Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Powerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My Presentation
Powerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My Presentation
Uploaded by
PoddmoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Powerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My Presentation
Powerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My Presentation
Uploaded by
PoddmoCopyright:
Available Formats
Powerpoint slide Presentation Script
Slide- 1:
Hello and welcome to my presentation
Slide- 2:
I am Jubayer Ahmed Jidny. Today I will be presenting about Mendelism and
understanding heredity. This presentation was given by our Honorable
Bio100 course Instructor Mrs. Noshin Azra Rahman ma’am.
Slide- 3:
Through this presentation I will be talking about
Genetics
Sexual Reproduction
What is Gene in Biology
What is Heredity
What is Mendelism and how it came
How Dominance works
Mendelian Genetic Definations
Mendel’s Law of inheritance
And lastly, The Necessity of knowing Mendelism and Heredity
Slide: 4
So, What is Genetics and Sexual reproduction? And what is the connection
between them? Genetics is the study of heredity and Heredity is a biological
method whereby a parent passes certain genes onto their children or
offspring through Sexual reproduction. In sexual reproduction 2 parents of
opposite sex participate along with fusion of male and female gametes. The
gametes are sperm in males and eggs in females. During fertilization both
female and male parent’s gametes combines together and creates a Zygote
which continues to develop as embrayo . The combination of gametes
contributes in creating genetic diversity.
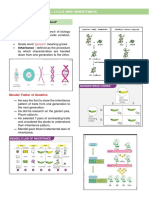
Slide: 5
Genes: A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. Genes are
made up of DNA.
As we can see in the picture then man wants to climb up the strand of DNA to
see where life takes him which relates to Heredity . How ? And what is this
Heredity thing ?
Slide: 6
Heredity: Heredity refers to the genetic heritage passed down by
our biological parents. It's why we look like them!
I think this picture is explaining a lot .
Slide: 7
Now we are prepare to know about Our main topic “ Mendelism”
Mendelism:
Mendelism is the principles of genetics, specifically of single-gene traits, based
on the work of Gregor Mendel who was born in July 22, 1822 and died in
January 6, 1884. He was an Austrian monk and biologist who established the
laws that are the foundation of classical genetics. Mendel carried out his key
experiments using the garden pea plants, as a model system. Mendel studied
the inheritance of seven different features in peas, including height, flower
color, seed color, and seed shape. To do so, he first established pea lines with
two different forms of a feature, such as tall vs. short height. He grew these
lines for generations until they were pure-breeding and pure-breeding is
always producing offspring identical to the parent, then breed them to each
other and observed how the traits were inherited.
Slide: 8
Now before we move on to those Mendelian laws , we need to know some
more things that are related to Mendelism.
Homozygous and Heterozygous:
Homozygous : Homo- means same; zygous means having genetic material. A
homozygous individual carries two copies of the same allele.
And Heterozygous : Hetero- means different; zygous means having genetic
material. A heterozygous individual carries two different alleles.
Slide: 9
Alleles, Genotype and Phenotype
Let’s focus on this picture:
Alleles Are the Different Version of a Gene
Genotype: Pairs of Genes, Responsible for particular trait
Phenotype: Physical expression of a trait.
Slide:10
As we can see the picture is already explaining a lot. ( Read slide )
Slide: 11
Read From Slide
Slide: 12
Read From Slide
Slide: 13
Read From Slide
Slide: 14
Read From Slide
Slide: 15
Here is an example of Knowing ourselves
Slide: 16
Read From Slide.
You might also like
- DNA From The Beginning - Mendelian Genetics Go To: Children Resemble Their ParentsDocument4 pagesDNA From The Beginning - Mendelian Genetics Go To: Children Resemble Their ParentsJose MonterrosaNo ratings yet
- 7 Science Workbook - HeredityDocument27 pages7 Science Workbook - HeredityJorge SanchezNo ratings yet
- Genetic CounsellingDocument5 pagesGenetic CounsellingSahaj Yadav100% (1)
- Gene Mapper Software v3.7 User GuideDocument138 pagesGene Mapper Software v3.7 User GuidesxjrenpNo ratings yet
- Module in GeneticsDocument48 pagesModule in GeneticsWilma TorinoNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My PresentationDocument3 pagesPowerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My PresentationPoddmoNo ratings yet
- Final Edit of Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesFinal Edit of Lesson PlanMerjorie BuatisNo ratings yet
- Document 84Document18 pagesDocument 84Mr JosephNo ratings yet
- Learning Module in Science 9: Subject Teacher WEEK 6, Quarter 1 TopicDocument4 pagesLearning Module in Science 9: Subject Teacher WEEK 6, Quarter 1 TopicJoanna Rose DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Notes Genetics and Selective Pressures 2017 TeacherDocument37 pagesNotes Genetics and Selective Pressures 2017 TeachersmedificationNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceBALMACEDA DIANA100% (1)
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument24 pagesHeredity and Evolutionethantravasso80No ratings yet
- Biology HeredityDocument19 pagesBiology Hereditybertha tandiNo ratings yet
- G8 - Sci SLM Q4 Wk3 CorrectedBeta TestedDocument16 pagesG8 - Sci SLM Q4 Wk3 CorrectedBeta TestedCristy Villamor100% (1)
- Biology M14 Genetics - The Study of Inherited TraitsDocument33 pagesBiology M14 Genetics - The Study of Inherited TraitsDiana Dealino-SabandalNo ratings yet
- Bio502 Handouts 1 50.pin2Document156 pagesBio502 Handouts 1 50.pin2Mohammadihsan NoorNo ratings yet
- Principles of GeneticsDocument26 pagesPrinciples of GeneticsKofoworola MikailNo ratings yet
- G-9 Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument5 pagesG-9 Non-Mendelian GeneticsMary-Rose Casuyon50% (2)
- Biology CH-3 GeneticsDocument12 pagesBiology CH-3 GeneticsAryan KumarNo ratings yet
- Heredity Line by LineDocument48 pagesHeredity Line by LineamaanmirzarollnoNo ratings yet
- BIO301 Handouts 1 167Document351 pagesBIO301 Handouts 1 167Tayyaba ArbabNo ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument26 pagesMendelian Geneticsdr.alkreissNo ratings yet
- Grade Level: Grade 11 Time: 1 Hour I. Objectives:: Teaching StrategyDocument7 pagesGrade Level: Grade 11 Time: 1 Hour I. Objectives:: Teaching StrategyKrd OngNo ratings yet
- And Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceDocument15 pagesAnd Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceMichelle Casayuran - Regala100% (2)
- Bio Class 12Document20 pagesBio Class 12Akanksha TiwariNo ratings yet
- Genetic and HeredityDocument9 pagesGenetic and HeredityKathleen DetoitoNo ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument26 pagesMendelian Geneticsdr.alkreissNo ratings yet
- Module - Lesson 6Document13 pagesModule - Lesson 6maria elaine melo colesioNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan #8Document6 pagesLesson Plan #8Val Daryl AnhaoNo ratings yet
- Apbd 1203 Topic 2Document30 pagesApbd 1203 Topic 2Anonymous wsqFdcNo ratings yet
- The Science of Human Behavior in The Social Environment GeneticsDocument2 pagesThe Science of Human Behavior in The Social Environment GeneticsJelah Chiara IINo ratings yet
- Activity 1.4 BioDocument2 pagesActivity 1.4 BioJamesNo ratings yet
- Genetics, DNA, and Heredity: The BasicsDocument34 pagesGenetics, DNA, and Heredity: The BasicsN'niel ËšpējöNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 14. Genetics - The Study of Inherited Traits2Document34 pagesBiology Module 14. Genetics - The Study of Inherited Traits2Kameshvra92% (12)
- SCIENCE-8 - Q4-Week 3 Mendelian GeneticsDocument20 pagesSCIENCE-8 - Q4-Week 3 Mendelian Geneticsjomarie estibal100% (1)
- Genetics and Heredity - Biology - 9th GradeDocument37 pagesGenetics and Heredity - Biology - 9th GradeSUDARAT THONGPHAYONGNo ratings yet
- Unit+7+study+guide AnswersDocument14 pagesUnit+7+study+guide Answersapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Notes of HeredityDocument2 pagesNotes of Hereditygayathris111No ratings yet
- Biol 12 Genetics Notes and University Entrance Exam Questions 2003Document66 pagesBiol 12 Genetics Notes and University Entrance Exam Questions 2003Tizita EmanaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Module 3Document20 pagesGrade 9 Module 3Paul AniceteNo ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument3 pagesMendelian Geneticsc4c8ng72jdNo ratings yet
- The Beginnings of Genetics - REPORT BY STUDENTS OF 10ADocument18 pagesThe Beginnings of Genetics - REPORT BY STUDENTS OF 10AFawwazNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument31 pagesGeneticsKumar AshishNo ratings yet
- 2 18KP2B06 2021012801523485Document45 pages2 18KP2B06 2021012801523485Rey OrbeNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAfRr3sSsuCAkrajXlVJlNW9CEtIjaaAShbzz53F - BV5yV6DzQdxtAJFRZXXlCzNJ2z436IplXhlNZcLstm s3JGzE2BiehEN5Wj1zYDQg1luLD89ztag DeLdXlbq5Nbv38FIU g05ICjDocument32 pagesACFrOgAfRr3sSsuCAkrajXlVJlNW9CEtIjaaAShbzz53F - BV5yV6DzQdxtAJFRZXXlCzNJ2z436IplXhlNZcLstm s3JGzE2BiehEN5Wj1zYDQg1luLD89ztag DeLdXlbq5Nbv38FIU g05ICjCarl SeanNo ratings yet
- EfB 7 - Introduction To GeneticsDocument13 pagesEfB 7 - Introduction To GeneticsOkti An Naafi'uNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document28 pagesModule 2Mark Dantes SanchezNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 9 Heredity and EvolutionDocument18 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 9 Heredity and EvolutionHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Module 2.biological DevelopmentDocument59 pagesModule 2.biological DevelopmentGlydle AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Genetics BookDocument77 pagesGenetics BookelctoyasNo ratings yet
- Genetics EverydayDocument7 pagesGenetics EverydayRando ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- Pedigree AnalysisDocument37 pagesPedigree Analysisshelren onlagadaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation - eMedicalPrepDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation - eMedicalPrepTUSHAR DASHNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionDocument25 pagesHeredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionRosalmi AyuNo ratings yet
- Nature, Nurture, and Human Diversity: Powerpoint® PresentationDocument60 pagesNature, Nurture, and Human Diversity: Powerpoint® PresentationPierce SmalleyNo ratings yet
- Science8WS Q4 Week3Document16 pagesScience8WS Q4 Week3Jay-ar RiosNo ratings yet
- LP-G9 GenesDocument6 pagesLP-G9 GenesJohnie Rey VillaruzNo ratings yet
- The DNA Detective: Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Genetic CodeFrom EverandThe DNA Detective: Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Genetic CodeNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My PresentationDocument3 pagesPowerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My PresentationPoddmoNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of Economics HomeworkDocument3 pages10 Principles of Economics HomeworkPoddmoNo ratings yet
- ENG101 Final Writing Test Answer To The Question No. 01: DifferencesDocument1 pageENG101 Final Writing Test Answer To The Question No. 01: DifferencesPoddmoNo ratings yet
- ENG 101 HomeworkDocument1 pageENG 101 HomeworkPoddmoNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics Student Edition Name: DateDocument14 pagesMendelian Genetics Student Edition Name: DateMish YouNo ratings yet
- Biology - Fly Lab ResultsDocument17 pagesBiology - Fly Lab ResultslanichungNo ratings yet
- Bio101Genetics IDocument22 pagesBio101Genetics IE CNo ratings yet
- Quiz BiolumDocument24 pagesQuiz Biolumb6e12No ratings yet
- 2nd Year Biology Guess Paper 2022Document7 pages2nd Year Biology Guess Paper 2022Malaika MinerNo ratings yet
- Genetics Study Guide 2013 - Answer KeyDocument3 pagesGenetics Study Guide 2013 - Answer Keyapi-211201625No ratings yet
- 5090 - w22 - QP - 12 Biology O-Level PypDocument20 pages5090 - w22 - QP - 12 Biology O-Level Pypmuiz phiNo ratings yet
- Slujba PastiDocument49 pagesSlujba PastiMihail ButurăNo ratings yet
- 1-100 Lect HandoutsDocument28 pages1-100 Lect HandoutszarbikhasnainNo ratings yet
- You've Evolved!: The Process of EvolutionDocument15 pagesYou've Evolved!: The Process of EvolutionJking MacapundagNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Inheritance (Monohybrid and Dihybrid Cross)Document80 pagesMendelian Inheritance (Monohybrid and Dihybrid Cross)jordan griersonNo ratings yet
- A01 3.7 Short Answer QuestionsDocument16 pagesA01 3.7 Short Answer Questionsmsuria06No ratings yet
- 7 Developmental, Genetic, & Pediatric DiseaseDocument62 pages7 Developmental, Genetic, & Pediatric DiseasecamsfNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4-Cell CycleDocument9 pagesMODULE 4-Cell CycleAlexes Paul TancioNo ratings yet
- Captura de Pantalla 2022-06-15 A La(s) 1.28.41 P.M.Document28 pagesCaptura de Pantalla 2022-06-15 A La(s) 1.28.41 P.M.jonymr1389No ratings yet
- The Use of GeneMapper IDX Software v1.1 For The Analysis of Mixed DNA SamplesDocument1 pageThe Use of GeneMapper IDX Software v1.1 For The Analysis of Mixed DNA Samplesbioq.applicationsNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Genetics: MutationDocument23 pagesGene Expression and Genetics: Mutationprimal100% (1)
- 17.2 Inheritance Igcse Cie Biology Ext Theory QPDocument11 pages17.2 Inheritance Igcse Cie Biology Ext Theory QPivannn510510No ratings yet
- 57-C-3 - BiologyDocument15 pages57-C-3 - BiologyAnshika YadavNo ratings yet
- Gerald Crabtree - Trends in Genetics. Our Fragile IntellectDocument6 pagesGerald Crabtree - Trends in Genetics. Our Fragile IntellectDemocracia real YA100% (1)
- Chromosome Rescue in Uniparental DisomyDocument12 pagesChromosome Rescue in Uniparental DisomyobiwamNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 4: Mendelian GeneticsDocument28 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 4: Mendelian GeneticsJoan Marie71% (7)
- Stress-Induced Perinatal and Transgenerational Epigenetic Programming of Brain Development and Mental Health PDFDocument22 pagesStress-Induced Perinatal and Transgenerational Epigenetic Programming of Brain Development and Mental Health PDFAbu ahsanNo ratings yet
- Punnett Square 1Document4 pagesPunnett Square 1andrea dyanne AzoresNo ratings yet
- MutationsDocument29 pagesMutationsiariajay100% (1)
- Genetics Learning Materials Bsa 2 1Document34 pagesGenetics Learning Materials Bsa 2 1Khy Renz Bajaj100% (1)
- Genetics: Mode of InheritanceDocument46 pagesGenetics: Mode of InheritanceHandrex MadrigalNo ratings yet