjurs UrsabiaNo ratings yet
- Uterine Bleeding-A Case StudyDocument4 pagesUterine Bleeding-A Case StudyRoanne Lagua0% (1)
- Intestinal Obstruction: EpidemiologyDocument11 pagesIntestinal Obstruction: EpidemiologyBereket temesgenNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Bladder Outlet Obstruction (BOO)Document73 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Bladder Outlet Obstruction (BOO)Swe Zin NaingNo ratings yet
- Case Discussion PD: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease/Tubo-ovarian AbscessDocument7 pagesCase Discussion PD: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease/Tubo-ovarian AbscessJASMEEN RAVALNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument11 pagesPericarditisrbarcellonaNo ratings yet
- Wound AssessmentDocument19 pagesWound Assessmentdrsonuchawla100% (1)
- Investigations in An Unconscious PatientDocument16 pagesInvestigations in An Unconscious Patientcyphochilus0% (1)
- Lung CancerDocument2 pagesLung CancerAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument59 pagesCervical CancerClaudiaNathaliaNo ratings yet
- Uterine Myoma CPDocument44 pagesUterine Myoma CPCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- Pid (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease)Document13 pagesPid (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease)Anandila MaulinaNo ratings yet
- Case Study PneumoniaDocument6 pagesCase Study PneumoniaBrian CornelNo ratings yet
- Uremic EncephalopathyDocument12 pagesUremic EncephalopathyRAechelle_Marc_4102No ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument51 pagesNeonatal SepsisAngelo Del VentoNo ratings yet
- Infection Urinary Tract Urine Bladder KidneyDocument18 pagesInfection Urinary Tract Urine Bladder KidneygdquijanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process OsteosarcomaDocument34 pagesNursing Process OsteosarcomaDonJohnNo ratings yet
- A Case Presentation On AppendecitisDocument30 pagesA Case Presentation On AppendecitisrodericpalanasNo ratings yet
- Bea-Case StudyDocument21 pagesBea-Case Studybea pegadNo ratings yet
- Uterine FibroidsDocument2 pagesUterine FibroidsKarlo BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CystsDocument40 pagesOvarian CystsassssssNo ratings yet
- Pyloric StenosisDocument5 pagesPyloric Stenosisensoooooooooo100% (1)
- Cellulitis PathoDocument1 pageCellulitis Pathoanon_1303746470% (1)
- Dilation and CurettageDocument2 pagesDilation and CurettageElisse GarciaNo ratings yet
- Dilation and CurettageDocument15 pagesDilation and Curettagenautilus81No ratings yet
- Ovarian New GrowthDocument215 pagesOvarian New GrowthKaissa GomezNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis ADocument21 pagesHepatitis Avanessa100% (6)
- Intrapartum Fetal MonitoringDocument9 pagesIntrapartum Fetal MonitoringYwagar YwagarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology BPH!Document1 pageAnatomy and Physiology BPH!Christian BuenaNo ratings yet
- Hereditary SpherocytosisDocument16 pagesHereditary Spherocytosisrizi2008No ratings yet
- Liver AbscessDocument6 pagesLiver AbscessKenneth SunicoNo ratings yet
- Case Study OBDocument19 pagesCase Study OBLele Alwayzthesame KearneyNo ratings yet
- Menstrual DisorderDocument17 pagesMenstrual Disorderalisaa100% (1)
- Cervical Insufficiency + Cord PresentationDocument2 pagesCervical Insufficiency + Cord PresentationMSNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Cyanosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCyanosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- FST5602 Presentation Risk AssessmentDocument24 pagesFST5602 Presentation Risk Assessmentahmadhareez8810No ratings yet
- Pae PutiDocument3 pagesPae Putimadimadi11No ratings yet
- Blaylock Hypertension 13Document16 pagesBlaylock Hypertension 13mohanp71No ratings yet
- Research Article: Incidence and Risk Factors For Early Acute Kidney Injury in Nonsurgical Patients: A Cohort StudyDocument9 pagesResearch Article: Incidence and Risk Factors For Early Acute Kidney Injury in Nonsurgical Patients: A Cohort StudyAbdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Early Antithrombotic Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack - UpToDateDocument27 pagesEarly Antithrombotic Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack - UpToDateEduardo QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Pranav SharmaDocument11 pagesPranav SharmaPranav SharmaNo ratings yet
- All in Adults ProtocolsDocument60 pagesAll in Adults ProtocolsH.B.ANo ratings yet
- The Antifungal Activity of OnionDocument28 pagesThe Antifungal Activity of OnionJeanetteEoniceRodriguez100% (1)
- AKI in ChildrenDocument43 pagesAKI in ChildrenYonas AwgichewNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases: Thea Brabb, Denise Newsome, Andrew Burich, and Martha HanesDocument47 pagesInfectious Diseases: Thea Brabb, Denise Newsome, Andrew Burich, and Martha HanescarlosNo ratings yet
- Cure & Prevent Type 2 Diabetes With DietDocument36 pagesCure & Prevent Type 2 Diabetes With DietCyndee777No ratings yet
- APPENDICITISDocument6 pagesAPPENDICITISJAN ACCEL PAGADUANNo ratings yet
- Mid Module 3rd Year MBBSDocument8 pagesMid Module 3rd Year MBBSShahzaib Ullah ChatthaNo ratings yet
- Vinblastine (Velban®) : Things That May Occur During or Within Hours of TreatmentDocument2 pagesVinblastine (Velban®) : Things That May Occur During or Within Hours of TreatmentVette Angelikka Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- CD HeightsDocument3 pagesCD HeightsTotal Pest ControlNo ratings yet
- UPDRS v1.0 Annotated CRF PDFDocument8 pagesUPDRS v1.0 Annotated CRF PDFAnaaaerobiosNo ratings yet
- PSY105wk8pt1chp11 Baron KalsherDocument11 pagesPSY105wk8pt1chp11 Baron KalsherThalia SandersNo ratings yet
- Related Teenshealth Links: Health Problems SeriesDocument13 pagesRelated Teenshealth Links: Health Problems SeriesMario BadayosNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Politics of Hiv/Aids: A Media Perspective: by Martha S. MalanDocument134 pagesThe Scientific Politics of Hiv/Aids: A Media Perspective: by Martha S. MalanMelquisedec Ferreira Da Silva SantosNo ratings yet
- Anaplastic Thyroid CancerDocument40 pagesAnaplastic Thyroid Cancershita febrianaNo ratings yet
- OET Writing Case Notes Nursing 16 35Document38 pagesOET Writing Case Notes Nursing 16 35adnanshakeelm1No ratings yet
- Genetic Predisposition in Type 2 Diabetes A PromisingDocument23 pagesGenetic Predisposition in Type 2 Diabetes A PromisingRa,i Al HaddadNo ratings yet
- Austin Journal of UrologyDocument10 pagesAustin Journal of UrologyAustin Publishing GroupNo ratings yet
- RH PATHO2022 - (Chapt 02 - Cell Injury, Death, Adaptations - A)Document9 pagesRH PATHO2022 - (Chapt 02 - Cell Injury, Death, Adaptations - A)Toka AlzoubiNo ratings yet
- Leopard Gecko Diseases and CareDocument5 pagesLeopard Gecko Diseases and CareUrielNo ratings yet
- Foot Functioning Paradigms: ArticleDocument6 pagesFoot Functioning Paradigms: Article杨钦杰No ratings yet
- Moses 1983Document7 pagesMoses 1983darkarotNo ratings yet
- Total Knee ReplacementDocument49 pagesTotal Knee Replacementefancoolhand09No ratings yet
- Session Schedule 20.4.2023Document32 pagesSession Schedule 20.4.2023Aditya RaiNo ratings yet