Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Yin and Yang in The Modern Era
Yin and Yang in The Modern Era
Uploaded by
Trung Hiệp Đào0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesThis document discusses acupuncture and how it can help regulate the autonomic nervous system. It explains that acupuncture signals travel along nerves to the central nervous system and can have effects such as reducing pain, altering organ function, and changing activity in the brain. The body's pre-existing state influences how it responds to acupuncture. Traditional Chinese medicine concepts like "yang excess" and "yin deficiency" refer to sympathetic hyperfunction and parasympathetic hypofunction, respectively. Disease states illustrate imbalances between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Original Description:
Original Title
4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses acupuncture and how it can help regulate the autonomic nervous system. It explains that acupuncture signals travel along nerves to the central nervous system and can have effects such as reducing pain, altering organ function, and changing activity in the brain. The body's pre-existing state influences how it responds to acupuncture. Traditional Chinese medicine concepts like "yang excess" and "yin deficiency" refer to sympathetic hyperfunction and parasympathetic hypofunction, respectively. Disease states illustrate imbalances between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesYin and Yang in The Modern Era
Yin and Yang in The Modern Era
Uploaded by
Trung Hiệp ĐàoThis document discusses acupuncture and how it can help regulate the autonomic nervous system. It explains that acupuncture signals travel along nerves to the central nervous system and can have effects such as reducing pain, altering organ function, and changing activity in the brain. The body's pre-existing state influences how it responds to acupuncture. Traditional Chinese medicine concepts like "yang excess" and "yin deficiency" refer to sympathetic hyperfunction and parasympathetic hypofunction, respectively. Disease states illustrate imbalances between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
the organism.
2,3,4,5,6 Sometimes, though, autoregulatory processes
either falter or fail. Acupuncture is simply a somatosensory input
that assists the body in making the neuromodulatory changes
necessary to regain health and homeostasis.7
Acupuncture neuromodulation signals initiated near needling
sites propagate along nerves toward the CNS.1 Connections at the
spinal cord can course in several directions. The cord may 1) send
efferent signals back out to the periphery (leading to antidromic
activation of free nerve endings at the site of needling), 2) loop into
related visceral neural networks and alter internal organ function
in a spinal segmental manner, 3) foster endogenous opioid release
in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord to reduce spinal facilitation,
or “wind-up”, and block pain, and/or 4) proceed to higher centers
in the brain, altering neural and hormonal functions. When these
impulses arrive at the brain, they influence activity there as well,
usually in a beneficial manner.
Exactly how the body responds and which parts of the body react
depend on the nerves stimulated.8 However, the body’s pre-needling state may also influence
outcomes.9,10 For example, the
point ST 36 treats both diarrhea and constipation, depending on
pre-treatment gastrointestinal motility status.11,12 In this way, the
same point can either “quiets things down” in cases of hyperfunction, or “fire them up” in
hypofunction.
Yin and Yang in the Modern Era
TCM terms such as “Yang Excess” and “Yin Deficiency” can
now be viewed as sympathetic hyperfunction or parasympathetic hypofunction.13,14 Disease
states that illustrate Yang Excess
The Tai Ji symbol illustrates the balanced, intertwining, and evolving
relationship between Yin (black) and Yang (white), with elements of the
complementary partner held by each component (represented by the
small circles).
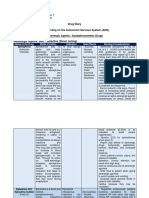
Effects of Sympathetic System Effects of Parasympathetic System
Organ
(Yang) (Yin)
Adipocyte metabolism Causes lipolysis ---
Adipocyte, brown Causes heat production ---
Causes adrenaline/epinephrine (80%)
and
Adrenal medulla ---
noradrenaline/norepinephrine (20%)
secretion
Arteries in cranium Vasoconstricts May vasodilate
Arteries in erectile tissue (helical
arteries Vasoconstricts Vasodilates
and sinusoids in penis and clitoris)
Arteries in heart20 (coronary Transient vasoconstriction, followed
Some vasodilation
arteries) by vasodilation
Vasoconstricts (via adrenergic fibers)
under resting tone
Arteries in skeletal muscle and vasodilates large arteries (via ---
cholinergic fibers)
during exercise
Arteries in skin and mucosa of face Vasoconstricts Vasodilates
Arteries in skin of trunk and limbs Vasoconstricts ----
Arteries in viscera Vasoconstricts ----
Motility decreases Motility increases
Esophagus
Sphincters contract Sphincters relax
Pupillary dilator muscle dilates pupil Pupillary sphincter muscle contracts
Eye Contracts tarsal muscle (lifts lid) pupil
Ciliary muscle relaxes for far vision Contracts ciliary muscle
Gallbladder and biliary ducts Relaxes Contracts
Table 2-1 Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
Functions18,19
include hyperthyroidism and acute fever. “Deficient Yin” describes
parasympathetic hypofunction, most dramatically depicted by
toxic exposure to anticholinergics, or parasympathetic antagonists. In this case, the victim turns “red as a beet, blind
as a bat,
dry as a bone, mad as a hatter, and hot as hell”.15
Conversely, “Excess Yin” connotes just the opposite, i.e.,
parasympathetic hyperfunction and/or sympathetic hypofunction.
One might even see a concatenation of autonomic disruption,
as in cluster headaches. These patients exhibit both sym
You might also like
- Lab Report - Smooth MuscleDocument8 pagesLab Report - Smooth Muscledhebbert100% (2)
- Anatomy & Physiology Bootcamp NotesDocument51 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Bootcamp Notesgeorgia robinsonNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology PPT (27 September 2018)Document72 pagesExercise Physiology PPT (27 September 2018)Surya Diatmika100% (1)
- Yin and Yang in The Modern EraDocument1 pageYin and Yang in The Modern EraTrung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 5Document13 pagesBiology Chapter 5Shahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Autonomic Nervous System Fall 2021Document22 pagesNervous System - Autonomic Nervous System Fall 2021ElenaNo ratings yet
- Cvs 4Document4 pagesCvs 4Kim Sa-buNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesChapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous SystemidjacobsNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesCardiovascular SystemPurple Ivy GuarraNo ratings yet
- Lecture - HeartDocument102 pagesLecture - HeartohmedicalstudyNo ratings yet
- Autonom NerveDocument27 pagesAutonom NerveMochammad Fariz AmsalNo ratings yet
- Nervous System DivisionsDocument52 pagesNervous System DivisionsJohn Toni OrtizNo ratings yet
- EMBRYOLOGYDocument33 pagesEMBRYOLOGYkhaledNo ratings yet
- 1.04 Autonomic Cardiovascular Physiology 2021Document19 pages1.04 Autonomic Cardiovascular Physiology 2021JedoNo ratings yet
- Lecture DPT 4 NEURO ANATOMY 'Autonomic Nervous System'Document57 pagesLecture DPT 4 NEURO ANATOMY 'Autonomic Nervous System'CHANGEZ KHAN SARDARNo ratings yet
- Your Nervous System Please Do Not Be NervousDocument13 pagesYour Nervous System Please Do Not Be Nervousrahaf qatawnehNo ratings yet
- Sistem Saraf OtonomDocument46 pagesSistem Saraf OtonomWorldhealthNo ratings yet
- SGS235T Fall2015Document73 pagesSGS235T Fall2015Sohaila HishamNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Studyaid (2ed)Document64 pagesNeuroanatomy Studyaid (2ed)Halima AtikuNo ratings yet
- SSO Ok-EditDocument60 pagesSSO Ok-EditNahla FaridaNo ratings yet
- The Circulation: Blood Pressure RegulationDocument42 pagesThe Circulation: Blood Pressure RegulationLouis JinNo ratings yet
- Phase 2 Cardiac Muscle - 1Document30 pagesPhase 2 Cardiac Muscle - 1erenyorulmaz143No ratings yet
- Body System Approach: Emdat Suprayitno S.Kep.,Ns.M.KepDocument50 pagesBody System Approach: Emdat Suprayitno S.Kep.,Ns.M.KepKartika SariNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Circulatory SystemDocument51 pagesUnit 4 Circulatory SystemNURIA VAZQUEZNo ratings yet
- C10Document318 pagesC10azfdin50% (2)
- Autonomic Nervous System: Ginus Partadiredja Department of PhysiologyDocument25 pagesAutonomic Nervous System: Ginus Partadiredja Department of PhysiologyElgitha BandasoNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemSUTHAN100% (4)
- Autonomic N S 2 - DentistryDocument33 pagesAutonomic N S 2 - DentistryMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument11 pagesHead and NeckHisham Chomany100% (1)
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesAutonomic Nervous Systemardywilliams01No ratings yet
- Autonomic Innervation of The Heart and Vasculature: Baroreceptors ChemoreceptorsDocument6 pagesAutonomic Innervation of The Heart and Vasculature: Baroreceptors ChemoreceptorsDede ApriyantoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument140 pagesPharmacology: Autonomic Nervous SystemSharifa Darayan100% (1)
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemShubham JainNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)Document8 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)202210034No ratings yet
- Robbins - 12 The HeartDocument5 pagesRobbins - 12 The HeartCM NajitoNo ratings yet
- Regulation of BPDocument17 pagesRegulation of BPLemon CatbaganNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: The Spinal CordDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: The Spinal CordMichelle MontemayorNo ratings yet
- CH 21: Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument21 pagesCH 21: Cardiovascular System - The HeartMadhuri DandamudiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 The Circulatoy System: Prepared By: LING MEI TENGDocument13 pages1.2 The Circulatoy System: Prepared By: LING MEI TENGJuliet LingNo ratings yet
- Human Body Minipedia - Nodrm-16-30Document15 pagesHuman Body Minipedia - Nodrm-16-30kailashNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument12 pagesBody Fluids and Circulationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Body Fluids & CirculationDocument34 pagesBody Fluids & CirculationNripendra TiwaryNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Regulation - SlidesDocument35 pagesBlood Pressure Regulation - Slidesمحمد السنجلاويNo ratings yet
- Autonomic SystemDocument29 pagesAutonomic Systemsanaya100% (1)
- Lecture 8 - Neural Regulation of Cardiac Activity and Cardiac ReflexesDocument35 pagesLecture 8 - Neural Regulation of Cardiac Activity and Cardiac ReflexesVishal BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- PHYS150 Tutorial 2 - Cardiovascular SystemDocument68 pagesPHYS150 Tutorial 2 - Cardiovascular Systemsamreenkaur1196No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCirculatory SystemGiane MadrigalNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: The Central Processing UnitDocument192 pagesThe Nervous System: The Central Processing UnitHossein KhorramiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Properties of Myocardium and Cardiac Cycle 2020-2021Document43 pagesLecture 4 Properties of Myocardium and Cardiac Cycle 2020-2021badarbhai222No ratings yet
- 2 AnsDocument97 pages2 AnsMahmoud AboudNo ratings yet
- 3-Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument89 pages3-Autonomic Nervous SystemYoueel IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Regulation of CVSDocument27 pagesRegulation of CVSvirajmore6222No ratings yet
- ArticuloDocument13 pagesArticuloGissela AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemLUKANo ratings yet
- ECG LecturesDocument144 pagesECG Lecturesİlayda KavascıkNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesLec 3 - Circulatory SystemJewel Jehd AlegriaNo ratings yet
- The Conducting System of The Heart 1Document6 pagesThe Conducting System of The Heart 1maxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - 2Document45 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - 2salahnwsNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument8 pagesCirculatory System Notesthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSDocument56 pagesPhysiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSDocument56 pagesPhysiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2:: Function Follows Form 29Document3 pagesChapter 2:: Function Follows Form 29Trung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Facet Joint CapsuleDocument3 pagesFacet Joint CapsuleTrung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Assembling Acupuncture Points To Impart A Meaningful Neuromodulatory InputDocument2 pagesAssembling Acupuncture Points To Impart A Meaningful Neuromodulatory InputTrung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Middle Cervical GanglionDocument2 pagesMiddle Cervical GanglionTrung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- The Rostral Ventral Lateral Medulla: Somato-Somatic ReflexesDocument2 pagesThe Rostral Ventral Lateral Medulla: Somato-Somatic ReflexesTrung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Extrasegmental Acupuncture Points and Autonomic FunctionDocument2 pagesExtrasegmental Acupuncture Points and Autonomic FunctionTrung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Yin and Yang in The Modern EraDocument1 pageYin and Yang in The Modern EraTrung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- ND NeckDocument2 pagesND NeckTrung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- The Needle-Tissue InterfaceDocument1 pageThe Needle-Tissue InterfaceTrung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- How Acupuncture Points Affect Internal OrgansDocument2 pagesHow Acupuncture Points Affect Internal OrgansTrung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic Preganglionic Levels Site of Synapse of Pre-And Post-Gan Glionic Sympathetic Neurons Course of Nociceptive Afferent Pathways Into The Central Nervous System Lungs (Including TheDocument2 pagesSympathetic Preganglionic Levels Site of Synapse of Pre-And Post-Gan Glionic Sympathetic Neurons Course of Nociceptive Afferent Pathways Into The Central Nervous System Lungs (Including TheTrung Hiệp ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Self Assessment Questions: Your Last Recorded Submission Was On 2021-09-27, 19:14 ISTDocument54 pagesUnit 1 - Self Assessment Questions: Your Last Recorded Submission Was On 2021-09-27, 19:14 ISTHeet Rathod50% (2)
- Introduction To Adrenal Fatigue DR LamDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Adrenal Fatigue DR Lamiri_bal0% (1)
- New Approaches To Managing StressDocument5 pagesNew Approaches To Managing Stresssmith.kevin1420344No ratings yet
- Adrenergic DrugsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic DrugsbezaleeljonelNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AgentsDocument7 pagesAdrenergic AgentsMuhamed ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 AddqDocument12 pagesChapter 21 AddqLenel John Giban Bagunas100% (1)
- Adrenergic Neurotransmitter PDFDocument4 pagesAdrenergic Neurotransmitter PDFFaddy OrahaNo ratings yet
- Course Code: BP402T Course Title: Medicinal Chemistry IDocument25 pagesCourse Code: BP402T Course Title: Medicinal Chemistry Isaurav prasadNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Endocrine SystemDocument48 pagesDisorders of Endocrine SystemSHARIM ASGHARNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System: Pharmacology (Lecture)Document6 pagesAutonomic Nervous System: Pharmacology (Lecture)AmaetenNo ratings yet
- Zalameda ANSDocument32 pagesZalameda ANSNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Nclex PharmaDocument22 pagesNclex Pharmakennedy14344No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ON Anatomy and Physiology of Endocrine System: Presented byDocument29 pagesLesson Plan ON Anatomy and Physiology of Endocrine System: Presented bydhanasundariNo ratings yet
- Inotrópicos y Vasopresores PDFDocument22 pagesInotrópicos y Vasopresores PDFJosé Luis Méndez ChagoyaNo ratings yet
- BrimonidineDocument8 pagesBrimonidinefiras qasimNo ratings yet
- Control Systems - KeyDocument2 pagesControl Systems - KeySamra ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Serotonin Dopamine and NeurotransmittersDocument6 pagesSerotonin Dopamine and Neurotransmittersapi-533834366No ratings yet
- CortisolDocument2 pagesCortisolkitu_alagappan4720No ratings yet
- Regulation of Intermediary MetabolismDocument9 pagesRegulation of Intermediary MetabolismDr Sanjeeb Kumar Dey BaidyaNo ratings yet
- Day 22 Signaling 1: General Concepts and cAMP Pathway: - You Should Be Able To ExplainDocument20 pagesDay 22 Signaling 1: General Concepts and cAMP Pathway: - You Should Be Able To Explainshouq huusainNo ratings yet
- Hormones: Test Yourself 15.1 (Page 287)Document3 pagesHormones: Test Yourself 15.1 (Page 287)leeNo ratings yet
- Shock Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesShock Lecture Notescolek22100% (7)
- Gingival Retraction Methods For Fabrication of FixDocument9 pagesGingival Retraction Methods For Fabrication of FixChokri SahbaniNo ratings yet
- Lisa Gromicko SleepDocument9 pagesLisa Gromicko SleepHien DaoNo ratings yet
- Master Emergency Drugs Before U Practise DR Vishwa Medical CoachingDocument6 pagesMaster Emergency Drugs Before U Practise DR Vishwa Medical Coachingابو عبد الرحمنNo ratings yet
- Adrenaline - EpinephrineDocument3 pagesAdrenaline - Epinephrinesweety DangiNo ratings yet
- Aklimatisasi Hewan CobaDocument6 pagesAklimatisasi Hewan CobaNurma FitriaNo ratings yet
- UpdatedProceedingsBookISBN978 1 63754 349 8sh - 221119 - 1700591Document390 pagesUpdatedProceedingsBookISBN978 1 63754 349 8sh - 221119 - 1700591Shribha SriiNo ratings yet