Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 - Intermolecular Sources
2 - Intermolecular Sources
Uploaded by
mostafa barakatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 - Intermolecular Sources
2 - Intermolecular Sources
Uploaded by
mostafa barakatCopyright:
Available Formats
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
50 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(1) Jan 2014 Q (19)
19 Some ionic solids, such as sodium chloride, are soluble in water because
(2) June 2014 Q (12, 13, 14, 15)
12 The table below gives the boiling temperatures of some alcohols.
From the data in the table, the boiling temperature of hexan-1-ol is most likely
to be
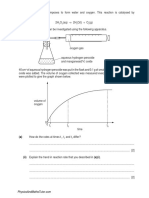
13 An experiment to determine the effect of an electrostatic force on a jet of
liquid is carried out using the apparatus as shown.
51 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
Which of the following liquids would not be significantly deflected by the
electrostatic force applied?
14 Although they have similar relative molecular masses, the boiling
temperatures of pentane (36 °C) and butan-1-ol (117 °C) are significantly
different. The reason for this is that, in comparison with pentane,
15 Compounds such as sodium chloride dissolve in water because the ions
interact with the water molecules. The interactions are
(3) Jan 2015 Q (1, 2)
1 Which of the following are properties of the liquid, 1-bromobutane?
52 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
2 (a) The strongest intermolecular forces in liquid ammonia are
(b) The graph below shows the boiling temperatures for the Group 5 hydrides.
Select the most likely boiling temperature for ammonia.
53 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(4) Jan 2016 Q (6)
6 Which of the following compounds has hydrogen bonding in the liquid
state?
(5) Jan 2016 Q (24_d)
(d) (i) When chlorine is passed over iodine crystals, iodine monochloride, ICl,
is formed.
Iodine monochloride, ICl, is a liquid at room temperature whereas chlorine,
Cl2, is a gas.
Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, why this is so.
(4)
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(6) June 2016 Q (12)
12 As Group 7 is descended, the boiling temperatures of the hydrogen
halides, from HF to HI,
54 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(7) Nov 2016 Q (4)
4 Which isomer, with the formula C7H16, will have the lowest boiling
temperature?
(8) Nov 2016 Q (22_d)
(d) The boiling temperatures of the hydrogen halides are shown.
*(i) London forces are present in all of these compounds.
Describe how these forces arise.
(2)
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(ii) State why the London forces are greater in hydrogen iodide than in
hydrogen bromide.
(1)
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
55 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(iii) Explain why the boiling temperature of hydrogen fluoride is higher than
that of hydrogen chloride.
(2)
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(9) Jan 2017 Q (5, 6)
5 At room temperature, iodine is a solid and bromine is a liquid.
The best explanation for this is that
6 Which molecule will have the highest boiling temperature?
56 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(10) Nov 2017 Q (5)
5 Which substance has more than one type of intermolecular force between
its molecules in the liquid state?
(11) Nov 2017 Q (24_b, c)
24 A hydrogen peroxide molecule can be represented by the structure shown.
(b) Hydrogen peroxide dissolves in water.
(i) State the strongest type of interaction that occurs between molecules of
hydrogen peroxide and water.
(1)
............................................................................................................................
(ii) Draw a diagram to show the interaction named in (b)(i) between one
molecule of hydrogen peroxide and one molecule of water.
Show any relevant lone pairs and dipoles in your diagram.
(3)
*(c) Explain, in terms of electronegativity, why the boiling temperature of H2S2
is lower than that of H2O2.
(2)
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
57 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(12) Jan 2018 Q (3, 11)
3 This question is about the hydrides of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine.
(a) The hydride with the highest boiling temperature is
(b) The hydride which has the strongest hydrogen bond in the pure liquid is
11 When potassium chloride dissolves in water, the main interaction between
the ions and water molecules is
(13) Jan 2018 Q (23_a)
23 Glucose occurs naturally in many fruits. It is a white powder at room
temperature and is extremely soluble in water. Glucose may be represented
by the structure below.
The fermentation of glucose is fundamental to brewing and baking. Glucose
breaks down to form carbon dioxide and ethanol.
Drinks with a high alcohol content are obtained by distillation from a
fermentation mixture.
For many years, the alcohol content of such drinks was measured as degrees
proof. Originally this was defined by the gunpowder test. A pellet of
gunpowder was soaked in the drink.
58 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
If the gunpowder would still ignite, the alcohol drink was at least 100° proof.
The reason for introducing this measure was that, from the sixteenth century,
the tax on alcoholic drinks was related to their alcohol content.
Nowadays, most countries have adopted alcohol percentage by volume
(ABV), which is the volume of ethanol, in cm3, present in 100 cm3 of the drink.
Today, most ethanol for chemical use is produced by an addition reaction of
ethene.
*(a) (i) Name all the intermolecular forces between glucose molecules. For
each type of force, indicate the atoms in the molecule involved.
A detailed explanation of how these forces arise is not required.
(6)
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(ii) Explain why glucose is very soluble in water.
(2)
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
59 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(14) Nov 2018 Q (10, 11, 12)
10 Which isomer of C6H14 has the lowest boiling temperature?
11 What is the trend in boiling temperatures for the hydrogen halides from HF
to HI?
12 Which compound is the most soluble in hexane?
60 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(15) Nov 2018 Q (24_c, iii)
(iii) Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, why nitrogen trichloride has a
similar boiling temperature to ethanol.
(4)
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
61 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(16) Sample Assessment Materials 2019 Q (1, 2, 3)
1 Which alkane has the highest boiling temperature?
2 Which is the order of increasing boiling temperature?
3 Which statement is not explained by hydrogen bonding?
62 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(17) Jan 2019 Q (5, 6)
5 In alkanes, increasing the length and branching of the carbon chain both
affect the boiling temperature.
Which of the following combination of effects is correct?
6 What is the correct order of boiling temperatures for the hydrogen halides,
from the lowest to highest?
(18) June 2019 Q (16) New
16 This question is about hydrogen bonding.
(a) Which property is not due to hydrogen bonding?
(b) Which diagram best represents a hydrogen bond between two water
molecules?
63 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(19) Nov 2019 Q (4)
4 What are the strongest interactions between molecules in solid hydrogen
iodide, HI?
(20) Jan 2020 Q (5)
5 Which compounds are arranged in order of decreasing boiling
temperature?
64 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit_2_Topic 2
(21) Jan 2020 Q (16_a)
16 This question is about trends in the Periodic Table.
*(a) The boiling temperatures of some isoelectronic hydrides are shown.
Explain the differences in these boiling temperatures by considering all the
intermolecular forces involved.
Detailed descriptions of the intermolecular forces involved are not required.
(6)
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
65 2 – Intermolecular Forces Mostafa Barakat (0100 165 44 62)
You might also like
- Core Network Services-High Level Design TemplateDocument15 pagesCore Network Services-High Level Design TemplateBryan Gavigan100% (1)
- 4CH1 2C Que 2022Document20 pages4CH1 2C Que 2022mostafa barakat100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/22 October/November 2020Document3 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/22 October/November 2020mostafa barakat100% (1)
- Thursday 23 May 2019: ChemistryDocument28 pagesThursday 23 May 2019: Chemistrymostafa barakat100% (3)
- Chemical Hardness Ralph G. PearsonDocument208 pagesChemical Hardness Ralph G. PearsonVasu NagpalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IG2EDocument20 pagesChemistry IG2Ealishairabbasi69No ratings yet
- Bond Polarity 1 QP AS ChemistryDocument8 pagesBond Polarity 1 QP AS ChemistryBabueNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - IAS - Itermolecular Forces - 1Document8 pagesEdexcel - IAS - Itermolecular Forces - 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Chemistry: C3 Chapter 1 HigherDocument25 pagesExampro GCSE Chemistry: C3 Chapter 1 HigherSamuel KalemboNo ratings yet
- General Properties of Transition Metals 1 QPDocument10 pagesGeneral Properties of Transition Metals 1 QPaanammanaNo ratings yet
- AS RedoxDocument20 pagesAS RedoxIbrahim AbidNo ratings yet
- Practicetopic 6 Paper 2.pagesDocument8 pagesPracticetopic 6 Paper 2.pagesnadia sykesNo ratings yet
- 2.4, 2.5, 2.6 TestDocument7 pages2.4, 2.5, 2.6 Testzafarchem_iqbalNo ratings yet
- Review Pack 1st Term (23-24)Document21 pagesReview Pack 1st Term (23-24)Teck TieNo ratings yet
- Y12 Group 2, 7 and Redox TestDocument10 pagesY12 Group 2, 7 and Redox TestAnela XVIINo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry 1 - Alkali Metals RevisioDocument7 pagesInorganic Chemistry 1 - Alkali Metals RevisioAshleyn Mary SandersNo ratings yet
- AS - Group 1,2,& 7Document25 pagesAS - Group 1,2,& 7vintu pvNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument24 pagesIntermolecular ForcesSyed Âãšhīr HûśšāînNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals PPQDocument6 pagesAlkali Metals PPQ张米No ratings yet
- Energy Changes, Rate, Reversible, NH3, H2SO4Document5 pagesEnergy Changes, Rate, Reversible, NH3, H2SO4HudaNo ratings yet
- A-Level Paper 1 pp1Document14 pagesA-Level Paper 1 pp1fibim38794No ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Group 2 Volume 2Document11 pagesTopic 4 - Group 2 Volume 2Abirame SivakaranNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education Practice QuestionslNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 BondingDocument23 pagesTopic 3 Bondingnaturecore9No ratings yet
- General Bonding QuestionsDocument5 pagesGeneral Bonding QuestionsEvan YEUNG [09N12]No ratings yet
- Topical Questions For Lesson 11 Alkali MetalsDocument5 pagesTopical Questions For Lesson 11 Alkali Metalsokguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- Reversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 1 QPDocument23 pagesReversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 1 QPKhasimNo ratings yet
- Rates and EquilibriaDocument24 pagesRates and EquilibriaMegan PhillipNo ratings yet
- PeriodicityDocument25 pagesPeriodicityKelvin ChoyNo ratings yet
- IBDP Chemistry Bonding QuestionsDocument14 pagesIBDP Chemistry Bonding QuestionssquailgeNo ratings yet
- Jason 291123Document12 pagesJason 291123msyahrulramdan050199No ratings yet
- Alkali MetalsDocument13 pagesAlkali MetalslarauchilNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument3 pagesBiologysrijeetjNo ratings yet
- 2.04 - 2.06 Redox Reactions, Halogens and Alkali Earth MetalsDocument37 pages2.04 - 2.06 Redox Reactions, Halogens and Alkali Earth Metalsgobod52280No ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Test AnswersDocument8 pagesIonic and Covalent Bonding Test Answersomirinn505No ratings yet
- Edexcel Chemistry Topic 3Document11 pagesEdexcel Chemistry Topic 3locopocpNo ratings yet
- Questions Paper 2 CHP 19Document5 pagesQuestions Paper 2 CHP 19FIKRIYE ONDEROLNo ratings yet
- Introducing Energy Changes in ReactionsDocument18 pagesIntroducing Energy Changes in ReactionsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet - Energetics, IntermolecularDocument7 pagesRevision Worksheet - Energetics, IntermolecularMilli AdamNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 1 QPDocument13 pagesPeriodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 1 QPmalakNo ratings yet
- Redox Worksheet 2023Document5 pagesRedox Worksheet 2023uzair ahmedNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Od Acids & BasesDocument6 pagesWorksheet Od Acids & BasesAreeba IftikharNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Homework PupilDocument8 pagesElectrolysis Homework Pupilnicole.fiorentini.almeidaNo ratings yet
- 1 Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposes To Form Water and Oxygen. This Reaction Is Catalysed byDocument9 pages1 Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposes To Form Water and Oxygen. This Reaction Is Catalysed byKelvin DenhereNo ratings yet
- C2 Representing Reactions HigherDocument11 pagesC2 Representing Reactions HigherdownendscienceNo ratings yet
- Reversible Reactions QDocument3 pagesReversible Reactions QVictor DyzeNo ratings yet
- DBQ For HL Review Gr11 and 12Document5 pagesDBQ For HL Review Gr11 and 12maria penagosNo ratings yet
- Halogenoalkanes Alcohol and Spectra Unit 2Document8 pagesHalogenoalkanes Alcohol and Spectra Unit 2Barminga KamurenNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 2 QPDocument14 pagesPeriodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 2 QPmalakNo ratings yet
- c1 Chapter 1Document10 pagesc1 Chapter 1legendary sportsNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 17Document16 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 17Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Anderson Serangoon Junior College: 2021 JC 2 Mid Year Common TestDocument24 pagesAnderson Serangoon Junior College: 2021 JC 2 Mid Year Common TestpianorificationNo ratings yet
- CHEMJUNE2002C4Document9 pagesCHEMJUNE2002C4api-3726022No ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry paper 4 Topical Questions- Electrode potential and cell potentialDocument32 pagesA Level Chemistry paper 4 Topical Questions- Electrode potential and cell potentialDeshpande ShashibhushanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics 3 QPDocument12 pagesChemical Energetics 3 QPSrijita RoyNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Acids PDFDocument62 pages3.1 Acids PDFGader ElmiNo ratings yet
- 3.1 AcidsDocument10 pages3.1 AcidsGeorge TongNo ratings yet
- Sayed Daniyal Ali - Kami Export - Sayed Daniyal Ali - Syed Daniyal Ali - 3C EquilibriumDocument8 pagesSayed Daniyal Ali - Kami Export - Sayed Daniyal Ali - Syed Daniyal Ali - 3C EquilibriumSayed Daniyal AliNo ratings yet
- (Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Chemistry 1Document7 pages(Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Chemistry 1DM0% (1)
- My TestDocument4 pagesMy TestMateusz MigdałNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 2Document79 pagesElectrolysis 2Kin Sana HlaingNo ratings yet
- 2: Bonding and Structure - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDocument13 pages2: Bonding and Structure - Topic Questions: Year Series Paper NumberSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 1 QPDocument11 pagesRate of Reaction 1 QPRobert EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 1 QPDocument11 pagesRate of Reaction 1 QPjunaidsaeed200No ratings yet
- 4CH1 2C Rms 20220825Document11 pages4CH1 2C Rms 20220825mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- 2 - Atomic Structure - P1Document14 pages2 - Atomic Structure - P1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- 4CH1 1C Rms 20220825Document18 pages4CH1 1C Rms 20220825mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/21Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/21mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/22 October/November 2020Document3 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/22 October/November 2020mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- 4CH1 1C Que 2022Document28 pages4CH1 1C Que 2022mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/21 October/November 2020Document3 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/21 October/November 2020mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/22mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/23Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/23mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- 1 - States of MatterDocument9 pages1 - States of Mattermostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- 1 - States of MatterDocument9 pages1 - States of Mattermostafa barakat100% (1)
- 8 - Chemical AnalysisDocument23 pages8 - Chemical Analysismostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - IAS - Organic Chemistry - 1Document21 pagesEdexcel - IAS - Organic Chemistry - 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit - 2 - Topic 1Document49 pagesEdexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit - 2 - Topic 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAS Energetics 1Document14 pagesEdexcel IAS Energetics 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - IAS - Itermolecular Forces - 1Document8 pagesEdexcel - IAS - Itermolecular Forces - 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - IAS - Group 2 and Group 7 - 1Document21 pagesEdexcel - IAS - Group 2 and Group 7 - 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - IAS - Chemical Analysis - 1Document12 pagesEdexcel - IAS - Chemical Analysis - 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - IAS - Organic Chemistry - 1Document27 pagesEdexcel - IAS - Organic Chemistry - 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAS Bonding 1Document14 pagesEdexcel IAS Bonding 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2019Document31 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2019clip215No ratings yet
- Revision - Worksheet - 2 Edexcel Chemistry IASDocument24 pagesRevision - Worksheet - 2 Edexcel Chemistry IASmostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Tuesday 4 June 2019: ChemistryDocument28 pagesTuesday 4 June 2019: Chemistrymostafa barakat25% (4)
- Examiners' Report Principal Examiner Feedback Summer 2019Document8 pagesExaminers' Report Principal Examiner Feedback Summer 2019mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - IAS - Atomic Structure - 1Document19 pagesEdexcel - IAS - Atomic Structure - 1mostafa barakat100% (2)
- Tuesday 4 June 2019: ChemistryDocument28 pagesTuesday 4 June 2019: Chemistrymostafa barakat25% (4)
- Tuesday 4 June 2019: ChemistryDocument28 pagesTuesday 4 June 2019: Chemistrymostafa barakat25% (4)
- Detergent Flushing of Pre Boiler System-Procedure 250Document11 pagesDetergent Flushing of Pre Boiler System-Procedure 250Sara LopezNo ratings yet
- M. Wolves 11Document7 pagesM. Wolves 11rakiny05No ratings yet
- Finished Goods Inventories XX Work in Progress XX To Record The Completed JobDocument6 pagesFinished Goods Inventories XX Work in Progress XX To Record The Completed JobClarissa TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Filtration Solution To Problems - Pdf-Midterm-Exam-AnswerDocument7 pagesFiltration Solution To Problems - Pdf-Midterm-Exam-AnswerDubu Kim100% (1)
- Islamic Architecture PDFDocument32 pagesIslamic Architecture PDFCamille CiokonNo ratings yet
- Marine Resources Landing Group Assignment 1-1Document22 pagesMarine Resources Landing Group Assignment 1-1Zhang LauNo ratings yet
- The Pure Land On Earth The Chronicles of PDFDocument9 pagesThe Pure Land On Earth The Chronicles of PDFBhikshu GovindaNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I Two Marks HMTDocument5 pagesUNIT - I Two Marks HMTHARI B SNo ratings yet
- Relate Tables, Graphs, and Equations: BatchesDocument2 pagesRelate Tables, Graphs, and Equations: Batchesahmeeeeeeeeee.expmdNo ratings yet
- D202466-18 UJF-3042HG, 6042 OperationManual eDocument160 pagesD202466-18 UJF-3042HG, 6042 OperationManual eAzure FistNo ratings yet
- Uv-Visibles Electronic TransitionDocument25 pagesUv-Visibles Electronic TransitionZareen Rashid Choudhury100% (1)
- Lesson 7B The PassDocument5 pagesLesson 7B The PassJessel GulfericaNo ratings yet
- Anyone Who Had A Heart - A Case Study in PhysiologyDocument9 pagesAnyone Who Had A Heart - A Case Study in PhysiologyJohnSnow0% (1)
- 1 Esdras (Ezra)Document20 pages1 Esdras (Ezra)Remus CalinaNo ratings yet
- Essential Orthopaedics 2Nd Edition Mark D Miller Full ChapterDocument67 pagesEssential Orthopaedics 2Nd Edition Mark D Miller Full Chaptermargaret.jones429100% (8)
- Stirling's FormulaDocument3 pagesStirling's FormulaAnnisa ZakiyaNo ratings yet
- Prerequisite For Service Entry Sheet SAP-FioriApp.Document4 pagesPrerequisite For Service Entry Sheet SAP-FioriApp.praveennbsNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Operations and Supply Chain Management For The 21st Century 1st Edition by BoyerDocument7 pagesSolution Manual For Operations and Supply Chain Management For The 21st Century 1st Edition by Boyergowdie.mornward.b50a100% (55)
- Holzer MethodDocument13 pagesHolzer Methodmeadot getachew100% (1)
- CV Pemateri - Kak Almadhia QisthinaDocument3 pagesCV Pemateri - Kak Almadhia QisthinaZidan DahlanNo ratings yet
- Metodo Hach HierroDocument6 pagesMetodo Hach HierroJESSICA VANESSA ARISMENDI AVILEZNo ratings yet
- Itext in Action 2Nd Edition: Chapter 4: Organizing Content in TablesDocument3 pagesItext in Action 2Nd Edition: Chapter 4: Organizing Content in Tablesalinux75No ratings yet
- PC/SC Partial Documentation of The API: PMDZ061-AE 24/09/2009Document32 pagesPC/SC Partial Documentation of The API: PMDZ061-AE 24/09/2009manskebe6121No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document Tofik ProposalDocument12 pagesNew Microsoft Word Document Tofik ProposalenbakomNo ratings yet
- Home - Link - 4.6 PerimeterDocument2 pagesHome - Link - 4.6 Perimetergiselle andalanNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 9Document25 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 9Randy Edrada0% (1)
- Manufacturing Planning and Control: MPC 6 EditionDocument44 pagesManufacturing Planning and Control: MPC 6 EditionSagar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Example #14 Tunnel With Concrete Lining: Civilfem Manual of Advanced Examples - Ingeciber, S.A.Document14 pagesExample #14 Tunnel With Concrete Lining: Civilfem Manual of Advanced Examples - Ingeciber, S.A.Andre OliveiraNo ratings yet