Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 07 & 11 Study Guide
Unit 07 & 11 Study Guide
Uploaded by
theda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesThis study guide covers key terms and concepts from Units 7 and 11 of an AP Psychology course. Unit 7 focuses on memory processes including sensory memory, short-term memory, long-term memory, and factors that influence memory like encoding, storage, and retrieval. Unit 11 discusses intelligence, including the nature of intelligence, theories of intelligence, and types of intelligence tests. Key terms defined include iconic memory, echoic memory, flashbulb memory, and more.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis study guide covers key terms and concepts from Units 7 and 11 of an AP Psychology course. Unit 7 focuses on memory processes including sensory memory, short-term memory, long-term memory, and factors that influence memory like encoding, storage, and retrieval. Unit 11 discusses intelligence, including the nature of intelligence, theories of intelligence, and types of intelligence tests. Key terms defined include iconic memory, echoic memory, flashbulb memory, and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesUnit 07 & 11 Study Guide
Unit 07 & 11 Study Guide
Uploaded by
thedaThis study guide covers key terms and concepts from Units 7 and 11 of an AP Psychology course. Unit 7 focuses on memory processes including sensory memory, short-term memory, long-term memory, and factors that influence memory like encoding, storage, and retrieval. Unit 11 discusses intelligence, including the nature of intelligence, theories of intelligence, and types of intelligence tests. Key terms defined include iconic memory, echoic memory, flashbulb memory, and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
AP Psychology
Study Guide: Unit 07 & 11
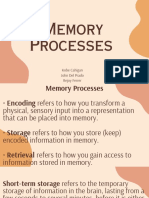
Unit 07 Terms/Concepts recall: the act of retrieving information or events
from the past when lacking a specific cue to help in
iconic memory: short-term visual memories retrieving the information
echoic memory: stored for longer than iconic, recognition: a form of remembering characterized
short-term auditory memories by a feeling of familiarity when something
flashbulb memory: vivid, enduring memories previously experienced is again encountered
relevant to significant personal events relearning: a way of measuring retention by
storage: maintaining information over time measuring how much faster one relearns material
retrieval: the ability to access information when that has been previously learned and then forgotten
you need it priming: a technique in which the introduction of
sensory memory: a short-term memory type that one stimulus influences how people respond to a
allows you to process and recall the sensations you subsequent stimulus
take in proactive interference: this occurs when old
short-term memory: the information you are learning interferes with new learning
currently aware of or thinking about retroactive interference: this occurs when new
long-term memory: the storage of information learning interferes with old learning
over an extended period repression: the exclusion of distressing memories,
working memory: the small amount of information thoughts, or feelings from the conscious mind
that can be held in mind and used in the execution misinformation effect
of cognitive tasks cognition: the mental processes involved in gaining
visual encoding: the process of encoding images knowledge and comprehension
and visual sensory information algorithm: a defined set of step-by-step procedures
acoustic encoding: the use of auditory stimuli or that provides the correct answer to a particular
hearing to implant memories problem
semantic encoding: the use of sensory input that representativeness heuristic: a cognitive bias in
has a specific meaning or can be applied to a which an individual categorizes a situation based on
context a pattern of previous experiences or beliefs about
mnemonics: any device or technique used to assist the scenario
memory, usually by forging a link or association availability heuristic: a cognitive bias in which an
between the new information to be remembered and individual categorizes a situation based on how
information previously encoded easily an example, instance, or case comes to mind
chunking: the process of taking individual pieces insight: the sudden discovery of the correct solution
of information and grouping them into larger units following incorrect attempts based on trial and error
amnesia: a form of memory loss confirmation bias: the tendency to process
implicit memory: a form of long-term memory that information by looking for, or interpreting,
doesn't require conscious retrieval information that is consistent with one's existing
explicit memory: a form of long-term memory that beliefs
involves the conscious recall of previously learned
information
fixation: the id's persistent focus of its mental age: a measure that expresses an
pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier stage of individual's mental level in terms of the number of
psychosexual development years it takes an average child to reach the same
level
mental set: a frame of mind involving a model that
Stanford-Binet: a cognitive ability and intelligence
represents a problem, a problem context, or a test that is used to diagnose developmental or
procedure for problem solving intellectual deficiencies in young children
intuition: immediate insight or perception intelligence quotient: a standard measure of an
language semantics: the meanings of words, signs, individual's intelligence level based on
symbols, and the phrases that represent them psychological tests
language syntax: the study of sentences and achievement test: a standardized test that is
designed to measure an individual's level of
phrases, or how people put words into the right knowledge in a particular area
order so that they can communicate meaningfully aptitude test: an standardized test that is designed
to measure a person's ability to acquire some
Unit 11 Terms/Concepts specific set of skills
standardization: consistency and objectivity of
intelligence: the ability to think, to learn from how tests are administered and scored
experience, to solve problems, and to adapt to new normal curve: a frequency curve where most
situations occurrences take place in the middle of the
factor analysis: a statistical procedure for distribution and taper off on either side
describing the interrelationships among a number of content validity: the extent to which a test
observed variables measures a representative sample of the subject
Savant syndrome: a rare condition where a person matter or behavior under investigation
of less than normal intelligence or severely limited predictive validity: the extent to which a score on a
emotional range has prodigious intellectual gifts in scale or test predicts scores on some criterion
a specific area measure
emotional intelligence: the ability to perceive,
control, and evaluate emotions
You might also like
- Cognitive Assessment For Clinicians 3rd EditionDocument298 pagesCognitive Assessment For Clinicians 3rd EditionInes Strenja Linić100% (4)
- 7 AmemoryDocument2 pages7 Amemoryapi-296059071No ratings yet
- Psychology Chapter 7 Cognition Language and Intelligence Flashcards - QuizletDocument6 pagesPsychology Chapter 7 Cognition Language and Intelligence Flashcards - Quizletsmk1983No ratings yet
- Lecture 8 MEMORY DefinitionsDocument6 pagesLecture 8 MEMORY DefinitionsMarcelineNo ratings yet
- Unfolding The Mental SelfDocument24 pagesUnfolding The Mental Selfmichael jan de celisNo ratings yet
- UTS ReviewerDocument8 pagesUTS Reviewerjmamaglalang.studentNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Exam 2 Study GuideDocument5 pagesMedical Terminology Exam 2 Study GuideDanielNo ratings yet
- Uts MidtermsDocument6 pagesUts Midtermswellalltoo13No ratings yet
- Unconscious and Past: Influences Behavior and Mental Process - Personality Is Influenced byDocument36 pagesUnconscious and Past: Influences Behavior and Mental Process - Personality Is Influenced byDeepa Merin TitusNo ratings yet
- EDUC 210 - Module 7 NotesDocument8 pagesEDUC 210 - Module 7 Noteserikalombardo8No ratings yet
- Complex Cognitive Processes What Is Cognition ?: Two General Modes of CognitionDocument9 pagesComplex Cognitive Processes What Is Cognition ?: Two General Modes of CognitionAhmad ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit II Lesson 2Document54 pagesUnit II Lesson 2Xandra Loren OrencioNo ratings yet
- Memory, Language & Creative Thinking: Lecture No. 5Document16 pagesMemory, Language & Creative Thinking: Lecture No. 5Raja Awais LiaqautNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Cognitive DevelopmentDocument24 pagesWeek 3 - Cognitive DevelopmentFerroMagzNo ratings yet
- Information Processing TheoryDocument13 pagesInformation Processing TheoryErikaNo ratings yet
- Psychological Foundation of CurriculumDocument34 pagesPsychological Foundation of CurriculumAlgen Jewel Balbin100% (1)
- 2023 Information Processing Model GLOSSARY Key VocabularyDocument2 pages2023 Information Processing Model GLOSSARY Key VocabularymandyngoaNo ratings yet
- Information ProcessingDocument4 pagesInformation ProcessingJeanelle Marie Ramos50% (2)
- Psychology Unitiii Thinking 200426103049Document37 pagesPsychology Unitiii Thinking 200426103049Mythili SaravanakumarNo ratings yet
- PsychologyDocument25 pagesPsychologymmohsinkundiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Memory ProcessesDocument25 pagesChapter 6 Memory ProcessesSeth Abes FernandezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - 7 Cognitive and Behavioral Views of LearningDocument50 pagesLecture 6 - 7 Cognitive and Behavioral Views of LearningKyla BulusNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology 12 MemoryDocument4 pagesAP Psychology 12 MemoryakaqwertyNo ratings yet
- Psyc Memory NotesDocument4 pagesPsyc Memory NotesAvesta FazelNo ratings yet
- This Cognitive Activity Is Directed Toward Some Creative WorkDocument11 pagesThis Cognitive Activity Is Directed Toward Some Creative WorkFRG13MAGNAYEELIJAHNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 MemoryDocument6 pagesLesson 7 MemoryTin BautistaNo ratings yet
- General Psychology ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Psychology ReviewerSherry Lyn Fernandez Lamsen-OrjaloNo ratings yet
- Short Notes For PsychologyDocument6 pagesShort Notes For PsychologyAnanya KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Inclass Notes (Unit 7 + 8)Document3 pagesInclass Notes (Unit 7 + 8)Charn BrarNo ratings yet
- Terminology Related To ResearchDocument3 pagesTerminology Related To ResearchKaruna JohnsonNo ratings yet
- COGNITIVE LEARNING THEORIES SummaryDocument7 pagesCOGNITIVE LEARNING THEORIES SummaryLoreto Dela Torre Marzan IIINo ratings yet
- Woolfolk7 AnnotationsDocument2 pagesWoolfolk7 AnnotationsCamel MacchiatoNo ratings yet
- Myers AP Psychology Chapter 7 PDFDocument2 pagesMyers AP Psychology Chapter 7 PDFChristopher BradleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Key Terms Consumer BehaviorDocument6 pagesChapter 4 Key Terms Consumer Behaviorquaintrelle joyNo ratings yet
- Awad KM Ch02Document16 pagesAwad KM Ch02Faou MadNo ratings yet
- Kepy 1 GLDocument11 pagesKepy 1 GLReusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document35 pagesChapter 7z1291916109No ratings yet
- Introduction To PsychologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Psychologynimra rafiNo ratings yet
- 001.reasoning TypesDocument15 pages001.reasoning TypesGuruNo ratings yet
- Psychology ReviewDocument7 pagesPsychology ReviewGiangNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Cognitive Psychology (Until 5.6)Document3 pagesUnit 5-Cognitive Psychology (Until 5.6)Muhammet SuleimanNo ratings yet
- Psychology Chapter 10 and 11Document3 pagesPsychology Chapter 10 and 11Khadija SankohNo ratings yet
- Review Mid-Term Spring24Document26 pagesReview Mid-Term Spring24Nadooosh 2000No ratings yet
- Declarative and Procedural ModelDocument1 pageDeclarative and Procedural ModelRonna Jean AndeNo ratings yet
- Information ProcessingDocument6 pagesInformation ProcessingCarl LibatiqueNo ratings yet
- Landasan Ilmu PendidikanDocument6 pagesLandasan Ilmu PendidikanRezqa GusrizalNo ratings yet
- Psychology #2 Test NotesDocument5 pagesPsychology #2 Test NotesPaolaNo ratings yet
- Education Department: Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachingDocument4 pagesEducation Department: Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachingChristopher Ian BuruangaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 PartTwoDocument13 pagesLecture 1 PartTwoXavi HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Psychology Chapter 7, 8, & 9Document4 pagesCognitive Psychology Chapter 7, 8, & 9DanielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 & Chapter 8 Test PreperationDocument5 pagesChapter 7 & Chapter 8 Test PreperationIWantToBelieve8728No ratings yet
- Higher Cognitive Functions 2Document60 pagesHigher Cognitive Functions 2Raghuram MiryalaNo ratings yet
- Studywise Brain Hacking - 2020Document37 pagesStudywise Brain Hacking - 2020Cristian LermaNo ratings yet
- Psych 101 Cornell Notes Mod 7Document6 pagesPsych 101 Cornell Notes Mod 7christianallenmlagosNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Psychology LEC 7 and 8Document10 pagesCognitive Psychology LEC 7 and 8chelanslaterNo ratings yet
- AQA Psychology MRN GlossaryDocument12 pagesAQA Psychology MRN GlossaryKaren FernandesNo ratings yet
- Memory-Learning #4Document13 pagesMemory-Learning #4usama iqbalNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument29 pagesMemoryguptaapeksha167No ratings yet
- CognitionDocument4 pagesCognition何景行No ratings yet
- Mnemonics: Memorization Techniques for Studying and Everyday UseFrom EverandMnemonics: Memorization Techniques for Studying and Everyday UseRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- Study Guide Unit #06Document2 pagesStudy Guide Unit #06thedaNo ratings yet
- Violence Against Prisoners of War in The First World War Britain, France, and Germany, 1914-1920Document4 pagesViolence Against Prisoners of War in The First World War Britain, France, and Germany, 1914-1920thedaNo ratings yet
- Final Paper WWI Research PaperDocument6 pagesFinal Paper WWI Research PaperthedaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide WHAPDocument2 pagesStudy Guide WHAPthedaNo ratings yet
- Short Answers ExampleDocument2 pagesShort Answers ExamplethedaNo ratings yet
- Workbook Answer Key Attitude 5 PDFDocument4 pagesWorkbook Answer Key Attitude 5 PDFJesus Garza50% (2)
- What Is The Nature of Memory?Document8 pagesWhat Is The Nature of Memory?Prithvi RajNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument4 pagesMental Status ExaminationSusan MaglaquiNo ratings yet
- IQ (The Intelligence Quotient) : Louis D Matzel Bruno SauceDocument10 pagesIQ (The Intelligence Quotient) : Louis D Matzel Bruno SauceHouho DzNo ratings yet
- AI Term-II Periodic TestDocument3 pagesAI Term-II Periodic TestSmriti RoutNo ratings yet
- Pseudo Label FinalDocument6 pagesPseudo Label FinaljustinthecoachNo ratings yet
- 2012 - Schacter - The Future of Memory Remembering, Imagining, and The Brain - Schacter Et Al PDFDocument18 pages2012 - Schacter - The Future of Memory Remembering, Imagining, and The Brain - Schacter Et Al PDFAna Maria RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI - Introduction To Deep LearningDocument38 pagesChapter VI - Introduction To Deep LearningHalbeega WaayahaNo ratings yet
- Memory ChunkingDocument13 pagesMemory ChunkingTanya Kim MehraNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Learning TheoryDocument5 pagesCognitive Learning Theoryapi-285312776No ratings yet
- WISCDocument13 pagesWISCMahrukh100% (1)
- Unsupervised LearningDocument29 pagesUnsupervised LearningUddalak BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Norms MisicDocument4 pagesNorms Misicvk100% (3)
- Elements of Episodic MemoryDocument350 pagesElements of Episodic MemoryRoberson MachadoNo ratings yet
- Ask and Its GivenDocument2 pagesAsk and Its GivenCristina ArizonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Chapter 4 Artificial Neural Networks Introduction To Data Mining, 2 EditionDocument20 pagesLecture Notes For Chapter 4 Artificial Neural Networks Introduction To Data Mining, 2 EditionUsman AliNo ratings yet
- 07 StrategiesDocument13 pages07 StrategiesJonathanNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Networks: CMSC 35246: Deep LearningDocument166 pagesConvolutional Neural Networks: CMSC 35246: Deep LearningDiego AntonioNo ratings yet
- Confusion Assessment Method - CAMDocument3 pagesConfusion Assessment Method - CAMAbdullah RababaahNo ratings yet
- Competitive Learning Neural Networks - Unit 8Document10 pagesCompetitive Learning Neural Networks - Unit 8Prasanth PreshuNo ratings yet
- Capsule Neural NetworkDocument42 pagesCapsule Neural NetworkMag Creation100% (1)
- Learning To LearnDocument6 pagesLearning To LearncsudipNo ratings yet
- Awareness: Attention, in Psychology, The Concentration ofDocument2 pagesAwareness: Attention, in Psychology, The Concentration ofalexNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Long Short Term Memory LSTMDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Long Short Term Memory LSTMJuan Gonzalez-EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Memory and Knowledge: Hoyer - Macinnis - PietersDocument14 pagesMemory and Knowledge: Hoyer - Macinnis - PietersAngelo P. NuevaNo ratings yet
- U1L8 Student GuideDocument4 pagesU1L8 Student Guideria wu50% (2)
- Anil Seth Teorias de La ConcienciaDocument38 pagesAnil Seth Teorias de La ConcienciaJose Andres AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 989 3611 3 PBDocument7 pages989 3611 3 PBAzhira telkomselNo ratings yet