Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learning Activity Sheet: Action and Reaction
Learning Activity Sheet: Action and Reaction
Uploaded by
Najmah Sirad AmpaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Activity Sheet: Action and Reaction
Learning Activity Sheet: Action and Reaction
Uploaded by
Najmah Sirad AmpaCopyright:
Available Formats
RC- AL KHWARIZMI INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE FOUNDATION, INC.
SCIENCE LABORATORY SCHOOL
Barrio Marawi, National Highway, Marawi City
School ID: 478017
S.Y. 2020-2021
LAS No. 14
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET
Name: ___________________________________________________
Grade Level and Section: 9 -_________________ Score: __________________
Subject: SCIENCE 9.3 (Mechanics, Oscillation, and Waves) Date: __________________
Type of Activity:
Concept Notes Laboratory Report Formal Theme Others:
z
Skills/ Exercise/ Drills Drawing/ Art Informal Theme
Activity Title: Newton’s Third Law of Motion: Law of Interaction
Learning Targets: To know and understand the Newton’s Third law of motion
References: Arciaga, M. E. and Rara, B.H. Exploring Science & Technology IV. pp. 59-64
In every action, there is always an equal and opposite reaction.
The force acting on an object is a result of its interaction with another object. There is no
such thing as an isolated force. When object A exerts a force on object B, Object B also exerts a
force on object A. They have the same magnitude but opposite in direction. The forces exerted by the
objects interacting with each other are called action and reaction force.
Have you tried hitting a table with your palm or fist? Did it hurt you? You exerted a force on
the table when you hit it (action). You may not see it, but the table exerted the same amount of
force (reaction) on your palm or fist.
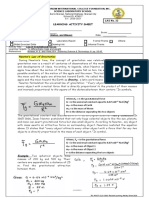
In figure below, It shows that action and reaction forces have equal magnitude and are
opposite in direction. Arrows A shows the force exerted by the palm on the table. Arrows B, on the
other hand, shows the force exerted by the table on the palm.
Figure: Action and Reaction Forces
The law of interaction can be summarized in the following statements:
1. When objects interact, they exert forces on each other.
2. The forces of interaction are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
3. Action and reaction forces do not cancel each other because they act on different objects.
Do the Exercise!
Give three real-life example that describes the newton’s third law of motion.
RC AKICFI-SLS OBILP Revised Learning Activity Sheet 2020
RC- AL KHWARIZMI INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE FOUNDATION, INC.
SCIENCE LABORATORY SCHOOL
Barrio Marawi, National Highway, Marawi City
School ID: 478017
S.Y. 2020-2021
LAS No. 15
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET
Name: ___________________________________________________
Grade Level and Section: 9 -_________________ Score: __________________
Subject: SCIENCE 9.3 (Mechanics, Oscillation, and Waves) Date: __________________
Type of Activity:
Concept Notes Laboratory Report Formal Theme Others:
z
Skills/ Exercise/ Drills Drawing/ Art Informal Theme
Activity Title: Newton’s Third Law of Motion: Law of Interaction
Learning Targets: To know and understand the Newton’s Third law of motion
References: Arciaga, M. E. and Rara, B.H. Exploring Science & Technology IV. pp. 59-64
Avtivity No.1
ANSWER AS DIRECTED. Solve the crossword puzzle below the missing term/word in each sentence.
It serves as your clue.
Across
1. Reactions always go in the _________________
direction of the action.
2. An action and its reaction are equal in ______________ .
3. Newton’s Third Law explains what happens when two
objects _________________ .
Down
4. Forces always come in pairs—so each
_________________ has a reaction.
5. The force of an action sends a reaction in
the opposite _________________ .
6. Every action and its reaction are
_________________ in size.
Avtivity No.2
Fill in the blank with the missing term/word to complete the thought of the sentence.
1. Newton’s third law of motion is also known as the LAW OF_________________________.
2. Newton’s third law states that every time there is an _______force, there is also a
________force that is __________ in size and acts in the ______________direction.
3. Newton’s third law states that forces must ALWAYS occur in ___________________________.
Avtivity No.3.
Listed below are ACTION forces. Indicate the REACTION force on each action.
a.Your bottom pushing on your desk seat --
b.A bat hitting a baseball --
c.Your finger pressing on your phone screen while texting --
RC AKICFI-SLS OBILP Revised Learning Activity Sheet 2020
You might also like
- Grade 3 - Elevate Science - WorkbookDocument38 pagesGrade 3 - Elevate Science - WorkbookMahmoud SolimanNo ratings yet
- Science 8-1st Quarter ModuleDocument59 pagesScience 8-1st Quarter ModuleAndrea Perez92% (24)
- Calculus: An Intuitive and Physical Approach (Second Edition)From EverandCalculus: An Intuitive and Physical Approach (Second Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Spectrophotometric Analysis of A Two Component MixtureDocument3 pagesSpectrophotometric Analysis of A Two Component MixtureDozdi100% (11)
- An Introduction To Atmospheric Modeling - Randall (2005) PDFDocument362 pagesAn Introduction To Atmospheric Modeling - Randall (2005) PDFavimanyu ray100% (1)
- Free Erotic Sex StoriesDocument14 pagesFree Erotic Sex Storiesanon_65905036528% (18)
- Practical Research 2 Quarter 1 Activity SheetsDocument8 pagesPractical Research 2 Quarter 1 Activity SheetsJonnis Estillore100% (1)
- Grade 7 4th Quarter 1-3 WeekDocument8 pagesGrade 7 4th Quarter 1-3 WeekCipriano Bayotlang100% (2)
- Research in Daily Life 2 (1st Prelim)Document3 pagesResearch in Daily Life 2 (1st Prelim)Love CHDCC100% (1)
- CLIL LESSON PLANpatrizia+annaDocument6 pagesCLIL LESSON PLANpatrizia+annaLuca Angelo LauriNo ratings yet
- A Push A Pull: Weight Normal Force Vector Quantity PairsDocument6 pagesA Push A Pull: Weight Normal Force Vector Quantity PairsNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: Ma F F F F F F F FDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Ma F F F F F F F FNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Examples: Rc-Al Khwarizmi International College Foundation, Inc. Science Laboratory SchoolDocument8 pagesExamples: Rc-Al Khwarizmi International College Foundation, Inc. Science Laboratory SchoolNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: EngineersDocument11 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: EngineersNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsDocument8 pagesThermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS G9 1stquarter Week8 LAS 16 21 2020 2021Document2 pagesPHYSICS G9 1stquarter Week8 LAS 16 21 2020 2021Najmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: Background InformationDocument2 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Background InformationJL IndianoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsDocument12 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument3 pagesForceRenezel Joy PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- GR 8 DLP CompilationDocument38 pagesGR 8 DLP CompilationEliot CabornayNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Grade 8 Science Worksheets Excluding STE 2Document26 pagesConsolidated Grade 8 Science Worksheets Excluding STE 2Sofia Abella100% (1)
- S8 - Q1 - Week 2Document9 pagesS8 - Q1 - Week 2Dhar Mulig OrculloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2: Forces and Motion: Third Law of MotionDocument3 pagesLesson 1.2: Forces and Motion: Third Law of MotionLaiza GranaNo ratings yet
- Do The Exercise!: Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsDocument8 pagesDo The Exercise!: Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Quarter 1 Activity SheetsDocument8 pagesPractical Research 2 Quarter 1 Activity SheetsJonnis EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Science: Newton's Law of Motion-Law of InteractionDocument13 pagesScience: Newton's Law of Motion-Law of InteractionFe Pakias GullodNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY SHEET IN SCIENCE Act 5Document4 pagesACTIVITY SHEET IN SCIENCE Act 5Jayjay RonielNo ratings yet
- Act 4 Cell Parts FunctionsDocument3 pagesAct 4 Cell Parts FunctionssamiNo ratings yet
- Learning Packet - Week 2 - Law of MotionDocument10 pagesLearning Packet - Week 2 - Law of MotionVioleta YutucNo ratings yet
- QI Module 2 Week 2Document3 pagesQI Module 2 Week 2Angel May RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 8 6Document3 pagesDaily Lesson Log Grade 8 6Ela Anjell AmparadoNo ratings yet
- Cut The Pictures of The Human Skeletal System. Paste It On A Bond PaperDocument20 pagesCut The Pictures of The Human Skeletal System. Paste It On A Bond PaperNailah IngcoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem 1st Periodical Exam RAWS 2022-2023Document3 pages2nd Sem 1st Periodical Exam RAWS 2022-2023Anne Cris AzorNo ratings yet
- Miaa 360 Zip Line PBLDocument12 pagesMiaa 360 Zip Line PBLapi-282517878No ratings yet
- Instituto Americano Leonardo Da Vinci Seccion Secundaria: I. Underline The Best OptionDocument2 pagesInstituto Americano Leonardo Da Vinci Seccion Secundaria: I. Underline The Best OptionAIván SánchezNo ratings yet
- Science 9: 4 Quarter Week 20Document7 pagesScience 9: 4 Quarter Week 20caroljoycaisNo ratings yet
- Sir Melan Learning Center, Inc.: First Mid-Quarter Examination in Science 8Document2 pagesSir Melan Learning Center, Inc.: First Mid-Quarter Examination in Science 8roman marambaNo ratings yet
- Third Law of MotionDocument6 pagesThird Law of MotionSer GutieNo ratings yet
- Monthly Test PR2Document2 pagesMonthly Test PR2Jonathan PacificoNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification SY. 2022-2023: TotalDocument5 pagesTable of Specification SY. 2022-2023: TotalSister Ma. Agnes Batasin-inNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Palusapis Integrated SchoolDocument6 pagesDepartment of Education: Palusapis Integrated SchoolRona May EsperanzateNo ratings yet
- Gen Physics 1 M.examDocument2 pagesGen Physics 1 M.examCamille ManlongatNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Examination in Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument2 pagesFirst Quarter Examination in Philosophy of The Human PersonRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 4 - Terminal VelocityDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 4 - Terminal Velocityapi-300725936No ratings yet
- DLL - General Chemistry - 2023-2024Document80 pagesDLL - General Chemistry - 2023-2024Apar DizonNo ratings yet
- Summative Test No. 4 Grade Iv - Science: Describe How Light Reflects or RefractsDocument36 pagesSummative Test No. 4 Grade Iv - Science: Describe How Light Reflects or RefractsRodel YapNo ratings yet
- Philippine Technological Institute of Science Arts and TradeDocument1 pagePhilippine Technological Institute of Science Arts and Traderommel monteroNo ratings yet
- Ela Unit 7 Lesson 3 AltDocument9 pagesEla Unit 7 Lesson 3 Altapi-373788220No ratings yet
- Ucsp 2ND Batch ActsheetDocument15 pagesUcsp 2ND Batch ActsheetAnnalie Delera CeladiñaNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Unit 1 Changes in Motion - Contact Vs Noncontact ForcesDocument5 pages5th Grade Unit 1 Changes in Motion - Contact Vs Noncontact ForcesiskenderbeyNo ratings yet
- G12 Q3 LAS Week5 3isDocument10 pagesG12 Q3 LAS Week5 3isJason Tagapan GullaNo ratings yet
- ScienceGrade12AppliedSubject Learning CAtivity Sheet Research I Q1Week1 2 1Document14 pagesScienceGrade12AppliedSubject Learning CAtivity Sheet Research I Q1Week1 2 1Myka RobertoNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarterly Exam in Grade 12 Practical Research 2Document3 pages1st Quarterly Exam in Grade 12 Practical Research 2Vee Jay BlanciaNo ratings yet
- 3 RdsciglcealignDocument7 pages3 Rdsciglcealignapi-231469705No ratings yet
- Week 4Document7 pagesWeek 4MARIAN TIMTIMANNo ratings yet
- English 10 Activities: St. Peter's College of OrmocDocument3 pagesEnglish 10 Activities: St. Peter's College of OrmocLacesand solesNo ratings yet
- Sept. 12 16Document8 pagesSept. 12 16Abby MagandaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 DLP Q1W3D1Document4 pagesScience 8 DLP Q1W3D1sophia tanNo ratings yet
- DLL Science-4 Q1 W1Document3 pagesDLL Science-4 Q1 W1Christian BacayNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument7 pagesMathematics in The Modern WorldabercrombieNo ratings yet
- SSC Research7 Q2 M3Document14 pagesSSC Research7 Q2 M3Chriszia Mae Alliana M. Alalim (yana)No ratings yet
- Learning Robotics, with Robotics, by Robotics: Educational RoboticsFrom EverandLearning Robotics, with Robotics, by Robotics: Educational RoboticsNo ratings yet
- Picture-Perfect STEM Lessons, 3-5: Using Children's Books to Inspire STEM LearningFrom EverandPicture-Perfect STEM Lessons, 3-5: Using Children's Books to Inspire STEM LearningNo ratings yet
- Letter For The Respondents - CSSDocument2 pagesLetter For The Respondents - CSSNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- 3 ManlapazDocument20 pages3 ManlapazNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Digital Literacy SkillsDocument27 pagesDigital Literacy SkillsNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Weathering Erosion DepositionDocument4 pagesWeathering Erosion DepositionNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- FuentesDocument23 pagesFuentesNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- 4 SaquezDocument17 pages4 SaquezNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- 18 (g6)Document20 pages18 (g6)Najmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- 2 AbuyabaorDocument23 pages2 AbuyabaorNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- 15 (g3)Document27 pages15 (g3)Najmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- 5 CgaisDocument31 pages5 CgaisNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Module 13Document28 pagesModule 13Najmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS G9 1stquarter Week8 LAS 16 21 2020 2021Document2 pagesPHYSICS G9 1stquarter Week8 LAS 16 21 2020 2021Najmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsDocument8 pagesThermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry g8 - 1stquarter (Week3-4)Document9 pagesChemistry g8 - 1stquarter (Week3-4)Najmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY G10 - 1stquarter (Week 14) (LAS 38-43) 2020-2021Document6 pagesCHEMISTRY G10 - 1stquarter (Week 14) (LAS 38-43) 2020-2021Najmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum and CollisionsDocument17 pagesConservation of Momentum and CollisionsNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY G9 - 1stquarter (Week 14) LAS No 56 To 64 2020-2021Document10 pagesCHEMISTRY G9 - 1stquarter (Week 14) LAS No 56 To 64 2020-2021Najmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Do The Exercise!: Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsDocument8 pagesDo The Exercise!: Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsDocument12 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Thermodynamics, Electromagnetism, Optics, & Modern PhysicsNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: Do The Exercise!Document9 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Do The Exercise!Najmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Examples: Rc-Al Khwarizmi International College Foundation, Inc. Science Laboratory SchoolDocument8 pagesExamples: Rc-Al Khwarizmi International College Foundation, Inc. Science Laboratory SchoolNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: Ma F F F F F F F FDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Ma F F F F F F F FNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: EngineersDocument11 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: EngineersNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- A Push A Pull: Weight Normal Force Vector Quantity PairsDocument6 pagesA Push A Pull: Weight Normal Force Vector Quantity PairsNajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- 30-07-2022 Jr.c-ipL (Incoming) Jee-Main WTM-04 Key & Sol'sDocument10 pages30-07-2022 Jr.c-ipL (Incoming) Jee-Main WTM-04 Key & Sol'sMurari MarupuNo ratings yet
- Conceptest Clicker Questions: Physics: For Scientists & Engineers With Modern Physics, 4Th EditionDocument49 pagesConceptest Clicker Questions: Physics: For Scientists & Engineers With Modern Physics, 4Th EditionDARIO CASTRO CASTRONo ratings yet
- Induction CookingDocument9 pagesInduction Cookingtechzones100% (1)
- SPM Definition ListDocument3 pagesSPM Definition ListWong Weng SiongNo ratings yet
- Part 12 Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Phased ArraysDocument7 pagesPart 12 Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Phased ArraysWahyu RiyandiNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Lesson Plan (Physics)Document9 pagesGrade 8 Science Lesson Plan (Physics)Gerick Dave Monencillo VenderNo ratings yet
- Subramanian1993 PDFDocument14 pagesSubramanian1993 PDFValeria BelénNo ratings yet
- Vector Integrals and Integral Theorems: R, R R RDocument23 pagesVector Integrals and Integral Theorems: R, R R RRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Michael Faraday 2Document6 pagesMichael Faraday 2MihaiNo ratings yet
- CFD Analysis and Comparison of Air Flow Within An Annulus, Airflow Over An Aerofoil and Convective Heat Transfer From A Heat Source of A Radiator Within An Enclosed RoomDocument0 pagesCFD Analysis and Comparison of Air Flow Within An Annulus, Airflow Over An Aerofoil and Convective Heat Transfer From A Heat Source of A Radiator Within An Enclosed RoomInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- AITS 1819 FT II JEEA Paper 2 Sol PDFDocument14 pagesAITS 1819 FT II JEEA Paper 2 Sol PDFM jhansiNo ratings yet
- StormmgmtDocument22 pagesStormmgmtAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Ieee 14 Bus System Load Flow Using NDocument14 pagesIeee 14 Bus System Load Flow Using NRadak RuduNo ratings yet
- 2aprob Sol 7Document7 pages2aprob Sol 7Gowrisankar RaoNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsTiktok FOOTBALLNo ratings yet
- PQT Chapter 9a Phase DiagramsDocument53 pagesPQT Chapter 9a Phase DiagramsDương Hữu PhươngNo ratings yet
- Electricity Student Ing 2013Document49 pagesElectricity Student Ing 2013Bengü MertNo ratings yet
- Theme - N 9Document5 pagesTheme - N 9Satya kaliprasad vangaraNo ratings yet
- Carnot Engine: by (Khlood Salim Al-Kafajy)Document11 pagesCarnot Engine: by (Khlood Salim Al-Kafajy)Ali Mohammed Alkafajy100% (1)
- Steel DesignDocument1 pageSteel Designsteven bianesNo ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis (ATH)Document5 pagesThermal Analysis (ATH)liapomiNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Quantum PhysicsDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Quantum Physicsegt39dvg100% (1)
- Introduction To Part 1Document39 pagesIntroduction To Part 1olgiasNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Bonding B KEYDocument3 pagesQuiz - Bonding B KEYRavin BoodhanNo ratings yet
- Rotameter CalibrationDocument5 pagesRotameter Calibrationengineer63No ratings yet
- Strahlenfolter Stalking - Sind Radiofrequenzwaffen Der Sputnik Der 80er JahreDocument7 pagesStrahlenfolter Stalking - Sind Radiofrequenzwaffen Der Sputnik Der 80er JahreParanoia.war.gesternNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Analysis of Indeterminate Beams and Frames by The Slope-Deflection Method PDFDocument42 pagesChapter 12 Analysis of Indeterminate Beams and Frames by The Slope-Deflection Method PDFYirga BezabehNo ratings yet