Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kami Export - 5 BIOLOGY GENETICS - MITOSIS
Kami Export - 5 BIOLOGY GENETICS - MITOSIS
Uploaded by
gefeg0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views11 pagesGenes determine characteristics and come in different forms called alleles. One gene controls handedness, with the R allele dominant for right-handedness and the r allele recessive for left-handedness. Genotype describes an individual's allele combination, like RR or Rr, while phenotype is the observable characteristic, such as being right-handed. Cells contain chromosomes in homologous pairs that separate into daughter cells through mitosis to maintain the chromosome number.
Original Description:
Biology genetics
Original Title
Kami Export - 5 BIOLOGY GENETICS- MITOSIS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGenes determine characteristics and come in different forms called alleles. One gene controls handedness, with the R allele dominant for right-handedness and the r allele recessive for left-handedness. Genotype describes an individual's allele combination, like RR or Rr, while phenotype is the observable characteristic, such as being right-handed. Cells contain chromosomes in homologous pairs that separate into daughter cells through mitosis to maintain the chromosome number.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views11 pagesKami Export - 5 BIOLOGY GENETICS - MITOSIS
Kami Export - 5 BIOLOGY GENETICS - MITOSIS
Uploaded by
gefegGenes determine characteristics and come in different forms called alleles. One gene controls handedness, with the R allele dominant for right-handedness and the r allele recessive for left-handedness. Genotype describes an individual's allele combination, like RR or Rr, while phenotype is the observable characteristic, such as being right-handed. Cells contain chromosomes in homologous pairs that separate into daughter cells through mitosis to maintain the chromosome number.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 11
GENETICS
Genes- A gene is in effect a section of
chromosomal DNA that gives the code for
particular characteristics. A gene is always
found in the same location on a given
chromosome, but the genes themselves can
take different forms. For example, one gene
determines whether you are right or left
handed.
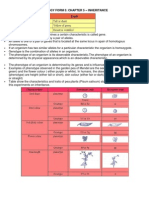
Alleles- This gene has two different forms or
alleles.The allele for right – handedness in
humans is denoted by R while the gene is for
left- handedness is denoted by r.
NB: Each chromosome in a pair carries one
allele for each particular characteristic. In
a pair of chromosomes you can either have
two identical alleles ( RR or rr) or you can
have two different alleles (Rr or rR)
Dominant- Usually one of the alleles is
stronger. This allele is said to be dominant and
it controls what happen when the characteristic
is passed on. For example , R is dominant , so a
right- handed person would have either the
RR alleles or the Rr alleles.
Recessive- only people with the rr
combinations of alleles will be left handed. We
say that the allele for left-handedness is
recessive.
Genotype- This describes the genetic make-up
of all the genes of an individual. (When you
write down the kinds of alleles on a
chromosome for example RR)
Phenotype- The physical appearance of each
individual is known as the phenotype ( for
example right- handed)
Homozygous- when an individual carries two
identical alleles (RR or rr), we say that the
individual is homozygous.
Heterozygous- When an individual carries two
different alleles (for example Rr) we say the
individual is heterozygous.
Each cell in the body has a specific number of
chromosomes, arranged in homologous pairs. In
humans, each cell of the body contains 23 pairs of
chromosomes to give 46 chromosomes in all. Gametes
(sperm, i.e. spermatozoa in males, and eggs, i.e. ova in
females) have only 23 chromosomes. This is half the
number of chromosomes in each body cell.
Each living organism has a specific number of
chromosomes in each cell. Different species have
different numbers of chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs,
cats have 19 pairs, chickens have 18 pairs etc.
When a new organism is formed, the chromosome
number in each cell must remain the same.
CELL DIVISION BY MITOSIS
You have seen that each new daughter cell formed by cell
division must have the correct number of chromosomes.
In the cells of the body, which have 46 chromosomes,
cell division takes place by mitosis.
Mitosis divides the chromosomes of the parent cell into
two identical groups. Cells that divide through mitosis to
receive the full number of chromosomes from their
parent cells and, in turn, pass these on to their daughter
cells are described as having diploid (2n) number of
Cont’d
Chromosomes.
IMPORTANCE OF MITOSIS
Because daughter cells each receive an identical full
(diploid) set of chromosomes from the parent cell,
daughter cells and the parent cell are genetically
identical. This is why mitosis is the way in which living
things repair damage to the body, grow and reproduce
asexually. For example:
▪ Parent cheek cells divide by mitosis into identical
daughter cheek cells.
▪ Parent skin cells divide by mitosis into identical
daughter skin cells
Parent root cells divide by mitosis into identical
daughter root cells.
You might also like
- Ebook PDF Comparative Anatomy Manual of Vertebrate Dissection 3rd Edition PDFDocument42 pagesEbook PDF Comparative Anatomy Manual of Vertebrate Dissection 3rd Edition PDFrubin.smith411100% (40)
- Full Download Human Resource Management 3rd Edition Lussier Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Human Resource Management 3rd Edition Lussier Test Bankdiacopefarcinuxieq100% (32)
- BT203 - Genetics Unit 2Document133 pagesBT203 - Genetics Unit 2Anand JoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Bio NotesDocument14 pagesChapter 18 Bio Notesgeezariana790No ratings yet
- 13 Inheritance Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFDocument33 pages13 Inheritance Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFJohn DeHans100% (1)
- Inheritance: Genetic InformationDocument15 pagesInheritance: Genetic InformationJorifNo ratings yet
- Genetics in PeriodontalDocument92 pagesGenetics in PeriodontalKupfermann100% (1)
- Genetics-Some-Basic-Fundamentals-1Document6 pagesGenetics-Some-Basic-Fundamentals-1Kamaljeet DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Genetics and HeredityDocument56 pagesGenetics and HeredityHnin NandarNo ratings yet
- Genes and Species CharacteristicDocument20 pagesGenes and Species Characteristicananda squireNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Classical GeneticsDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts of Classical Geneticsganesandec27No ratings yet
- HeredityDocument39 pagesHereditySamantha CunananNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Genetics Is The Scientific Study of Heredity and Inherited VariationDocument13 pagesGenetics: Genetics Is The Scientific Study of Heredity and Inherited VariationDanielle GuerraNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument54 pagesGeneticsBrian James BurtonNo ratings yet
- Science Notes PDFDocument7 pagesScience Notes PDFakidelavega19No ratings yet
- 03.chromosomes and MeiosisDocument4 pages03.chromosomes and Meiosisgabrielsalazar.tvNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - Heredity and GeneticsDocument5 pagesPart 2 - Heredity and GeneticsAngelSCNo ratings yet
- Genetics Class 10Document7 pagesGenetics Class 10Manjit KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 - Genetics NotesDocument8 pagesUNIT 3 - Genetics NotesJB - 10SS 731765 Harold M Brathwaite SSNo ratings yet
- 3.0 DNA Is The Inherited Material Responsible For VariationDocument62 pages3.0 DNA Is The Inherited Material Responsible For VariationNick YamNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument64 pagesInheritanceSUDARAT THONGPHAYONGNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Variation-1Document53 pagesGenetics and Variation-1Hashim SelashiNo ratings yet
- B12 Inheritance - Updated 2023Document15 pagesB12 Inheritance - Updated 2023Alejandro SotoNo ratings yet
- Inheritance NotesDocument3 pagesInheritance NotesTashwaar TamimNo ratings yet
- GRADE 12 A, B Variation and GeneticsDocument6 pagesGRADE 12 A, B Variation and Geneticsᴘʀᴏғ. HammadNo ratings yet
- Inherited Change and Evolution-Topic 6Document20 pagesInherited Change and Evolution-Topic 6Kundiso NakomaNo ratings yet
- Human ChromosomesDocument1 pageHuman ChromosomesSir LeafNo ratings yet
- Fruit Fly ExperimentDocument24 pagesFruit Fly ExperimentHarry BerryNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2Document12 pagesGenetics 2tayestewart14No ratings yet
- Review of Terms ReproductionDocument5 pagesReview of Terms Reproductionaijiel talisikNo ratings yet
- Genetics, Mitosis & MeiosisDocument7 pagesGenetics, Mitosis & MeiosisSeher Masood - 43458/TCHR/BNINo ratings yet
- Introduction To Animal Science - 1Document14 pagesIntroduction To Animal Science - 1Jesus Gomez Cortizzo100% (1)
- Pop GenDocument38 pagesPop GenRaju KharelNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5: Chapter 5 - InheritanceDocument3 pagesBiology Form 5: Chapter 5 - InheritanceTang Tiong Min 郑中铭No ratings yet
- Study Material Unit 2Document27 pagesStudy Material Unit 2api-264649244No ratings yet
- 7A Genes, Allele and Genome CheckpointDocument2 pages7A Genes, Allele and Genome CheckpointMarissaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Mendel: Meiosis: The Process of Producing Haploid Sex CellsDocument32 pagesMeiosis and Mendel: Meiosis: The Process of Producing Haploid Sex CellsshiyiNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter - GenesDocument57 pages1st Quarter - Genesreinko9019No ratings yet
- Genetics Course 3 M-1Document161 pagesGenetics Course 3 M-1Shiko LoveNo ratings yet
- Bio Exam NotesDocument22 pagesBio Exam NotesThalia VladimirouNo ratings yet
- ChromosomesDocument19 pagesChromosomesJosephine VinaraoNo ratings yet
- DNA Genes and ChromosomesDocument17 pagesDNA Genes and ChromosomesLovejoy TiñaNo ratings yet
- Genes and DiseasesDocument31 pagesGenes and DiseasesT FNo ratings yet
- Pp6 Genetics An Inheritance JangeDocument31 pagesPp6 Genetics An Inheritance JangeoptimallethumusaNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument2 pagesDefinitions - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSEIsini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics and ChromosomesDocument48 pagesMendelian Genetics and Chromosomesreginedelamarquez14No ratings yet
- 3 Genetics: 3.1 GenesDocument22 pages3 Genetics: 3.1 Genesapi-285490927100% (1)
- Add Ons GeneticsDocument6 pagesAdd Ons GeneticsNoob MeNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Evolution SUMMARY NOTESDocument6 pagesGenetics and Evolution SUMMARY NOTESPrabhNo ratings yet
- 17 - InheritanceDocument4 pages17 - InheritanceAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Genetics NotesDocument26 pagesGenetics Notesapi-655732711No ratings yet
- Introduction To Genetics: Genetics Is The Study ofDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Genetics: Genetics Is The Study ofThe Epic XerneasNo ratings yet
- Review of Terms ReproductiveDocument5 pagesReview of Terms Reproductiveaijiel talisikNo ratings yet
- Biology 10 2 DNA Genes and ChromosomesDocument26 pagesBiology 10 2 DNA Genes and ChromosomesAvegail YsidoroNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 3 Revision NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 3 Revision NotesBHUPENDRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- 18 InheritanceDocument46 pages18 Inheritances1139221No ratings yet
- Genatics 1Document11 pagesGenatics 1rasha nadaNo ratings yet
- Genes Environment AND DevelopmentDocument29 pagesGenes Environment AND Developmentsushmita bhartiaNo ratings yet
- 2.meiosis 1Document36 pages2.meiosis 1taskmask37No ratings yet
- CXC Physics P1 June 2017Document15 pagesCXC Physics P1 June 2017gefegNo ratings yet
- CXC Physics P1 June 2015Document13 pagesCXC Physics P1 June 2015gefegNo ratings yet
- Saturated and Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesSaturated and Unsaturated HydrocarbonsgefegNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab #14Document4 pagesPhysics Lab #14gefegNo ratings yet
- The Ongoing Manufacturing Revolution - The Internet of ThingsDocument13 pagesThe Ongoing Manufacturing Revolution - The Internet of ThingsgefegNo ratings yet
- Modern Trends in The Manufacturing IndustryDocument8 pagesModern Trends in The Manufacturing IndustrygefegNo ratings yet
- Revised School Based AssignmentDocument27 pagesRevised School Based AssignmentgefegNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology: RectifiersDocument6 pagesElectrical Technology: RectifiersgefegNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology: MagnetismDocument7 pagesElectrical Technology: MagnetismgefegNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - 5TH FORM OCT 21Document3 pagesKami Export - 5TH FORM OCT 21gefegNo ratings yet
- TLE 6 - Week3Document6 pagesTLE 6 - Week3Luis SalengaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem PresentationDocument32 pagesEcosystem PresentationJanna Gomez100% (1)
- Tragedy of The Commons - ArticleDocument13 pagesTragedy of The Commons - ArticleAguasNo ratings yet
- Falenissa - Pemicu 3 Blok Etika Dan Hukum KedokteranDocument108 pagesFalenissa - Pemicu 3 Blok Etika Dan Hukum KedokteranIcarus WingsNo ratings yet
- Upland RiceDocument44 pagesUpland RiceVictorio RustiaNo ratings yet
- Cats Claw Ethnopharmacology 1999Document12 pagesCats Claw Ethnopharmacology 1999Jency SamNo ratings yet
- 2 1 The World at Our Fingertips Answer KeyDocument2 pages2 1 The World at Our Fingertips Answer KeySaptarshi Sanyal100% (1)
- Biological Molecules 2 QPDocument7 pagesBiological Molecules 2 QPTatiana Vardaramatou0% (1)
- Dog Coat Colour Genetics - A Review, Saif Et Al. 2020Document11 pagesDog Coat Colour Genetics - A Review, Saif Et Al. 2020Emmanuel A. Sessarego Dávila100% (1)
- Work 1Document12 pagesWork 1Islem MannaiNo ratings yet
- BiokitDocument19 pagesBiokitKrisha TampingcoNo ratings yet
- Steroid Dysregulation and Stomatodynia (Burning Mouth Syndrome)Document9 pagesSteroid Dysregulation and Stomatodynia (Burning Mouth Syndrome)EnzoNo ratings yet
- Quiz ReproductionDocument16 pagesQuiz Reproductionelenacatiggay83No ratings yet
- Techniques of Liposomes Prep.Document17 pagesTechniques of Liposomes Prep.Sonam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Slide Lipide PDFDocument37 pagesSlide Lipide PDFMrr Kva Rmx Music-ProducerNo ratings yet
- Blangly - Ecotourism and Ecological RestorationDocument4 pagesBlangly - Ecotourism and Ecological RestorationRamanditya WimbardanaNo ratings yet
- Tissue CultureDocument24 pagesTissue CulturecryssmNo ratings yet
- Transgenics For Abiotic StressDocument46 pagesTransgenics For Abiotic StressAmit BallaniNo ratings yet
- HIRARC Template From HIRARC GuidelinesDocument2 pagesHIRARC Template From HIRARC GuidelinesMeck LotfiNo ratings yet
- From Monkey Brain To Human BrainDocument419 pagesFrom Monkey Brain To Human BrainKaushik Deka100% (3)
- GrapeDocument70 pagesGrapeananiya dawitNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Test Bank For Intermediate Accounting 11th Edition Nikolai PDF EbookDocument32 pagesInstant Download Test Bank For Intermediate Accounting 11th Edition Nikolai PDF EbookDianeBoyerqmjs100% (13)
- BN6209 NotesDocument3 pagesBN6209 NotesShaun BuxaniNo ratings yet
- Seabass ManualDocument55 pagesSeabass ManualDimuthu Daluwatte50% (2)
- SkeletonDocument5 pagesSkeletonAnonymous x62KIL4xNo ratings yet
- The Roles of Folate, Vitamin B, and Iron: EW Nsights Into RythropoiesisDocument30 pagesThe Roles of Folate, Vitamin B, and Iron: EW Nsights Into Rythropoiesisarbolita3000No ratings yet
- Parasitology (Lect #2) TransDocument2 pagesParasitology (Lect #2) TransSherlyn Giban InditaNo ratings yet
- Frog Farming 00Document4 pagesFrog Farming 00api-3704111No ratings yet