Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 viewsStability: ME211 Control System Engineering
Stability: ME211 Control System Engineering
Uploaded by
Muhammad Junaid JahangirThis document contains lecture notes on stability from Chapter 6 of the textbook. It introduces definitions of stability, including that a system is stable if every bounded input yields a bounded output. It describes using a Routh table to check stability by determining the number of poles in the right half plane from the number of sign changes in the first column of the table. An example Routh table is provided and explained. The notes cover material from the previous lecture and preview what will be discussed in the next lecture on additional stability techniques.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Polyphonic HMI Case PresentationDocument48 pagesPolyphonic HMI Case PresentationUtpal Biyani100% (4)
- Transient & Steady State Response AnalysisDocument32 pagesTransient & Steady State Response AnalysisMisbah Sajid ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- ME3245 Spring 2023 Chapter 6 NotesDocument37 pagesME3245 Spring 2023 Chapter 6 NotesK LugujeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - StabilityDocument19 pagesChapter 6 - StabilityDL ArtsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - StabilityDocument42 pagesChapter 7 - Stabilityvenosyah devanNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Theory: Transient Response Stability STB 35103Document68 pagesControl Systems Theory: Transient Response Stability STB 35103Muhammad Irvan FNo ratings yet
- CS II Lab Manual 5Document5 pagesCS II Lab Manual 5Ibtsaam ElahiNo ratings yet
- KON 317E Control Systems Stability of Linear Control Systems Assoc. Prof. Dr. Tufan KumbasarDocument23 pagesKON 317E Control Systems Stability of Linear Control Systems Assoc. Prof. Dr. Tufan KumbasarDogukan KarabeyinNo ratings yet
- Lecture15-15 14704 Lecture14-14 17822 RH Error PDFDocument49 pagesLecture15-15 14704 Lecture14-14 17822 RH Error PDFanuj jainNo ratings yet
- Control System (Unit-3)Document38 pagesControl System (Unit-3)sravaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 System StabilityDocument32 pagesChapter 6 System StabilityIzzat AiresNo ratings yet
- StabilityDocument66 pagesStabilityLiying ChewNo ratings yet
- 11 StabilityDocument32 pages11 StabilityLufrenzNo ratings yet
- Multiple Subsystem Reduction& RepresentationDocument13 pagesMultiple Subsystem Reduction& RepresentationRayana rayNo ratings yet
- Lesson No. 6 System StabilityDocument12 pagesLesson No. 6 System StabilityJorge BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - System StabilityDocument27 pagesChapter 5 - System StabilityANDREW LEONG CHUN TATT STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Laplace TTDocument56 pagesLaplace TTFares AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Comments On "Routh Stability Criterion" PDFDocument2 pagesComments On "Routh Stability Criterion" PDFJuan Camilo Charris HernandezNo ratings yet
- Routh-Hurwitz Criterion: Name: Aamir Irshad Section:B SAB NO:70065601 REG NO:BSME-016-047 Assignment No:02Document8 pagesRouth-Hurwitz Criterion: Name: Aamir Irshad Section:B SAB NO:70065601 REG NO:BSME-016-047 Assignment No:02Äâmïř ÌřşhądNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document20 pagesChapter 6Duncan KingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - StabilityDocument20 pagesChapter 6 - StabilityThanes WaranNo ratings yet
- 6 Module 6 Routh Hurwitz CriterionDocument30 pages6 Module 6 Routh Hurwitz CriterionJyotirmayee Panda100% (1)
- Stability CriterionDocument34 pagesStability CriterionNina ButtNo ratings yet
- Transient and Steady State Response Analysis: Module - 3Document22 pagesTransient and Steady State Response Analysis: Module - 3Rajath UpadhyaNo ratings yet
- Stability AnalysisDocument14 pagesStability Analysisgayatri jaltareNo ratings yet
- 6 Stability Routh Hurwitz BasicDocument2 pages6 Stability Routh Hurwitz BasicathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document19 pagesChapter 6hari17101991No ratings yet
- 05 Time Response AnalysisDocument41 pages05 Time Response AnalysisFadly ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Stability in Control SystemsDocument20 pagesStability in Control Systemssamir100% (1)
- Lecture 380-14 - RHDocument29 pagesLecture 380-14 - RH- FBANo ratings yet
- NMB 34203 Control Systems: System Stability: The Routh-Hurwitz CriterionDocument37 pagesNMB 34203 Control Systems: System Stability: The Routh-Hurwitz CriterionfatinNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Stability of Linear Control Systems - PDFDocument45 pagesWeek 6 - Stability of Linear Control Systems - PDFgigoNo ratings yet
- ECE317 L10 - RouthHurwitzExDocument25 pagesECE317 L10 - RouthHurwitzExumarsaboNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Stability Analysis: 1. What Is BIBO Stability?Document4 pagesUnit-Iv Stability Analysis: 1. What Is BIBO Stability?Kumar MadhuNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 StabilityDocument30 pagesChap 6 StabilitySumeyye AstalNo ratings yet
- System Stability:: Asst. Prof. Dr. Qasim Abbas Automatic Control II 1Document3 pagesSystem Stability:: Asst. Prof. Dr. Qasim Abbas Automatic Control II 1Mohamed KadhimNo ratings yet
- 12 StabilityDocument41 pages12 StabilityMaria KapiyaNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Simulation Lab Assignment-5Document5 pagesPower Systems Simulation Lab Assignment-5kiran panditNo ratings yet
- Lab 08 PDFDocument10 pagesLab 08 PDFAbdul Rehman AfzalNo ratings yet
- 2 - Stability of Linear Control SystemsDocument34 pages2 - Stability of Linear Control SystemsHassan El SayedNo ratings yet
- StabilityDocument20 pagesStabilityravalNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1675687445777 7028342556573838859Document30 pagesOrca Share Media1675687445777 7028342556573838859NanaNo ratings yet
- Stability: Dr. Issam ELGMATIDocument27 pagesStability: Dr. Issam ELGMATI7moud alajlaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document19 pagesLecture 4Houssam moussaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 StabilityDocument26 pagesLecture 14 StabilityHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- ME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapDocument4 pagesME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapSerdar BilgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document47 pagesChapter 2Emilia HermitNo ratings yet
- Regulation and Control: by Tewedage SileshiDocument22 pagesRegulation and Control: by Tewedage SileshihermelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - : The Stability of Linear Feedback SystemsDocument19 pagesChapter 6 - : The Stability of Linear Feedback SystemsNikhil V NainoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document19 pagesLecture 7Derrick Maatla MoadiNo ratings yet
- Transient and Steady State Response Analysis 2Document37 pagesTransient and Steady State Response Analysis 2ikhlasahmedsadikikhNo ratings yet
- FeedCon (Unit 5)Document18 pagesFeedCon (Unit 5)Christelle Cha LotaNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control Systems (FCS) : Lecture-26 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument19 pagesFeedback Control Systems (FCS) : Lecture-26 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionSARTHAK BAPATNo ratings yet
- Experiement 3 Feedback and Control System Manual 48921260Document6 pagesExperiement 3 Feedback and Control System Manual 48921260Eldeen EscuadroNo ratings yet
- Workshop 2 Feedback Control Loop Concepts: Prior To Attempting This Workshop, You Should Review Chapter 3 in The BookDocument5 pagesWorkshop 2 Feedback Control Loop Concepts: Prior To Attempting This Workshop, You Should Review Chapter 3 in The Bookshashikant0288No ratings yet
- Cs 8343 Stability Concept AnalysisDocument59 pagesCs 8343 Stability Concept AnalysisCrescent MnyamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 - Ver 1Document16 pagesChapter6 - Ver 1George MathaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14, 15 StabilityDocument45 pagesLecture 14, 15 StabilityHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Lcs 9Document5 pagesLcs 9MianNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Stability of Feedback Control SystemsDocument30 pages2.3 Stability of Feedback Control SystemsJust RobotNo ratings yet
- ME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 16 March, 2021Document41 pagesME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 16 March, 2021Muhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 12 March, 2021Document19 pagesME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 12 March, 2021Muhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 10 March, 2021Document11 pagesME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 10 March, 2021Muhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 9 March, 2021Document10 pagesME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 9 March, 2021Muhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 5 March, 2021Document12 pagesME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 5 March, 2021Muhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME211 Lec8 Fall20 DrIrtizaDocument5 pagesME211 Lec8 Fall20 DrIrtizaMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Multiple Systems: ME211 Control System EngineeringDocument6 pagesReduction of Multiple Systems: ME211 Control System EngineeringMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Controls: ME211 Control System EngineeringDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Controls: ME211 Control System EngineeringMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME211 Lec11 Fall20 DrIrtizaDocument5 pagesME211 Lec11 Fall20 DrIrtizaMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Modelling in Frequency Domain: ME211 Control System EngineeringDocument6 pagesModelling in Frequency Domain: ME211 Control System EngineeringMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME211 Lec8 Fall20 DrIrtizaDocument5 pagesME211 Lec8 Fall20 DrIrtizaMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Controls: ME211 Control System EngineeringDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Controls: ME211 Control System EngineeringMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Controls Engineering 2-1: DR Syed Irtizaali ShahDocument11 pagesControls Engineering 2-1: DR Syed Irtizaali ShahMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Upcat 2014 - Simulated Exam - Set A - Section 2 - Science Proficiency v.5.26Document14 pagesUpcat 2014 - Simulated Exam - Set A - Section 2 - Science Proficiency v.5.26Regina MercurioNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in The Outdoors 1Document13 pagesRisk Management in The Outdoors 1api-278802103No ratings yet
- Cockateil Pairing DetailsDocument4 pagesCockateil Pairing DetailsWaseem UllahNo ratings yet
- HPTM Machine DetailsDocument7 pagesHPTM Machine DetailsK Srinivasa Sagar100% (1)
- Dio125 and Hornet2 RepsolDocument2 pagesDio125 and Hornet2 RepsolSibi SundarNo ratings yet
- ECG-Based Biometric Schemes For Healthcare: A Systematic ReviewDocument23 pagesECG-Based Biometric Schemes For Healthcare: A Systematic ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Part EM - Classical ElectrodynamicsDocument415 pagesPart EM - Classical Electrodynamicsapoorva singhNo ratings yet
- IOF Circular-Online RegistrationDocument2 pagesIOF Circular-Online Registration7A04Aditya MayankNo ratings yet
- A Handbook of Art SmithingDocument232 pagesA Handbook of Art SmithingArtisan Ideas100% (3)
- URS Barrier Isolator v0904Document33 pagesURS Barrier Isolator v0904ipatoff50% (2)
- Slem Pc11ag Quarter1 Week8-SlmDocument22 pagesSlem Pc11ag Quarter1 Week8-SlmJuna Marie SuarezNo ratings yet
- CDP Virtual Appliance Getting Started GuideDocument18 pagesCDP Virtual Appliance Getting Started GuideJulio RodanesNo ratings yet
- PagesfromICSSR Volume2 1stproofDocument25 pagesPagesfromICSSR Volume2 1stproofTechno GamingNo ratings yet
- Fire PreventionDocument2 pagesFire PreventionMarlon Arian Conde AhorroNo ratings yet
- EnPI V5.0 Algorithm DocumentDocument14 pagesEnPI V5.0 Algorithm DocumentDalila AmmarNo ratings yet
- Sealwell-Pump Mechanical SealsDocument8 pagesSealwell-Pump Mechanical SealsVaibhav JainNo ratings yet
- IBS CaseDocument8 pagesIBS CaseStarr NewmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Mohammad Nasir AliNo ratings yet
- BC 367 Experiment 4 Kinetic Properties of Acid Phosphatase: Roh + Hpo Phosphatase + H ODocument8 pagesBC 367 Experiment 4 Kinetic Properties of Acid Phosphatase: Roh + Hpo Phosphatase + H OAliceKeikoNo ratings yet
- What I Need To Know? What I Need To Know?: Quarter 1Document16 pagesWhat I Need To Know? What I Need To Know?: Quarter 1Aileen gay PayunanNo ratings yet
- L4Tnm-Psa: Product ClassificationDocument4 pagesL4Tnm-Psa: Product Classificationhassan329No ratings yet
- Causes For Tempdb Full - SQL ServerDocument4 pagesCauses For Tempdb Full - SQL Serverarunkumarco0% (1)
- Rose Water OintmentDocument1 pageRose Water OintmentThomas Niccolo Filamor ReyesNo ratings yet
- Fluency ReflectionDocument7 pagesFluency Reflectionapi-316375440No ratings yet
- Turino Thomas Peircean Phenomenology and PDFDocument13 pagesTurino Thomas Peircean Phenomenology and PDFFelipe BarãoNo ratings yet
- Review of Random ProcessesDocument34 pagesReview of Random Processesali_rehman87No ratings yet
- PROWESS User ManualDocument33 pagesPROWESS User ManualSachin Dhiman100% (9)
- Hank Kolb 3Document3 pagesHank Kolb 3gr8_amaraNo ratings yet
Stability: ME211 Control System Engineering
Stability: ME211 Control System Engineering
Uploaded by
Muhammad Junaid Jahangir0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views7 pagesThis document contains lecture notes on stability from Chapter 6 of the textbook. It introduces definitions of stability, including that a system is stable if every bounded input yields a bounded output. It describes using a Routh table to check stability by determining the number of poles in the right half plane from the number of sign changes in the first column of the table. An example Routh table is provided and explained. The notes cover material from the previous lecture and preview what will be discussed in the next lecture on additional stability techniques.
Original Description:
Original Title
ME211_Lec20_Fall20_DrIrtiza
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains lecture notes on stability from Chapter 6 of the textbook. It introduces definitions of stability, including that a system is stable if every bounded input yields a bounded output. It describes using a Routh table to check stability by determining the number of poles in the right half plane from the number of sign changes in the first column of the table. An example Routh table is provided and explained. The notes cover material from the previous lecture and preview what will be discussed in the next lecture on additional stability techniques.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views7 pagesStability: ME211 Control System Engineering
Stability: ME211 Control System Engineering
Uploaded by
Muhammad Junaid JahangirThis document contains lecture notes on stability from Chapter 6 of the textbook. It introduces definitions of stability, including that a system is stable if every bounded input yields a bounded output. It describes using a Routh table to check stability by determining the number of poles in the right half plane from the number of sign changes in the first column of the table. An example Routh table is provided and explained. The notes cover material from the previous lecture and preview what will be discussed in the next lecture on additional stability techniques.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
ME211 Control System Engineering
Dr Syed Irtiza Ali Shah
Stability
REF: TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 6 (TCH6)
Lecture notes by Dr Syed Irtiza Ali Shah
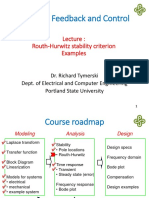
Where we are
Last time
◦ Chapter 5: Reduction of multiple subsystems
◦ Block diagrams
◦ Block Diagram Reduction
◦ Equivalent transfer functions
◦ Reduction of State Space Systems
◦ Signal flow graphs
◦ Mason’s rule
Now
◦ Chapter 6: Stability
◦ Introduction, Definitions
◦ Creating a Routh table
◦ Stability via reverse coefficients
◦ Stability via Routh table with row of zeros
◦ Stability design via Routh Hurwitz
Lecture notes by Dr Syed Irtiza Ali Shah
Introduction, Definitions
Stability (Recall Chapter 1: Lecture 2)
◦ Total response= natural + forced response; natural response must diminish to
almost zero with time
◦ A system must be stable in order to produce proper transient and steady state
response
Another definition: A system is stable if every bounded input yields a
bounded output
A stable system has closed-loop transfer function poles in left half
plane only
◦ Unstable system has at least one pole in right half or more than one pole on
imaginary axis
◦ A marginally stable system has one pole on imaginary axis and other poles in left
half
Lecture notes by Dr Syed Irtiza Ali Shah
Response of stable/unstable systems
First find closed loop Transfer function
(Recall lecture 17)
C = G E (1) and E = R – C H (2)
(2) In (1) => C = G (R – C H)
=> C (1+GH) = G R
=> C/R = G / (1+GH)
For fig 6.1(a) C/R = 3 / (s3+3s2+2s+3)
Solve denominator using Matlab to get poles
Lecture notes by Dr Syed Irtiza Ali Shah
Creating a Routh Table
Alternate technique to Matlab/Numerical/Factorization, finding closed loop poles to
check stability, is called Routh- Hurwitz criterion
Step 3
We first set up a Routh Table as follows
Step 1
Step 2
Routh Hurwitz Criteria of knowing Stability from
Routh Table:
No. of sign changes in 1st column = No. of poles
in right half plane
Lecture notes by Dr Syed Irtiza Ali Shah
Routh Table Example
Step 2
Note: You can divide any full row by any number e.g R2 was divided by 10
Step 3
Step 1 1
Routh Hurwitz Criteria =>2 poles in rt half =>unstable system
Reading Assignment
Skill Assessment Exercise 6.1
Lecture notes by Dr Syed Irtiza Ali Shah
Summary
We covered today:
◦ Chapter 6: Stability
◦ Introduction, Definitions
◦ Creating a Routh table
Next Time:
◦ Stability via reverse coefficients
◦ Stability via Routh table with row of zeros
◦ Stability design via Routh Hurwitz
Lecture notes by Dr Syed Irtiza Ali Shah
You might also like
- Polyphonic HMI Case PresentationDocument48 pagesPolyphonic HMI Case PresentationUtpal Biyani100% (4)
- Transient & Steady State Response AnalysisDocument32 pagesTransient & Steady State Response AnalysisMisbah Sajid ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- ME3245 Spring 2023 Chapter 6 NotesDocument37 pagesME3245 Spring 2023 Chapter 6 NotesK LugujeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - StabilityDocument19 pagesChapter 6 - StabilityDL ArtsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - StabilityDocument42 pagesChapter 7 - Stabilityvenosyah devanNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Theory: Transient Response Stability STB 35103Document68 pagesControl Systems Theory: Transient Response Stability STB 35103Muhammad Irvan FNo ratings yet
- CS II Lab Manual 5Document5 pagesCS II Lab Manual 5Ibtsaam ElahiNo ratings yet
- KON 317E Control Systems Stability of Linear Control Systems Assoc. Prof. Dr. Tufan KumbasarDocument23 pagesKON 317E Control Systems Stability of Linear Control Systems Assoc. Prof. Dr. Tufan KumbasarDogukan KarabeyinNo ratings yet
- Lecture15-15 14704 Lecture14-14 17822 RH Error PDFDocument49 pagesLecture15-15 14704 Lecture14-14 17822 RH Error PDFanuj jainNo ratings yet
- Control System (Unit-3)Document38 pagesControl System (Unit-3)sravaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 System StabilityDocument32 pagesChapter 6 System StabilityIzzat AiresNo ratings yet
- StabilityDocument66 pagesStabilityLiying ChewNo ratings yet
- 11 StabilityDocument32 pages11 StabilityLufrenzNo ratings yet
- Multiple Subsystem Reduction& RepresentationDocument13 pagesMultiple Subsystem Reduction& RepresentationRayana rayNo ratings yet
- Lesson No. 6 System StabilityDocument12 pagesLesson No. 6 System StabilityJorge BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - System StabilityDocument27 pagesChapter 5 - System StabilityANDREW LEONG CHUN TATT STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Laplace TTDocument56 pagesLaplace TTFares AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Comments On "Routh Stability Criterion" PDFDocument2 pagesComments On "Routh Stability Criterion" PDFJuan Camilo Charris HernandezNo ratings yet
- Routh-Hurwitz Criterion: Name: Aamir Irshad Section:B SAB NO:70065601 REG NO:BSME-016-047 Assignment No:02Document8 pagesRouth-Hurwitz Criterion: Name: Aamir Irshad Section:B SAB NO:70065601 REG NO:BSME-016-047 Assignment No:02Äâmïř ÌřşhądNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document20 pagesChapter 6Duncan KingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - StabilityDocument20 pagesChapter 6 - StabilityThanes WaranNo ratings yet
- 6 Module 6 Routh Hurwitz CriterionDocument30 pages6 Module 6 Routh Hurwitz CriterionJyotirmayee Panda100% (1)
- Stability CriterionDocument34 pagesStability CriterionNina ButtNo ratings yet
- Transient and Steady State Response Analysis: Module - 3Document22 pagesTransient and Steady State Response Analysis: Module - 3Rajath UpadhyaNo ratings yet
- Stability AnalysisDocument14 pagesStability Analysisgayatri jaltareNo ratings yet
- 6 Stability Routh Hurwitz BasicDocument2 pages6 Stability Routh Hurwitz BasicathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document19 pagesChapter 6hari17101991No ratings yet
- 05 Time Response AnalysisDocument41 pages05 Time Response AnalysisFadly ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Stability in Control SystemsDocument20 pagesStability in Control Systemssamir100% (1)
- Lecture 380-14 - RHDocument29 pagesLecture 380-14 - RH- FBANo ratings yet
- NMB 34203 Control Systems: System Stability: The Routh-Hurwitz CriterionDocument37 pagesNMB 34203 Control Systems: System Stability: The Routh-Hurwitz CriterionfatinNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Stability of Linear Control Systems - PDFDocument45 pagesWeek 6 - Stability of Linear Control Systems - PDFgigoNo ratings yet
- ECE317 L10 - RouthHurwitzExDocument25 pagesECE317 L10 - RouthHurwitzExumarsaboNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Stability Analysis: 1. What Is BIBO Stability?Document4 pagesUnit-Iv Stability Analysis: 1. What Is BIBO Stability?Kumar MadhuNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 StabilityDocument30 pagesChap 6 StabilitySumeyye AstalNo ratings yet
- System Stability:: Asst. Prof. Dr. Qasim Abbas Automatic Control II 1Document3 pagesSystem Stability:: Asst. Prof. Dr. Qasim Abbas Automatic Control II 1Mohamed KadhimNo ratings yet
- 12 StabilityDocument41 pages12 StabilityMaria KapiyaNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Simulation Lab Assignment-5Document5 pagesPower Systems Simulation Lab Assignment-5kiran panditNo ratings yet
- Lab 08 PDFDocument10 pagesLab 08 PDFAbdul Rehman AfzalNo ratings yet
- 2 - Stability of Linear Control SystemsDocument34 pages2 - Stability of Linear Control SystemsHassan El SayedNo ratings yet
- StabilityDocument20 pagesStabilityravalNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1675687445777 7028342556573838859Document30 pagesOrca Share Media1675687445777 7028342556573838859NanaNo ratings yet
- Stability: Dr. Issam ELGMATIDocument27 pagesStability: Dr. Issam ELGMATI7moud alajlaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document19 pagesLecture 4Houssam moussaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 StabilityDocument26 pagesLecture 14 StabilityHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- ME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapDocument4 pagesME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapSerdar BilgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document47 pagesChapter 2Emilia HermitNo ratings yet
- Regulation and Control: by Tewedage SileshiDocument22 pagesRegulation and Control: by Tewedage SileshihermelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - : The Stability of Linear Feedback SystemsDocument19 pagesChapter 6 - : The Stability of Linear Feedback SystemsNikhil V NainoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document19 pagesLecture 7Derrick Maatla MoadiNo ratings yet
- Transient and Steady State Response Analysis 2Document37 pagesTransient and Steady State Response Analysis 2ikhlasahmedsadikikhNo ratings yet
- FeedCon (Unit 5)Document18 pagesFeedCon (Unit 5)Christelle Cha LotaNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control Systems (FCS) : Lecture-26 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument19 pagesFeedback Control Systems (FCS) : Lecture-26 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionSARTHAK BAPATNo ratings yet
- Experiement 3 Feedback and Control System Manual 48921260Document6 pagesExperiement 3 Feedback and Control System Manual 48921260Eldeen EscuadroNo ratings yet
- Workshop 2 Feedback Control Loop Concepts: Prior To Attempting This Workshop, You Should Review Chapter 3 in The BookDocument5 pagesWorkshop 2 Feedback Control Loop Concepts: Prior To Attempting This Workshop, You Should Review Chapter 3 in The Bookshashikant0288No ratings yet
- Cs 8343 Stability Concept AnalysisDocument59 pagesCs 8343 Stability Concept AnalysisCrescent MnyamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 - Ver 1Document16 pagesChapter6 - Ver 1George MathaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14, 15 StabilityDocument45 pagesLecture 14, 15 StabilityHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Lcs 9Document5 pagesLcs 9MianNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Stability of Feedback Control SystemsDocument30 pages2.3 Stability of Feedback Control SystemsJust RobotNo ratings yet
- ME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 16 March, 2021Document41 pagesME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 16 March, 2021Muhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 12 March, 2021Document19 pagesME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 12 March, 2021Muhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 10 March, 2021Document11 pagesME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 10 March, 2021Muhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 9 March, 2021Document10 pagesME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 9 March, 2021Muhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 5 March, 2021Document12 pagesME-329 - Mechanical Vibrations: Dated: 5 March, 2021Muhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME211 Lec8 Fall20 DrIrtizaDocument5 pagesME211 Lec8 Fall20 DrIrtizaMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Multiple Systems: ME211 Control System EngineeringDocument6 pagesReduction of Multiple Systems: ME211 Control System EngineeringMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Controls: ME211 Control System EngineeringDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Controls: ME211 Control System EngineeringMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME211 Lec11 Fall20 DrIrtizaDocument5 pagesME211 Lec11 Fall20 DrIrtizaMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Modelling in Frequency Domain: ME211 Control System EngineeringDocument6 pagesModelling in Frequency Domain: ME211 Control System EngineeringMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- ME211 Lec8 Fall20 DrIrtizaDocument5 pagesME211 Lec8 Fall20 DrIrtizaMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Controls: ME211 Control System EngineeringDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Controls: ME211 Control System EngineeringMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Controls Engineering 2-1: DR Syed Irtizaali ShahDocument11 pagesControls Engineering 2-1: DR Syed Irtizaali ShahMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Upcat 2014 - Simulated Exam - Set A - Section 2 - Science Proficiency v.5.26Document14 pagesUpcat 2014 - Simulated Exam - Set A - Section 2 - Science Proficiency v.5.26Regina MercurioNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in The Outdoors 1Document13 pagesRisk Management in The Outdoors 1api-278802103No ratings yet
- Cockateil Pairing DetailsDocument4 pagesCockateil Pairing DetailsWaseem UllahNo ratings yet
- HPTM Machine DetailsDocument7 pagesHPTM Machine DetailsK Srinivasa Sagar100% (1)
- Dio125 and Hornet2 RepsolDocument2 pagesDio125 and Hornet2 RepsolSibi SundarNo ratings yet
- ECG-Based Biometric Schemes For Healthcare: A Systematic ReviewDocument23 pagesECG-Based Biometric Schemes For Healthcare: A Systematic ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Part EM - Classical ElectrodynamicsDocument415 pagesPart EM - Classical Electrodynamicsapoorva singhNo ratings yet
- IOF Circular-Online RegistrationDocument2 pagesIOF Circular-Online Registration7A04Aditya MayankNo ratings yet
- A Handbook of Art SmithingDocument232 pagesA Handbook of Art SmithingArtisan Ideas100% (3)
- URS Barrier Isolator v0904Document33 pagesURS Barrier Isolator v0904ipatoff50% (2)
- Slem Pc11ag Quarter1 Week8-SlmDocument22 pagesSlem Pc11ag Quarter1 Week8-SlmJuna Marie SuarezNo ratings yet
- CDP Virtual Appliance Getting Started GuideDocument18 pagesCDP Virtual Appliance Getting Started GuideJulio RodanesNo ratings yet
- PagesfromICSSR Volume2 1stproofDocument25 pagesPagesfromICSSR Volume2 1stproofTechno GamingNo ratings yet
- Fire PreventionDocument2 pagesFire PreventionMarlon Arian Conde AhorroNo ratings yet
- EnPI V5.0 Algorithm DocumentDocument14 pagesEnPI V5.0 Algorithm DocumentDalila AmmarNo ratings yet
- Sealwell-Pump Mechanical SealsDocument8 pagesSealwell-Pump Mechanical SealsVaibhav JainNo ratings yet
- IBS CaseDocument8 pagesIBS CaseStarr NewmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Mohammad Nasir AliNo ratings yet
- BC 367 Experiment 4 Kinetic Properties of Acid Phosphatase: Roh + Hpo Phosphatase + H ODocument8 pagesBC 367 Experiment 4 Kinetic Properties of Acid Phosphatase: Roh + Hpo Phosphatase + H OAliceKeikoNo ratings yet
- What I Need To Know? What I Need To Know?: Quarter 1Document16 pagesWhat I Need To Know? What I Need To Know?: Quarter 1Aileen gay PayunanNo ratings yet
- L4Tnm-Psa: Product ClassificationDocument4 pagesL4Tnm-Psa: Product Classificationhassan329No ratings yet
- Causes For Tempdb Full - SQL ServerDocument4 pagesCauses For Tempdb Full - SQL Serverarunkumarco0% (1)
- Rose Water OintmentDocument1 pageRose Water OintmentThomas Niccolo Filamor ReyesNo ratings yet
- Fluency ReflectionDocument7 pagesFluency Reflectionapi-316375440No ratings yet
- Turino Thomas Peircean Phenomenology and PDFDocument13 pagesTurino Thomas Peircean Phenomenology and PDFFelipe BarãoNo ratings yet
- Review of Random ProcessesDocument34 pagesReview of Random Processesali_rehman87No ratings yet
- PROWESS User ManualDocument33 pagesPROWESS User ManualSachin Dhiman100% (9)
- Hank Kolb 3Document3 pagesHank Kolb 3gr8_amaraNo ratings yet