Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photosynthesis Notes
Photosynthesis Notes
Uploaded by
api-544344393Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS-Student Worksheet (With Answers)Document8 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS-Student Worksheet (With Answers)Daniella Gabrielle Gerodias50% (12)
- Handout - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesHandout - Cell Transport Review Worksheetapi-502781581No ratings yet
- 1-Cell Organelles WS 2016 KEYDocument2 pages1-Cell Organelles WS 2016 KEYElvin Hoyo-a Logroño100% (2)
- Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet - KEYDocument6 pagesCell Membrane Coloring Worksheet - KEYsapphire284583% (12)
- Photosynthesis Worksheet Version 2 SHORT 2018 KEYDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Worksheet Version 2 SHORT 2018 KEYDeonLeo Cuenca100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Grade 11Document12 pagesPhotosynthesis Grade 11T Sivajini100% (1)
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheetapi-4218787360% (1)
- General Biology 1 TG PDFDocument190 pagesGeneral Biology 1 TG PDFRaquelito Belmonte Cenal50% (2)
- Edited - Amoeba Sisters Cell TransportDocument2 pagesEdited - Amoeba Sisters Cell TransportTalha 1075% (4)
- General Biology 1 As v1.0Document19 pagesGeneral Biology 1 As v1.0John Rex100% (4)
- WORKSHEET 3.2 The Structure of The Plasma MembraneDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 3.2 The Structure of The Plasma MembraneRosmainah Osman40% (5)
- TG SHS Earth ScienceDocument107 pagesTG SHS Earth ScienceErsan Resurreccion100% (1)
- Photosynthesis: Animations Student WorksheetDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis: Animations Student WorksheetChelsea MansuetoNo ratings yet
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 4 Module 7 Mitosis and Meiosis 2Document21 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 4 Module 7 Mitosis and Meiosis 2James Aringo100% (1)
- Activity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument8 pagesActivity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAdrian Neneng100% (1)
- ANSWERS Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis TEST REVIEWDocument2 pagesANSWERS Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis TEST REVIEWGen Li Togy100% (3)
- Photosynthesis TestDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis TestLester Eslava OrpillaNo ratings yet
- 11 STEM General Biology 1 FIRST QUARTER LMsDocument10 pages11 STEM General Biology 1 FIRST QUARTER LMsNeil Trezley Sunico Balajadia50% (2)
- Photosynthesis Worksheet Version 2 SHORT 2018 KEYDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Worksheet Version 2 SHORT 2018 KEYRosty Ann GrabilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisionbhupeshgalani100% (2)
- Bio Worksheet (Calvin Cycle)Document2 pagesBio Worksheet (Calvin Cycle)jerell100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Diagrams WorksheetDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Diagrams WorksheetG Meera Prem Kumar33% (6)
- CELLULAR RESPIRATION Review WorksheetDocument8 pagesCELLULAR RESPIRATION Review WorksheetMhai MontanoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Cellular Respiration#2 - Ch9 PDFDocument6 pagesWorksheet Cellular Respiration#2 - Ch9 PDFTaniaBarrios-ChongNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis StudentWS AnimationDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis StudentWS AnimationAayushi JainNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Electron Configuration: 8-27-2005 Joshua Perez-LunaDocument14 pagesStudent Exploration: Electron Configuration: 8-27-2005 Joshua Perez-LunaJoshua Perez-Luna67% (3)
- Photosynthesis Hhmi BiointeractiveDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis Hhmi BiointeractivemariaNo ratings yet
- CELLULAR RESPIRATION Review Worksheet KEY VufgteDocument2 pagesCELLULAR RESPIRATION Review Worksheet KEY VufgteRosalyn Marie SugayNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 (Chloroplast, Chlorophyll and Pigment)Document6 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (Chloroplast, Chlorophyll and Pigment)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Plant & Animal TissueDocument39 pagesPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- 15 Quarter 1 Module 15-light-INDEPENDENT-reactionsDocument19 pages15 Quarter 1 Module 15-light-INDEPENDENT-reactionsMah Jane Divina0% (1)
- STEM Biology 1 SET 11 Week 7 EnzymesDocument20 pagesSTEM Biology 1 SET 11 Week 7 EnzymesAlea Apruebo67% (3)
- Photosynthesis Worksheet KeyDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Worksheet Keychristine channn100% (1)
- Science Pocket Lesson in General Biology 2Document37 pagesScience Pocket Lesson in General Biology 2Kylie Zhane Uy100% (1)
- Patterns of Electron Flow Through Light Reaction EventsDocument25 pagesPatterns of Electron Flow Through Light Reaction EventsMar'J50% (2)
- Transport Across Membranes FinalDocument77 pagesTransport Across Membranes FinalLorraine Eve Abila100% (1)
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 2Document23 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 2Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- Biology Test With TOSDocument4 pagesBiology Test With TOSRaymund Platilla100% (3)
- Cell Structures and Their Functions SLADocument19 pagesCell Structures and Their Functions SLAMaricar Baria100% (2)
- SLM Q1 Matter and Its Properties Week 1Document19 pagesSLM Q1 Matter and Its Properties Week 1Robert JohnNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY Grade 11-1S-W1Document15 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY Grade 11-1S-W1Nuur EmNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 QuizDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology 1 QuizQueng ElediaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1Pril Gueta100% (2)
- Notes For Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesNotes For Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationxXxXxXxXxNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document35 pagesGeneral Biology 2Claries Cuenca100% (1)
- Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsDocument22 pagesCell Organelles and Their FunctionsJoseph Al Bayonas100% (2)
- Biology M4 PhotosynthesisDocument31 pagesBiology M4 PhotosynthesisDiana Dealino-SabandalNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in General Biology IDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Test in General Biology ISamantha RullaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Hand OutDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Hand OutAraquel Nunez100% (1)
- General Biology 2 TG PDFDocument269 pagesGeneral Biology 2 TG PDFCamille Sison-Almirol100% (2)
- Module 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)Document24 pagesModule 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)greggcllam619076100% (7)
- Cellular RespirationDocument44 pagesCellular RespirationGhizlane El FazaziNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Ilovepdf CompressedDocument270 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Ilovepdf CompressedAnonymous nICTJN0sjU65% (37)
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument26 pagesBiological MacromoleculesGomez Agustin LeslieNo ratings yet
- ATP-ADP CycleDocument15 pagesATP-ADP CycleMay PaviaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Nelson Biology Pages 204 - 228Document60 pagesCellular Respiration: Nelson Biology Pages 204 - 228allie3d100% (14)
- Finals - Biology 2Document12 pagesFinals - Biology 2Leonel Mendoza100% (1)
- Student WorksheetDocument7 pagesStudent Worksheetsankata.blasioNo ratings yet
- HHMI Biointeractive Photosynthesis WSDocument7 pagesHHMI Biointeractive Photosynthesis WSJrNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformation and PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesEnergy Transformation and PhotosynthesisYumeko JabamiNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Biology Life On Earth With Physiology 11th Edition Audesirk Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument37 pagesInstant Download PDF Biology Life On Earth With Physiology 11th Edition Audesirk Solutions Manual Full Chapteratasiijurij100% (5)
- ENGL 267 British Literature - Guiding Questions Literary Analysis - Argument EssayDocument2 pagesENGL 267 British Literature - Guiding Questions Literary Analysis - Argument Essayapi-544344393No ratings yet
- NewsletterDocument3 pagesNewsletterapi-544344393No ratings yet
- Animal FarmDocument8 pagesAnimal Farmapi-544344393No ratings yet
- Woodrow WilsonDocument7 pagesWoodrow Wilsonapi-544344393No ratings yet
- Notes PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesNotes Photosynthesisapi-544344393No ratings yet
- AnnexureDocument3 pagesAnnexureqamarNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Screw Chiller R134aDocument12 pagesAir Cooled Screw Chiller R134aalkaf08No ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument4 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrosAye Ei MonNo ratings yet
- 3 LAB ACTIVITY SHEET 3 Precipitation and Solubility 1Document3 pages3 LAB ACTIVITY SHEET 3 Precipitation and Solubility 1Jurel JohnNo ratings yet
- Section 02360 Soil TreatmentDocument3 pagesSection 02360 Soil TreatmentMØhãmmed ØwięsNo ratings yet
- AlkalinityDocument11 pagesAlkalinitySivakumar NagarathinamNo ratings yet
- Environmental LawDocument37 pagesEnvironmental LawNishaath ShareefNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biochemical Characteristics of Living MatterDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Biochemical Characteristics of Living MatterJoyce Jimenez0% (1)
- Solution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd EditionDocument31 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd EditionChristianGonzalezsrybm100% (94)
- COLPHENE BSW BrochureDocument6 pagesCOLPHENE BSW BrochureDesigner 2No ratings yet
- (1994) - Shen - Development of An Aluminiumhea Water Battery For Subsea ApplicationsDocument9 pages(1994) - Shen - Development of An Aluminiumhea Water Battery For Subsea ApplicationsK A ThomasNo ratings yet
- Instruction Sheet 384 34: Heating Apparatus (384 34)Document2 pagesInstruction Sheet 384 34: Heating Apparatus (384 34)Maria RincónNo ratings yet
- Dr. Chan Kook Weng Dr. Chan Kook Weng Hj. Wahid Omar Hj. Wahid OmarDocument23 pagesDr. Chan Kook Weng Dr. Chan Kook Weng Hj. Wahid Omar Hj. Wahid OmarkoperasiNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 4 - PsDocument4 pagesSummative Test 4 - PsKennedy Fieldad VagayNo ratings yet
- Bendezu & Fontboté PDFDocument12 pagesBendezu & Fontboté PDFJesusNo ratings yet
- QNBN Vendor List For MaterialsDocument1 pageQNBN Vendor List For Materialshatem hamaidiNo ratings yet
- 2014 2 2 3 EnwaDocument10 pages2014 2 2 3 EnwaAdela Cynthia AltairaNo ratings yet
- Justiz-Smith 2008 Materials-CharacterizationDocument6 pagesJustiz-Smith 2008 Materials-CharacterizationArif HidayatNo ratings yet
- Steripen Classic EnglishDocument4 pagesSteripen Classic Englishben123456789benNo ratings yet
- Soldering Basic GuideDocument6 pagesSoldering Basic GuidechchuanNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument11 pagesHeat ExchangerMangesh MandgeNo ratings yet
- J. Electrochem. Soc.-1952-Blake-202C-3CDocument2 pagesJ. Electrochem. Soc.-1952-Blake-202C-3CGeovanny JaenzNo ratings yet
- Borewell Chlorination TreatmentDocument10 pagesBorewell Chlorination TreatmentjayanthNo ratings yet
- US20120282834A1Document7 pagesUS20120282834A1subramanian.sNo ratings yet
- A Review of A New Voltammetric Method For Determining AcidsDocument11 pagesA Review of A New Voltammetric Method For Determining Acidspuspa sandra pNo ratings yet
- TCP - Ii FinishesDocument82 pagesTCP - Ii FinishesNabarupa BoseNo ratings yet
- 2017 MMFX PresentationDocument38 pages2017 MMFX PresentationaljaycruzadoNo ratings yet
- The Application of Membrane Separation TechnologyDocument13 pagesThe Application of Membrane Separation TechnologyElif UsluNo ratings yet
- ScribdDocument22 pagesScribdmonkeydluffyNo ratings yet
Photosynthesis Notes
Photosynthesis Notes
Uploaded by
api-544344393Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Photosynthesis Notes
Photosynthesis Notes
Uploaded by
api-544344393Copyright:
Available Formats
HHMI PHOTOSYNTHESIS BIOINTERACTIVE MODELING
INTRODUCTION
This worksheet complements the HHMI animation series Photosynthesis. After watching the animation video for
each part, answer the questions. You will be assessed on your answers to the summary questions in part 8 for
standard RS2: Matter and Energy. Please review the rubric at the end of the document for specific details.
PROCEDURE
1. This animation series contains seven parts.
2. Click HERE to access the video animations for each part.
3. After watching each part, answer the questions in the spaces provided using complete
sentences.
4. After completing all seven parts of the animation, answer the summary questions in
Part 8.
QUESTIONS
PART 1: OVERVIEW
1. Which of the following kinds of organisms do photosynthesis? HIGHLIGHT all that apply.
____plants ____fungi ____animals ____algae ____all bacteria ____some bacteria
2. What is the overall purpose of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis’ overall purpose is to nourish the entire world.
3. On Diagram 1, fill in the labels with photosynthesis’s main inputs and outputs of matter and energy.
Photosynthesis Published March 2019
www.BioInteractive.org Page 1 of 10
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Published March 2019
www.BioInteractive.org Page 2 of 10
Photosynthesis
PART 2: CHEMICAL PROCESS
1. Complete the following sentence.
Photosynthesis is a set of _chemical reactions_ in which __light__energy is converted to
____chemical____energy.
2. On Diagram 2, fill in the labels with the following descriptions. Some of the objects have multiple labels.
● water (H2O)
● carbon dioxide (CO2)
● oxygen (O2)
● G3P (sugar)
● electron acceptor
● electron donor
● carbohydrates
● energy input
3PART : LEAF STRUCTURE
1. In what plant structures does photosynthesis occur? Make your description as specific as you can.
The chloroplasts in the middle of the leaf, in most cells, is the process in which photosynthesis
occurs.
2. On Diagram 3, complete the following tasks.
a) Draw how CO2 gets into
the leaf.
b) Draw how O2 gets out of
the leaf.
c) Label the name of the
structure through which
these gases pass.
3. What structure is used to transport organic molecules from the leaf to other parts of the plant?
Photosynthesis Published March 2019
www.BioInteractive.org Page 3 of 10
Photosynthesis
The structure that is required for the transportation of organic molecules from the leaf to other parts
of the plant is the vascular bundle.
4. Why are leaves green?
Leaves are green due to the pigment coloration of the chloroplasts.
PART 4: CHLOROPLASTS
1. On Diagram 4, label the following items. Multiple labels may apply to the same part of the diagram.
● location of the light reactions
● location of the Calvin cycle
● thylakoid
● stroma
2. On Diagram 5, fill in the labels with the following descriptions to show the connections between the light
reactions and the Calvin cycle.
● carbon dioxide (CO2)
● oxygen (O2)
● G3P (sugar)
● ATP
● NADPH
3. How does a plant increase its biomass?
The plant increases its biomass with the use of having more new organic molecules.
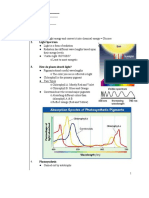
PART 5: LIGHT REACTIONS
Photosystems I and II (PSI and PSII)
1. What is the function of the photosystems?
Photosynthesis Published March 2019
www.BioInteractive.org Page 4 of 10
Photosynthesis
The function of the photosystems is to transform light energy into chemical energy with the help of
the electron transport chain process.
2. On Diagram 6, complete the following tasks.
a) Label PSI
and PSII.
b) Draw the
path of the
electron
transport
chain.
The Events of the Light Reactions
3. For PSII, the cytochrome complex, and PSI, draw and label what happens at that structure on Diagram 6.
Then describe the events in a bulleted list in Table 1.
Table 1: Descriptions of the steps in the light reactions.
Structure What is happening with matter? What is happening with energy?
PSII
The water is being used with the light The energy that is occurring here is
energy to be split into oxygen and increased with the electron due to
hydrogen ions. The electron is then used the light reaction with the
in the chlorophyll to be excited with
chlorophyll.
energy and continue onto the next
process.
Photosynthesis Published March 2019
www.BioInteractive.org Page 5 of 10
Photosynthesis
cytochrome
complex
The electron is transported to the Some energy from the electron is
cytochrome complex that then uses used in this process in order to pump
the energy to pump hydrogen ions into the hydrogen ions in. The electron is
the Thylakoid lumen. then sent to the PSI reaction.
PSI
The electron is rescued and recharged The electron is recharged with a lot
with the light energy with the help of the of energy. Overall, the energy is
chlorophyll. It is then sent off to the next increased in this process.
process.
4. At the end of the electron transport chain, where is the light energy that was absorbed and converted by
chlorophyll stored? List two answers.
1. The light energy is stored in the molecule NADPH.
2. The ATP is the other molecule that stores the energy.
Chemiosmosis and ATP Synthase
5. Label the ATP synthase on Diagram 6.
6. Describe how the proton (H+) gradient is used to make ATP.
The proton gradient is used to make ATP by passing through the stroma into an enzyme called ATP
Synthase. The concentration is higher on the inside, so the lower concentration on the outside allows
the hydrogen ions to pass through.
7. What two molecules bring chemical energy from the light reactions to the next stage of photosynthesis, the
Calvin cycle?
The two molecules that bring chemical energy from the light reactions to the next state of
photosynthesis are the molecules NADPH and ATP. Before they are energized, they are NADP and
ADP.
Photosynthesis Published March 2019
www.BioInteractive.org Page 6 of 10
Photosynthesis
PART 6: CALVIN CYCLE
1. Label Diagram 7 with the three phases of the Calvin cycle.
Briefly describe what is going on in each phase and answer the questions shown.
Phase 1 (Diagram 8)
Description:
The 3 carbon dioxide molecules are incorporated with
3 RuBP to create 6 3-PGA.
What enzyme catalyzes the reaction in this phase?
This process is all done with the help of a PuBisCO
enzyme.
Photosynthesis Published March 2019
www.BioInteractive.org Page 7 of 10
Photosynthesis
Phase 2 (Diagram 9)
Description:
The 3-PGA molecules accept the electrons from the 6
ATP molecules and 6 NADPH molecules. This then
creates 6 G3P molecules. One of the G3P molecules
leave the cycle in order to be used to create other
organic molecules.
Phase 3 (Diagram 10)
Description:
Why is the series of reactions in the Calvin cycle called a
“cycle”?
The series of reactions in the Calvin cycle are called a
“cycle,” because it is using organic molecules to create
new organic molecules. It recreates the molecules
needed for the first phase.
2. At the end of the Calvin cycle, what molecules have the energy that originally came from light?
In the end of the Calvin cycle, the molecules that have the energy that originally came from light are
the ATP and NADPH molecules.
PART 7: BIOSYNTHESIS
1. Complete the following sentence based on Diagram 11.
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) can be used by plant cells to make
___Sucrose____ and ____Starch____.
2. Which molecule in Diagram 11 is used to transport energy to other parts of
the plant?
The molecule that is transported to other parts of the plant is sucrose.
3. Which molecule in Diagram 11 is stored in the plant for later use as an
energy source?
Photosynthesis Published March 2019
www.BioInteractive.org Page 8 of 10
Photosynthesis
The molecule that is stored in the plant for later on as an energy source
is starch.
PART 8: TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
1. Based on everything you’ve learned from the animations, what is the overall purpose of photosynthesis?
The overall purpose of photosynthesis is to help support all life on earth.
2. Describe how oxygen gas (O2) is produced during photosynthesis. Include the specific structures in the plant
where the reaction occurs.
Oxygen gas is produced as a byproduct of the Photosystem II process when water is split. The proper
wavelength of energy splits the water into oxygen and hydrogen ions. This process is done with the
Thylakoid. The oxygen is then released out the stroma of the leaf.
3. Describe the path of an electron from a molecule of water to the sugar G3P.
The electron is charged and transported through the light-dependent cycle between the proteins of
the Thylakoid. It then is combined with organic molecules in order to be used in the Calvin Cycle.
4. Describe how ATP is produced in the light reactions.
ATP is produced in the light reactions by having the ATP Synthase, fueled by the traveling of hydrogen
ions through the enzyme, by combining with a Pi and an electron. The hydrogen, for this reaction to
occur, comes from the splitting of the water, with the help of strong wavelengths of light. Other
hydrogen ions come from the Cytochrome Complex, pumping them into the Thylakoid.
5. Which of the following statements best explains how the energy in a photon of light is stored in a molecule of
the sugar G3P? Option C. More specifically would be certain wavelengths of light energy.
a. Light energy directly provides energy to RuBP and CO2, which produce G3P in the Calvin cycle.
b. Light energy directly provides energy to ATP synthase, which produces ATP during the light reactions.
c. Light energy energizes electrons to make ATP and NADPH, which provide energy to produce G3P in the
Calvin cycle.
6. When three molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) react with three molecules of RuBP during the Calvin cycle, six
molecules of the sugar G3P are produced. One G3P molecule exits the Calvin cycle during Phase 2. What
happens to the other five G3P molecules?
What occurs with the other five G3P molecules in the Calvin cycle is the recreation of the 3 RuBP
molecules used in the beginning of the process. The other five G3P molecules becoming 3 RuBP
molecules are what allow the Calvin Cycle to be a cycle.
RUBRIC FOR SELF ASSESSMENT AND GRADING (PART 8)
Photosynthesis Published March 2019
www.BioInteractive.org Page 9 of 10
Photosynthesis
RS2: ● Construct an explanation based on evidence for how energy and matter change
Matter & and/or flow into, out of, and within the system during the processes involved in
Energy photosynthesis.
4 In addition to a 3.0 score, student demonstrates sophisticated applications such as:
☐ In depth analysis and explanations of changes in energy and matter such as:
● Explicit details, names of structures, and steps involved in the photosynthetic
process
☐ Connections made beyond the context of the topic such as:
● Relating and explaining the processes of photosynthesis based on prior
knowledge such as enzyme structure and function, pigment and wavelength
absorption and reflection, cellular transport mechanisms, and membrane
structure
3 While engaged in grade appropriate tasks, the student demonstrates the following:
☐ Thorough explanation of changes in energy and matter during photosynthesis
including details about each of the following:
● production of oxygen gas
● structures of photosynthesis that relate to specific functions
● path of electrons from water to G3P
● production of ATP during the light reactions
● carbon counting and regeneration of RUBP in the Calvin Cycle
2 No major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details such as:
☐ Basic explanation of the changes in energy and matter during photosynthesis; details
are incomplete and/or lacking in detail
1 Major errors or omissions present.
☐ Explanations of changes in energy and matter during photosynthesis are incorrect
Photosynthesis Published March 2019
www.BioInteractive.org Page 10 of 10
You might also like
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS-Student Worksheet (With Answers)Document8 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS-Student Worksheet (With Answers)Daniella Gabrielle Gerodias50% (12)
- Handout - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesHandout - Cell Transport Review Worksheetapi-502781581No ratings yet
- 1-Cell Organelles WS 2016 KEYDocument2 pages1-Cell Organelles WS 2016 KEYElvin Hoyo-a Logroño100% (2)
- Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet - KEYDocument6 pagesCell Membrane Coloring Worksheet - KEYsapphire284583% (12)
- Photosynthesis Worksheet Version 2 SHORT 2018 KEYDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Worksheet Version 2 SHORT 2018 KEYDeonLeo Cuenca100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Grade 11Document12 pagesPhotosynthesis Grade 11T Sivajini100% (1)
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheetapi-4218787360% (1)
- General Biology 1 TG PDFDocument190 pagesGeneral Biology 1 TG PDFRaquelito Belmonte Cenal50% (2)
- Edited - Amoeba Sisters Cell TransportDocument2 pagesEdited - Amoeba Sisters Cell TransportTalha 1075% (4)
- General Biology 1 As v1.0Document19 pagesGeneral Biology 1 As v1.0John Rex100% (4)
- WORKSHEET 3.2 The Structure of The Plasma MembraneDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 3.2 The Structure of The Plasma MembraneRosmainah Osman40% (5)
- TG SHS Earth ScienceDocument107 pagesTG SHS Earth ScienceErsan Resurreccion100% (1)
- Photosynthesis: Animations Student WorksheetDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis: Animations Student WorksheetChelsea MansuetoNo ratings yet
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 4 Module 7 Mitosis and Meiosis 2Document21 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 4 Module 7 Mitosis and Meiosis 2James Aringo100% (1)
- Activity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument8 pagesActivity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAdrian Neneng100% (1)
- ANSWERS Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis TEST REVIEWDocument2 pagesANSWERS Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis TEST REVIEWGen Li Togy100% (3)
- Photosynthesis TestDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis TestLester Eslava OrpillaNo ratings yet
- 11 STEM General Biology 1 FIRST QUARTER LMsDocument10 pages11 STEM General Biology 1 FIRST QUARTER LMsNeil Trezley Sunico Balajadia50% (2)
- Photosynthesis Worksheet Version 2 SHORT 2018 KEYDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Worksheet Version 2 SHORT 2018 KEYRosty Ann GrabilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisionbhupeshgalani100% (2)
- Bio Worksheet (Calvin Cycle)Document2 pagesBio Worksheet (Calvin Cycle)jerell100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Diagrams WorksheetDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Diagrams WorksheetG Meera Prem Kumar33% (6)
- CELLULAR RESPIRATION Review WorksheetDocument8 pagesCELLULAR RESPIRATION Review WorksheetMhai MontanoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Cellular Respiration#2 - Ch9 PDFDocument6 pagesWorksheet Cellular Respiration#2 - Ch9 PDFTaniaBarrios-ChongNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis StudentWS AnimationDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis StudentWS AnimationAayushi JainNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Electron Configuration: 8-27-2005 Joshua Perez-LunaDocument14 pagesStudent Exploration: Electron Configuration: 8-27-2005 Joshua Perez-LunaJoshua Perez-Luna67% (3)
- Photosynthesis Hhmi BiointeractiveDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis Hhmi BiointeractivemariaNo ratings yet
- CELLULAR RESPIRATION Review Worksheet KEY VufgteDocument2 pagesCELLULAR RESPIRATION Review Worksheet KEY VufgteRosalyn Marie SugayNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 (Chloroplast, Chlorophyll and Pigment)Document6 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (Chloroplast, Chlorophyll and Pigment)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Plant & Animal TissueDocument39 pagesPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- 15 Quarter 1 Module 15-light-INDEPENDENT-reactionsDocument19 pages15 Quarter 1 Module 15-light-INDEPENDENT-reactionsMah Jane Divina0% (1)
- STEM Biology 1 SET 11 Week 7 EnzymesDocument20 pagesSTEM Biology 1 SET 11 Week 7 EnzymesAlea Apruebo67% (3)
- Photosynthesis Worksheet KeyDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Worksheet Keychristine channn100% (1)
- Science Pocket Lesson in General Biology 2Document37 pagesScience Pocket Lesson in General Biology 2Kylie Zhane Uy100% (1)
- Patterns of Electron Flow Through Light Reaction EventsDocument25 pagesPatterns of Electron Flow Through Light Reaction EventsMar'J50% (2)
- Transport Across Membranes FinalDocument77 pagesTransport Across Membranes FinalLorraine Eve Abila100% (1)
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 2Document23 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 2Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- Biology Test With TOSDocument4 pagesBiology Test With TOSRaymund Platilla100% (3)
- Cell Structures and Their Functions SLADocument19 pagesCell Structures and Their Functions SLAMaricar Baria100% (2)
- SLM Q1 Matter and Its Properties Week 1Document19 pagesSLM Q1 Matter and Its Properties Week 1Robert JohnNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY Grade 11-1S-W1Document15 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY Grade 11-1S-W1Nuur EmNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 QuizDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology 1 QuizQueng ElediaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1Pril Gueta100% (2)
- Notes For Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesNotes For Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationxXxXxXxXxNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document35 pagesGeneral Biology 2Claries Cuenca100% (1)
- Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsDocument22 pagesCell Organelles and Their FunctionsJoseph Al Bayonas100% (2)
- Biology M4 PhotosynthesisDocument31 pagesBiology M4 PhotosynthesisDiana Dealino-SabandalNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in General Biology IDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Test in General Biology ISamantha RullaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Hand OutDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Hand OutAraquel Nunez100% (1)
- General Biology 2 TG PDFDocument269 pagesGeneral Biology 2 TG PDFCamille Sison-Almirol100% (2)
- Module 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)Document24 pagesModule 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)greggcllam619076100% (7)
- Cellular RespirationDocument44 pagesCellular RespirationGhizlane El FazaziNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Ilovepdf CompressedDocument270 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Ilovepdf CompressedAnonymous nICTJN0sjU65% (37)
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument26 pagesBiological MacromoleculesGomez Agustin LeslieNo ratings yet
- ATP-ADP CycleDocument15 pagesATP-ADP CycleMay PaviaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Nelson Biology Pages 204 - 228Document60 pagesCellular Respiration: Nelson Biology Pages 204 - 228allie3d100% (14)
- Finals - Biology 2Document12 pagesFinals - Biology 2Leonel Mendoza100% (1)
- Student WorksheetDocument7 pagesStudent Worksheetsankata.blasioNo ratings yet
- HHMI Biointeractive Photosynthesis WSDocument7 pagesHHMI Biointeractive Photosynthesis WSJrNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformation and PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesEnergy Transformation and PhotosynthesisYumeko JabamiNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Biology Life On Earth With Physiology 11th Edition Audesirk Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument37 pagesInstant Download PDF Biology Life On Earth With Physiology 11th Edition Audesirk Solutions Manual Full Chapteratasiijurij100% (5)
- ENGL 267 British Literature - Guiding Questions Literary Analysis - Argument EssayDocument2 pagesENGL 267 British Literature - Guiding Questions Literary Analysis - Argument Essayapi-544344393No ratings yet
- NewsletterDocument3 pagesNewsletterapi-544344393No ratings yet
- Animal FarmDocument8 pagesAnimal Farmapi-544344393No ratings yet
- Woodrow WilsonDocument7 pagesWoodrow Wilsonapi-544344393No ratings yet
- Notes PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesNotes Photosynthesisapi-544344393No ratings yet
- AnnexureDocument3 pagesAnnexureqamarNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Screw Chiller R134aDocument12 pagesAir Cooled Screw Chiller R134aalkaf08No ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument4 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrosAye Ei MonNo ratings yet
- 3 LAB ACTIVITY SHEET 3 Precipitation and Solubility 1Document3 pages3 LAB ACTIVITY SHEET 3 Precipitation and Solubility 1Jurel JohnNo ratings yet
- Section 02360 Soil TreatmentDocument3 pagesSection 02360 Soil TreatmentMØhãmmed ØwięsNo ratings yet
- AlkalinityDocument11 pagesAlkalinitySivakumar NagarathinamNo ratings yet
- Environmental LawDocument37 pagesEnvironmental LawNishaath ShareefNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biochemical Characteristics of Living MatterDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Biochemical Characteristics of Living MatterJoyce Jimenez0% (1)
- Solution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd EditionDocument31 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd EditionChristianGonzalezsrybm100% (94)
- COLPHENE BSW BrochureDocument6 pagesCOLPHENE BSW BrochureDesigner 2No ratings yet
- (1994) - Shen - Development of An Aluminiumhea Water Battery For Subsea ApplicationsDocument9 pages(1994) - Shen - Development of An Aluminiumhea Water Battery For Subsea ApplicationsK A ThomasNo ratings yet
- Instruction Sheet 384 34: Heating Apparatus (384 34)Document2 pagesInstruction Sheet 384 34: Heating Apparatus (384 34)Maria RincónNo ratings yet
- Dr. Chan Kook Weng Dr. Chan Kook Weng Hj. Wahid Omar Hj. Wahid OmarDocument23 pagesDr. Chan Kook Weng Dr. Chan Kook Weng Hj. Wahid Omar Hj. Wahid OmarkoperasiNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 4 - PsDocument4 pagesSummative Test 4 - PsKennedy Fieldad VagayNo ratings yet
- Bendezu & Fontboté PDFDocument12 pagesBendezu & Fontboté PDFJesusNo ratings yet
- QNBN Vendor List For MaterialsDocument1 pageQNBN Vendor List For Materialshatem hamaidiNo ratings yet
- 2014 2 2 3 EnwaDocument10 pages2014 2 2 3 EnwaAdela Cynthia AltairaNo ratings yet
- Justiz-Smith 2008 Materials-CharacterizationDocument6 pagesJustiz-Smith 2008 Materials-CharacterizationArif HidayatNo ratings yet
- Steripen Classic EnglishDocument4 pagesSteripen Classic Englishben123456789benNo ratings yet
- Soldering Basic GuideDocument6 pagesSoldering Basic GuidechchuanNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument11 pagesHeat ExchangerMangesh MandgeNo ratings yet
- J. Electrochem. Soc.-1952-Blake-202C-3CDocument2 pagesJ. Electrochem. Soc.-1952-Blake-202C-3CGeovanny JaenzNo ratings yet
- Borewell Chlorination TreatmentDocument10 pagesBorewell Chlorination TreatmentjayanthNo ratings yet
- US20120282834A1Document7 pagesUS20120282834A1subramanian.sNo ratings yet
- A Review of A New Voltammetric Method For Determining AcidsDocument11 pagesA Review of A New Voltammetric Method For Determining Acidspuspa sandra pNo ratings yet
- TCP - Ii FinishesDocument82 pagesTCP - Ii FinishesNabarupa BoseNo ratings yet
- 2017 MMFX PresentationDocument38 pages2017 MMFX PresentationaljaycruzadoNo ratings yet
- The Application of Membrane Separation TechnologyDocument13 pagesThe Application of Membrane Separation TechnologyElif UsluNo ratings yet
- ScribdDocument22 pagesScribdmonkeydluffyNo ratings yet