Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 3 Section 4
Unit 3 Section 4
Uploaded by
api-5397001390 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views2 pagesThe Supreme Court can decide if laws passed by Congress or the president are constitutional through the process of judicial review established in Marbury v. Madison in 1803. Some key Supreme Court cases that shaped federalism include Fletcher v. Peck in 1810, Gibbons v. Ogden in 1824, and McCulloch v. Maryland in 1819. Later important rulings included Gitlow v. New York in 1925, Baker v. Carr in 1963, and Wesberry v. Sanders in 1964 related to civil rights and equal representation. The death penalty was stopped by Furman v. Georgia in 1972 but allowed to continue with guidelines in Gregg v. Georgia in 1976.
Original Description:
Original Title
unit 3 section 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Supreme Court can decide if laws passed by Congress or the president are constitutional through the process of judicial review established in Marbury v. Madison in 1803. Some key Supreme Court cases that shaped federalism include Fletcher v. Peck in 1810, Gibbons v. Ogden in 1824, and McCulloch v. Maryland in 1819. Later important rulings included Gitlow v. New York in 1925, Baker v. Carr in 1963, and Wesberry v. Sanders in 1964 related to civil rights and equal representation. The death penalty was stopped by Furman v. Georgia in 1972 but allowed to continue with guidelines in Gregg v. Georgia in 1976.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views2 pagesUnit 3 Section 4
Unit 3 Section 4
Uploaded by
api-539700139The Supreme Court can decide if laws passed by Congress or the president are constitutional through the process of judicial review established in Marbury v. Madison in 1803. Some key Supreme Court cases that shaped federalism include Fletcher v. Peck in 1810, Gibbons v. Ogden in 1824, and McCulloch v. Maryland in 1819. Later important rulings included Gitlow v. New York in 1925, Baker v. Carr in 1963, and Wesberry v. Sanders in 1964 related to civil rights and equal representation. The death penalty was stopped by Furman v. Georgia in 1972 but allowed to continue with guidelines in Gregg v. Georgia in 1976.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
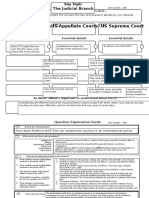
CORNELL NOTES Name: Mercedes Cross
Class: Block 1 Topic: Unit 3 Section 4
SHEET
Questions / Main Ideas Notes / Details / Definitions / etc.
The Supreme Court and (1803) Marbury v. Madison
Federalism • Justice John Marshall (1801-1835 Sup. Court)
Judicial Review:
The Supreme Court can decide if a law/act of Congress and/or the president is
Constitutional
When does the Supreme (1810) Fletcher v. Peck
court step in? • Supreme Court rules state law unconstitutional
(1824) Gibbons v. Ogden
• Steamboats
• Only Federal Govt. regulates interstate (between states) commerce (business)
Other cases (1819) McCulloch v. Maryland
• States can’t tax the fed. Govt.
• Fed. Govt. can create a national bank (Elastic Clause)
• Reinforces Supremacy Clause
(1925) Gitlow v. New York
• 1st amendment applies to the states
(1963) Baker v. Carr
• All people of a state should be represented equally in state districts. One
person one vote
(1964) Wesberry v. Sanders
• Congressional Voting districts should have similar populations
(1972) Furman v. Georgia
• Stop the death penalty
• Racist, arbitrary
(1976) Gregg v. Georgia
• Death Penalty can continue if you follow certain guidelines.
Themes I see in the Federalism, Rule of Law, Justice, Truth
information
Other Questions I may What are the certain guidelines to follow if the death penalty were to continue?
have about the
information (Required)
Please list three things 1.) The difference between Furman v. Georgia & Gregg v. Georgia cases
you learned today 2.) Where the supreme court comes into cases (Judicial Review)
(Required) 3.) What the Baker v. Carr case was
Please explain how one The results of each of these cases have had a direct effect on the state of the
thing you learned today country I live in today. If the results were different, I think things might be much
relates to you. BE more chaotic or at least different.
SPECIFIC!!!!
You might also like
- The State vs. Dosso and Other (PLD 1958 S.C. 533)Document4 pagesThe State vs. Dosso and Other (PLD 1958 S.C. 533)Vamel Siva100% (2)
- Marbury v. Madison: "But The President Said I Could Be A Judge!"Document3 pagesMarbury v. Madison: "But The President Said I Could Be A Judge!"Subh AshishNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Section 3Document2 pagesUnit 5 Section 3api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Section 4Document1 pageUnit 2 Section 4api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Section 2Document2 pagesUnit 3 Section 2api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Section 1Document2 pagesUnit 5 Section 1api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Section 1Document1 pageUnit 3 Section 1api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Section 3Document2 pagesUnit 2 Section 3api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Section 6Document1 pageUnit 2 Section 6api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Section 4 NotesDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Section 4 Notesapi-630591023No ratings yet
- Con Law Mini OutlinesDocument20 pagesCon Law Mini OutlinesBon Qui Qui100% (1)
- Unit 6 Section 2Document1 pageUnit 6 Section 2api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Section 5Document2 pagesUnit 2 Section 5api-539700139No ratings yet
- CH 1 GOBC 2019Document6 pagesCH 1 GOBC 2019armaanNo ratings yet
- SochaDocument3 pagesSochaapi-525021077No ratings yet
- Golden Rule of InterpretationDocument12 pagesGolden Rule of InterpretationSNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notes Sheet: Questions / Main Ideas Notes / Details / Definitions / EtcDocument2 pagesCornell Notes Sheet: Questions / Main Ideas Notes / Details / Definitions / Etcapi-524761808No ratings yet
- LTD Outline. Titling (New)Document9 pagesLTD Outline. Titling (New)arellano lawschoolNo ratings yet
- One Person, One Vote Viewing QuestionsDocument2 pagesOne Person, One Vote Viewing QuestionsJacob OrrNo ratings yet
- Keywordsch 11Document3 pagesKeywordsch 11api-366289413No ratings yet
- International Law OutlineDocument37 pagesInternational Law OutlineLinda ShenNo ratings yet
- Rights Pol-Sci Class 11Document2 pagesRights Pol-Sci Class 11harshita dograNo ratings yet
- Pil AssignmentDocument4 pagesPil AssignmentFatima SladjannaNo ratings yet
- PIL-Syllabus-Arellano-Law by Atty. Evecar Cruz-FerrerDocument6 pagesPIL-Syllabus-Arellano-Law by Atty. Evecar Cruz-FerrerBethNo ratings yet
- Constitution Test 7 PDFDocument4 pagesConstitution Test 7 PDFAkanksha DubeyNo ratings yet
- Americas HistoryDocument29 pagesAmericas Historyapi-285307384No ratings yet
- AghhhDocument1 pageAghhhShin Thant MaungNo ratings yet
- Common Law Part 2Document114 pagesCommon Law Part 2Marechal CNo ratings yet
- 2023 Consti II Course OutlineSyllabus With CasesDocument4 pages2023 Consti II Course OutlineSyllabus With CasesVince Quicho MatutinaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Ap 10 26 22Document11 pages2022 Ap 10 26 22api-543292029No ratings yet
- Dreelin Sim StrategiesDocument8 pagesDreelin Sim Strategiesapi-329181923No ratings yet
- Advocacy - 32062699Document5 pagesAdvocacy - 32062699Ajit ShahiNo ratings yet
- Read Article 3 Section 1 of The US Constitution. Identify The Powers of The Judicial BranchDocument33 pagesRead Article 3 Section 1 of The US Constitution. Identify The Powers of The Judicial BranchPepedNo ratings yet
- Sen. Courtney's SJR26 TestimonyDocument2 pagesSen. Courtney's SJR26 TestimonyStatesman JournalNo ratings yet
- AP Gov Unit 7 Review GuideDocument4 pagesAP Gov Unit 7 Review GuidejimNo ratings yet
- Civil Law Review I - Course GuideDocument18 pagesCivil Law Review I - Course GuideGLENDEL GUEVARRANo ratings yet
- PP Japan FSCDocument2 pagesPP Japan FSCJavier AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Supreme CourtDocument12 pagesSupreme Courtapi-239586706No ratings yet
- Chapter-22 Reading With Understanding: WorksheetDocument2 pagesChapter-22 Reading With Understanding: WorksheetAnjali SHNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Law Notes Fall 2021Document34 pagesIntroduction To Law Notes Fall 2021Katie CrawfordNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Social Studies CRCT Study Guide IIDocument10 pages4th Grade Social Studies CRCT Study Guide IIapi-248791808No ratings yet
- A Time to Speak: Selected Writings and ArgumentsFrom EverandA Time to Speak: Selected Writings and ArgumentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Period 4 1800 - 1848 Review Sheet 1Document7 pagesPeriod 4 1800 - 1848 Review Sheet 1api-4623395070% (1)
- Gibbons V Ogden PDFDocument42 pagesGibbons V Ogden PDFDonald KingNo ratings yet
- Bayardv Singleton NCDocument14 pagesBayardv Singleton NCCitizen WellsNo ratings yet
- Marshall Court APUSH AssignmentDocument5 pagesMarshall Court APUSH AssignmentBridgettttNo ratings yet
- Greater Georgia Amicus BriefDocument30 pagesGreater Georgia Amicus BriefFox NewsNo ratings yet
- Feb 25, Class 4 PDFDocument26 pagesFeb 25, Class 4 PDFELSA MARTIN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Awoke United States Inc Is A PEDO CORPORATION To Understand Their Crimes Against Humanity Read May 2022 Study Ref Residential Schools and Understand Why They Harm Our Children - Next GenerationDocument283 pagesAwoke United States Inc Is A PEDO CORPORATION To Understand Their Crimes Against Humanity Read May 2022 Study Ref Residential Schools and Understand Why They Harm Our Children - Next GenerationSue BozgozNo ratings yet
- Middleschool Typesoftextstructuresininformationaltexts PDFDocument1 pageMiddleschool Typesoftextstructuresininformationaltexts PDFGerald LastaNo ratings yet
- Tomorrow Begins Now: Teen Heroes Who Faced Down InjusticeFrom EverandTomorrow Begins Now: Teen Heroes Who Faced Down InjusticeNo ratings yet
- Homework AssignmentsDocument5 pagesHomework AssignmentsCristina GrigorasNo ratings yet
- 15 Essential Cases - AP GovDocument75 pages15 Essential Cases - AP GovMichelle XianNo ratings yet
- COL Class NotesDocument35 pagesCOL Class Notesluckystar384No ratings yet
- Day 3 Educ 377 - Foundations of American DemocracyDocument17 pagesDay 3 Educ 377 - Foundations of American Democracyapi-584001941No ratings yet
- Black Mondays: Worst Decisions of the Supreme Court (Fifth Edition)From EverandBlack Mondays: Worst Decisions of the Supreme Court (Fifth Edition)No ratings yet
- APGovJudiciaryCh16 2Document31 pagesAPGovJudiciaryCh16 2jimNo ratings yet
- Homestead Act Research PaperDocument6 pagesHomestead Act Research Paperc9s9h7r7100% (1)
- COL Syllabus - 17-18 - Senchi VersionDocument9 pagesCOL Syllabus - 17-18 - Senchi VersionTimore FrancisNo ratings yet
- Gibbons V Ogden Research PaperDocument4 pagesGibbons V Ogden Research Paperleukqyulg100% (1)
- Correct Us Citizen PampletDocument2 pagesCorrect Us Citizen Pampletapi-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Section 3Document1 pageUnit 4 Section 3api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 6 Section 2Document1 pageUnit 6 Section 2api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Section 3Document2 pagesUnit 5 Section 3api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Section 1Document2 pagesUnit 5 Section 1api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Section 4Document2 pagesUnit 4 Section 4api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Section 1Document2 pagesUnit 4 Section 1api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Section 2 NotesDocument1 pageUnit 4 Section 2 Notesapi-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Section 2Document1 pageUnit 4 Section 2api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Section 3Document2 pagesUnit 3 Section 3api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Section 2Document2 pagesUnit 3 Section 2api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Section 1Document1 pageUnit 3 Section 1api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Section 3Document2 pagesUnit 2 Section 3api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Section 6Document1 pageUnit 2 Section 6api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Section 4Document1 pageUnit 2 Section 4api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Section 2Document2 pagesUnit 2 Section 2api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Section 5Document2 pagesUnit 2 Section 5api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Section 1Document2 pagesUnit 2 Section 1api-539700139No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Section 1 Cornell NotesDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Section 1 Cornell Notesapi-539700139No ratings yet
- GW Space Law Society Draft ConstitutionDocument5 pagesGW Space Law Society Draft ConstitutionGWSpaceLawSocietyNo ratings yet
- Admin 2023Document11 pagesAdmin 2023Thando MalingaNo ratings yet
- Imbong Vs ComelecDocument2 pagesImbong Vs ComelecSid SidNo ratings yet
- Question Bank FederalismDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank Federalismsana022009No ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Salient Features and Characteristics of The Constitution of IndiaDocument5 pagesChapter - 3: Salient Features and Characteristics of The Constitution of IndiaVaishal GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Main Features of The Constitution of ArgentinaDocument2 pagesMain Features of The Constitution of ArgentinaPamela Andrea100% (1)
- The Philosophy of The Indian ConstitutionDocument3 pagesThe Philosophy of The Indian ConstitutionAnshu RajNo ratings yet
- Next Toppersfederalism Class 4 Next Topper sst-1Document20 pagesNext Toppersfederalism Class 4 Next Topper sst-1Kshitiz sharmaNo ratings yet
- Citizenship ActDocument8 pagesCitizenship ActSumanth RoxtaNo ratings yet
- 1976 Amendments To The 1973Document2 pages1976 Amendments To The 1973Emrys PendragonNo ratings yet
- Three Branches of GovernmentDocument17 pagesThree Branches of GovernmentJhez Magno PelagioNo ratings yet
- Lco500 2024 01 AsmtDocument4 pagesLco500 2024 01 Asmtdangale418No ratings yet
- Maharashtra Fisheries Act, 1960Document10 pagesMaharashtra Fisheries Act, 1960Latest Laws TeamNo ratings yet
- Polity 02 - Daily Class Notes - UPSC Prahar 2024 (Hinglish)Document3 pagesPolity 02 - Daily Class Notes - UPSC Prahar 2024 (Hinglish)kartikira12No ratings yet
- Tescon ConstitutionDocument5 pagesTescon ConstitutionEmmanuel Awuah100% (5)
- Legislative Role in PakistanDocument2 pagesLegislative Role in PakistanHafiz Farhan YousafNo ratings yet
- Any Three Features of Federal Form of GovernmentDocument2 pagesAny Three Features of Federal Form of GovernmentSudit BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Facts To Be Remembered Constitution: Indian Polity / 3Document2 pagesFacts To Be Remembered Constitution: Indian Polity / 3MUKESH GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Handout Monarchy and RepublicDocument4 pagesHandout Monarchy and RepublicThảo NhiênNo ratings yet
- Constitutional LawDocument26 pagesConstitutional LawMarvin CabantacNo ratings yet
- Philippine Government and Politics Quiz 012018Document1 pagePhilippine Government and Politics Quiz 012018Mello Jane Garcia DedosinNo ratings yet
- 1.basic Structure of The Constitution of IndiaDocument23 pages1.basic Structure of The Constitution of IndiaMeenaaa Balakrishnan Mudhalayar100% (1)
- CH 2 Constitutional Design Class Ix Questions - AnswersDocument2 pagesCH 2 Constitutional Design Class Ix Questions - AnswersVandana GahlautNo ratings yet
- Case Digest - PACU v. Secretary of Education 97 Phil 806Document2 pagesCase Digest - PACU v. Secretary of Education 97 Phil 806Nilfpe SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Iloilo City Regulation Ordinance 2014-325Document2 pagesIloilo City Regulation Ordinance 2014-325Iloilo City CouncilNo ratings yet
- Minerva Mills Ltd. & Ors vs. Union of IndiaDocument2 pagesMinerva Mills Ltd. & Ors vs. Union of IndiaK S UPENDRANo ratings yet
- Planas v. COMELEC Case Digest PDFDocument4 pagesPlanas v. COMELEC Case Digest PDFLawiswisNo ratings yet
- Features of 1956 ConstitutionDocument2 pagesFeatures of 1956 ConstitutionHamad Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- 49 Scra 105Document2 pages49 Scra 105Johnny EnglishNo ratings yet
- Government Is Born Shorts 2Document1 pageGovernment Is Born Shorts 2Jorge A VillarrealNo ratings yet