Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Defining Performance Measurement
Defining Performance Measurement
Uploaded by
Charice Anne VillamarinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Defining Performance Measurement
Defining Performance Measurement
Uploaded by
Charice Anne VillamarinCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 11
Performance Measurement
Defining performance measurement
Performance measurement is the process of evaluating how well organizations are managed and the value they deliver
for customers and other stakeholders. For the improvement within the business operations, it is important to have the
performance measured or quantified, and have the individual receive feedbacks. Feedback is having the outcomes of work
communicated to the employee, work group, or company. Through performance measurement, we can evaluate whether
our business operations and processes are effective to guarantee success and achievement of goals.
Types of performance measures
Performance measures can be grouped into two basic types: those that relate to results (outputs or outcomes such as
competitiveness or financial performance) and those that focus on the determinants of the results (inputs such as quality,
flexibility, resource utilization, and innovation).
In the business operations, performance can be measure using productivity measures, quality measures, inventory
measures, lead-time measures, preventive maintenance, performance to schedule, and utilization. Specific measures
could include:
• Cost of quality—measured as budgeted versus actual.
• Variances— measured as standard absorbed cost versus actual expenses.
• Period expenses— measured as budgeted versus actual expenses.
• Safety— measured on some common scale such as number of hours without an accident.
• Profit contribution— measured in dollars or some common scale.
• Inventory turnover— measured as actual versus budgeted turnover.
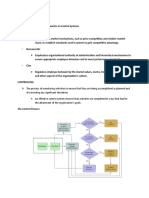
Designing the performance measurement system
Wisner and Fawcett provide a nine-step process for developing a performance measurement system:
1. Clearly define the firm's mission statement.
2. Identify the firm's strategic objectives using the mission statement as a guide (profitability, market share, quality,
cost, flexibility, dependability, and innovation).
3. Develop an understanding of each functional area's role in achieving the various strategic objectives.
4. For each functional area, develop global performance measures capable of defining the firm's overall competitive
position to top management.
5. Communicate strategic objectives and performance goals to lower levels in the organization. Establish more
specific performance criteria at each level.
6. Assure consistency with strategic objectives among the performance criteria used at each level.
7. Assure the compatibility of performance measures used in all functional areas.
8. Use the performance measurement system to identify competition, locate problem areas, assist the firm in
updating strategic objectives and making tactical decisions to achieve these objectives, and supply feedback after
the decisions are implemented.
9. Periodically reevaluate the appropriateness of the established performance measurement system in view of the
current competitive environment
Reference used:
• Performance Measurement. https://www.referenceforbusiness.com/management/Or-Pr/Performance-
Measurement.html
• Thompson M., Definition of Performance Measurement. https://smallbusiness.chron.com/definition-performance-
measurement-45759.html
You might also like
- Operation Management ReviewerDocument10 pagesOperation Management ReviewerMebelle LoronoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Problem - SolutionDocument9 pagesQuiz 2 Problem - SolutionCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Corporations in Financial Difficulty: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument26 pagesCorporations in Financial Difficulty: Multiple Choice QuestionsInsatiable LifeNo ratings yet
- Build Operate Transfer (Bot)Document8 pagesBuild Operate Transfer (Bot)aparnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Strategy, Balanced Scorecard, and Strategic Profitability AnalysisDocument5 pagesChapter 13 Strategy, Balanced Scorecard, and Strategic Profitability AnalysisdamayNo ratings yet
- TQM Chapter 7 Performance Measures RevisedDocument15 pagesTQM Chapter 7 Performance Measures RevisedHaziiMughal100% (1)
- MODULE 5 Strategic ManagementDocument18 pagesMODULE 5 Strategic ManagementRintu RajeshNo ratings yet
- Performance Measurement and Information ManagementDocument32 pagesPerformance Measurement and Information ManagementJoe GarciaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 3Document6 pagesAssignment - 3karthikNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Performance Measurement: ObjectivesDocument16 pagesUnit 9 Performance Measurement: ObjectivesAnonymous 6iIGqlDMNo ratings yet
- AMA - Essay 5Document9 pagesAMA - Essay 5Deborah WilliamsNo ratings yet
- CHPT V ST EvaluationDocument58 pagesCHPT V ST EvaluationYared BitewNo ratings yet
- Performance Measurement: Lesson StructureDocument9 pagesPerformance Measurement: Lesson StructureAnkur DhirNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Performance ManagementDocument33 pagesSupply Chain Performance ManagementDebashishDolon100% (1)
- Strategic EvaluationDocument4 pagesStrategic EvaluationMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Speech Sobre Los ValoresDocument11 pagesSpeech Sobre Los ValoresmakkrzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document6 pagesChapter 7Glace AbellanaNo ratings yet
- Quality Management SystemDocument11 pagesQuality Management SystemSTEM 11.2No ratings yet
- Measurement and Cost of QualityDocument11 pagesMeasurement and Cost of QualityNaukhezIlyasNo ratings yet
- MBA0210 EBS 10 Performance ManagementDocument38 pagesMBA0210 EBS 10 Performance ManagementjairamhalNo ratings yet
- Operations and Supply SummariesDocument7 pagesOperations and Supply SummariesHuten VasellNo ratings yet
- Performance MeasurementDocument5 pagesPerformance MeasurementSangamesh UmasankarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2Document46 pagesChapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2JeSsica Joy P. SantiagoNo ratings yet
- RCM-5 TH UnitDocument13 pagesRCM-5 TH UnitPoovarasan KarnanNo ratings yet
- Acc7 Perf MeasuresDocument7 pagesAcc7 Perf MeasuresZerjo CantalejoNo ratings yet
- Data-Driven ManagementDocument31 pagesData-Driven Managementpretti situmeangNo ratings yet
- Effective ProcessDocument16 pagesEffective Processajelena83No ratings yet
- Core Processes in TQMDocument5 pagesCore Processes in TQMĐiền Lê GiaNo ratings yet
- Group 12 CBMEDocument42 pagesGroup 12 CBMEReynaNo ratings yet
- Controlling 12Document27 pagesControlling 12Muhammed RashidNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Performance ManagementDocument19 pagesGroup 2 - Performance ManagementCARLYN JANE SALVADORNo ratings yet
- NAME: M.FARAZ ALI (MBF1800284) CLASS: MBA3.5 Year SESSION: 2018-2022 Submitted To: Sir Awais University of Education, Lower Mall Campus, LahoreDocument6 pagesNAME: M.FARAZ ALI (MBF1800284) CLASS: MBA3.5 Year SESSION: 2018-2022 Submitted To: Sir Awais University of Education, Lower Mall Campus, LahoregulafshanNo ratings yet
- Putting Balanced Scorecard To Work Group 8Document3 pagesPutting Balanced Scorecard To Work Group 8Rohan Rai100% (1)
- By Sreelatha Sd. Thahaseen Venkatesh V Vinod JDocument34 pagesBy Sreelatha Sd. Thahaseen Venkatesh V Vinod JVin odNo ratings yet
- Balanced Score Card:: Performance ManagementDocument4 pagesBalanced Score Card:: Performance Managementtappu0410No ratings yet
- CONTROLDocument5 pagesCONTROLkiborNo ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument6 pagesBudgetingHasnat AsifNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - Activity 1Document3 pagesStrategic Management - Activity 1CooleenNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial Management-Balanced Score Card: Assignment-2Document19 pagesStrategic Financial Management-Balanced Score Card: Assignment-2jhafjfNo ratings yet
- GrouP 2 PresentationDocument19 pagesGrouP 2 Presentationcy lifeNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Rewarding Performance-Pay For Performance - Challenges - Meeting The Challenges For Pay - For - Performance SystemsDocument25 pagesUnit Ii Rewarding Performance-Pay For Performance - Challenges - Meeting The Challenges For Pay - For - Performance SystemsmanojNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Performance Measurement and NonDocument9 pagesA Guide To Performance Measurement and NonmohammadhadiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PMS Non-Financial MeasuresDocument10 pagesTutorial PMS Non-Financial MeasuresAisyah ShahidanNo ratings yet
- Operations Management 1 - BeaDocument27 pagesOperations Management 1 - BeaBea Renela Gabinete ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Performance Measures: 1. Measuring and Improving PerformanceDocument9 pagesPerformance Measures: 1. Measuring and Improving PerformanceTerry Jieyu ZhangNo ratings yet
- Epm PresentationDocument60 pagesEpm PresentationAkanksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Balanced ScorecardDocument45 pagesBalanced ScorecardKshitij TyagiNo ratings yet
- When You Can Measure What You Are Speaking About and Express It in Numbers, You Know Something About It'Document10 pagesWhen You Can Measure What You Are Speaking About and Express It in Numbers, You Know Something About It'Mani KandanNo ratings yet
- BSCDocument31 pagesBSCRashed MiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document2 pagesChapter 9Sara khanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank With Answer EpmDocument14 pagesQuestion Bank With Answer Epmspteck1415No ratings yet
- DPS 401 (Day)Document25 pagesDPS 401 (Day)Deqah Mumtaz GacalNo ratings yet
- Perspectives in Balanced ScorecardDocument6 pagesPerspectives in Balanced ScorecardInah SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Performance and Evaluation of Manufacturing SystemsDocument16 pagesPerformance and Evaluation of Manufacturing SystemsMochammad Ridwan Aditya100% (1)
- CTEA 3227 Management Accounting III Topic 7 Performance Management Systems 2 (Contemporary Approach)Document36 pagesCTEA 3227 Management Accounting III Topic 7 Performance Management Systems 2 (Contemporary Approach)Nero ShaNo ratings yet
- SOM Unit IDocument16 pagesSOM Unit Ishabeena ShahNo ratings yet
- Controlling: Source: Management - A Global Perspective by Weihrich and Koontz 11 EditionDocument26 pagesControlling: Source: Management - A Global Perspective by Weihrich and Koontz 11 EditionMaritoni MercadoNo ratings yet
- LECTURE-3 Non-Financial Performance MeasuresDocument8 pagesLECTURE-3 Non-Financial Performance MeasuresHarusiNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting EssayDocument8 pagesManagerial Accounting EssayPatrick PetitNo ratings yet
- Performance MeasurementDocument22 pagesPerformance MeasurementPrakash KNo ratings yet
- Strategic Control and OutsourcingDocument5 pagesStrategic Control and OutsourcingSandeep KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Performance Measures: Marc Lester Jose Laureana Veronika S. VicedoDocument31 pagesPerformance Measures: Marc Lester Jose Laureana Veronika S. VicedoManikandan100% (1)
- The Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successFrom EverandThe Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Life Problem: Direct Killing of Oneself On One's Own AuthorityDocument20 pagesLife Problem: Direct Killing of Oneself On One's Own AuthorityCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Module 13Document11 pagesModule 13Charice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument2 pagesSupply Chain ManagementCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- 1st Preliminary LecturesDocument33 pages1st Preliminary LecturesCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Table Tennis Equipment and FacilitiesDocument7 pagesTable Tennis Equipment and FacilitiesCharice Anne Villamarin100% (1)
- Problem Set 1 Problem SolvingDocument1 pageProblem Set 1 Problem SolvingCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Investment in AssociateDocument7 pagesModule 1 Investment in AssociateCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Uself Midterm LectureDocument21 pagesUself Midterm LectureCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Sinking Fund and DerivativesDocument4 pagesSinking Fund and DerivativesCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Investment Property and FundsDocument6 pagesModule 2 Investment Property and FundsCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Eastern and WesternDocument39 pagesEastern and WesternCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 2: Problem 1Document1 pageActivity No. 2: Problem 1Charice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- 2.3-Manufacturing Overhead (Answer Key)Document3 pages2.3-Manufacturing Overhead (Answer Key)Charice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Controlling Material FlowDocument2 pagesControlling Material FlowCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- MODULE DWCC - Obligation and Contracts Part3 OnlineDocument8 pagesMODULE DWCC - Obligation and Contracts Part3 OnlineCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- MODULE DWCC - Obligation and Contracts Part1 OnlineDocument17 pagesMODULE DWCC - Obligation and Contracts Part1 OnlineCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Module 4.1 Consumption TheoryDocument12 pagesModule 4.1 Consumption TheoryCharice Anne Villamarin100% (1)
- Module 5 The Theory of Cost and ProfitDocument22 pagesModule 5 The Theory of Cost and ProfitCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- MODULE DWCC - Obligation and Contracts Part2 OnlineDocument15 pagesMODULE DWCC - Obligation and Contracts Part2 OnlineCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Production TheoryDocument27 pagesModule 5 Production TheoryCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Dynamics of Demand and SupplyDocument22 pagesModule 3 Dynamics of Demand and SupplyCharice Anne Villamarin100% (1)
- Module 3 Concept of ElasticityDocument35 pagesModule 3 Concept of ElasticityCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Demand and SupplyDocument18 pagesModule 3 Demand and SupplyCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Managerial EconomicsDocument29 pagesModule 2 Managerial EconomicsCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Module 2.1 Managerial EconomicsDocument18 pagesModule 2.1 Managerial EconomicsCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Journal EntriesDocument8 pagesAdjusting Journal EntriesChaaaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Assignment Case Study Alibaba - Andika Daffa Elianto - 12010119190124Document2 pagesMarketing Management Assignment Case Study Alibaba - Andika Daffa Elianto - 12010119190124Andika Daffa EliantoNo ratings yet
- Accounting For IstisnaDocument17 pagesAccounting For Istisnarajes wariNo ratings yet
- Contract of LeaseDocument6 pagesContract of LeaseAilen Rose PuertasNo ratings yet
- Bharti Airtel: Outsourcing of Network OperationsDocument6 pagesBharti Airtel: Outsourcing of Network OperationsADITYA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Accounting 0452/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Accounting 0452/12jpranav611.hNo ratings yet
- Invoice: Bill From Customer DetailsDocument1 pageInvoice: Bill From Customer DetailsKanjarla Hanmonthrao Panthulu LaxmanaNo ratings yet
- Delivery ChallanDocument1 pageDelivery ChallanNTR CHARANNo ratings yet
- Chocolate IndustryDocument16 pagesChocolate IndustrySudhakar NadarNo ratings yet
- Correcting - Entries (Compatibility Mode)Document6 pagesCorrecting - Entries (Compatibility Mode)MahediNo ratings yet
- Quotation: Estimate Date: Expiry Date: Reference#: Bill ToDocument3 pagesQuotation: Estimate Date: Expiry Date: Reference#: Bill ToAbdul HadiNo ratings yet
- VAHAN 4.0 (Citizen Services) SP-MORTH-WS03 175 8013Document1 pageVAHAN 4.0 (Citizen Services) SP-MORTH-WS03 175 8013Divyansh chaturvediNo ratings yet
- Rule 4 and Rule 5 Exercises Name Key Unit Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7Document3 pagesRule 4 and Rule 5 Exercises Name Key Unit Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7akmalhamizanNo ratings yet
- An International Business PlanDocument2 pagesAn International Business Planishwar_chheda75% (4)
- Rezka Prakasa S: InvoiceDocument99 pagesRezka Prakasa S: InvoiceThink Indonesia MovementNo ratings yet
- VIII - SST - 7 - Ruling The CountrysideDocument2 pagesVIII - SST - 7 - Ruling The CountrysideTheWeird GsNo ratings yet
- Linc Pen Case StudyDocument13 pagesLinc Pen Case StudySHAHEER THEKKEYILNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument6 pagesIntroduction To AccountingKathlyn BesaNo ratings yet
- Tourism Development Planning StrategiesDocument11 pagesTourism Development Planning StrategiesMary Rose LinihanNo ratings yet
- 2019 Debt Sustainability Analysis (DSA) ReportDocument39 pages2019 Debt Sustainability Analysis (DSA) ReportsenohiNo ratings yet
- Marx Modes of ProductionDocument10 pagesMarx Modes of Productionnandini negiNo ratings yet
- Company Car Tax in Hungary - ACCA GlobalDocument6 pagesCompany Car Tax in Hungary - ACCA GlobalhfdghdhNo ratings yet
- Claims Vendor ManagementDocument2 pagesClaims Vendor Managementamol.d.kelkarNo ratings yet
- BFC 35503 Chapter 4 BuilduprateDocument17 pagesBFC 35503 Chapter 4 BuilduprateariaNo ratings yet
- Data BaseDocument29 pagesData BaseSundararajan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- List of ASX Registered Companies 22 Nov 2019Document92 pagesList of ASX Registered Companies 22 Nov 2019roopNo ratings yet
- A. Gas Deposit Grenada - Brief-2Document3 pagesA. Gas Deposit Grenada - Brief-2Phan CongNo ratings yet
- Brand Imitation in The Modern Simulacrum Market Versus Marketing EthicsDocument24 pagesBrand Imitation in The Modern Simulacrum Market Versus Marketing EthicsВиталлий ЧеренковNo ratings yet