Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FALLSEM2019-20 MEE1030 ETH VL2019201002279 Reference Material I 19-Jul-2019 Workspace Analysis
FALLSEM2019-20 MEE1030 ETH VL2019201002279 Reference Material I 19-Jul-2019 Workspace Analysis
Uploaded by
Shivam Kumar Singh 18BME00660 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesrobotics
Original Title
FALLSEM2019-20_MEE1030_ETH_VL2019201002279_Reference_Material_I_19-Jul-2019_Workspace_analysis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentrobotics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 MEE1030 ETH VL2019201002279 Reference Material I 19-Jul-2019 Workspace Analysis
FALLSEM2019-20 MEE1030 ETH VL2019201002279 Reference Material I 19-Jul-2019 Workspace Analysis
Uploaded by
Shivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066robotics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 4
Workspace
The analysis of the workspace is very important for
the design, selection and programming of robots.
The workspace W is the set of positions and orientations
reachable by the robot end-effector.
The boundaries are defined by the singularities and the
joints limits.
Depending on their configuration and size of their links
and wrist joints, robots can reach a collection of points
called a workspace.
Let q be an element of joint space and X be the
corresponding element in the task space.
X=f(@)
The joint domain Q is defined as the set of all reachable
configurations taking into account joint limits.
Q = {4 | Gimin $41 $ dimax V i= 1, ...4n}
The image of Q by the direct geometric model DGM
defines the workspace W of the robot.
W=fQ,
PLANAR 3R MANIPULATOR
Workspace: All (x, y, @) such that inverse kinematic solution exists.
Planar 3R Manipulator Workspace of a planar 3R robot
bhi
th
a thy
oe
Projection of a workspace of a planar 3R robot
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- WISEM-2020-21 PHY1701 ETH VL2020211000264 Reference Material II 10-Nov-2020 Schroendinger Time Dependent and Independent Wave EquationsDocument11 pagesWISEM-2020-21 PHY1701 ETH VL2020211000264 Reference Material II 10-Nov-2020 Schroendinger Time Dependent and Independent Wave EquationsShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet
- WISEM-2020-21 PHY1701 ETH VL2020211000264 Reference Material IV 09-Nov-2020 de Broglie HypothesisDocument19 pagesWISEM-2020-21 PHY1701 ETH VL2020211000264 Reference Material IV 09-Nov-2020 de Broglie HypothesisShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet
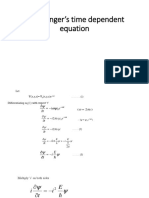
- Schrodinger's Time Dependent EquationDocument4 pagesSchrodinger's Time Dependent EquationShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet
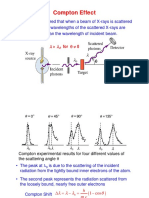
- WISEM-2020-21 PHY1701 ETH VL2020211000264 Reference Material II 09-Nov-2020 Compton EffectDocument6 pagesWISEM-2020-21 PHY1701 ETH VL2020211000264 Reference Material II 09-Nov-2020 Compton EffectShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 MEE1030 ETH VL2019201002279 Reference Material I 06-Sep-2019 SENSORDocument5 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 MEE1030 ETH VL2019201002279 Reference Material I 06-Sep-2019 SENSORShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management Digital Assignment - 1 I) Milk Run For Milk: GopaljeeDocument3 pagesLogistics and Supply Chain Management Digital Assignment - 1 I) Milk Run For Milk: GopaljeeShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet
- Economics Aspects of Robotics System in Industrial AutomationsDocument6 pagesEconomics Aspects of Robotics System in Industrial AutomationsShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet
- Unit-I Basic Concepts and First Law: ThermodynamicsDocument42 pagesUnit-I Basic Concepts and First Law: ThermodynamicsShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet
- Coursera Z5FFEU43T3YUDocument1 pageCoursera Z5FFEU43T3YUShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2018-19 - STS1001 - SS - SMV110 - VL2018191000015 - Reference Material I - Lessons On Excellence - Change ManagementDocument17 pagesFALLSEM2018-19 - STS1001 - SS - SMV110 - VL2018191000015 - Reference Material I - Lessons On Excellence - Change ManagementShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet
- Part I: Numerical Solution For Single Variable: 1.1. Newton-Raphson MethodDocument9 pagesPart I: Numerical Solution For Single Variable: 1.1. Newton-Raphson MethodShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2018-19 HUM1021 TH CDMM103 VL2018191002223 Reference Material I Gandhian PrinciplesDocument3 pagesFALLSEM2018-19 HUM1021 TH CDMM103 VL2018191002223 Reference Material I Gandhian PrinciplesShivam Kumar Singh 18BME0066No ratings yet