Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anaesthesia Science 15
Anaesthesia Science 15
Uploaded by
KelompokC IPDOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anaesthesia Science 15
Anaesthesia Science 15
Uploaded by
KelompokC IPDCopyright:
Available Formats
4 Chapter 1
log ionized concentration/ by this route. However, for all other routes of drug
pH = pKa +
unionized concentration (2) administration, the drug must be absorbed from the
site of application before being carried in the circula-
For basic drugs, this results in: tion to its site of action.
log unionized concentration/
pH = pKa + Intramuscular or
ionized concentration (3)
subcutaneous administration
Ionization is not only important in determining Many factors affect the rate of absorption after intra-
the rate of which a compound can move across muscular or subcutaneous injection. The molecular
a membrane, it is also important in determining weight of the compound, the vehicle in which the
the partition of a drug between compartments with a drug is dissolved, the volume that is given and, last
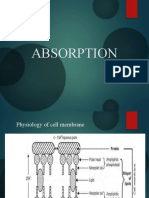
different ambient pH. Diffusion of water-soluble but not least, the local perfusion of the muscle and fat
drugs is restricted by passage through aqueous pores tissue are important [5]. Some drugs are absorbed
that span the cell membrane. However, these chan- very easily, but for others the absorption is poor or
nels are too small to let most drugs pass through unpredictable (e.g. diazepam) [6]. After the injec-
them. Endothelial membranes in the capillaries tion of water-soluble drugs, the plasma level can in-
can have larger pores allowing bulky molecules to crease rapidly, because these compounds enter the
pass through [4]. Diffusion can also be facilitated circulation very fast. This is especially true for drugs
by carrier-mediated mechanisms that operate with low molecular weight, which can reach the sys-
along a concentration gradient without making temic circulation by entering the capillaries directly
use of an energy source. This is called ‘facilitated [5]. The use of vasoconstrictors or vasodilators, as
diffusion’ [1]. well as individual patient haemodynamics, can also
Active transfer mechanisms require energy. The markedly influence the rate of absorption.
energy can be supplied by the hydrolysis of adeno-
sine triphosphate (ATP) directly, as for instance in Inhalation
the case of Na+/K+ ATPase, or indirectly by the cou- Depending on the particle size, inhaled drugs will
pling of the passive transfer of one compound along mainly reach airway mucosa from the larynx to the
its ionic gradient with the movement of another bronchioles, creating local effects, or reach the alve-
molecule against its concentration gradient [3]. An olus, allowing largely systemic effects. However, sys-
example of such a transport system is the absorption temic absorption may still occur in both cases [5].
of amino acids from the small bowel lumen into in- Volatile molecules readily reach the alveolar space
testinal cells [1]. This transfer is achieved by a cou- and can enter the systemic circulation within sec-
pling with Na+ diffusion that occurs down its onds. The rate of absorption of volatile anaesthetics is
electrochemical gradient. Maintenance of the latter determined by adequacy of pulmonary ventilation,
requires energy and ultimately depends on the Na+/ cardiac output, inspired concentration and anaes-
K+ ATPase system [3]. thetic solubility [7].
Pinocytosis transports large molecules [3]. In this
process a part of the cell membrane is invaginated to Epidural, intrathecal and
form a vesicle, which engulfs extracellular material, perineural administration
and is removed via exocytotic mechanisms. Epidural, intrathecal or perineural administration of
drugs is used for providing regional analgesia and an-
Drug administration techniques aesthesia. The onset time depends on the concentra-
in anaesthesia tion of unionized local anaesthetic around the axon.
There are many ways in which a drug can be given. Because local anaesthetics are bases, adding sodium
Although most drugs are given orally, in anaesthesia bicarbonate reduces onset time in epidural solutions.
many drugs are administered intravenously. Be- Addition of a vasoconstrictor increases the duration
cause absorption is bypassed, drug action is very fast of the block [1].
WEB_01.indd 4 7/5/2006 10:10:33 AM
You might also like
- Home Brewing Log Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesHome Brewing Log Sheet PDFStefanita0% (1)
- Fillable Anesthesia SheetDocument2 pagesFillable Anesthesia Sheetetchemendyvet70790% (1)
- Anesthesia For Endovascular Aortic Repair - UpToDateDocument48 pagesAnesthesia For Endovascular Aortic Repair - UpToDatematheusbbragacNo ratings yet
- Psychological Interventions To Reduce Postoperative Pain and Opioid Consumption: A Narrative Review of LiteratureDocument38 pagesPsychological Interventions To Reduce Postoperative Pain and Opioid Consumption: A Narrative Review of LiteraturedrsubramanianNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Quality Indicators For NABH Accreditation PreparationDocument11 pagesChecklist of Quality Indicators For NABH Accreditation PreparationQUALITY SIDARTH HOSPITALSNo ratings yet
- Gap Analysis Report District Hospital HardoiDocument58 pagesGap Analysis Report District Hospital HardoiDr. Sachendra Raj100% (3)
- Drug Absorption: Dr. Chandane R. DDocument54 pagesDrug Absorption: Dr. Chandane R. DBandameedi RamuNo ratings yet
- 1introDocument158 pages1introDea MaharanisNo ratings yet
- 1.pharmacology OpeningDocument6 pages1.pharmacology OpeningHOPENo ratings yet
- Ico Kin Etic S& Ico Dyn Am Ics: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDocument34 pagesIco Kin Etic S& Ico Dyn Am Ics: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanMelkamu AyeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document42 pagesUnit 1hasan.aliNo ratings yet
- Absorption of DrugsDocument186 pagesAbsorption of DrugsKannan Arumugam A50% (2)
- The Ladmer SystemDocument12 pagesThe Ladmer Systemkriss WongNo ratings yet
- Absorption of Drug - BiopharmDocument10 pagesAbsorption of Drug - BiopharmTanu nathnaiNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Drugs and The BodyDocument46 pagesNCM 106 Drugs and The BodyYra JhaneNo ratings yet
- Absorption of DrugsDocument145 pagesAbsorption of DrugsSunith KanakuntlaNo ratings yet
- PHBP Ass3 Nrdabu Drug Absorption AnselsDocument7 pagesPHBP Ass3 Nrdabu Drug Absorption AnselsYunoNo ratings yet
- Uc PDFDocument6 pagesUc PDFPenNo ratings yet
- Morgan 140 149Document10 pagesMorgan 140 149Marta DumitracheNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics PHDocument71 pagesPharmacokinetics PHCasper ScholesNo ratings yet
- 3 PharmacokineticsDocument36 pages3 PharmacokineticsTanvir FahimNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Science 16Document1 pageAnaesthesia Science 16KelompokC IPDNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy in Dental PracticeDocument7 pagesDrug Therapy in Dental Practiceclinicadealix1No ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics - DrdhritiDocument83 pagesPharmacokinetics - Drdhritidbrahma100% (1)
- Module 4: Pharmacokinetics: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesModule 4: Pharmacokinetics: Learning ObjectivesShaina JavierNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport: 1. Passive DiffusionDocument12 pagesCellular Transport: 1. Passive DiffusionDaniel MontesNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument83 pagesPharmacokineticsdv94gw9zd8No ratings yet
- A Review On Nasal Drug Delivery System and Its Contribution in TherapeuticDocument6 pagesA Review On Nasal Drug Delivery System and Its Contribution in Therapeuticedgar palominoNo ratings yet
- AbsorptionDocument23 pagesAbsorptionprashil charkariNo ratings yet
- Pharma 1,2Document10 pagesPharma 1,2Ahmed KafajiNo ratings yet
- D A GIT: RUG Bsorption From TheDocument47 pagesD A GIT: RUG Bsorption From TheAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- Unit.1 Absorption-Mechanisms of Drug Absorption Through GIT.Document25 pagesUnit.1 Absorption-Mechanisms of Drug Absorption Through GIT.deepshah6068No ratings yet
- Drug AbsorptionDocument30 pagesDrug AbsorptionShiva KantNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 Pharmacokinetics 2022 - 2023Document65 pages1.1.1 Pharmacokinetics 2022 - 2023brightgyan082No ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument8 pagesPharmacokineticsPinay YaunNo ratings yet
- BIOPHARM - Mod 4Document2 pagesBIOPHARM - Mod 4LAONo ratings yet
- Drug AbsorptionDocument36 pagesDrug AbsorptionLawal AbidatNo ratings yet
- General PharmacologyDocument76 pagesGeneral PharmacologyMiyuru HasarangaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bio PharmaceuticsDocument88 pagesIntroduction To Bio PharmaceuticsSohan PrasathNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Drug Abosrtion and DistributionDocument5 pagesFactors Affecting Drug Abosrtion and DistributionBruno Adriel ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Absorption - RevisedDocument130 pagesChapter 2 - Absorption - RevisedMinal NadeemNo ratings yet
- Share Pharmacology Book 1Document101 pagesShare Pharmacology Book 1Jmcle AhmedNo ratings yet
- Absorption of DrugsDocument24 pagesAbsorption of DrugsShrikant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocument25 pagesIntroduction To PharmacologyGaurav SaxenaNo ratings yet
- BIOPHARMACEUTICSDocument169 pagesBIOPHARMACEUTICSFitria Shizuoka Jiyeon100% (5)
- Pharmacokinetics and Drug MetabolismDocument54 pagesPharmacokinetics and Drug MetabolismDeirdreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document7 pagesLecture 2parmarkeval1610No ratings yet
- PharmacDocument101 pagesPharmacpai.parthjana2020No ratings yet
- Anastesi Clode - OCULARANESTHETICSDocument4 pagesAnastesi Clode - OCULARANESTHETICSAdrin Ma'rufNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics and Drug Delivery SystemsDocument15 pagesBiopharmaceutics and Drug Delivery SystemsSabiruddin Mirza DipuNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Drugs and The BodyDocument18 pagesWeek 2 - Drugs and The BodyDino MicaNo ratings yet
- Nasal Drug Delivery System A ReviewDocument8 pagesNasal Drug Delivery System A ReviewEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Sublingual Drug Delivery: An Indication of Potential Alternative RouteDocument3 pagesSublingual Drug Delivery: An Indication of Potential Alternative RouteMeisy Tarian AyuNo ratings yet
- Cology ShivaniDocument15 pagesCology ShivaniPharmacyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: What The Body Does To A DrugDocument108 pagesPharmacokinetics: What The Body Does To A Drugallen tdlNo ratings yet
- AbsorptionDocument64 pagesAbsorptionZsazsaNo ratings yet
- 42 2161 PDFDocument7 pages42 2161 PDFEsha JainNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-4 Pharmacology-I New SemDocument61 pagesLecture 3-4 Pharmacology-I New SemHareem FatimaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 3 PDFDocument10 pagesPharmacology 3 PDFJASMINE VERGANo ratings yet
- Lectura FX Cinética1Document7 pagesLectura FX Cinética1Jeraldiin BeltranNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument2 pagesPharmacokineticsSimonNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Organic Pharmaceutical Chemistry of MedicinalsDocument3 pagesPharmaceutical Organic Pharmaceutical Chemistry of MedicinalsAbigael PescasioNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 4 (PHARMACOKINETICS - Mechanism of Drug Transport Processes)Document9 pagesLecture No. 4 (PHARMACOKINETICS - Mechanism of Drug Transport Processes)tejasbhukal567No ratings yet
- Drug Absorption Mechanism: by Anisa Altaf 18205 Presented To DR Daniyal Baig PharmacologyDocument22 pagesDrug Absorption Mechanism: by Anisa Altaf 18205 Presented To DR Daniyal Baig PharmacologyArsal MushtaqNo ratings yet
- NANOTECHNOLOGY REVIEW: LIPOSOMES, NANOTUBES & PLGA NANOPARTICLESFrom EverandNANOTECHNOLOGY REVIEW: LIPOSOMES, NANOTUBES & PLGA NANOPARTICLESNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Science 24Document1 pageAnaesthesia Science 24KelompokC IPDNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Science 26Document1 pageAnaesthesia Science 26KelompokC IPDNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Science 23Document1 pageAnaesthesia Science 23KelompokC IPDNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Science 14Document1 pageAnaesthesia Science 14KelompokC IPDNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Science 17Document1 pageAnaesthesia Science 17KelompokC IPDNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Science 16Document1 pageAnaesthesia Science 16KelompokC IPDNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Science 8Document1 pageAnaesthesia Science 8KelompokC IPDNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Science 9Document1 pageAnaesthesia Science 9KelompokC IPDNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Science 10Document1 pageAnaesthesia Science 10KelompokC IPDNo ratings yet
- Elderly Hip Fracture PatientsDocument7 pagesElderly Hip Fracture PatientspamancastroNo ratings yet
- Penlon SP Service ManualDocument164 pagesPenlon SP Service ManualRAUL LANDIMNo ratings yet
- Solidum Vs PeopleDocument10 pagesSolidum Vs Peopleyan_saavedra_1No ratings yet
- Tulisan 5 Tahun terakhir-FIXDocument54 pagesTulisan 5 Tahun terakhir-FIXAnthony AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Complications of AnesthesiaDocument100 pagesComplications of Anesthesianaufal456No ratings yet
- Update EmergenciesDocument84 pagesUpdate EmergenciesElaineNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Health - SBFR ORHB PresentationDocument115 pagesMinistry of Health - SBFR ORHB PresentationJani TesfayeNo ratings yet
- NZRDA Textbook + CoursesDocument2 pagesNZRDA Textbook + CoursesiamseraNo ratings yet
- Announcement IndoanesthesiaDocument24 pagesAnnouncement IndoanesthesiaAndrian100% (1)
- 193436advice About Xanthelasma Eyes That'll Help You UnderstandDocument10 pages193436advice About Xanthelasma Eyes That'll Help You Understando2fwdvw108No ratings yet
- Phil Irri ReadingsDocument13 pagesPhil Irri ReadingsGec Anthony CubillanNo ratings yet
- NurseCorps Part 6Document38 pagesNurseCorps Part 6smith.kevin1420344No ratings yet
- Atagi Advice On Use of Sedation For Covid 19 Vaccination - 1Document2 pagesAtagi Advice On Use of Sedation For Covid 19 Vaccination - 1Sumaya WebsterNo ratings yet
- M M M M: MR - Vijayakumar MR - Vijayakumar M.SC., M.SC., M.Phil. M.Phil., PGDCA.., PGDCA.Document23 pagesM M M M: MR - Vijayakumar MR - Vijayakumar M.SC., M.SC., M.Phil. M.Phil., PGDCA.., PGDCA.murugs92No ratings yet
- Foreign Body Aspiration 21Document40 pagesForeign Body Aspiration 21Rinaldi Sani NasutionNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia For Cataract Surgery: Chapter - 4Document8 pagesAnesthesia For Cataract Surgery: Chapter - 4Anggi Junita Endamia BangunNo ratings yet
- Central Ot 6Document15 pagesCentral Ot 6Vilarx MasengiNo ratings yet
- Procedures: Basic Format Cesarean SectionDocument53 pagesProcedures: Basic Format Cesarean Sectionzamurd76No ratings yet
- Aspects of Quality Management PlanDocument16 pagesAspects of Quality Management PlanJohnNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing Cesarean SectionDocument13 pagesPerioperative Nursing Cesarean Sectionmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Surgery & Oncology - Theory - Passmed - PLAB 1Document171 pagesSurgery & Oncology - Theory - Passmed - PLAB 1Naveen ChandanNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Regional AnaesthesiaDocument24 pagesPaediatric Regional Anaesthesiazatvit100% (2)
- General Anesthesia For BronchosDocument7 pagesGeneral Anesthesia For BronchosMarites L. DomingoNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action of Local AnaestheticsDocument19 pagesMechanism of Action of Local AnaestheticsSumit Bhardwaj100% (1)