Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name: - Year and Section
Name: - Year and Section
Uploaded by
jeff tanales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesThis document provides equations for kinematic motion in one dimension (along the x-axis) with constant velocity or constant acceleration, free fall motion along the y-axis under gravity, and projectile motion along both the x-axis and y-axis. Key relationships presented include equations relating displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time for constant velocity and acceleration motions, as well as relationships for upward and downward free fall motion under gravity and projectile motion trajectories.
Original Description:
Equations
Original Title
Equations Physics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides equations for kinematic motion in one dimension (along the x-axis) with constant velocity or constant acceleration, free fall motion along the y-axis under gravity, and projectile motion along both the x-axis and y-axis. Key relationships presented include equations relating displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time for constant velocity and acceleration motions, as well as relationships for upward and downward free fall motion under gravity and projectile motion trajectories.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesName: - Year and Section
Name: - Year and Section
Uploaded by
jeff tanalesThis document provides equations for kinematic motion in one dimension (along the x-axis) with constant velocity or constant acceleration, free fall motion along the y-axis under gravity, and projectile motion along both the x-axis and y-axis. Key relationships presented include equations relating displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time for constant velocity and acceleration motions, as well as relationships for upward and downward free fall motion under gravity and projectile motion trajectories.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Name: ______________________________ Year and Section: ___________
PHYS 1E Kinematic Equations
Scalar quantity: time (t)
Vector quantities: displacement (x and y), velocity (v), acceleration (a and g)
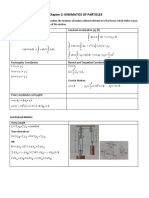
I. Motion in One Dimension (motion of object along the x axis)
A. Motion with Constant Velocity
1. x=v x t
B. Motion with Constant Acceleration
1. v xf =v xi+ a x t
1
2. x= ( V xi +V xf ) t
2
1
3. x=v xi t+ a x t 2
2
2 2
4. v xf =v xi +2 a x x
II. Free Fall Motion (motion of object along the y axis, under the influence of gravity)
A. Relationships in Free Fall Motion
1.| y U|=| y D|(for Case 2 , Free Fall)
2.|v yiU|=|v yfD|( for Case 2, Free Fall )
3. t U =t D (for Case 2 , Free Fall)
B. Case 1: Downward motion ( v yiD=0 )
1. v yfD =g t D
1
2. y D = v yfD t D
2
1 2
3. y D = g t D
2
2
4. v yfD=2 g y D
C. Case 2: Upward motion, Downward motion
C.1 Upward Motion ( v yfU =0 )
1. v yiU =−g t U
1
2. y U = v yiU t U
2
1
3. y U =v yiU t U + g t 2U
2
2
4. v yiU =−2 g y U
C.2 Downward Motion ( v yiD=0 )
1. v yfD =g t D
1
2. y D = v yfD t D
2
1 2
3. y D = g t D
2
2
4. v yfD=2 g y D
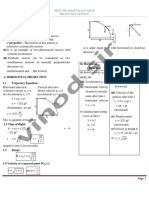
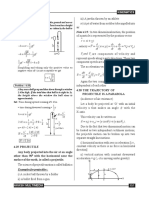
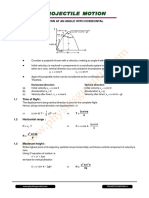
III. Projectile Motion (motion of object along x axis and y axis, under the influence of gravity)
A. Relationships in Projectile Motion
1. ⃗v =⃗v x +⃗ v y (at any point∈motion of object , Projectile Motion)
2.|v yiU|=|v yfD|( Projectile Motion)
3. t U =t D (Projectile Motion)
4. t TOTAL=2 t U (Projectile Motion)
v i sin θi
5. t U = ( Projectile Motion)
g
6. R=|x|( Projectile Motion)
v 2i sin 2θi
7. R= ( Projectile Motion)
g
8. h=| y U|=| y D|( Projectile Motion )
v 2i sin 2 θi
9. h= ( Projectile Motion)
2g
B. Horizontal Motion ( v x is constant )
1. x=v x t TOTAL
C. Vertical Motion (Upward motion, Downward motion)
C.1 Upward Motion ( v yfU =0 )
1. v yiU =−g t U
1
2. y U = v yiU t U
2
1
3. y U =v yiU t U + g t 2U
2
2
4. v yiU =−2 g y U
C.2 Downward Motion ( v yiD=0 )
1. v yfD =g t D
1
2. y D = v yfD t D
2
1 2
3. y D = g t D
2
4. v 2yfD=2 g y D
You might also like
- Formula Sheet For Physics HallidayDocument6 pagesFormula Sheet For Physics HallidayTayyab Chaudhary0% (1)
- Projectile MotionDocument32 pagesProjectile MotionSuresh100% (2)
- ProjectileDocument29 pagesProjectileJhi Ghi Rawring75% (4)
- Smith & Burstone-Mechanic Tooth MovementDocument14 pagesSmith & Burstone-Mechanic Tooth MovementGisselaMaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: Physics Unit 5 Lesson 1Document18 pagesProjectile Motion: Physics Unit 5 Lesson 1Shivam KhemariyaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics With Calculus 1Document8 pagesKinematics With Calculus 1julianne sanchezNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Midterm I IDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet Midterm I IDavid ChangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Kinematics in 2D: X y X yDocument11 pagesChapter 4: Kinematics in 2D: X y X yMac MagsinoNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - General Two Dimensional MotionDocument8 pagesCH 3 - General Two Dimensional Motionswarupp482No ratings yet
- Projectile Motion 2023 ChughDocument8 pagesProjectile Motion 2023 ChughAryan KumarNo ratings yet
- 4.motion in A PlaneDocument9 pages4.motion in A PlaneArvindhkandhavel RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Kinematics of Particles: Constrained MotionDocument3 pagesChapter 2: Kinematics of Particles: Constrained MotionRicardo TapiaNo ratings yet
- Eccf696b 1594699537815Document21 pagesEccf696b 1594699537815Priya Dharshini VNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion 12optDocument32 pagesProjectile Motion 12optKrish CvNo ratings yet
- Free Fall NotesDocument3 pagesFree Fall Notesalkirstenlexie.galvezNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Senior High School Physics: Lech Jedral 2006Document32 pagesProjectile Motion Senior High School Physics: Lech Jedral 2006kentNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument32 pagesProjectile MotionIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document32 pagesLecture 4Asad SamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: One-Dimensional Kinematics: Av AvDocument3 pagesChapter 2: One-Dimensional Kinematics: Av AvVivian DoanNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes - Projectile MotionDocument6 pagesRevision Notes - Projectile Motionvineeth67229No ratings yet
- Motion in Two Dimensions: Physics For Scientists and Engineers, 10e Raymond A. Serway John W. Jewett, JRDocument74 pagesMotion in Two Dimensions: Physics For Scientists and Engineers, 10e Raymond A. Serway John W. Jewett, JRameliawenston3No ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument32 pagesProjectile MotionMae ThereseNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Senior High School Physics: Lech Jedral 2006Document32 pagesProjectile Motion Senior High School Physics: Lech Jedral 2006SureshNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion 1Document32 pagesProjectile Motion 1apple llegadoNo ratings yet
- Motion in 2 Dimensions Vidyamandir ClassesDocument19 pagesMotion in 2 Dimensions Vidyamandir ClassesYadav100% (1)
- DistanceDocument2 pagesDistanceAeveil PalejaroNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion-Horizontal Launched ProjectileDocument27 pagesProjectile Motion-Horizontal Launched ProjectileLhaine FantilananNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument40 pagesProjectile MotionTrilok AkhaniNo ratings yet
- Some Useful Formulae: A A A A A A + + + +Document3 pagesSome Useful Formulae: A A A A A A + + + +leichihouNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Senior High School Physics: Lech Jedral 2006Document32 pagesProjectile Motion Senior High School Physics: Lech Jedral 2006Ciara Adrianne Tiongzon - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Motion in 2D Notes Iit JeeDocument28 pagesMotion in 2D Notes Iit JeeSaumya Singh100% (1)
- 105 Eq Sheet 2Document1 page105 Eq Sheet 2NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Projectile MotionDocument16 pages1.4 Projectile MotioneltytanNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two and Three Dimensions: R X I y J Z KDocument11 pagesMotion in Two and Three Dimensions: R X I y J Z KWahyu SipahutarNo ratings yet
- Gen. Physics Unit 1 Lesson 5 Motion in 2 and 3 DimensionsDocument9 pagesGen. Physics Unit 1 Lesson 5 Motion in 2 and 3 DimensionsMary Love JuanicoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics (Dynamics, Statics, Strength)Document15 pagesEngineering Mechanics (Dynamics, Statics, Strength)Shan BarbastroNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy and Energy ConservationDocument32 pagesPotential Energy and Energy Conservationelchappoo kalboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 PDFDocument23 pagesChapter 03 PDFMihir PatelNo ratings yet
- Motion in One-Dimension: X T T X X T X VDocument6 pagesMotion in One-Dimension: X T T X X T X VDezsy Beibz AjjahNo ratings yet
- Phys 111 Final Exam Formulas - Fall 2011: DT DWDocument1 pagePhys 111 Final Exam Formulas - Fall 2011: DT DWVenkataramanan SureshNo ratings yet
- MAF - Kuliah Pertemuan Ke 3Document19 pagesMAF - Kuliah Pertemuan Ke 3RISETIA GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Exam3 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesExam3 Formula SheetMario GlezNo ratings yet
- Mechanics P1Document32 pagesMechanics P1Lilian ChriciaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet-Chapter 13-Quiz 2Document1 pageFormula Sheet-Chapter 13-Quiz 2Beny Gonzales MaldiniNo ratings yet
- MHTCET Compendium PCM 1644831007255Document180 pagesMHTCET Compendium PCM 1644831007255dfgb fbnNo ratings yet
- Bouncing Ball EquationsDocument5 pagesBouncing Ball EquationsFatih TSPNo ratings yet
- Aoun Haider 1B MorningDocument1 pageAoun Haider 1B Morningchaoun147741147No ratings yet
- 3.2 Accelerated Motion TheoryDocument5 pages3.2 Accelerated Motion Theoryoxunjonergashov1607No ratings yet
- Ch3b 2D Motion SJPDocument12 pagesCh3b 2D Motion SJPBelay AyalewNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion Iit JeeDocument23 pagesRotational Motion Iit JeeSahil0% (1)
- Projectile Motion Quick NotesDocument4 pagesProjectile Motion Quick NotesJoseph CruzNo ratings yet
- Motion in 2DDocument28 pagesMotion in 2DnaguNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument24 pagesProjectile MotionChirag HegdeNo ratings yet
- (Combined PDF 4.0) Kinematics 2DDocument265 pages(Combined PDF 4.0) Kinematics 2DVinay SinghNo ratings yet
- A.1.5 Kinematics PracticeDocument16 pagesA.1.5 Kinematics PracticezmedendoNo ratings yet
- Modul Xi Sem 1 2009-2010Document64 pagesModul Xi Sem 1 2009-2010Herman_MLNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Final Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics Final Formula SheetHarryNips100% (1)
- PCM Offline Test - 03 (Integrated) (Paper 2) (NP 03 - 20212) Q + Soln (Version 3)Document20 pagesPCM Offline Test - 03 (Integrated) (Paper 2) (NP 03 - 20212) Q + Soln (Version 3)mj drawsNo ratings yet
- Physics Week 5 Lesson 1Document7 pagesPhysics Week 5 Lesson 1Gabriel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document105 pagesChapter 2antutu100% (1)
- Chapter - 4 Motion in A PlaneDocument15 pagesChapter - 4 Motion in A PlaneTrilok AkhaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Gyroscope 131127011945 Phpapp02Document40 pagesUnit 7 Gyroscope 131127011945 Phpapp02VarunRajNo ratings yet
- Gyroscopic EffectsDocument28 pagesGyroscopic EffectsrathanNo ratings yet
- Illuminati - 2020: Advanced Physics Assignment-3Document22 pagesIlluminati - 2020: Advanced Physics Assignment-3Yash Dhoke100% (1)
- Galileo GalileiDocument11 pagesGalileo GalileiSHUBHAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- Newman 1968Document16 pagesNewman 1968Gabriel Leonardo Tacchi NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Physics of BoomerangDocument1 pagePhysics of Boomerangray_tan_11No ratings yet
- AH - RMA - PPT - 5. Torque Moment of InertiaDocument29 pagesAH - RMA - PPT - 5. Torque Moment of InertiaFrank SkellyNo ratings yet
- DPP 71 Rotation 18-11-2022 - ANSDocument2 pagesDPP 71 Rotation 18-11-2022 - ANSneoisonlyoneNo ratings yet
- 05 Instantaneous Axis of RotationDocument14 pages05 Instantaneous Axis of RotationSupriyo DuttaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Objectives: at The End of This Lecture, Students Will Be Able ToDocument16 pagesLecture Objectives: at The End of This Lecture, Students Will Be Able ToVinayak HNo ratings yet
- Wang2014 PDFDocument17 pagesWang2014 PDFfernandoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document4 pagesExercise 1Nabil IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Physics Note Midterm 3Document3 pagesPhysics Note Midterm 3Jong MoonNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument26 pagesPHYSICSDannah Kaye AmancioNo ratings yet
- Plane Frame and Grid EquationsDocument63 pagesPlane Frame and Grid EquationsAshutoshAparajNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (Part I) General PhysicsDocument51 pagesUnit 2 (Part I) General PhysicsTedros Ras TeshomeNo ratings yet
- APL 100: Minor 2Document3 pagesAPL 100: Minor 2kamleshNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper: Shaftless Screw ConveyorsDocument18 pagesWhitepaper: Shaftless Screw ConveyorsPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Manual EncoderDocument7 pagesManual EncoderSyahrul FitriaNo ratings yet
- Agri - Traction and Braking Force On Three Surfaces of Agricultural Tire LugDocument9 pagesAgri - Traction and Braking Force On Three Surfaces of Agricultural Tire LugNihal SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechanics: Cbse Neet JEE Mains AdvancedDocument11 pages1 Mechanics: Cbse Neet JEE Mains Advancedvsrajkumar100% (6)
- Spring PDFDocument28 pagesSpring PDFselvarajumit0% (1)
- 1101 B.P.S. XI Physics Worksheet PDFDocument31 pages1101 B.P.S. XI Physics Worksheet PDFPraveen MaramNo ratings yet
- A Smart Experimental Setup For Vibration Measurement andDocument11 pagesA Smart Experimental Setup For Vibration Measurement andEng Bagaragaza RomualdNo ratings yet
- 02 Electric FieldDocument7 pages02 Electric FieldFirdous ANo ratings yet
- Lanze N Doer FerDocument1 pageLanze N Doer FerAsemota OghoghoNo ratings yet