Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PocketGuide-Feature Control Frame Details
PocketGuide-Feature Control Frame Details
Uploaded by
zeez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pagePocketGuide-Feature Control Frame Details
PocketGuide-Feature Control Frame Details
Uploaded by
zeezCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
14 THE POCKET BEST PRACTICES GUIDE
3. Feature Control Frame Details
Geometry Control Tools are applied to individual part fea-
tures by placing them in Feature Control Frames:
Figure 3/1 Feature Control Frame Anatomy
Feature Control Frames can be either “read” or “decoded”:
Reading: Flatness within 0.1 mm
Decoding: Flatness requires every point on the consid-
ered feature to lie within a “slab-like” tolerance zone of
thickness 0.1 mm, unconstrained by a DRF.
Reading: Position within a diameter of 0.5 mm at MMC
relative to A,B RFS and C at MMC.
Decoding: Position requires the bounded axis of the
considered feature to lie within a “cylindrical” tolerance
zone of diameter 0.5 mm at MMC, expanding by as much
as 0.4 mm as the considered feature departs from MMC
toward LMC, oriented and located by Basic dimensions
relative to a DRF established using Datum Feature A,
Datum Feature B simulated regardless of its size, and
Datum Feature C simulated at its Virtual MMC.
You might also like
- Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T)Document43 pagesGeometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T)Victor Manuel Estrada0% (1)
- GDT-True PositionDocument32 pagesGDT-True Positionhamartinez100% (1)
- Tutorial MathCadDocument12 pagesTutorial MathCadmapasabc0% (1)
- GD&T Best Practices and TrainingDocument4 pagesGD&T Best Practices and TrainingtrandangbkNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) : Part Production Communication ModelDocument76 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) : Part Production Communication ModelPedro SalinasNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Design Interview Questions and AnswersDocument16 pagesMechanical Design Interview Questions and Answersarshad khanNo ratings yet
- Rules: Three Dimensioning and Tolerancing Rules Defined by The 2009 StandardDocument3 pagesRules: Three Dimensioning and Tolerancing Rules Defined by The 2009 StandardRamesh PeddagoudNo ratings yet
- EPM212 - Chapter 9 Slides GD T HandoutDocument15 pagesEPM212 - Chapter 9 Slides GD T HandoutJosephRomeraloNo ratings yet
- GSM - Lecture (Chapter 3)Document92 pagesGSM - Lecture (Chapter 3)mkbreaktherulesNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimension IngDocument106 pagesGeometric Dimension IngjamesliouNo ratings yet
- MDC Submission GuidelinesDocument12 pagesMDC Submission GuidelinesEdward PongracNo ratings yet
- GD & T-2Document29 pagesGD & T-221adNo ratings yet
- Cell Reselect ParameterDocument13 pagesCell Reselect ParameterEka KosasihNo ratings yet
- GD&T Day 1 Part 1Document22 pagesGD&T Day 1 Part 1harshkallani100% (2)
- Chapter 9 Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) : FPOLR-52332Document12 pagesChapter 9 Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) : FPOLR-52332Jackie HwangNo ratings yet
- Michel SonDocument8 pagesMichel Sonsaba1388No ratings yet
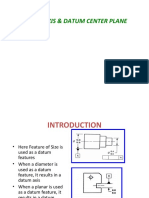
- Datum Axis & Datum Center PlaneDocument43 pagesDatum Axis & Datum Center Planegc_rama100% (1)
- GSM Base StationDocument34 pagesGSM Base Stationervis cikuNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Alignment Considerations For Switchbeams 3.5.1 GeneralDocument4 pages3.5 Alignment Considerations For Switchbeams 3.5.1 GeneralRaymond CiaoNo ratings yet
- Gsmbasetransceiverstation 160912171635Document34 pagesGsmbasetransceiverstation 160912171635Kudo ShinichiNo ratings yet
- Symbol: None - Always Implied Default Condition (Abreviated: RFS) Category: Feature of Size DefinitionDocument2 pagesSymbol: None - Always Implied Default Condition (Abreviated: RFS) Category: Feature of Size Definitionvin_ckNo ratings yet
- 01 Basic (CDMA)Document43 pages01 Basic (CDMA)harish sNo ratings yet
- Maxum III Instruction ManualDocument58 pagesMaxum III Instruction ManualSergio Fabian ValienteNo ratings yet
- Alcatel BTS Presentation Complete UpdatedDocument91 pagesAlcatel BTS Presentation Complete UpdatedKhurram ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- 23 Abis InterfaceDocument20 pages23 Abis InterfacePaul KabeyaNo ratings yet
- GD TQuestionssetDocument5 pagesGD TQuestionssetyashchopraNo ratings yet
- BSS InterfacesDocument75 pagesBSS Interfaceskazem_mirNo ratings yet
- M2 Geometrical Measurement TMM CMM PDFDocument17 pagesM2 Geometrical Measurement TMM CMM PDFRohith M. AthreyaNo ratings yet
- Specifying The Position Tolerance at MMC: 856 Salt Lake Court San Jose, Ca 95133 (408) 251-5329Document3 pagesSpecifying The Position Tolerance at MMC: 856 Salt Lake Court San Jose, Ca 95133 (408) 251-5329Ravindra IwaleNo ratings yet
- Profile ControlDocument9 pagesProfile ControlSahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Coordinate Measuring MachinesDocument6 pages10.2 Coordinate Measuring MachinesVenkateshYadavCivarlaNo ratings yet
- CMMDocument37 pagesCMMSachin AggarwalNo ratings yet
- 05 StraightnessMeasurement90Document90 pages05 StraightnessMeasurement90maddy_scribdNo ratings yet
- Mobile Station: Functions of MSDocument51 pagesMobile Station: Functions of MSSathish RajaNo ratings yet
- Straightness Tolerance and ErrorDocument22 pagesStraightness Tolerance and ErrorAdel AbdelmaboudNo ratings yet
- Datum ShiftDocument11 pagesDatum ShiftHarshottam DhakadNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge For CDMA SystemDocument42 pagesBasic Knowledge For CDMA SystemSanjay GiriNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Input Shaping On Coordinate Measuring Machine RepeatabilityDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Input Shaping On Coordinate Measuring Machine RepeatabilitytuongnvNo ratings yet
- Profile of A LineDocument6 pagesProfile of A LinemooninjaNo ratings yet
- hyperMILL 5XDocument148 pageshyperMILL 5XX800XL100% (2)
- Active Pixel Sensors Seminar Report: Harikumar.K. E7B, 16Document12 pagesActive Pixel Sensors Seminar Report: Harikumar.K. E7B, 16Hari KumarNo ratings yet
- Basics of GD&TDocument50 pagesBasics of GD&T2023ht30006No ratings yet
- DATUMSDocument84 pagesDATUMSmaddy_scribd100% (2)
- ROBOTICDocument13 pagesROBOTICcardozogonzalezerikaNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Miscellaneous MetrologyDocument15 pagesUnit 11 Miscellaneous Metrologybhuyanuttam7No ratings yet
- Network Access Technology Security FinDocument140 pagesNetwork Access Technology Security FinPARASPKKATHURIANo ratings yet
- F 5 Geo TolerancesDocument23 pagesF 5 Geo TolerancesRodrigo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Digsilent Powerfactory: Relay Model DescriptionDocument10 pagesDigsilent Powerfactory: Relay Model DescriptionjdhajhaFDJHJNo ratings yet
- Datum TargetDocument200 pagesDatum TargetprasenjitsayantanNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument10 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing25aprilNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: 1.1 CantileverDocument6 pagesObjectives:: 1.1 CantileverramaNo ratings yet
- Metrology Measurement Unit-5Document27 pagesMetrology Measurement Unit-5R NAVEEN KUMAR MECHNo ratings yet
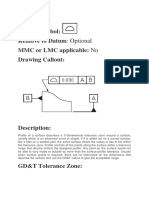
- Profile of A Line: GD&T Symbol: Relative To Datum MMC or LMC Applicable: Drawing CalloutDocument2 pagesProfile of A Line: GD&T Symbol: Relative To Datum MMC or LMC Applicable: Drawing CalloutanishNo ratings yet
- 3D Vision Sensor: FZD SeriesDocument12 pages3D Vision Sensor: FZD SeriesBasetty SumanthNo ratings yet
- Handout On BTS MtceDocument45 pagesHandout On BTS MtcepugalNo ratings yet
- GD & T PresentationDocument63 pagesGD & T PresentationPuneet Birla100% (2)
- Procedural Surface: Exploring Texture Generation and Analysis in Computer VisionFrom EverandProcedural Surface: Exploring Texture Generation and Analysis in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Hidden Surface Determination: Unveiling the Secrets of Computer VisionFrom EverandHidden Surface Determination: Unveiling the Secrets of Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Lord KuberaDocument2 pagesLord KuberaKaveri SomasundaramNo ratings yet
- Series Overview: ArrowDocument2 pagesSeries Overview: ArrowKaveri SomasundaramNo ratings yet
- McNaught Books ListDocument1 pageMcNaught Books ListKaveri SomasundaramNo ratings yet
- Kow Your Broadbad: 1. Check The WiresDocument4 pagesKow Your Broadbad: 1. Check The WiresKaveri SomasundaramNo ratings yet
- Tamil For MedicosDocument32 pagesTamil For MedicosKaveri Somasundaram100% (1)
- Analogies ChartDocument3 pagesAnalogies ChartKaveri SomasundaramNo ratings yet