Professional Documents
Culture Documents
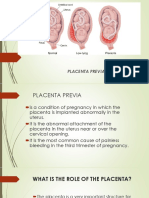
Placenta Previa Abruptio Placenta Placenta Location: During Pregnancy
Placenta Previa Abruptio Placenta Placenta Location: During Pregnancy
Uploaded by
Bryan Mortera0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views3 pagesPlacenta previa occurs when the placenta covers part or all of the cervix, which can cause painless bleeding in the third trimester. Abruptio placenta occurs when the placenta separates from the uterus prematurely, causing dark red bleeding with abdominal pain in the third trimester. Both are diagnosed using ultrasound and medical history, though abruptio placenta may not be confirmed until delivery when blood clots are seen. The amount of external bleeding is not a reliable indicator for abruptio placenta, as bleeding can clot internally instead of exiting vaginally.
Original Description:
placenta previa
Original Title
Placenta Previa
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPlacenta previa occurs when the placenta covers part or all of the cervix, which can cause painless bleeding in the third trimester. Abruptio placenta occurs when the placenta separates from the uterus prematurely, causing dark red bleeding with abdominal pain in the third trimester. Both are diagnosed using ultrasound and medical history, though abruptio placenta may not be confirmed until delivery when blood clots are seen. The amount of external bleeding is not a reliable indicator for abruptio placenta, as bleeding can clot internally instead of exiting vaginally.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views3 pagesPlacenta Previa Abruptio Placenta Placenta Location: During Pregnancy
Placenta Previa Abruptio Placenta Placenta Location: During Pregnancy
Uploaded by
Bryan MorteraPlacenta previa occurs when the placenta covers part or all of the cervix, which can cause painless bleeding in the third trimester. Abruptio placenta occurs when the placenta separates from the uterus prematurely, causing dark red bleeding with abdominal pain in the third trimester. Both are diagnosed using ultrasound and medical history, though abruptio placenta may not be confirmed until delivery when blood clots are seen. The amount of external bleeding is not a reliable indicator for abruptio placenta, as bleeding can clot internally instead of exiting vaginally.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Placenta Previa Abruptio Placenta
Placenta
Location
Total placenta previa. The placenta
completely covers the cervix.
Placenta develops in the uterus
during pregnancy.
Partial placenta previa. The placenta
is partially over the cervix.
Marginal placenta previa. The
placenta is near the edge of the cervix.
Character of Bright red vaginal bleeding. Bleeding often The most common symptom of
Bleeding occurs as the lower part of the uterus thins placental abruption is dark red
during the third trimester of pregnancy in vaginal bleeding with pain
preparation for labor. This causes the area of during the third trimester of
the placenta over the cervix to bleed. The pregnancy. It also can occur
more of the placenta that covers the cervical during labor. However, each
os (the opening of the cervix), the greater the woman may experience
risk for bleeding. symptoms differently. Some
women may not have vaginal
bleeding that is detectable, but
there may be bleeding inside
the uterus.
Presence of painless Abdominal pain and back pain
Pain often begin suddenly.
Uterine Activity Contractions along with the bleeding. Uterine tenderness
cramping or tightening that comes or rigidity
with contractions,.
Uterine
contractions, often
coming one right
after another
Diagnosis An ultrasound examination is used to The symptoms and signs of
establish the diagnosis of placenta previa. placental abruption can mimic
Either a transabdominal (using a probe on the those of other pregnancy
abdominal wall) or transvaginal (with a probe conditions, such as placenta
inserted inside the vagina but away from the previa and pre-eclampsia.
cervical opening) ultrasound evaluation may Information that may be used
be performed, depending upon the location to diagnose placental abruption
of the placenta. Sometimes both types of includes:
ultrasound examination are necessary. Medical history
Physical examination,
It is important that the ultrasound
including checking the
examination be performed before a physical
tenderness and tone of
examination of the pelvis in women with
the uterus
suspected placenta previa, since the pelvic
physical examination may lead to further Internal examination of
bleeding. the vagina and cervix,
using a speculum
Blood tests
Ultrasound to check the
placenta
Fetal heartbeat
monitoring.
Sometimes, the diagnosis of
placental abruption can’t be
confirmed until childbirth, when
the placenta is delivered with
an attached blood clot that
appears old rather than fresh.
The placenta is usually sent to a
laboratory for further diagnostic
testing.
2. Why is the amount of external bleeding in abruptio placenta not a reliable indicator of the
true amount of blood loss?
bleeding may occur but the blood may clot between the placenta and the wall of the uterus, so
vaginal bleeding may be scanty or even non-existent. This is known as a ‘retroplacental clot’.
You might also like
- Research ProposalDocument6 pagesResearch Proposalpaakwesi101590% (62)
- Human Anatomy 7th Edition Marieb Test BankDocument20 pagesHuman Anatomy 7th Edition Marieb Test BankKerriAdamsdwroi100% (14)
- Acupuncture For Infertility PDFDocument91 pagesAcupuncture For Infertility PDFLuis Damas100% (1)
- Maternal Midterm TransesDocument24 pagesMaternal Midterm TransesTaegyu IS SAILING Periodt.No ratings yet
- E. DR David - Ruptur Serviks Kelompok 30Document25 pagesE. DR David - Ruptur Serviks Kelompok 30wawan saifullahNo ratings yet
- (ObstetricsA) Prenatal Care - Dr. San Jose (Lea Pacis)Document12 pages(ObstetricsA) Prenatal Care - Dr. San Jose (Lea Pacis)Karen EstavilloNo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument3 pagesPlacenta PreviaVicente TurasNo ratings yet
- MCN 2Document7 pagesMCN 2GabNo ratings yet
- Third Trimester: Place The Woman Immediately On Side-Lying PositionDocument7 pagesThird Trimester: Place The Woman Immediately On Side-Lying PositionZoila Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- 1st Trimester BleedingDocument67 pages1st Trimester BleedingRaiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- OB BessDocument4 pagesOB BessKate SantosNo ratings yet
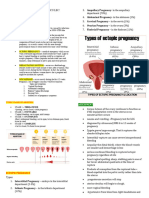
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument76 pagesEctopic PregnancyVivian Jean TapayaNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa: DefinitionDocument4 pagesPlacenta Previa: DefinitionCT Johara MusorNo ratings yet
- 2C Orev Compilation TopicDocument56 pages2C Orev Compilation TopicPaolo AntonioNo ratings yet
- Case-Presentation Final Nagd Ni ShetDocument7 pagesCase-Presentation Final Nagd Ni ShetMary Beth AbelidoNo ratings yet
- CMCP M1Document312 pagesCMCP M1evangdelacruz1010No ratings yet
- (R2) Prenatal Detection of Birth DefectsDocument2 pages(R2) Prenatal Detection of Birth DefectsNicole HonradoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 APH, PP, VP, AbruptioDocument55 pagesTutorial 3 APH, PP, VP, AbruptioBahirahNo ratings yet
- Vaginal ExaminationDocument2 pagesVaginal ExaminationRhobin Petate67% (3)
- First Trimester BleedingDocument37 pagesFirst Trimester BleedingkikiNo ratings yet
- Anomalies of The Placenta and CordDocument2 pagesAnomalies of The Placenta and CordLuiciaNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPlacenta Previa PathophysiologySeth Elijah CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Clinical Topics 2021Document18 pagesGynecology - Clinical Topics 2021Nehal LakdawalaNo ratings yet
- Intrartum/Intrapartal Period: Phenomena and Process of Labor and Delivery I. Onset of LaborDocument14 pagesIntrartum/Intrapartal Period: Phenomena and Process of Labor and Delivery I. Onset of Laborclaireaongchua1275No ratings yet
- ABNORMALDocument33 pagesABNORMALJc Mae CuadrilleroNo ratings yet
- Au Ca1-Clp - 01-Dexel Lorren R. Valdez Ob DownloadableDocument2 pagesAu Ca1-Clp - 01-Dexel Lorren R. Valdez Ob DownloadableDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Study of Illness ConditionDocument7 pagesStudy of Illness ConditionAsylla PajijiNo ratings yet
- Amplify The Learning (Ob) Week #4 - 2: Vidon, Aubrey Rose A. April 18, 2020 BSN 2Y2-2Document1 pageAmplify The Learning (Ob) Week #4 - 2: Vidon, Aubrey Rose A. April 18, 2020 BSN 2Y2-2AriaNo ratings yet
- And Women With Placental Abruption Were More Likely To Be of Higher Parity Thus Was Ruled-OutDocument3 pagesAnd Women With Placental Abruption Were More Likely To Be of Higher Parity Thus Was Ruled-OutTaeyomiNo ratings yet
- 05 - Practical Class Matherial - Anterpartal Hemorrhagic DisordersDocument161 pages05 - Practical Class Matherial - Anterpartal Hemorrhagic DisordersDike Obiora-EzeNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa: Case 4 RPS I - Low Lying Placenta Source: Williams Obstetrics 24e, Chapter 41Document20 pagesPlacenta Previa: Case 4 RPS I - Low Lying Placenta Source: Williams Obstetrics 24e, Chapter 41Michael Nobel SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Ca1 DLP 03 Obstetric Nursing Adam Sealtiel Bito Au PasayDocument3 pagesCa1 DLP 03 Obstetric Nursing Adam Sealtiel Bito Au PasayYoungbloodNo ratings yet
- Midwife Care Plan AbruptioDocument6 pagesMidwife Care Plan AbruptioDivina Gracia Vibal CieloNo ratings yet
- Mother Baby TermsDocument3 pagesMother Baby TermschadnelsonNo ratings yet
- Term Alive Intra Abdominal Ectopic Pregnancy: Case ReportDocument3 pagesTerm Alive Intra Abdominal Ectopic Pregnancy: Case ReportLeannarys Mendoza DelgadoNo ratings yet
- VASA Previa CaseDocument3 pagesVASA Previa CasewijeNo ratings yet
- 3rd Triemster BleedingDocument69 pages3rd Triemster BleedingRaiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Perdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaDocument26 pagesPerdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaEmilia NazmaNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Submitted By: William Leo ManongdoDocument5 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Submitted By: William Leo Manongdoliam0831No ratings yet
- USG Trimester 2 & 3 PatologisDocument48 pagesUSG Trimester 2 & 3 PatologisanggitaNo ratings yet
- USG Trimester 2 & 3 PatologisDocument48 pagesUSG Trimester 2 & 3 PatologisanggitaNo ratings yet
- DR Case Presentation FinalDocument35 pagesDR Case Presentation FinalLord Allen B. GomezNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument3 pagesEctopic PregnancyforbiddenleiNo ratings yet
- Name: Year & Course: Test Type Timing Process ResultsDocument3 pagesName: Year & Course: Test Type Timing Process ResultsAllyah Anthonette Ferwelo100% (1)
- Placenta PreviaDocument6 pagesPlacenta Previamiss RN93% (14)
- 8412-Article Text-29472-1-10-20130809Document8 pages8412-Article Text-29472-1-10-20130809NenyNo ratings yet
- Cervical InsufficiencyDocument2 pagesCervical InsufficiencyShe that BoyNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CystDocument1 pageOvarian CystLoriene LopezNo ratings yet
- 3RD TrimesterDocument7 pages3RD TrimesterAmethystNo ratings yet
- Subacute Uterine Inversion With Shock - A Distinct Surgical ManagementDocument3 pagesSubacute Uterine Inversion With Shock - A Distinct Surgical ManagementBima GhovaroliyNo ratings yet
- ReferatDocument3 pagesReferatGita AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Prelim NCM 109 Lecture HandoutsDocument21 pagesPrelim NCM 109 Lecture HandoutsLillabin71% (7)
- Ectopic Pregnancy Final EditDocument11 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Final EditBRAIMA JOHNNo ratings yet
- Threatened Abortion DiscussionDocument5 pagesThreatened Abortion Discussionkimadlo656No ratings yet
- Multiple Gestation: Complications of Labor and Birth Problems With The PassengerDocument4 pagesMultiple Gestation: Complications of Labor and Birth Problems With The PassengerAmethystNo ratings yet
- Bleeding DisordersDocument20 pagesBleeding DisordersSheene Ainasthazia Diego AngNo ratings yet
- MCN Lect Module 2.5 Complications of Labor and Birth 4Document6 pagesMCN Lect Module 2.5 Complications of Labor and Birth 4AmethystNo ratings yet
- Complications of Pregnancy 2Document4 pagesComplications of Pregnancy 2MENDIETA, JACQUELINE V.No ratings yet
- Uterine ProlapseDocument1 pageUterine ProlapseJeivey VercideNo ratings yet
- Trans - OB 2 (Placenta Previa & Morbidly Adherent Placenta) PDFDocument5 pagesTrans - OB 2 (Placenta Previa & Morbidly Adherent Placenta) PDFMary Stephanie Parcon ChongNo ratings yet
- 4 Theories of Labor Onset 0 Signs of LaborDocument13 pages4 Theories of Labor Onset 0 Signs of Labormamsh KlangNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- Mortera, Bryan - 40hrsDocument1 pageMortera, Bryan - 40hrsBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document12 pagesBook 1Bryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Bryan Florentino M. Mortera !V Sales and Operations: Name Working Hours 8 Department DATE SUBMITTED 8/08/2022Document5 pagesBryan Florentino M. Mortera !V Sales and Operations: Name Working Hours 8 Department DATE SUBMITTED 8/08/2022Bryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Keefer, MichelleDocument1 pageKeefer, MichelleBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Dsmes Intervention Tracking Form: 8/15/1938 Participant 7Document1 pageDsmes Intervention Tracking Form: 8/15/1938 Participant 7Bryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- CPT Code 99091 KovacDocument3 pagesCPT Code 99091 KovacBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Corp CasesDocument15 pagesCorp CasesBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- In-House Timesheet: Bryan F. M. Mortera IvDocument1 pageIn-House Timesheet: Bryan F. M. Mortera IvBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Patient List As of 09-01-2023 06 - 45 AMDocument20 pagesPatient List As of 09-01-2023 06 - 45 AMBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Bass, PatriciaDocument1 pageBass, PatriciaBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- CPT Code 99091 ButlerDocument1 pageCPT Code 99091 ButlerBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- CPT Code 99091 BrewerDocument2 pagesCPT Code 99091 BrewerBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- CPT Code 99091 LathropDocument2 pagesCPT Code 99091 LathropBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Barnes WinnieDocument1 pageBarnes WinnieBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Challenges For Completion ofDocument11 pagesChallenges For Completion ofBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Weekly ActivityDocument5 pagesWeekly ActivityBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- WE 8-14-22 BryDocument1 pageWE 8-14-22 BryBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Cta 2D CV 07823 D 2014feb18 AssDocument100 pagesCta 2D CV 07823 D 2014feb18 AssBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- CPT Code 99091 AcheyDocument6 pagesCPT Code 99091 AcheyBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- TS WE 8-21-22 BryanDocument1 pageTS WE 8-21-22 BryanBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Baker, AundraDocument1 pageBaker, AundraBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- ACHEYDocument1 pageACHEYBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Template For DSMT Education For Documentation in Charts 1Document4 pagesTemplate For DSMT Education For Documentation in Charts 1Bryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Kataza TaifaDocument1 pageKataza TaifaBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- AllardDocument1 pageAllardBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Cosby, SharonDocument1 pageCosby, SharonBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Incident Report - Aaron BeasleyDocument1 pageIncident Report - Aaron BeasleyBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Donald CartheuserDocument1 pageDonald CartheuserBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- NowRPM Incident Report Form (1) Rose Nelson Call DispositionDocument1 pageNowRPM Incident Report Form (1) Rose Nelson Call DispositionBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Kinney, SandraDocument1 pageKinney, SandraBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Oral Contraceptive MCQs With Answer KeyDocument7 pagesOral Contraceptive MCQs With Answer KeyShaista AkbarNo ratings yet
- Physiology of PregnancyDocument27 pagesPhysiology of PregnancysabaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DinoprostoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study DinoprostoneMva AgueroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Life Science EmbryologyDocument20 pagesLecture 2 Life Science EmbryologyjoeNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Pregnancy and ChildbirthDocument16 pagesIntegrated Management of Pregnancy and ChildbirthLea Foy-os CapiliNo ratings yet
- Module 1 The Philippine Family Planning ProgramDocument67 pagesModule 1 The Philippine Family Planning ProgramJhunna TalanganNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument10 pagesStatisticsSaba mahatNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine and Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesThe Endocrine and Reproductive SystemTenshi JoiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Chapter #17 Human ReproductionDocument18 pagesIGCSE Biology Chapter #17 Human ReproductionAazif JafriNo ratings yet
- "At Least You Have A Healthy Baby": Birth Trauma, Manufactured Crises, and The Denial of Women's Experience in ChildbirthDocument82 pages"At Least You Have A Healthy Baby": Birth Trauma, Manufactured Crises, and The Denial of Women's Experience in ChildbirthDamien ElijahNo ratings yet
- Methods of Contraception 1. Permanent ContraceptionDocument7 pagesMethods of Contraception 1. Permanent ContraceptionCaurrine MonsaludNo ratings yet
- Libro Medicina Reproductiva 2022Document645 pagesLibro Medicina Reproductiva 2022Luisa Moreno100% (1)
- Exercise 2 - FP Form 1 A and B (1) TDocument2 pagesExercise 2 - FP Form 1 A and B (1) TJohn Alfred TanNo ratings yet
- Agron Hospital-Cases FinalDocument11 pagesAgron Hospital-Cases Finalfaker than fakeNo ratings yet
- Transverse and Oblique LieDocument7 pagesTransverse and Oblique Liekirtyy20No ratings yet
- Knowledge On Infertility Among People at Gairigaun, Tokha - 9Document45 pagesKnowledge On Infertility Among People at Gairigaun, Tokha - 9shiva sharmaNo ratings yet
- India and Family Planning: An: BackgroundDocument8 pagesIndia and Family Planning: An: BackgroundShekhar MishraNo ratings yet
- Manager - Handbook - Managing Employees - On - Maternity Leave - India PDFDocument13 pagesManager - Handbook - Managing Employees - On - Maternity Leave - India PDFS HanbalNo ratings yet
- Macaraig, Jhena S.reportDocument14 pagesMacaraig, Jhena S.reportHYUNGNo ratings yet
- 4 Uterine RuptureDocument14 pages4 Uterine RuptureAamal AlhamiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Family C NewbornDocument18 pagesNursing Care of A Family C NewbornAudreySalvadorNo ratings yet
- A Stem Cell Story ReflectionDocument2 pagesA Stem Cell Story ReflectionCharlize Mae ArboladuraNo ratings yet
- Rekap Clinical Pathway 2022Document54 pagesRekap Clinical Pathway 2022Aulia Alya RatnaNo ratings yet
- Forceps Delivery CCDocument27 pagesForceps Delivery CCNithiya NadesanNo ratings yet
- Stepping in Module 5Document3 pagesStepping in Module 5JASMINE CEDE�ONo ratings yet
- Brochure Arogya Sanjeevani Policy V 1 0204 Web PDFDocument8 pagesBrochure Arogya Sanjeevani Policy V 1 0204 Web PDFsurendra reddyNo ratings yet
- Traumatic PPHDocument30 pagesTraumatic PPHRizwana BanuNo ratings yet