Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cognitive Meds
Cognitive Meds
Uploaded by
RNStudent1100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
159 views2 pages1. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists are used to treat Alzheimer's disease by reducing acetylcholine breakdown and limiting glutamate effects, slowing cognitive decline.
2. Conventional and atypical antipsychotics treat psychosis and schizophrenia by blocking dopamine receptors, decreasing positive and negative symptoms.
3. Anxiolytics and SSRIs decrease anxiety and depression symptoms by inhibiting serotonin reuptake.
Original Description:
Cognitive Meds
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists are used to treat Alzheimer's disease by reducing acetylcholine breakdown and limiting glutamate effects, slowing cognitive decline.
2. Conventional and atypical antipsychotics treat psychosis and schizophrenia by blocking dopamine receptors, decreasing positive and negative symptoms.
3. Anxiolytics and SSRIs decrease anxiety and depression symptoms by inhibiting serotonin reuptake.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
159 views2 pagesCognitive Meds
Cognitive Meds
Uploaded by
RNStudent11. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists are used to treat Alzheimer's disease by reducing acetylcholine breakdown and limiting glutamate effects, slowing cognitive decline.
2. Conventional and atypical antipsychotics treat psychosis and schizophrenia by blocking dopamine receptors, decreasing positive and negative symptoms.
3. Anxiolytics and SSRIs decrease anxiety and depression symptoms by inhibiting serotonin reuptake.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
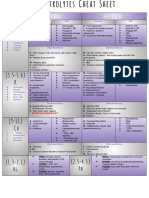
CLASSIFICATION & DRUG
MECHANISM OF ACTION NURSING IMPLICATIONS
EXAMPLES
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors reduce acetylcholine breakdown,
examples:Donepezil (Aricept) whereas NMDA receptor antagonists Explain the importance of taking medication
Galantamine (Razadyne, Reminyl) limit the effects of glutamate. Both as directed; teach about discontinuation & decline
Rivastigmine (Exelon) drugs have a modest effect in slowing in function.
an individual’s rate of cognitive Provide patient education regarding dizziness,
N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) decline in Alzheimer disease. headache, gastrointestinal (GI) upset, & fatigue.
Receptor Antagonists examples:
Promote adequate fluid intake.
Memantine (Namenda) combination May also be used for: Monitor patient’s pulse rate.
NMDA receptor antagonist &
Vascular dementia Use with caution in patients with respiratory
acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Parkinson-related dementia. conditions (e.g., asthma, COPD).
Combination agent (Namzaric) Avoid the use of tricyclics & anticholinergic
Memantine hydrochloride extended-
used only after patients have been drugs because of their antagonistic effects.
release & donepezil hydrochloride
(Namzaric) stabilized on memantine &
donepezil
Monitor for anticholinergic symptoms, such as
dry mouth, orthostatic hypotension, constipation,
urinary retention, sedation, & sexual dysfunction.
Teach patient strategies to address
Conventional Antipsychotics
anticholinergic effects (e.g., rising slowly,
Both phenothiazines & increasing fluid intake, & increasing fiber intake).
Phenothiazines: examples: nonphenothiazines block D2 Monitor for extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS),
Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) dopamine receptors in the brain, such as acute dystonia, akathisia, parkinsonism, &
Fluphenazine increasing synaptic levels of tardive dyskinesia (TD).
Perphenazine dopamine & leading to a decrease in Monitor for signs of hyperprolactemia
Prochlorperazine (Compazine) symptoms of psychosis (including (menstrual irregularities, decreased libido,
Thioridazine delusions & hallucinations). gynecomastia, & osteoporosis). Adjunctive
Trifluoperazine
therapies, counseling, or changing to a different
May also be used for: agent may improve some aspects of sexual
Nonphenothiazines: examples:
Schizophrenia & other psychotic dysfunction.
Haloperidol (Haldol)
disorders Monitor for autonomic instability associated
Loxapine (Loxitane)
Tourette syndrome. with neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
Pimozide (Orap)
Teach patients importance of adhering to
Thiothixene (Navene)
medication regimen & not to abruptly discontinue
medication.
Teach patients importance of wearing
sunscreen.
Atypical Antipsychotics Block D2 & serotonin receptors; treat
examples: both positive & negative symptoms of Monitor for adverse effects, such as alterations
Risperidone (Risperdal) schizophrenia & psychotic disorders, in glucose metabolism, hyperlipidemia,
Olanzapine (Zyprexa) exert mood-stabilizing effect. cardiovascular & cerebrovascular alterations &
Clozapine (Clozaril) blood abnormalities.
Asenapine (Saphris) May also be used for: Teach importance of healthy diet & exercise.
Paliperidone (Invega) Schizophrenia & other psychotic Monitor for EPS & neuroleptic malignant
Quetiapine (Seroquel) disorders syndrome.
Ziprasidone (Geodon) Bipolar disorder.
Although generally well tolerated, patients
should still be monitored for EPS, neuroleptic
malignant syndrome (NMS), & medical effects
Third-generation associated with atypical antipsychotics.
Antipsychotics Partial agonists of D2 receptors, also Akathisia & restlessness may be more
examples: Aripiprazole (Abilify) block serotonin receptors. pronounced with this medication.
Brexpiprazole (Rexulti) Teaching should address healthy diet &
exercise, importance of adherence, & recognizing
& reporting adverse effects.
Monitor for dependency, drowsiness,
Anxiolytics Probably inhibits serotonin reuptake
hypotension, tolerance, dizziness, & GI upset.
Nonbenzodiazepines & activates dopamine receptors in the
These agents may increase confusion.
examples: brain, leading to a decrease in
Abrupt discontinuation may lead to rebound
Buspirone (BuSpar) symptoms of anxiety.
anxiety.
Inhibits reuptake of serotonin in the
central nervous system, leading to a Monitor for suicide risk.
decrease in symptoms of depression Monitor for serotonin syndrome.
& anxiety. Abrupt discontinuation may cause serotonin
Selective Serotonin Reuptake
May also be used for: withdrawal.
Inhibitors (SSRIs) examples:
Depression Provide patient education regarding dizziness,
Sertraline (Zoloft), Fluoxetine
insomnia, somnolence, GI upset, nausea or
(Prozac) Anxiety
diarrhea, & avoiding over-the-counter (OTC)
Obsessive-compulsive disorder
preparations that may increase risk of serotonin
Posttraumatic stress disorder syndrome.
Social anxiety disorder.
You might also like
- Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing Renal - Quiz PerformanceDocument50 pagesElsevier Adaptive Quizzing Renal - Quiz PerformanceSaul Benavidez100% (3)
- Evidence-Based Practice - Nursing Test QuestionsDocument18 pagesEvidence-Based Practice - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent1100% (5)
- Electrolyte Cheat SheetDocument1 pageElectrolyte Cheat SheetRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Informatics - Nursing Test QuestionsDocument23 pagesInformatics - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent175% (4)
- Ethics - Nursing Test QuestionsDocument31 pagesEthics - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent1100% (10)
- Adaptive QuizzingDocument166 pagesAdaptive QuizzingHuawei Li100% (1)
- Module 21 Tissue Integrity: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document50 pagesModule 21 Tissue Integrity: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1100% (1)
- AS1530.7 1998 Part 7 Smoke Control Door and Shutter Assemblies - Ambient and Medium Temperature Leakage Test ProcedureDocument18 pagesAS1530.7 1998 Part 7 Smoke Control Door and Shutter Assemblies - Ambient and Medium Temperature Leakage Test Procedureluke hainesNo ratings yet
- Ams 11Document702 pagesAms 11CrazyNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorder QuestionsDocument4 pagesMood Disorder QuestionsMackenzie Lehman0% (1)
- M31 Stress & CopingDocument68 pagesM31 Stress & CopingRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Chapter 28: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases Harding: Lewis's Medical-Surgical Nursing, 11th EditionDocument15 pagesChapter 28: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases Harding: Lewis's Medical-Surgical Nursing, 11th EditionKrishna RamaNo ratings yet
- Infection - Nursing Test QuestionsDocument58 pagesInfection - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent1100% (3)
- Nursing Pharmacology Inflammation Study GuideDocument11 pagesNursing Pharmacology Inflammation Study GuideChelsea Smith100% (1)
- Exam 3 Review Med SurgDocument18 pagesExam 3 Review Med SurgCarol ReidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 049Document20 pagesChapter 049dtheart2821100% (7)
- Flash Cards Vocab For Exam 1. Jarvis CH 1-3, 8, 9, 12, 13http - P.quizlet - Com - Settitle Health Assessment Vocab For Exam 1Document22 pagesFlash Cards Vocab For Exam 1. Jarvis CH 1-3, 8, 9, 12, 13http - P.quizlet - Com - Settitle Health Assessment Vocab For Exam 1tipredd100% (1)
- Test Bank For Introductory Mental Health Nursing 2nd Edition, WombleDocument26 pagesTest Bank For Introductory Mental Health Nursing 2nd Edition, WombleILL10150% (4)
- Accountability - Nursing Test QuestionsDocument25 pagesAccountability - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Advocacy - Nursing Test QuestionsDocument19 pagesAdvocacy - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent1100% (3)
- Module 36 Clinical Decision Making: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document43 pagesModule 36 Clinical Decision Making: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1No ratings yet
- M27 Grief and LossDocument33 pagesM27 Grief and LossRNStudent1100% (1)
- M31 Stress & CopingDocument68 pagesM31 Stress & CopingRNStudent1No ratings yet
- BBS Book (PT 14) NeglyDocument7 pagesBBS Book (PT 14) Neglyapi-3871208No ratings yet
- 120lab Report 3Document4 pages120lab Report 3Valerie Mae Librero Areño100% (2)
- Medication To Treat WithdrawalDocument2 pagesMedication To Treat WithdrawalRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Childhood Infectious DiseasesDocument17 pagesChildhood Infectious DiseasesRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Drug Overdose: Withdrawal ChartDocument4 pagesDrug Overdose: Withdrawal ChartRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Contraception Chart SexualityDocument8 pagesContraception Chart SexualityRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Drug Cards 1Document20 pagesDrug Cards 1Keying Chen100% (1)
- Chapter 29: Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases Test BankDocument15 pagesChapter 29: Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases Test BankBriseidaSolisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 64 - Administration of Injectable MedicationsDocument11 pagesChapter 64 - Administration of Injectable Medicationskristie donaldNo ratings yet
- Module 35 Caring Interventions: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document13 pagesModule 35 Caring Interventions: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1No ratings yet
- Module 41 Teaching and Learning: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document42 pagesModule 41 Teaching and Learning: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1No ratings yet
- Pre-Test Psychiatric NursingDocument17 pagesPre-Test Psychiatric NursingDefensor Pison Gringgo100% (1)
- Varcolis FUNDAMENTAL OF PSY - NURSING - NCLEX RNDocument20 pagesVarcolis FUNDAMENTAL OF PSY - NURSING - NCLEX RNisapatrick8126100% (1)
- Module 38 Communication: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document56 pagesModule 38 Communication: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1No ratings yet
- Practice Questions 1-9 (FINAL)Document38 pagesPractice Questions 1-9 (FINAL)Riz Austria RN0% (1)
- Chapter 47 Diabetes Mellitus PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 47 Diabetes Mellitus PDFRLLT100% (1)
- Quiz PsychopharmacologyDocument1 pageQuiz PsychopharmacologySolsona Natl HS MaanantengNo ratings yet
- CH 32Document8 pagesCH 32Elizabeth PetersenNo ratings yet
- M28 Mood and AffectDocument34 pagesM28 Mood and AffectRNStudent1No ratings yet
- CH 51 Assessment and Management of Patients With DiabetesDocument17 pagesCH 51 Assessment and Management of Patients With Diabetesfiya33No ratings yet
- Module 39 Managing Care: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document32 pagesModule 39 Managing Care: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1No ratings yet
- Schizophrenia/Mood Disorders/Grief & Loss: MENTAL HEALTH NURSINGDocument19 pagesSchizophrenia/Mood Disorders/Grief & Loss: MENTAL HEALTH NURSINGJessica100% (1)
- Nclex Question and Rationale Week 4Document10 pagesNclex Question and Rationale Week 4Winnie Okoth100% (1)
- Pharm Exam ReviewDocument13 pagesPharm Exam ReviewAshleyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Practice TestDocument7 pagesCardiac Practice TestroseNo ratings yet
- Psych Practice 1 QuestionDocument8 pagesPsych Practice 1 QuestionAngela Eun AnNo ratings yet
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDocument33 pagesPharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarnamitaNo ratings yet
- Pedia Note1Document38 pagesPedia Note1FreeNursingNotes100% (1)
- How To Study Pharmacology Checklist Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesHow To Study Pharmacology Checklist Cheat SheetJOSHUA DICHOSONo ratings yet
- Answers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: The Client With Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument12 pagesAnswers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: The Client With Peripheral Vascular DiseaseNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- DRUGS Flash CardsDocument9 pagesDRUGS Flash Cardsdrp2011No ratings yet
- Drug CalculationsDocument3 pagesDrug Calculationsapi-3739910100% (4)
- Chapter 12: Basic Principles of Neuropharmacology Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesChapter 12: Basic Principles of Neuropharmacology Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceNurse UtopiaNo ratings yet
- Medsurg 3 Exam 1Document55 pagesMedsurg 3 Exam 1Melissa Blanco100% (1)
- Pharmacology Practice Test For NclexDocument10 pagesPharmacology Practice Test For NclexKira99% (96)
- TestBank Lewis Medical Surgical Nursing 11th 2020.pdf-282-305Document24 pagesTestBank Lewis Medical Surgical Nursing 11th 2020.pdf-282-305هدوء النسمةNo ratings yet
- Anti Psychotic DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti Psychotic DrugsJohn Corpuz100% (1)
- Chapter 11: Parenteral Administration: Intradermal, Subcutaneous, and Intramuscular Routes Test BankDocument7 pagesChapter 11: Parenteral Administration: Intradermal, Subcutaneous, and Intramuscular Routes Test BankLuna TunaNo ratings yet
- Question PsychDocument23 pagesQuestion PsychChucky VergaraNo ratings yet
- MedSurg Ch30-31Document8 pagesMedSurg Ch30-31Vanessa Da Cruz100% (1)
- Navigating Long-Term Care - A Practical Approach for NursesFrom EverandNavigating Long-Term Care - A Practical Approach for NursesNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic or Neuroleptic DrugsDocument12 pagesAntipsychotic or Neuroleptic Drugscamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY HndoutDocument12 pagesPSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY HndoutMhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapeutic AgentsDocument2 pagesPsychotherapeutic AgentsjustinahorroNo ratings yet
- NPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesDocument83 pagesNPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesValeria AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Subiaga Antiparkinsonismmuscle-RelaxantsDocument15 pagesSubiaga Antiparkinsonismmuscle-RelaxantsNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Meds For Personality DisordersDocument2 pagesMeds For Personality DisordersRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Medication To Treat WithdrawalDocument2 pagesMedication To Treat WithdrawalRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Drug Overdose: Withdrawal ChartDocument4 pagesDrug Overdose: Withdrawal ChartRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Contraception Chart SexualityDocument8 pagesContraception Chart SexualityRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Electrolytes NotesDocument6 pagesElectrolytes NotesRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Fluids NCLEX Quick RefrenceDocument1 pageFluids NCLEX Quick RefrenceRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Childhood Infectious DiseasesDocument17 pagesChildhood Infectious DiseasesRNStudent1No ratings yet
- 1.3 Fluid ImbalancesDocument2 pages1.3 Fluid ImbalancesRNStudent1No ratings yet
- 1.3 Fluid ImbalancesDocument2 pages1.3 Fluid ImbalancesRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Module 39 Managing Care: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document32 pagesModule 39 Managing Care: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1No ratings yet
- Module 38 Communication: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document56 pagesModule 38 Communication: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1No ratings yet
- Module 41 Teaching and Learning: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document42 pagesModule 41 Teaching and Learning: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1No ratings yet
- Module 40 Professional Behaviors: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document29 pagesModule 40 Professional Behaviors: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1100% (1)
- Module 35 Caring Interventions: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document13 pagesModule 35 Caring Interventions: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1No ratings yet
- M28 Mood and AffectDocument34 pagesM28 Mood and AffectRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson) Module 30 SpiritualityDocument29 pagesNursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson) Module 30 SpiritualityRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Case 621F, 721F Tier 4 Wheel Loader AxelDocument15 pagesCase 621F, 721F Tier 4 Wheel Loader AxelJose CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Neisseria Gonorrhoeae and Neisseria MeningitidesDocument3 pagesNeisseria Gonorrhoeae and Neisseria MeningitidesAmador Gielas0% (1)
- Macro Chapter 7Document12 pagesMacro Chapter 7Mary Jane PelaezNo ratings yet
- An Extended Force Density MethodDocument14 pagesAn Extended Force Density MethodSamuellgerard SamuellgerardNo ratings yet
- The Harrod-Domar Growth ModelDocument6 pagesThe Harrod-Domar Growth ModelSimeonNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering Professor Step III: Ucsd Academic Biography/Bibliography FormDocument30 pagesStructural Engineering Professor Step III: Ucsd Academic Biography/Bibliography FormCesar Paul Purihuaman MoraNo ratings yet
- Chapter8-Campuran Pada Tingkat Molekuler - Part 1Document58 pagesChapter8-Campuran Pada Tingkat Molekuler - Part 1Uswatun KhasanahNo ratings yet
- TinyMobileRobots TinySurveyor FlyerDocument4 pagesTinyMobileRobots TinySurveyor FlyerfelipeNo ratings yet
- Kerr EffectDocument5 pagesKerr EffectJose GalvanNo ratings yet
- Sri Lank An Airline IndustryDocument29 pagesSri Lank An Airline IndustryTuan RifkhanNo ratings yet
- (2001) (Sun) (Two-Group Interfacial Area Transport Equation For A Confined Test Section)Document367 pages(2001) (Sun) (Two-Group Interfacial Area Transport Equation For A Confined Test Section)Erol BicerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document24 pagesLecture 4Geeta AroraNo ratings yet
- هاشم عدي حاتم سيارات ثاني التجربة الثانيهDocument6 pagesهاشم عدي حاتم سيارات ثاني التجربة الثانيههاشم عديNo ratings yet
- 5 25 17 Migraines PowerPointDocument40 pages5 25 17 Migraines PowerPointSaifi AlamNo ratings yet
- COMPRE - MODULE 4 (Pharmacology and Toxicology) : Attempt ReviewDocument40 pagesCOMPRE - MODULE 4 (Pharmacology and Toxicology) : Attempt ReviewLance RafaelNo ratings yet
- Brochure Keor S GBDocument8 pagesBrochure Keor S GBFernando CespedesNo ratings yet
- Ebffiledoc - 204download PDF Logic and Algebraic Structures in Quantum Computing 1St Edition Jennifer Chubb Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesEbffiledoc - 204download PDF Logic and Algebraic Structures in Quantum Computing 1St Edition Jennifer Chubb Ebook Full Chapterkevin.carter759100% (3)
- Background of Philippine Art and Literature in Romantic RealismDocument2 pagesBackground of Philippine Art and Literature in Romantic RealismRaldz CoyocaNo ratings yet
- Free Download All Aeronautical Engg Books: AERO 3-1 BOOKSDocument11 pagesFree Download All Aeronautical Engg Books: AERO 3-1 BOOKSMacen SnoodleNo ratings yet
- A. Title of Experiment B. Date and Time of Experiment: Wednesday, 10Document15 pagesA. Title of Experiment B. Date and Time of Experiment: Wednesday, 10LichaNo ratings yet
- English Final Test Grade XiiDocument9 pagesEnglish Final Test Grade XiiLiza RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- EuropeDocument5 pagesEuropeAmicus CuriaeNo ratings yet
- Mec R2018Document227 pagesMec R2018Kishore Kumar RNo ratings yet
- Metzeler TDB 2019 LRDocument246 pagesMetzeler TDB 2019 LRGabriel BruschiNo ratings yet
- Yuxi CatalogueDocument16 pagesYuxi CatalogueSoltani AliNo ratings yet
- Mouser TestsectionDocument33 pagesMouser TestsectionalltheloveintheworldNo ratings yet
- 400PNR CDocument3 pages400PNR CmdisicNo ratings yet