Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01
Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01
Uploaded by
hweta173Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01
Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01
Uploaded by
hweta173Copyright:
Available Formats
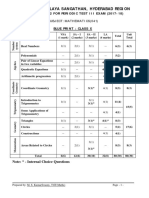
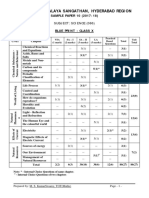
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
SAMPLE PAPER 01 FOR PERIODIC TEST III EXAM (2017-18)
SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS(041)
BLUE PRINT : CLASS X
VSA SA – I SA – II LA Unit
Unit Chapter Total
(1 mark) (2 marks) (3 marks) (4 marks) Total
Number
system
Real Numbers 1(1) 2(1) 3(1) -- 6(3) 6(3)
Polynomials -- 2(1) 3(1) -- 5(2)
Pair of Linear Equations
Algebra
-- 2(1) 3(1) 4(1)* 9(3)
in two variables
26(10)
Quadratic Equations 1(1) -- -- 4(1)* 5(2)
Arithmetic progression 1(1) 2(1) -- 4(1) 7(3)
Coordinate
Geometry
Coordinate Geometry 1(1) -- 3(1)* 4(1) 8(3) 8(3)
Introduction to 3(1)
Trigonometry
1(1) -- 4(1) 11(4)
Trigonometry 3(1)*
15(5)
Some Applications of
-- -- -- 4(1) 4(1)
Trigonometry
Triangles 1(1) -- 3(1)* 4(1)* 8(3)
Geometry
Circles -- 2(1) 3(1) -- 5(2) 17(6)
Constructions -- -- -- 4(1) 4(1)
Mensuration
3(1)
Areas Related to Circles -- 2(1) -- 8(3) 8(3)
3(1)*
Total 6(6) 12(6) 30(10) 32(8) 80(30) 80(30)
Note: * - Internal Choice Questions
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
SAMPLE PAPER 01 FOR PERIODIC TEST III EXAM (2017-18)
SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS MAX. MARKS : 80
CLASS : X DURATION : 3 HRS
General Instruction:
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) This question paper contains 30 questions divided into four Sections A, B, C and D.
(iii) Section A comprises of 6 questions of 1 mark each. Section B comprises of 6 questions of 2
marks each. Section C comprises of 10 questions of 3 marks each and Section D comprises of 8
questions of 4 marks each.
(iv) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in four questions of 3
marks each and three questions of 4 marks each. You have to attempt only one of the alternatives in all
such questions.
(v) Use of Calculators is not permitted
SECTION – A
Questions 1 to 6 carry 1 mark each.
1. Find the values of k for quadratic equation 2x2 + kx + 3 = 0, so that they have two equal roots.
3
2. If sinA = , find the value of tanA.
5
3. If HCF of two numbers 96 and 404 is 4, then find LCM
4. Let Δ ABC ~ Δ DEF and their areas be, respectively, 64 cm2 and 121 cm2. If EF = 15.4 cm, find
BC.
5. Find the coordinates of a point A, where AB is the diameter of a circle whose centre is (2, – 3)
and B is (1, 4).
6. Which term of the AP : 21, 18, 15, . . . is – 81?
SECTION – B
Questions 6 to 12 carry 2 marks each.
7. The length of the minute hand of a clock is 14 cm. Find the area swept by the minute hand in 5
minutes.
8. Find the zeroes of the polynomial 2x2 – 5x + 7, and verify the relation between the coefficients
and the zeroes of the polynomial.
9. Using Euclid’s division algorithm, find the HCF of 2160 and 3520.
10. Solve 2x + 3y = 11 and 2x – 4y = – 24 and hence find the value of ‘m’ for which y = mx + 3.
11. If tangents PA and PB from a point P to a circle with centre O are inclined to each other at angle
of 80°, then find POA
12. Find the sum of first 24 terms of the list of numbers whose nth term is given by an = 3 + 2n
SECTION – C
Questions 13 to 22 carry 3 marks each.
13. Prove that 2 3 5 is an irrational number.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 2 -
14. Prove that the parallelogram circumscribing a circle is a rhombus.
15. If two zeroes of the polynomial 2x4 – 3x3 – 3x2 + 6x – 2 are 2 and 2 , find the other zeroes
of the polynomial.
16. If A(–5, 7), B(– 4, –5), C(–1, –6) and D(4, 5) are the vertices of a quadrilateral, find the area of
the quadrilateral ABCD.
OR
Find the area of the triangle formed by joining the mid-points of the sides of the triangle whose
vertices are (0, –1), (2, 1) and (0, 3). Find the ratio of this area to the area of the given triangle.
17. In the below figure, O is a point in the interior of a triangle ABC, OD BC, OE AC and OF
AB. Show that
(i) OA2 + OB2 + OC2 – OD2 – OE2 – OF2 = AF2 + BD2 + CE2,
(ii) AF2 + BD2 + CE2 = AE2 + CD2 + BF2.
OR
In the below figure, ABC and DBC are two triangles on the same base BC. If AD intersects BC
ar (ABC ) AO
at O, show that
ar (DBC ) DO
18. In the below figure, ABC is a quadrant of a circle of radius 14 cm and a semicircle is drawn
with BC as diameter. Find the area of the shaded region.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 3 -
1
19. If tan (A + B) = 3 and tan (A – B) = ; 0° < A + B ≤ 90°; A > B, find A and B.
3
OR
cot A cos A cos ecA 1
Prove that: .
cot A cos A cos ecA 1
20. In Δ OPQ, right-angled at P, OP = 7 cm and OQ – PQ = 1 cm. Determine the values of sin Q
and cos Q.
21. The sum of the digits of a two-digit number is 9. Also, nine times this number is twice the
number obtained by reversing the order of the digits. Find the number.
22. A chord of a circle of radius 10 cm subtends a right angle at the centre. Find the area of the
corresponding : (i) minor segment (ii) major sector. (Use π = 3.14)
OR
A horse is tied to a peg at one corner of a square shaped grass field of side 15 m by means of a 5
m long rope.
Find (i) the area of that part of the field in which the horse can graze.
(ii) the increase in the grazing area if the rope were 10 m long instead of 5 m. (Use π = 3.14)
SECTION – D
Questions 23 to 30 carry 4 marks each.
23. A straight highway leads to the foot of a tower. A man standing at the top of the tower observes
a car at an angle of depression of 30°, which is approaching the foot of the tower with a uniform
speed. Six seconds later, the angle of depression of the car is found to be 60°. Find the time
taken by the car to reach the foot of the tower from this point.
24. A motor boat whose speed is 18 km/h in still water takes 1 hour more to go 24 km upstream
than to return downstream to the same spot. Find the speed of the stream.
OR
An express train takes 1 hour less than a passenger train to travel 132 km between Mysore and
Bangalore (without taking into consideration the time they stop at intermediate stations). If the
average speed of the express train is 11km/h more than that of the passenger train, find the
average speed of the two trains.
25. Prove that “The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of the ratio of
their corresponding sides.”
OR
Prove that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of
the other two sides.
26. If the sum of first 7 terms of an AP is 49 and that of 17 terms is 289, find the sum of first n
terms.
27. Determine the ratio in which the line 2x + y – 4 = 0 divides the line segment joining the points
A(2, – 2) and B(3, 7).
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 4 -
28. Draw a circle of radius 3 cm. Take two points P and Q on one of its extended diameter each at a
distance of 7 cm from its centre. Draw tangents to the circle from these two points P and Q.
cos A sin A 1
29. Prove that cos ecA cot A
cos A sin A 1
30. Draw the graphs of the equations x – y + 1 = 0 and 3x + 2y – 12 = 0. Determine the coordinates
of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and the x-axis, and shade the triangular
region.
OR
1 1 3 1 1 1
Solve the equations: and
3 x y 3x y 4 2(3x y ) 2(3x y ) 8
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 5 -
You might also like
- Class 2 Spell BeeDocument48 pagesClass 2 Spell Beehweta173100% (5)
- TM 11398Document592 pagesTM 11398krill.copco50% (2)
- Yamaha CLP 170 Service ManualDocument122 pagesYamaha CLP 170 Service ManualicaroheartNo ratings yet
- Major Test 01 7th PDFDocument4 pagesMajor Test 01 7th PDFKids robotics TeamNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions On Arithmetic Progressions Class 10Document16 pagesMCQ Questions On Arithmetic Progressions Class 10Krishnamurthy HosahalliNo ratings yet
- Apex Entrance Exam Test PaperDocument12 pagesApex Entrance Exam Test PaperApex Institute100% (1)
- Yts 09 Xi Maths Sample Papers O.P. GuptaDocument5 pagesYts 09 Xi Maths Sample Papers O.P. GuptaIshan AhujaNo ratings yet
- Reso-Fast Sample Test Paper: For Students Moving in Class-Ix in 2019-20Document10 pagesReso-Fast Sample Test Paper: For Students Moving in Class-Ix in 2019-20ChaudharyAV: THE GURUNo ratings yet
- Permutation and Combination: Sri Chaitanya Iit Academy, IndiaDocument14 pagesPermutation and Combination: Sri Chaitanya Iit Academy, IndiaNisha MehtaNo ratings yet
- 11 Number, Ranking - Time Sequence TestDocument12 pages11 Number, Ranking - Time Sequence TestAashishsainiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Math Important FormulasDocument2 pagesClass 10 Math Important FormulasCREATIVING TAMILANNo ratings yet
- ADSAT Set-2 Sample Paper Class X To XI JEE Paper K0uxvoDocument9 pagesADSAT Set-2 Sample Paper Class X To XI JEE Paper K0uxvoleenakonde1No ratings yet
- Imo - Class-8 - 2021 Sample Paper SofDocument2 pagesImo - Class-8 - 2021 Sample Paper SofManoj Pandey100% (1)
- 10th CBSE (SA - 1) Revision Pack Booklet - 2 (Maths)Document18 pages10th CBSE (SA - 1) Revision Pack Booklet - 2 (Maths)anon_708612757No ratings yet
- GOA-Mathematics Sample Paper-1-Class 10 Question Paper (SA-I)Document6 pagesGOA-Mathematics Sample Paper-1-Class 10 Question Paper (SA-I)Firdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document32 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Ladukishore RathNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Imo PaperDocument6 pagesClass 10 Imo PaperYatish Goyal80% (5)
- Standard Sample Paper XyzDocument7 pagesStandard Sample Paper XyzMaurya Sachin100% (1)
- Online Test 2 (Math)Document2 pagesOnline Test 2 (Math)THANIGAINATHAN.G.D 10A3No ratings yet
- Maths (Standard) Class - X - SET-1 (English Version)Document7 pagesMaths (Standard) Class - X - SET-1 (English Version)shanmugan rajNo ratings yet
- Mat Ntse 2020 Stage 1 Paper Solutions Odisha PDFDocument25 pagesMat Ntse 2020 Stage 1 Paper Solutions Odisha PDFPunam Kumari100% (1)
- ANTHE Sample Paper 2011Document8 pagesANTHE Sample Paper 2011Umang Duggal60% (10)
- Ftre 2023 Sample Paper Class X p2 PCMDocument19 pagesFtre 2023 Sample Paper Class X p2 PCMpriyagvspv100% (1)
- STD7 2021 4th JulyDocument4 pagesSTD7 2021 4th JulyRatnesh Kumar100% (1)
- 01 Subjective Test-02 X Science 25122022 QPDocument6 pages01 Subjective Test-02 X Science 25122022 QPViswa DharshanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 1 (Unsolved)Document8 pagesClass 10 Maths Sample Paper 1 (Unsolved)lego/gameing club100% (1)
- 2015 Hauts Solutions: Chess With A TwistDocument8 pages2015 Hauts Solutions: Chess With A TwistChampion ReaderNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Limit Continuity and Differentiability Important QuestionsDocument21 pagesJEE Main Limit Continuity and Differentiability Important Questionsshreenath gajalwarNo ratings yet
- ITMO 2019 - Keystage 3 - Team - SolDocument8 pagesITMO 2019 - Keystage 3 - Team - SolLong NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Anthe-2014Document14 pagesSample Paper Anthe-2014Mitchell Jackson50% (6)
- Maths-Class-X - Paper - 3 PDFDocument7 pagesMaths-Class-X - Paper - 3 PDFPrabha sharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ntse Practice Test MatDocument13 pages1 Ntse Practice Test MatPratham VsNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Math Sample Paper 1Document8 pagesClass 10 Math Sample Paper 1Bharath RajNo ratings yet
- Workshop DPP's NTSE - Stage-2 - With PDFDocument40 pagesWorkshop DPP's NTSE - Stage-2 - With PDFUmang PatelNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 2 PolynomialsDocument9 pagesCBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 2 PolynomialsParas VaidNo ratings yet
- Advanced Maths Test: Class: IXDocument9 pagesAdvanced Maths Test: Class: IXKamalNo ratings yet
- Class - X - Social Science - QP - Second Periodic Test - Set - C - 2018-19Document1 pageClass - X - Social Science - QP - Second Periodic Test - Set - C - 2018-19Laksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: Class: X Time: 3 HoursDocument10 pagesSample Paper: Class: X Time: 3 HoursBhushan KadNo ratings yet
- MTRP 2018 - 9Document2 pagesMTRP 2018 - 9Nimai RoyNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths Set BDocument12 pages10 Maths Set BDeepika VNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Chapter 01 Real Numbers Practice Paper 01Document3 pagesMaths Class X Chapter 01 Real Numbers Practice Paper 01Mannan GuptaNo ratings yet
- F SQP Maths 2023-1Document5 pagesF SQP Maths 2023-1Harekrishna DasNo ratings yet
- Pre RMO Solved Paper 2012Document3 pagesPre RMO Solved Paper 2012geddam061088250% (2)
- ANTHE2020 - Engg - FS - (X Moving To XI) - Sample PaperDocument16 pagesANTHE2020 - Engg - FS - (X Moving To XI) - Sample Paperrashmi kohliNo ratings yet
- E-CAPS-28 - For CoE (XI) - Mathematics - (Que. - Answer Key)Document3 pagesE-CAPS-28 - For CoE (XI) - Mathematics - (Que. - Answer Key)darling dean100% (1)
- Class-8 Mix TestDocument2 pagesClass-8 Mix TestStorage AccountNo ratings yet
- 7th Code-A Final PrintingDocument15 pages7th Code-A Final PrintingAnkeshNo ratings yet
- IMO Class 9 Solved Sample PaperDocument7 pagesIMO Class 9 Solved Sample PaperDivyansh DuggadNo ratings yet
- Allen: Ntse (Stage-Ii) Test SeriesDocument11 pagesAllen: Ntse (Stage-Ii) Test SeriesKishlay anandNo ratings yet
- M15 Probability 2Document4 pagesM15 Probability 2Krishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Xii - Mock Test - 1Document6 pagesXii - Mock Test - 1Kartik ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 04 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersDocument15 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 04 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersMohanalakshmi ManoharNo ratings yet
- ITMO 2019 - Keystage 3 - Individual - SolDocument13 pagesITMO 2019 - Keystage 3 - Individual - SolLong NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - IMO 2Document5 pagesClass 8 - IMO 2JTO CALL CENTERNo ratings yet
- 2016 Aakash Anthe Junior Sample Paper Class10Document16 pages2016 Aakash Anthe Junior Sample Paper Class10ats edu100% (1)
- Maths IIT-JEE Best Approach': Total Marks: 40 Time: 40 Min. Factorization Type-1Document2 pagesMaths IIT-JEE Best Approach': Total Marks: 40 Time: 40 Min. Factorization Type-1Vansh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Class X Mathematics Question Bank 2017-18Document41 pagesClass X Mathematics Question Bank 2017-18akhil.jNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Document5 pagesMaths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Document5 pagesMaths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03hweta173No ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesMaths Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01veeNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Sample Paper 01 For Sessing Ending Exam (2017-18)Document5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Sample Paper 01 For Sessing Ending Exam (2017-18)SanjayNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 03 For Board Exam 2018 4Document5 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper 03 For Board Exam 2018 4Írfäñ MøhdNo ratings yet
- Icse 2011 Maths Solution 1aDocument5 pagesIcse 2011 Maths Solution 1aSanjayNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Question Bank Exam Guru LEARN VIBRANTDocument232 pagesClass 10 Social Science Term 2 Question Bank Exam Guru LEARN VIBRANThweta173100% (1)
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Mankhurd: Periodic Test (2021-22)Document2 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Mankhurd: Periodic Test (2021-22)hweta173No ratings yet
- Class 10 Social Science Term 2 XamideaDocument198 pagesClass 10 Social Science Term 2 Xamideahweta173No ratings yet
- Cbse Class 10 Introduction To Financial Markets Set 4 Compartment Annual Question Paper 2018 PDF Question Papers vqp2019.htmlDocument8 pagesCbse Class 10 Introduction To Financial Markets Set 4 Compartment Annual Question Paper 2018 PDF Question Papers vqp2019.htmlhweta173No ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Class - X Session - 2021-22 Term 1 Subject-Mathematics (Standard) 041Document7 pagesSample Question Paper Class - X Session - 2021-22 Term 1 Subject-Mathematics (Standard) 041hweta173No ratings yet
- Cbse Class 10 Indtroduction To Financial Markets Annual Question Paper 2018 PDF Question Papers vqp1357.htmlDocument8 pagesCbse Class 10 Indtroduction To Financial Markets Annual Question Paper 2018 PDF Question Papers vqp1357.htmlhweta173No ratings yet
- 19194class 10 PBDocument16 pages19194class 10 PBhweta173No ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial MarketsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Financial Marketshweta173No ratings yet
- ..International School: Periodic Test - 2Document4 pages..International School: Periodic Test - 2hweta173No ratings yet
- AOC - Junior AnnualDocument7 pagesAOC - Junior Annualhweta173No ratings yet
- 815maths Sample PaperDocument7 pages815maths Sample Paperhweta173No ratings yet
- STD 2 SyllabusDocument6 pagesSTD 2 Syllabushweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173100% (1)
- STD 2 Sample Question PaperDocument6 pagesSTD 2 Sample Question Paperhweta173100% (1)
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- POwer Sharing ImpDocument5 pagesPOwer Sharing Imphweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Exercise # 1: Statistics and ProbabilityDocument6 pagesExercise # 1: Statistics and ProbabilityAszyla ArzaNo ratings yet
- Case Study of WapdaDocument34 pagesCase Study of WapdaImran Chaudhry100% (1)
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitleddwky KrnwnNo ratings yet
- Pablocastillo PDFDocument44 pagesPablocastillo PDFPabloNo ratings yet
- Arthur Lumley Davi̇ds-Sultan Ii. Mahmuta-1832Document318 pagesArthur Lumley Davi̇ds-Sultan Ii. Mahmuta-1832cengizozakinciNo ratings yet
- Recycling Hexane and EtOAcDocument1 pageRecycling Hexane and EtOAcjmiscNo ratings yet
- Green Building Toward Construction Sustainability: Energy Efficiency With Material and Design AspectsDocument11 pagesGreen Building Toward Construction Sustainability: Energy Efficiency With Material and Design AspectsghchgNo ratings yet
- Asma G.SDocument5 pagesAsma G.SAfia FaheemNo ratings yet
- Advanced Landscape DesignDocument10 pagesAdvanced Landscape DesignSomhita DasNo ratings yet
- Textbook Pediatric Behavioral Nutrition Factors Environment Education and Self Regulation 1St Edition Areej Hassan Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument39 pagesTextbook Pediatric Behavioral Nutrition Factors Environment Education and Self Regulation 1St Edition Areej Hassan Ebook All Chapter PDFjanet.galloway812100% (8)
- Technical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosDocument4 pagesTechnical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosKamatchi NathanNo ratings yet
- CR Unit 1 &11 (Part A &B)Document12 pagesCR Unit 1 &11 (Part A &B)durai muruganNo ratings yet
- EuropeDocument5 pagesEuropeAmicus CuriaeNo ratings yet
- BDA 542 V3 - powerCON TRUE 1 TOP - NAC3MX-W-TOPDocument2 pagesBDA 542 V3 - powerCON TRUE 1 TOP - NAC3MX-W-TOPluis manuelNo ratings yet
- Allotrope Partners Indonesia Renewable Energy Project AssociateDocument2 pagesAllotrope Partners Indonesia Renewable Energy Project AssociateRizal ZulkarnaenNo ratings yet
- Drawing Details: Cie 332 Quantity Surveying and Estimation Lecture Two Lecturer: Eng. Goodson MashekaDocument23 pagesDrawing Details: Cie 332 Quantity Surveying and Estimation Lecture Two Lecturer: Eng. Goodson MashekaPerpetual hubbyNo ratings yet
- Anthropological Thought Session by DR G. VivekanandaDocument277 pagesAnthropological Thought Session by DR G. Vivekanandahamtum7861No ratings yet
- Electronics Cooling: Mechanical Power Engineering DeptDocument22 pagesElectronics Cooling: Mechanical Power Engineering DeptneilNo ratings yet
- Koch - Control ChartsDocument40 pagesKoch - Control ChartsAkash MarathakamNo ratings yet
- Cobra XRS9690Document45 pagesCobra XRS9690marwan71No ratings yet
- Inverse of A FunctionDocument10 pagesInverse of A Functionnitin30100% (2)
- Kore Network Device ConfigurationDocument61 pagesKore Network Device ConfigurationEllaziaNo ratings yet
- Da0bl7mb6d0 Rev DDocument44 pagesDa0bl7mb6d0 Rev DFerreira da CunhaNo ratings yet
- ToR For Fiberglass Biogas Plants Installation - EOI PDFDocument4 pagesToR For Fiberglass Biogas Plants Installation - EOI PDFmy09No ratings yet
- Grammar 04 18Document5 pagesGrammar 04 18zsuzsi_harangoz2218No ratings yet
- Question: Consider A Point in A Structural Member That Is Subjected To PLDocument1 pageQuestion: Consider A Point in A Structural Member That Is Subjected To PLTekin EnerjiNo ratings yet
- Free Download All Aeronautical Engg Books: AERO 3-1 BOOKSDocument11 pagesFree Download All Aeronautical Engg Books: AERO 3-1 BOOKSMacen SnoodleNo ratings yet
- Production of Biodegradable Plastics AsDocument6 pagesProduction of Biodegradable Plastics AsEbenezer EffisahNo ratings yet