Professional Documents
Culture Documents
P15.1 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Magnets and Magnetic Fields
P15.1 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Magnets and Magnetic Fields
Uploaded by
Benjamin WatsonCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nicholls David One DayDocument112 pagesNicholls David One DayJuan Perez100% (6)
- P15 Tests ElectromagnetismDocument5 pagesP15 Tests ElectromagnetismAshleyNo ratings yet
- Gamma Ray Spectroscopy Lab ReportDocument15 pagesGamma Ray Spectroscopy Lab ReportLizelleNiit100% (1)
- P1.2 Student Practical: Bungee JumpingDocument6 pagesP1.2 Student Practical: Bungee JumpingAlenNo ratings yet
- Text BookDocument386 pagesText BookBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Oxo AQA16 P7uu T801 CsaannDocument10 pagesOxo AQA16 P7uu T801 CsaannemailusageNo ratings yet
- Rastrick School ElectromagneticDocument37 pagesRastrick School Electromagneticathmi SNo ratings yet
- P15.1 Buyg AnsDocument3 pagesP15.1 Buyg AnstholmesNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision SheetDocument21 pagesPhysics Revision SheetCAPTAIN COSM1CNo ratings yet
- Fields - QP IBDP PhysicsDocument9 pagesFields - QP IBDP PhysicsArham ShahNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - JanuaryExam2 QP (1) - 2Document11 pagesKami Export - JanuaryExam2 QP (1) - 2Vincey LuNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 1Document19 pagesPhysics Unit 1mariam saidNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument12 pagesMagnetism and ElectromagnetismJoyce LimNo ratings yet
- C9 WS 3 PHY ElectromagnetDocument5 pagesC9 WS 3 PHY ElectromagnetantokibaNo ratings yet
- Oxo AQA16 P1uu T801 XxaannDocument8 pagesOxo AQA16 P1uu T801 Xxaann4cpzx7fp52No ratings yet
- Revision Sheet - ForcesDocument49 pagesRevision Sheet - ForcesHoba BobaNo ratings yet
- 4.4 E and M FieldsDocument145 pages4.4 E and M FieldsMozammel AnowarNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction QuestionsDocument10 pagesReflection and Refraction QuestionsnguyentrongtinNo ratings yet
- P12.3 WSDocument4 pagesP12.3 WStholmesNo ratings yet
- Oxo AQA16 P4uu T401 XxaannDocument6 pagesOxo AQA16 P4uu T401 Xxaannsalt saltNo ratings yet
- SeismicWaves KerboodleDocument4 pagesSeismicWaves Kerboodlekavan.avnishNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Revision DoubleDocument40 pagesTopic 7 Revision DoubleHannah YeungNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 IB DP Physics Mock Exam - Chapters 1.1 - 4.1 QuestionsDocument29 pagesGrade 11 IB DP Physics Mock Exam - Chapters 1.1 - 4.1 QuestionsRahul RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Y S KX: (Total 1 Mark)Document5 pagesY S KX: (Total 1 Mark)Romeo SiriguNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields and Magnetism - Practice TestDocument5 pagesElectric Fields and Magnetism - Practice Testharkeerat singhNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionsDocument10 pagesRevision Questionshr3618720No ratings yet
- P3 Chapter 2 End-Of-Chapter Test (Higher)Document7 pagesP3 Chapter 2 End-Of-Chapter Test (Higher)Paul LloydNo ratings yet
- SH 4 G 7 Phy 3Document5 pagesSH 4 G 7 Phy 3pnppyfs8bqNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Magnetic Fields and Motor EffectDocument42 pages12.1 Magnetic Fields and Motor EffectNisali MendisNo ratings yet
- 11 Electromagnetism PPQs 2017-2018Document10 pages11 Electromagnetism PPQs 2017-2018Ethan Ruan [CH]No ratings yet
- Magnetic CompassDocument5 pagesMagnetic CompassjothipriyagNo ratings yet
- MyTest (18) - Electrical QuantitiesDocument19 pagesMyTest (18) - Electrical QuantitiesBazar Yalalt MainNo ratings yet
- PoS 2014Document103 pagesPoS 2014Ladla Prince MNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Combined FoundationDocument21 pagesMagnetism Combined FoundationJakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 & 17Document5 pagesChapter 16 & 17Adrián Castillo SantillánNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electricity and Magnetism: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Electricity and Magnetism: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIp_k_soni_iit_physicsNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics Practice Test 2Document6 pagesAstrophysics Practice Test 2sharm111069No ratings yet
- 3.7.5.2 Moving Charges in A Magnetic FieldDocument67 pages3.7.5.2 Moving Charges in A Magnetic Fieldtheolamey1No ratings yet
- James Ruse Agricultural High School: PhysicsDocument12 pagesJames Ruse Agricultural High School: PhysicsLisWeiNo ratings yet
- Electricity Worksheet Physics GcseDocument5 pagesElectricity Worksheet Physics Gcsetun1123tNo ratings yet
- Phy Rev MaterialDocument15 pagesPhy Rev Materiald.tharun37No ratings yet
- U1 Quantum Lattice GaugeDocument19 pagesU1 Quantum Lattice GaugeJohnson LiuNo ratings yet
- Physics Year 9 Mid-TermDocument9 pagesPhysics Year 9 Mid-TermPeter TaremwaNo ratings yet
- Crystal Nonlinear Optics With SNLO Examples (Arlee v. Smith)Document129 pagesCrystal Nonlinear Optics With SNLO Examples (Arlee v. Smith)xibolaj800No ratings yet
- 3foundation Transformers and Fields Self Study QuestionsDocument34 pages3foundation Transformers and Fields Self Study Questionswill bNo ratings yet
- Quasicrystals, C - Algebras and K-Theory: Fonger YpmaDocument132 pagesQuasicrystals, C - Algebras and K-Theory: Fonger YpmaAdele ZampellaNo ratings yet
- Izumiya - Differential Geometry From Singularity Theory Viewpoint PDFDocument383 pagesIzumiya - Differential Geometry From Singularity Theory Viewpoint PDFtatoes n lases100% (2)
- Oxo Aqa16 p8cs xq01 XxaannDocument6 pagesOxo Aqa16 p8cs xq01 XxaannAlt BoiNo ratings yet
- 3.3.2.2 DiffractionDocument69 pages3.3.2.2 Diffractionnewynaw75No ratings yet
- Magnetic Skyrmions: Theory and Applications: Lalla Btissam Drissi, El Hassan Saidi, Mosto Bousmina, Omar Fassi-FehriDocument36 pagesMagnetic Skyrmions: Theory and Applications: Lalla Btissam Drissi, El Hassan Saidi, Mosto Bousmina, Omar Fassi-FehriVictor AguilarNo ratings yet
- Workhseet 01 Annual TermDocument5 pagesWorkhseet 01 Annual Termtanvir.md.ahsanNo ratings yet
- Trace Anomaly Driven InflationDocument42 pagesTrace Anomaly Driven InflationKaustubhNo ratings yet
- Working As A Physicist - A Level Physics RevisionDocument73 pagesWorking As A Physicist - A Level Physics RevisionSaswata MohantaNo ratings yet
- 02 Fe 24842876Document5 pages02 Fe 24842876arikapralikNo ratings yet
- Y9D Waves test no answersDocument6 pagesY9D Waves test no answershydrochlorusNo ratings yet
- 3.7.5.1 Magnetic Flux DensityDocument24 pages3.7.5.1 Magnetic Flux Densitymata4cholNo ratings yet
- Special Relativity Worksheet, A-Level, IB, APDocument34 pagesSpecial Relativity Worksheet, A-Level, IB, APbobNo ratings yet
- AS Level Physics A Thursday 9 June 2016 - Afternoon: Time Allowed: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument20 pagesAS Level Physics A Thursday 9 June 2016 - Afternoon: Time Allowed: 1 Hour 30 MinutesTankioNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Time Allotted: 3hrs. Max. Marks: 70Document5 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Time Allotted: 3hrs. Max. Marks: 70varrshuNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkDocument10 pagesPIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Activity: What Is The Global Positioning System?Document3 pagesActivity: What Is The Global Positioning System?Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- PIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkDocument10 pagesPIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- This Is Where We Used To Live. Mei Daniel KeziahDocument1 pageThis Is Where We Used To Live. Mei Daniel KeziahBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 10,000 Reasons (Bless The Lord) : Chorus 1A G D A/C# BM G D A A G BM G A BM G A G/D D G/D DDocument2 pages10,000 Reasons (Bless The Lord) : Chorus 1A G D A/C# BM G D A A G BM G A BM G A G/D D G/D DBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Task 1 UR WITH ANSWERSDocument9 pagesTask 1 UR WITH ANSWERSBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources)Document6 pagesChapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources)Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Worked Solutions Higher Revision Pack 24.04.21Document35 pagesWorked Solutions Higher Revision Pack 24.04.21Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- NH (Aq) + Hno (Aq) NH No (Aq) Ammonia + Nitric Acid Ammonium NitrateDocument9 pagesNH (Aq) + Hno (Aq) NH No (Aq) Ammonia + Nitric Acid Ammonium NitrateBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- AQA Gcse Chemistry Unit C10 Revision (Using Resources)Document53 pagesAQA Gcse Chemistry Unit C10 Revision (Using Resources)Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Making Fertiliser Practical SheetDocument3 pagesMaking Fertiliser Practical SheetBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Topic: Using The Earth's Resources: Water WaterDocument8 pagesTopic: Using The Earth's Resources: Water WaterBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources) : Tasks 2Document6 pagesChapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources) : Tasks 2Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 13.6 Gene Expression and Mutation (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsDocument28 pages13.6 Gene Expression and Mutation (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 13.4 Why Does The Genome Matter WorksheetDocument3 pages13.4 Why Does The Genome Matter WorksheetBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Using Materials Questions For LS Revision Quick Fire QuestionsDocument2 pagesUsing Materials Questions For LS Revision Quick Fire QuestionsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 13.3 Exam QuestionsDocument6 pages13.3 Exam QuestionsBenjamin Watson100% (1)
- Chemsheets GCSE 111 (Haber Process)Document1 pageChemsheets GCSE 111 (Haber Process)Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: B13.4 DNA and The Human Genome Project: Connector: Questions On Prior Learning Linked To Todays LessonDocument46 pagesLesson Title: B13.4 DNA and The Human Genome Project: Connector: Questions On Prior Learning Linked To Todays LessonBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Haber Process Task 2Document6 pagesHaber Process Task 2Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Energy-Efficient and Book Mountain Public Library of Urdaneta CityDocument142 pagesEnergy-Efficient and Book Mountain Public Library of Urdaneta CityDarwin PaladoNo ratings yet
- Natres Pe Benito MidtermsDocument27 pagesNatres Pe Benito MidtermsJay TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 Ramsey ModelDocument34 pagesCh.2 Ramsey ModelDimitris HatzidimosNo ratings yet
- Lab Diagnosis of NeoplasiaDocument14 pagesLab Diagnosis of Neoplasiasapphiresia100% (6)
- AP World History Summer AssignmentDocument9 pagesAP World History Summer AssignmentAnonymous tvG8tBNo ratings yet
- DHI-KTP01 Datasheet 20200218 PDFDocument3 pagesDHI-KTP01 Datasheet 20200218 PDFDeltaz AZNo ratings yet
- End-Time Events and The Last Generation by George R Knight Z-LiborgDocument138 pagesEnd-Time Events and The Last Generation by George R Knight Z-LiborgyaneciticaNo ratings yet
- DDAL5-17 - Hartkiller's HornDocument34 pagesDDAL5-17 - Hartkiller's HornDarian MacCuish-Rudderham0% (2)
- Rak25nh5 Service ManualDocument112 pagesRak25nh5 Service ManualbastienargaudNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Leader Recr 2015Document1 pageFiitjee Leader Recr 2015Mahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Modified Revised Leave Rules 1981Document44 pagesModified Revised Leave Rules 1981Mohsina TariqNo ratings yet
- Ada Blackjack Answers (11-09-2021)Document4 pagesAda Blackjack Answers (11-09-2021)Blob BlobbyNo ratings yet
- Manual de Motor Fuera de Borda Mercury XP 115 ProDocument150 pagesManual de Motor Fuera de Borda Mercury XP 115 ProGestión De MantenimientoNo ratings yet
- Ipcc Law Case Studies 2Document12 pagesIpcc Law Case Studies 2Vaibhav MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Bio ResonanceDocument32 pagesBio ResonanceJuan Pablo RosasNo ratings yet
- 3 Grade: Unit of Study 1 Elements of Drama-Script Quarter 1 Key Concepts: SkillsDocument4 pages3 Grade: Unit of Study 1 Elements of Drama-Script Quarter 1 Key Concepts: SkillsSheila Mae Cordero TabuenaNo ratings yet
- WMT PPT 4Document15 pagesWMT PPT 4SamNo ratings yet
- Concept of Developmental LinesDocument5 pagesConcept of Developmental LinesJuan PabloNo ratings yet
- Rút Gọn Câu Dùng Having V3: I. Rewrite The Sentences, Using Perfect ParticiplesDocument6 pagesRút Gọn Câu Dùng Having V3: I. Rewrite The Sentences, Using Perfect ParticiplesKỳ Anh PhạmNo ratings yet
- Laporan UPGRIS, 24 Sept 21Document61 pagesLaporan UPGRIS, 24 Sept 21hastrirosiyanti14No ratings yet
- Ashirvad uPVC Casing PipesDocument2 pagesAshirvad uPVC Casing PipeskalloliNo ratings yet
- AAVV, Future Husserlian PhenomenologyDocument175 pagesAAVV, Future Husserlian Phenomenologybrevi1100% (1)
- Babylonian Magic and Sorcery by Leonard W. KingDocument388 pagesBabylonian Magic and Sorcery by Leonard W. KingSteven St.ThomasNo ratings yet
- Wearable Technologies: Scott Mcgregor President & Ceo, Broadcom CorporationDocument23 pagesWearable Technologies: Scott Mcgregor President & Ceo, Broadcom CorporationRavi PilgarNo ratings yet
- Oral Health ProgramDocument11 pagesOral Health Programapi-233877887No ratings yet
- Design of A Material Handling Equipment: Belt Conveyor System For Crushed Limestone Using 3 Roll IdlersDocument10 pagesDesign of A Material Handling Equipment: Belt Conveyor System For Crushed Limestone Using 3 Roll IdlersJake OkuyeNo ratings yet
- Kusudama MeteoroidDocument24 pagesKusudama MeteoroidRaffaela LinetzkyNo ratings yet
- The Old Man and Two GoatsDocument13 pagesThe Old Man and Two GoatshassNo ratings yet
- 4in1 Template Item Analysis With MPS Mastery Level Frequency of Errors 1 NCR3Document5 pages4in1 Template Item Analysis With MPS Mastery Level Frequency of Errors 1 NCR3Babette CeletariaNo ratings yet
P15.1 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Magnets and Magnetic Fields
P15.1 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Magnets and Magnetic Fields
Uploaded by
Benjamin WatsonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
P15.1 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Magnets and Magnetic Fields
P15.1 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Magnets and Magnetic Fields
Uploaded by
Benjamin WatsonCopyright:
Available Formats
P15.
1
Student bump up your grade
Name....................................................................... Class................... Date......................
Magnets and magnetic fields
Specification reference:
P7.1 Permanent and induced magnetism, magnetic forces and fields
Aims
In this exercise you will cover the nature and behaviour of magnets and
magnetism. You will answer questions relating to magnetic fields and the nature
of permanent and induced magnetism. You will also look at the uses of
magnetism in the everyday world and the way in which magnetism provided
evidence for scientists about how the Earth has changed over many thousands
of years.
Learning outcomes
After completing this activity, you should be able to:
state the names of the magnetic poles
label the magnetic field that is produced around various magnetic materials
describe how magnets behave and link this to magnetic field lines
describe the difference between permanent and induced magnetism
apply an understanding of magnetism to ideas about the Earth
explain why magnetic materials, e.g. iron or nickel, can be picked up by a magnet.
Questions
1 Complete the following sentences by filling in the gaps with the words in
the box.
Attract North (N) repel compass South (S)
Like poles will ____________ .
Unlike poles will ____________ .
Lines of magnetic force come out of the ____________ Pole and go into the
____________ Pole.
Lines of magnetic field can be plotted using a ____________. (5 marks)
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 1
P15.1
Student bump up your grade
Name....................................................................... Class................... Date......................
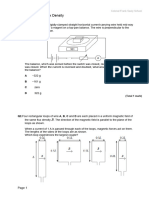
2 Two magnets are brought close together as shown. Explain what will happen.
(3 marks)
3 Look at the magnets below. Draw in the missing field lines either around the
magnet or between the poles of the magnet, showing the shape and the
direction.
a (3 marks)
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 2
P15.1
Student bump up your grade
Name....................................................................... Class................... Date......................
b (3 marks)
4 Use the artwork below to help you to fill in the gaps in the text that follows.
A magnet that has a N pole and a S pole all of the time is called a ____________
magnet. If this magnet is placed near a piece of iron, then the pole nearest to the
end of the iron bar will ____________ the ____________ pole at that point. For
example, if a N pole is placed near it, then it will become a ____________ pole
and it will be ____________by the N pole of the magnet. (5 marks)
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 3
P15.1
Student bump up your grade
Name....................................................................... Class................... Date......................
5 The table shows some examples of magnetism.
(9 marks)
Permanent Temporary Induced
Example
magnetism magnetism magnetism
a Iron paper clips
being picked up by a
magnet
b A coil of wire rotating
inside a motor
c An electric bell
working when
pressed
d An electromagnet
being used to pick
up scrap
e The Earth’s
magnetic field
Explain the behaviour shown by referring to any permanent magnets,
temporary magnets, and induced magnets that are being used.
(2 marks)
(2 marks)
(2 marks)
(2 marks)
e (1 mark)
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 4
P15.1
Student bump up your grade
Name....................................................................... Class................... Date......................
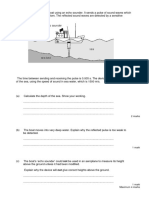
6 The Earth has a magnetic field as shown.
a Explain how scientists know that the Earth has its own magnetic field.
(1 mark)
b Fill in the missing magnetic field lines on the diagram, showing their direction.
(3 marks)
c Every ten thousand years or so, the Earth’s magnetic field changes
direction. Suggest how scientists know that this happens.
(1 mark)
d Explain how a change in field direction might impact on animals.
(2 marks)
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 5
You might also like
- Nicholls David One DayDocument112 pagesNicholls David One DayJuan Perez100% (6)
- P15 Tests ElectromagnetismDocument5 pagesP15 Tests ElectromagnetismAshleyNo ratings yet
- Gamma Ray Spectroscopy Lab ReportDocument15 pagesGamma Ray Spectroscopy Lab ReportLizelleNiit100% (1)
- P1.2 Student Practical: Bungee JumpingDocument6 pagesP1.2 Student Practical: Bungee JumpingAlenNo ratings yet
- Text BookDocument386 pagesText BookBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Oxo AQA16 P7uu T801 CsaannDocument10 pagesOxo AQA16 P7uu T801 CsaannemailusageNo ratings yet
- Rastrick School ElectromagneticDocument37 pagesRastrick School Electromagneticathmi SNo ratings yet
- P15.1 Buyg AnsDocument3 pagesP15.1 Buyg AnstholmesNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision SheetDocument21 pagesPhysics Revision SheetCAPTAIN COSM1CNo ratings yet
- Fields - QP IBDP PhysicsDocument9 pagesFields - QP IBDP PhysicsArham ShahNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - JanuaryExam2 QP (1) - 2Document11 pagesKami Export - JanuaryExam2 QP (1) - 2Vincey LuNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 1Document19 pagesPhysics Unit 1mariam saidNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument12 pagesMagnetism and ElectromagnetismJoyce LimNo ratings yet
- C9 WS 3 PHY ElectromagnetDocument5 pagesC9 WS 3 PHY ElectromagnetantokibaNo ratings yet
- Oxo AQA16 P1uu T801 XxaannDocument8 pagesOxo AQA16 P1uu T801 Xxaann4cpzx7fp52No ratings yet
- Revision Sheet - ForcesDocument49 pagesRevision Sheet - ForcesHoba BobaNo ratings yet
- 4.4 E and M FieldsDocument145 pages4.4 E and M FieldsMozammel AnowarNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction QuestionsDocument10 pagesReflection and Refraction QuestionsnguyentrongtinNo ratings yet
- P12.3 WSDocument4 pagesP12.3 WStholmesNo ratings yet
- Oxo AQA16 P4uu T401 XxaannDocument6 pagesOxo AQA16 P4uu T401 Xxaannsalt saltNo ratings yet
- SeismicWaves KerboodleDocument4 pagesSeismicWaves Kerboodlekavan.avnishNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Revision DoubleDocument40 pagesTopic 7 Revision DoubleHannah YeungNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 IB DP Physics Mock Exam - Chapters 1.1 - 4.1 QuestionsDocument29 pagesGrade 11 IB DP Physics Mock Exam - Chapters 1.1 - 4.1 QuestionsRahul RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Y S KX: (Total 1 Mark)Document5 pagesY S KX: (Total 1 Mark)Romeo SiriguNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields and Magnetism - Practice TestDocument5 pagesElectric Fields and Magnetism - Practice Testharkeerat singhNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionsDocument10 pagesRevision Questionshr3618720No ratings yet
- P3 Chapter 2 End-Of-Chapter Test (Higher)Document7 pagesP3 Chapter 2 End-Of-Chapter Test (Higher)Paul LloydNo ratings yet
- SH 4 G 7 Phy 3Document5 pagesSH 4 G 7 Phy 3pnppyfs8bqNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Magnetic Fields and Motor EffectDocument42 pages12.1 Magnetic Fields and Motor EffectNisali MendisNo ratings yet
- 11 Electromagnetism PPQs 2017-2018Document10 pages11 Electromagnetism PPQs 2017-2018Ethan Ruan [CH]No ratings yet
- Magnetic CompassDocument5 pagesMagnetic CompassjothipriyagNo ratings yet
- MyTest (18) - Electrical QuantitiesDocument19 pagesMyTest (18) - Electrical QuantitiesBazar Yalalt MainNo ratings yet
- PoS 2014Document103 pagesPoS 2014Ladla Prince MNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Combined FoundationDocument21 pagesMagnetism Combined FoundationJakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 & 17Document5 pagesChapter 16 & 17Adrián Castillo SantillánNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electricity and Magnetism: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Electricity and Magnetism: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIp_k_soni_iit_physicsNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics Practice Test 2Document6 pagesAstrophysics Practice Test 2sharm111069No ratings yet
- 3.7.5.2 Moving Charges in A Magnetic FieldDocument67 pages3.7.5.2 Moving Charges in A Magnetic Fieldtheolamey1No ratings yet
- James Ruse Agricultural High School: PhysicsDocument12 pagesJames Ruse Agricultural High School: PhysicsLisWeiNo ratings yet
- Electricity Worksheet Physics GcseDocument5 pagesElectricity Worksheet Physics Gcsetun1123tNo ratings yet
- Phy Rev MaterialDocument15 pagesPhy Rev Materiald.tharun37No ratings yet
- U1 Quantum Lattice GaugeDocument19 pagesU1 Quantum Lattice GaugeJohnson LiuNo ratings yet
- Physics Year 9 Mid-TermDocument9 pagesPhysics Year 9 Mid-TermPeter TaremwaNo ratings yet
- Crystal Nonlinear Optics With SNLO Examples (Arlee v. Smith)Document129 pagesCrystal Nonlinear Optics With SNLO Examples (Arlee v. Smith)xibolaj800No ratings yet
- 3foundation Transformers and Fields Self Study QuestionsDocument34 pages3foundation Transformers and Fields Self Study Questionswill bNo ratings yet
- Quasicrystals, C - Algebras and K-Theory: Fonger YpmaDocument132 pagesQuasicrystals, C - Algebras and K-Theory: Fonger YpmaAdele ZampellaNo ratings yet
- Izumiya - Differential Geometry From Singularity Theory Viewpoint PDFDocument383 pagesIzumiya - Differential Geometry From Singularity Theory Viewpoint PDFtatoes n lases100% (2)
- Oxo Aqa16 p8cs xq01 XxaannDocument6 pagesOxo Aqa16 p8cs xq01 XxaannAlt BoiNo ratings yet
- 3.3.2.2 DiffractionDocument69 pages3.3.2.2 Diffractionnewynaw75No ratings yet
- Magnetic Skyrmions: Theory and Applications: Lalla Btissam Drissi, El Hassan Saidi, Mosto Bousmina, Omar Fassi-FehriDocument36 pagesMagnetic Skyrmions: Theory and Applications: Lalla Btissam Drissi, El Hassan Saidi, Mosto Bousmina, Omar Fassi-FehriVictor AguilarNo ratings yet
- Workhseet 01 Annual TermDocument5 pagesWorkhseet 01 Annual Termtanvir.md.ahsanNo ratings yet
- Trace Anomaly Driven InflationDocument42 pagesTrace Anomaly Driven InflationKaustubhNo ratings yet
- Working As A Physicist - A Level Physics RevisionDocument73 pagesWorking As A Physicist - A Level Physics RevisionSaswata MohantaNo ratings yet
- 02 Fe 24842876Document5 pages02 Fe 24842876arikapralikNo ratings yet
- Y9D Waves test no answersDocument6 pagesY9D Waves test no answershydrochlorusNo ratings yet
- 3.7.5.1 Magnetic Flux DensityDocument24 pages3.7.5.1 Magnetic Flux Densitymata4cholNo ratings yet
- Special Relativity Worksheet, A-Level, IB, APDocument34 pagesSpecial Relativity Worksheet, A-Level, IB, APbobNo ratings yet
- AS Level Physics A Thursday 9 June 2016 - Afternoon: Time Allowed: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument20 pagesAS Level Physics A Thursday 9 June 2016 - Afternoon: Time Allowed: 1 Hour 30 MinutesTankioNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Time Allotted: 3hrs. Max. Marks: 70Document5 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Time Allotted: 3hrs. Max. Marks: 70varrshuNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkDocument10 pagesPIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Activity: What Is The Global Positioning System?Document3 pagesActivity: What Is The Global Positioning System?Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- PIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkDocument10 pagesPIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- This Is Where We Used To Live. Mei Daniel KeziahDocument1 pageThis Is Where We Used To Live. Mei Daniel KeziahBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 10,000 Reasons (Bless The Lord) : Chorus 1A G D A/C# BM G D A A G BM G A BM G A G/D D G/D DDocument2 pages10,000 Reasons (Bless The Lord) : Chorus 1A G D A/C# BM G D A A G BM G A BM G A G/D D G/D DBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Task 1 UR WITH ANSWERSDocument9 pagesTask 1 UR WITH ANSWERSBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources)Document6 pagesChapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources)Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Worked Solutions Higher Revision Pack 24.04.21Document35 pagesWorked Solutions Higher Revision Pack 24.04.21Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- NH (Aq) + Hno (Aq) NH No (Aq) Ammonia + Nitric Acid Ammonium NitrateDocument9 pagesNH (Aq) + Hno (Aq) NH No (Aq) Ammonia + Nitric Acid Ammonium NitrateBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- AQA Gcse Chemistry Unit C10 Revision (Using Resources)Document53 pagesAQA Gcse Chemistry Unit C10 Revision (Using Resources)Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Making Fertiliser Practical SheetDocument3 pagesMaking Fertiliser Practical SheetBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Topic: Using The Earth's Resources: Water WaterDocument8 pagesTopic: Using The Earth's Resources: Water WaterBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources) : Tasks 2Document6 pagesChapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources) : Tasks 2Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 13.6 Gene Expression and Mutation (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsDocument28 pages13.6 Gene Expression and Mutation (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 13.4 Why Does The Genome Matter WorksheetDocument3 pages13.4 Why Does The Genome Matter WorksheetBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Using Materials Questions For LS Revision Quick Fire QuestionsDocument2 pagesUsing Materials Questions For LS Revision Quick Fire QuestionsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 13.3 Exam QuestionsDocument6 pages13.3 Exam QuestionsBenjamin Watson100% (1)
- Chemsheets GCSE 111 (Haber Process)Document1 pageChemsheets GCSE 111 (Haber Process)Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: B13.4 DNA and The Human Genome Project: Connector: Questions On Prior Learning Linked To Todays LessonDocument46 pagesLesson Title: B13.4 DNA and The Human Genome Project: Connector: Questions On Prior Learning Linked To Todays LessonBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Haber Process Task 2Document6 pagesHaber Process Task 2Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Energy-Efficient and Book Mountain Public Library of Urdaneta CityDocument142 pagesEnergy-Efficient and Book Mountain Public Library of Urdaneta CityDarwin PaladoNo ratings yet
- Natres Pe Benito MidtermsDocument27 pagesNatres Pe Benito MidtermsJay TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 Ramsey ModelDocument34 pagesCh.2 Ramsey ModelDimitris HatzidimosNo ratings yet
- Lab Diagnosis of NeoplasiaDocument14 pagesLab Diagnosis of Neoplasiasapphiresia100% (6)
- AP World History Summer AssignmentDocument9 pagesAP World History Summer AssignmentAnonymous tvG8tBNo ratings yet
- DHI-KTP01 Datasheet 20200218 PDFDocument3 pagesDHI-KTP01 Datasheet 20200218 PDFDeltaz AZNo ratings yet
- End-Time Events and The Last Generation by George R Knight Z-LiborgDocument138 pagesEnd-Time Events and The Last Generation by George R Knight Z-LiborgyaneciticaNo ratings yet
- DDAL5-17 - Hartkiller's HornDocument34 pagesDDAL5-17 - Hartkiller's HornDarian MacCuish-Rudderham0% (2)
- Rak25nh5 Service ManualDocument112 pagesRak25nh5 Service ManualbastienargaudNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Leader Recr 2015Document1 pageFiitjee Leader Recr 2015Mahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Modified Revised Leave Rules 1981Document44 pagesModified Revised Leave Rules 1981Mohsina TariqNo ratings yet
- Ada Blackjack Answers (11-09-2021)Document4 pagesAda Blackjack Answers (11-09-2021)Blob BlobbyNo ratings yet
- Manual de Motor Fuera de Borda Mercury XP 115 ProDocument150 pagesManual de Motor Fuera de Borda Mercury XP 115 ProGestión De MantenimientoNo ratings yet
- Ipcc Law Case Studies 2Document12 pagesIpcc Law Case Studies 2Vaibhav MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Bio ResonanceDocument32 pagesBio ResonanceJuan Pablo RosasNo ratings yet
- 3 Grade: Unit of Study 1 Elements of Drama-Script Quarter 1 Key Concepts: SkillsDocument4 pages3 Grade: Unit of Study 1 Elements of Drama-Script Quarter 1 Key Concepts: SkillsSheila Mae Cordero TabuenaNo ratings yet
- WMT PPT 4Document15 pagesWMT PPT 4SamNo ratings yet
- Concept of Developmental LinesDocument5 pagesConcept of Developmental LinesJuan PabloNo ratings yet
- Rút Gọn Câu Dùng Having V3: I. Rewrite The Sentences, Using Perfect ParticiplesDocument6 pagesRút Gọn Câu Dùng Having V3: I. Rewrite The Sentences, Using Perfect ParticiplesKỳ Anh PhạmNo ratings yet
- Laporan UPGRIS, 24 Sept 21Document61 pagesLaporan UPGRIS, 24 Sept 21hastrirosiyanti14No ratings yet
- Ashirvad uPVC Casing PipesDocument2 pagesAshirvad uPVC Casing PipeskalloliNo ratings yet
- AAVV, Future Husserlian PhenomenologyDocument175 pagesAAVV, Future Husserlian Phenomenologybrevi1100% (1)
- Babylonian Magic and Sorcery by Leonard W. KingDocument388 pagesBabylonian Magic and Sorcery by Leonard W. KingSteven St.ThomasNo ratings yet
- Wearable Technologies: Scott Mcgregor President & Ceo, Broadcom CorporationDocument23 pagesWearable Technologies: Scott Mcgregor President & Ceo, Broadcom CorporationRavi PilgarNo ratings yet
- Oral Health ProgramDocument11 pagesOral Health Programapi-233877887No ratings yet
- Design of A Material Handling Equipment: Belt Conveyor System For Crushed Limestone Using 3 Roll IdlersDocument10 pagesDesign of A Material Handling Equipment: Belt Conveyor System For Crushed Limestone Using 3 Roll IdlersJake OkuyeNo ratings yet
- Kusudama MeteoroidDocument24 pagesKusudama MeteoroidRaffaela LinetzkyNo ratings yet
- The Old Man and Two GoatsDocument13 pagesThe Old Man and Two GoatshassNo ratings yet
- 4in1 Template Item Analysis With MPS Mastery Level Frequency of Errors 1 NCR3Document5 pages4in1 Template Item Analysis With MPS Mastery Level Frequency of Errors 1 NCR3Babette CeletariaNo ratings yet