Professional Documents
Culture Documents
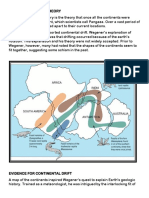
E MGH: Potential and Kinetic Energy
E MGH: Potential and Kinetic Energy
Uploaded by
Dominique FordeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
E MGH: Potential and Kinetic Energy
E MGH: Potential and Kinetic Energy
Uploaded by
Dominique FordeCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: _____________________
Ch. 5:2
Period: _____________________ Potential and Kinetic Energy
Potential Energy mass (in kilograms)
Potential
Energy
(in Joules)
Ep = mgh height (in meters)
Potential Energy is energy of position. acceleration due to
gravity (9.8 m/s2 )
An object gets potential energy from height, mass and Potential energy equals
gravity. An object with potential energy has the mass times gravity times height.
potential to do work. This potential is only And since Fw = mg, then Ep = Fwh
released if the object falls. The energy is then trans-
formed into energy of motion or transformed into work.
Ex: How much potential energy does a 4 kg object
have that is 5 meters off the ground?
More mass = more Ep More height = more Ep
m = 4 kg Ep = mgh
h=5m Ep = (4 kg)(10 m/s2)(5 m)
More Ep g = 10 m/s2 = (40 kgm/s2)(5 m)
Less Ep More Ep
Ep = ? = 200 Joules
Less Ep
10 kg 20 kg 10 kg
10 kg Potential energy
Ep
helps us generate
electricity in
5m 5m 3m hydroelectric dams.
When the water falls, h
gravity helps turn
energy of height to
electrical energy.
mass (in kilograms)
Kinetic Energy Kinetic
Energy
(in Joules)
Ek = (½)mv2
velocity (m/s)
Kinetic Energy is energy of motion. Kinetic energy equals one-half times
mass times velocity squared.
An object gets kinetic energy from its mass and velocity.
An object with kinetic energy has energy stored in motion.
When the object slows down the energy is released into
Ex: How much kinetic energy does
potential energy (if going up) or some other kind of energy
a 10 kg object traveling 3 m/s?
(like heat [thermal energy] in the brakes of car).
m = 10 kg Ek = ½mv2
v = 3 m/s Ek = ½(10 kg)(3 m/s)2
Ek = ? = (5 kg)(9 m2/s2)
More mass = more Ek More velocity = more Ek = 45 Joules
More Ek More Ek
10 m/s 10 m/s
20 kg 10 kg Ek
Kinetic energy helps
you bike up a hill. The
Less Ek Less Ek energy of motion helps
10 m/s
v you overcome gravity.
10 kg 10 kg 5 m/s The faster you are
moving, the easier it is
to get up a hill.
www.aisd.net/smurray Copyright © 2004, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Ch. 5:2
Period: _____________________
1. F or Fw = _________________ 8w 1. Kinetic A. Uses energy and can create energy; calcu-
Energy lated by multiplying force times distance.
2. v = ______________________ 8N
3. p = ______________________ 8m 2. Potential B. How far above the ground an object is.
Energy
4. h = ______________________ 8 kgm/s C. Energy of motion.
3. Work
5. W or E= __________________ 8J
4. Joules D. Units for energy and work.
6. P = ______________________ 8 m/s
5. h E. Energy of position.
Potential (Ep) or Kinetic (Ek) Energy
___ A car is traveling 45 mph. Circle the one with more Potential Energy
___ A rock is on a ledge 5 meters high. A 25 kg mass or a 30 kg mass at the top of a hill?
___ A car is resting at the top of a hill. A car at the top of the hill or the bottom of a hill?
___ A ball is thrown into the air and is still moving. A plane on the ground or a plane in the air?
___ A ball rolling on the ground. A full plane or an empty plane (both are flying)?
Circle the one with more Kinetic Energy A 4 kg rock is rolling 10 m/s. Find its kinetic energy.
A 25 kg mass or a 30 kg mass going 5 m/s.
Two 10 kg masses, one going 75 m/s, one going 45 m/s.
A car at rest or a car rolling down a hill.
______________________________________________
A heavy bike or a light bike. A 8 kg cat is running 4 m/s. How much kinetic energy does it
have?
Calculate the potential energy of a 5 kg object sitting on a
3 meter ledge.
______________________________________________
A rolling ball has 18 joules of kinetic energy and is rolling
3 m/s. Find its mass.
__________________________________________________
A rock is at the top of a 20 meter tall hill. The rock has a mass
of 10 kg. How much potential energy does it have?
______________________________________________
__________________________________________________
A 4 kg bird has 8 joules of kinetic energy. How fast is it flying?
A 25 N object is 3 meters up. How much potential energy does
it have. (Hint, notice the units of the object.)
__________________________________________________
How high up is a 3 kg object that has 300 joules of energy? ______________________________________________
Find the work done by a 25 N force applied for 6 meters.
www.aisd.net/smurray Copyright © 2004, C. Stephen Murray
You might also like
- Minimum Orifice Plate Thickness To Avoid Plastic Deformation (Buckling)Document10 pagesMinimum Orifice Plate Thickness To Avoid Plastic Deformation (Buckling)Hadi VeyseNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design and Construction in Limestone - Case StudyDocument24 pagesFoundation Design and Construction in Limestone - Case Studypatricklim1982No ratings yet
- Energy Levels and Sublevels BookletDocument4 pagesEnergy Levels and Sublevels BookletGray HatNo ratings yet
- Model Ra-D: Instruction ManualDocument128 pagesModel Ra-D: Instruction ManualBruce Adorno0% (1)
- Fourth Quarter ExaminationDocument10 pagesFourth Quarter ExaminationJay Ronnie PranadaNo ratings yet
- 2nd SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT IN SCIENCE 8Document3 pages2nd SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT IN SCIENCE 8Marie Fe ForesNo ratings yet
- Q2 Summative Test in Science 8Document3 pagesQ2 Summative Test in Science 8MARICEL CANTARANo ratings yet
- Grade 8 MEDocument4 pagesGrade 8 MEEhr WinNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Faults LectureDocument41 pagesEarthquakes and Faults Lectureervynsana100% (1)
- The Earth's Interior NEWDocument2 pagesThe Earth's Interior NEWRon Adrian Sarte SebastianNo ratings yet
- TOS (1stPT)Document2 pagesTOS (1stPT)Sally Pocamas100% (1)
- Activity 1 Types of FaultDocument1 pageActivity 1 Types of FaultShie LANo ratings yet
- S8 - Q2 - Week 4Document6 pagesS8 - Q2 - Week 4Dabe Genesis LigaligNo ratings yet
- Science 9 ReviewerDocument2 pagesScience 9 ReviewerSamuel Arthur G. DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Earthquakes Seismic Slinky Spring1Document4 pagesLab Report Earthquakes Seismic Slinky Spring1Renee Dwi Permata MessakaraengNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.5 TyphoonsDocument2 pagesActivity 2.5 TyphoonsTricia Superio100% (2)
- I. Choose and Shade The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Answer SheetDocument2 pagesI. Choose and Shade The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Answer SheetJOSEL VINLUANNo ratings yet
- Pingol, Jessica - LAS Q2 W1 EARTHQUAKES AND FAULTSDocument8 pagesPingol, Jessica - LAS Q2 W1 EARTHQUAKES AND FAULTSjhzcartNo ratings yet
- TyphoonDocument2 pagesTyphoonJulia Geonzon LabajoNo ratings yet
- Typhoon LPDocument13 pagesTyphoon LPMaykhaila GallegoNo ratings yet
- Science 8 2nd Summative TestDocument2 pagesScience 8 2nd Summative TestEmerlyn JosephNo ratings yet
- Second Monthly Test in Science 8Document8 pagesSecond Monthly Test in Science 8Marianne SerranoNo ratings yet
- Energy Level N : Name: - Electron Configuration Modeling Activity BackgroundDocument7 pagesEnergy Level N : Name: - Electron Configuration Modeling Activity Backgroundzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- Human Activities and Their Impact On The EnvironmentDocument58 pagesHuman Activities and Their Impact On The Environmentrorlando lewis100% (1)
- LONG-TEST-SECOND Science 8Document2 pagesLONG-TEST-SECOND Science 8Manongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 PretestDocument3 pagesGrade 8 PretestAvrìl Labrador SaquinNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesMultiple ChoiceJustine PamaNo ratings yet
- Exam in Science Grade 8Document8 pagesExam in Science Grade 8Leonard RuizNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes Crossword PuzzleDocument2 pagesEarthquakes Crossword PuzzleWendy Mari PadernalNo ratings yet
- Gerecords/46000/46425/megi - Tmo - 201029 1 - LRG - JPG: Grade8scienceDocument96 pagesGerecords/46000/46425/megi - Tmo - 201029 1 - LRG - JPG: Grade8scienceBea Nerly EugenioNo ratings yet
- 7 G8 Science Q1 Week 4 Explain The Hierarchy of Colors in Relation To EnergyDocument18 pages7 G8 Science Q1 Week 4 Explain The Hierarchy of Colors in Relation To EnergyCirille Agpaoa100% (1)
- Kinematics in Two DiamensionsDocument34 pagesKinematics in Two Diamensionsemanuel coatesNo ratings yet
- Science8 - Q2 - EarthquakesAnd Faults - V1Document19 pagesScience8 - Q2 - EarthquakesAnd Faults - V1QUEENIE JAM ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Science 8 Second QRTR Summative TestDocument5 pagesScience 8 Second QRTR Summative Testian barcenaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 2nd Grading ExamDocument5 pagesScience 8 2nd Grading ExamJaylineMaeNionesCamineroNo ratings yet
- Learning Module Science 8: The Notre Dame of Masiag, Inc. Grade 8, Quarter 2Document34 pagesLearning Module Science 8: The Notre Dame of Masiag, Inc. Grade 8, Quarter 2richardsamrano100% (1)
- Summative EXAM Q2 GRADE8 2Document2 pagesSummative EXAM Q2 GRADE8 2Anthony P. Pertez100% (1)
- Fourth Quarter Examination in Science 9: For Items 6-8, Refer To This SituationDocument5 pagesFourth Quarter Examination in Science 9: For Items 6-8, Refer To This SituationJ DNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Geothermal EnergyDocument1 pageSummative Test in Geothermal EnergyRoxy Lific100% (1)
- Beautiful Pagadian SATBDocument4 pagesBeautiful Pagadian SATBEdward Rey Acasio De JesusNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Week 1Document2 pagesWorksheet Week 1Jaybie Tejada100% (1)
- Long Quiz EARTHQUAKE 22Document1 pageLong Quiz EARTHQUAKE 22Camille LiqueNo ratings yet
- Science 8 TQ 2nd GradingDocument3 pagesScience 8 TQ 2nd GradingmyleneNo ratings yet
- VOLCANO MendeleevDocument62 pagesVOLCANO MendeleevJuliana deLunaNo ratings yet
- First Periodicals Grade 8Document3 pagesFirst Periodicals Grade 8Salve Gregorio Aguirre100% (1)
- Distribution of Active Volcanoes Earthquake Epicenters and Mountain RangesDocument3 pagesDistribution of Active Volcanoes Earthquake Epicenters and Mountain RangesBRILLIANT MARK BALABAGNo ratings yet
- Science8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy v2Document23 pagesScience8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy v2Keith Genesis Ruiz AglubaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Worksheet 2Document2 pagesScience 10 Worksheet 2Washima Bentulina SabtalNo ratings yet
- Review Review Im CryingggDocument11 pagesReview Review Im CryingggMaryann San JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Dissecting A TyphoonDocument8 pagesDissecting A TyphoonAPPLE JEAN YECYECNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesGrade 8 QuestionnaireRenzo MarcellaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Second Periodic TestDocument7 pagesGrade 8 Science Second Periodic TestAngelita MenesesNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 10 2nd Week 2Document6 pagesDaily Lesson Log Grade 10 2nd Week 2Queeny Pantoja-HondradaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentJessa Mae LabasanNo ratings yet
- SECOND PERIODICAL EXAMINATION g-8Document3 pagesSECOND PERIODICAL EXAMINATION g-8Gladys G. CandidoNo ratings yet
- Science 8: Reviewer For The Monthly ExamDocument4 pagesScience 8: Reviewer For The Monthly Examtwinckel mae bienesNo ratings yet
- Released ItemsDocument8 pagesReleased Itemsapi-299499242No ratings yet
- Summative Test - Understanding TyphoonDocument18 pagesSummative Test - Understanding TyphoonRamir BecoyNo ratings yet
- TYPHOONSDocument2 pagesTYPHOONSJessie Gainsan100% (2)
- Science 9 Failed 2nd QuarterDocument34 pagesScience 9 Failed 2nd Quarterjoy100% (1)
- 1 Summative Test Science 10Document3 pages1 Summative Test Science 10kimjay languitaNo ratings yet
- Energy - : VocabularyDocument13 pagesEnergy - : Vocabularyrumbi16No ratings yet
- 3E Sci Phy - Chap 7 - TRDocument40 pages3E Sci Phy - Chap 7 - TRXu JianhangNo ratings yet
- Gagemaker Catalog 2020Document156 pagesGagemaker Catalog 2020Ronald RaphelNo ratings yet
- External FlowDocument27 pagesExternal Flowraghu.entrepreneurNo ratings yet
- Wascomat SU620 Spare Parts CatalogDocument74 pagesWascomat SU620 Spare Parts CatalogIgor GrytsenkoNo ratings yet
- LC240CP, LC340CP - Service Manual (3828A20911A) - 122206Document61 pagesLC240CP, LC340CP - Service Manual (3828A20911A) - 122206Lim JohnvynNo ratings yet
- Beating Weathercock PDFDocument3 pagesBeating Weathercock PDFMarco PalloneNo ratings yet
- Tank DesignDocument108 pagesTank DesignFRBM2No ratings yet
- Aficio 3035 3045 Parts ManualDocument162 pagesAficio 3035 3045 Parts Manualbill3759No ratings yet
- BJ2 Ch9Document4 pagesBJ2 Ch9Shivendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual ZSX SDocument97 pagesTechnical Manual ZSX SkingreadyNo ratings yet
- 4 - Review Notes - MOTORS & ENGINESDocument17 pages4 - Review Notes - MOTORS & ENGINESJoebert SabidoNo ratings yet
- Instruction and Operating Manual: Smart Valve PositionerDocument47 pagesInstruction and Operating Manual: Smart Valve PositionerMarvin June HitaliaNo ratings yet
- Mallory Ignition Box WiringDocument12 pagesMallory Ignition Box Wiringbigdakota98No ratings yet
- QC PostersDocument13 pagesQC PostersGerry Dan ChanliongcoNo ratings yet
- Slip Lock: Differential AdditiveDocument1 pageSlip Lock: Differential AdditiveTudor RatiuNo ratings yet
- MT 1440 E3 Operator ManuelDocument138 pagesMT 1440 E3 Operator ManuelEmrah MertyürekNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water Pump Station Optimization Using CFD and Physical Model TestDocument19 pagesCooling Water Pump Station Optimization Using CFD and Physical Model TestRicardo BarrosNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Lab ManualDocument20 pagesSoil Mechanics Lab ManualJunaid AshrafNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 Controller PrinciplesDocument40 pagesChapter 09 Controller PrinciplesMuthuMuthuNo ratings yet
- Shutdown SIS Previous Screen: Truck 793F Truck SSP 793F Off-Highway Truck SSP00001-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY C175-16 EngineDocument11 pagesShutdown SIS Previous Screen: Truck 793F Truck SSP 793F Off-Highway Truck SSP00001-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY C175-16 EngineIsrael MirandaNo ratings yet
- TEST (Units, Dimensions&Vector)Document3 pagesTEST (Units, Dimensions&Vector)subhajitbose634No ratings yet
- Automobile GearboxDocument65 pagesAutomobile GearboxSankalp SharmaNo ratings yet
- Excess Flow Valves For Natural Gas ServiceDocument5 pagesExcess Flow Valves For Natural Gas ServiceHernando Andrés Ramírez GilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction & Fick's LawDocument15 pagesChapter 1 Introduction & Fick's Lawkiran367No ratings yet
- Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics and Temperature Measurement Thermal ExpansionDocument19 pagesZeroth Law of Thermodynamics and Temperature Measurement Thermal ExpansionHannah LNo ratings yet
- BEST PRACTICES Hydrostatic Pressure Testing Rev01.1webDocument15 pagesBEST PRACTICES Hydrostatic Pressure Testing Rev01.1webehsan.sadeghi1545No ratings yet
- Ds BurnDocument63 pagesDs BurnmahsaNo ratings yet
- Standar Kapal Nonkonvensi Berbendera Indonesia DikonversiDocument140 pagesStandar Kapal Nonkonvensi Berbendera Indonesia DikonversiRahmat FauziNo ratings yet