Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Effluent Treatment in The Textile Industry
Effluent Treatment in The Textile Industry
Uploaded by
Weixuan ZhangCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- SK07.I.2013 Halal Positive List of Materials (English)Document10 pagesSK07.I.2013 Halal Positive List of Materials (English)FinaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry McqsDocument5 pagesAnalytical Chemistry McqsAll For U100% (3)
- A Review of Textile Industry: Wet Processing, Environmental Impacts, and Effluent Treatment MethodsDocument11 pagesA Review of Textile Industry: Wet Processing, Environmental Impacts, and Effluent Treatment MethodsShantoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Fenton Process On Treatment of Simulated Textile Wastewater: Optimization Using Response Surface MethodologyDocument14 pagesEffect of Fenton Process On Treatment of Simulated Textile Wastewater: Optimization Using Response Surface MethodologyMuhammad Hidayat Bin MazlanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Research: Shubham Sutar, Prasanna Patil, Jyoti JadhavDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Research: Shubham Sutar, Prasanna Patil, Jyoti JadhavKristina FilipovićNo ratings yet
- Cytotoxicity Reduction of Wastewater Treated by Advanced Oxidation ProcessDocument7 pagesCytotoxicity Reduction of Wastewater Treated by Advanced Oxidation ProcessilhamNo ratings yet
- Study of Environmental Issues in TeDocument12 pagesStudy of Environmental Issues in TeSimoni KhetaniNo ratings yet
- Mycoremediation For The Treatment of Dye Containing EffluentsDocument5 pagesMycoremediation For The Treatment of Dye Containing EffluentsiirNo ratings yet
- High-Performance Photocatalytic Membranes For Water PurificationDocument20 pagesHigh-Performance Photocatalytic Membranes For Water PurificationMihaiNo ratings yet
- Textile Dye Wastewater Characteristics and Constituents of Synthetic Effluents: A Critical ReviewDocument34 pagesTextile Dye Wastewater Characteristics and Constituents of Synthetic Effluents: A Critical ReviewAli HassanNo ratings yet
- Metagenomic Insight of A Full Scale Eco-Friendly Treatment System of Textile Dye Wastewater 2Document19 pagesMetagenomic Insight of A Full Scale Eco-Friendly Treatment System of Textile Dye Wastewater 2Tai Ning ZhangNo ratings yet
- Degradation of AzoDocument12 pagesDegradation of AzoANGELICA RAMOS RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Heliyon: R. Venkataraghavan, R. Thiruchelvi, D. SharmilaDocument15 pagesHeliyon: R. Venkataraghavan, R. Thiruchelvi, D. SharmilaVenkatNo ratings yet
- Biological Removal of Impurities From Textile Industry Wastewaters: An AssessmentDocument5 pagesBiological Removal of Impurities From Textile Industry Wastewaters: An Assessmentcsk909No ratings yet
- SaeefM 2022Document20 pagesSaeefM 2022josias vitorNo ratings yet
- Impact of Textile Wastewater On Water QualityDocument11 pagesImpact of Textile Wastewater On Water QualityCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Journal of Hazardous MaterialsDocument13 pagesJournal of Hazardous MaterialsRahul MandalNo ratings yet
- 1-s2.0-S221334372030049X-mainDocument9 pages1-s2.0-S221334372030049X-mainAbderrahim JbelNo ratings yet
- Removal of Dyes From Textile Industry Effluent: A ReviewDocument5 pagesRemoval of Dyes From Textile Industry Effluent: A ReviewBinu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- 71 76 PJAEC 12112014 16 OkDocument6 pages71 76 PJAEC 12112014 16 OkBhaskar BethiNo ratings yet
- Al Buriahi 2022Document14 pagesAl Buriahi 2022shipraNo ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: SciencedirectDocument17 pagesJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: SciencedirectNicholas YeohNo ratings yet
- Biological Ways of Water FiltrationDocument1 pageBiological Ways of Water FiltrationKe ShaneNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Ashfaq and Amna Khatoon2Document8 pagesAhmad Ashfaq and Amna Khatoon2Dian PiresNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0013935121014377 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0013935121014377 MainHassan juttNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0959652621019764 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0959652621019764 Mainmarcus_2009No ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles, Bioactivity Profiling and Assessment of Photocatalytic Dye Degradation Activity in Punica Granatum JuiceDocument16 pagesBiosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles, Bioactivity Profiling and Assessment of Photocatalytic Dye Degradation Activity in Punica Granatum JuiceIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- 5.5. Newly Isolated Ligninolytic Bacteria and Its Applications For Multiple Dye Degradation - CSDocument13 pages5.5. Newly Isolated Ligninolytic Bacteria and Its Applications For Multiple Dye Degradation - CSFarida RahayuNo ratings yet
- s11270 023 06217 8Document18 pagess11270 023 06217 8Vân VuNo ratings yet
- Gnest 03201 PublishedDocument7 pagesGnest 03201 Publishedshelbylevine1No ratings yet
- Ozonation Pre and Post Treatment of Denim Textile Mill Effluents Effect of Cleaner Production MeasuresDocument9 pagesOzonation Pre and Post Treatment of Denim Textile Mill Effluents Effect of Cleaner Production MeasuresGizem D.No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0013935122005539 Main 1Document11 pages1 s2.0 S0013935122005539 Main 1Rita karen Pacheco CabañasNo ratings yet
- Samia Asif XXXDocument60 pagesSamia Asif XXXAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- Azo Dyes Degradation by Microorganisms PDFDocument9 pagesAzo Dyes Degradation by Microorganisms PDFANGELICA RAMOS RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Reports: Selvaraj Barathi, K.N. Aruljothi, Chinnannan Karthik, Indra Arulselvi PadikasanDocument7 pagesBiotechnology Reports: Selvaraj Barathi, K.N. Aruljothi, Chinnannan Karthik, Indra Arulselvi PadikasanMrmc CovidNo ratings yet
- Investigation of The Removal Kinetics ThermodynamiDocument14 pagesInvestigation of The Removal Kinetics ThermodynamiRachid MakhloufiNo ratings yet
- South African Journal of Chemical Engineering: Kamal Sukla Baidya, Upendra KumarDocument11 pagesSouth African Journal of Chemical Engineering: Kamal Sukla Baidya, Upendra KumarCici refieyanaNo ratings yet
- Asgher 2010Document6 pagesAsgher 2010Finoana niainaNo ratings yet
- The Degradation of Textile Industry Dyes Using The EffectiveDocument10 pagesThe Degradation of Textile Industry Dyes Using The EffectiveShirley ramosNo ratings yet
- Applied Catalysis B: Environmental: SciencedirectDocument12 pagesApplied Catalysis B: Environmental: Sciencedirectapriya_ninaniNo ratings yet
- EvaluationoftheefficacyofupflowanaerobicsludgeblanketreactorinremovalofcolourandreductionofCODinrealtextilewastewater1Document9 pagesEvaluationoftheefficacyofupflowanaerobicsludgeblanketreactorinremovalofcolourandreductionofCODinrealtextilewastewater1ThereNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2773111123000086 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S2773111123000086 MainRavindu AriyarathneNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Ozonation Process For Industrial Wastewater TreatmentDocument21 pagesHybrid Ozonation Process For Industrial Wastewater Treatmentfrank2593No ratings yet
- Water Environment Research - 2018 - Deng - Textiles Wastewater TreatmentDocument15 pagesWater Environment Research - 2018 - Deng - Textiles Wastewater TreatmentShirley ramosNo ratings yet
- Cleaner Engineering and Technology: A.M. Elgarahy, K.Z. Elwakeel, S.H. Mohammad, G.A. ElshoubakyDocument15 pagesCleaner Engineering and Technology: A.M. Elgarahy, K.Z. Elwakeel, S.H. Mohammad, G.A. ElshoubakyPriya Vijay kumaarNo ratings yet
- Biodegradation of Synthetic Dyes of Textile Effluent by Microorganisms 1Document5 pagesBiodegradation of Synthetic Dyes of Textile Effluent by Microorganisms 1Tai Ning ZhangNo ratings yet
- Journal of Cleaner Production: Nabil A. Ibrahim, Faten H.H. Abdellatif, Mohamed S. Hasanin, Mohamed M. AbdellatifDocument12 pagesJournal of Cleaner Production: Nabil A. Ibrahim, Faten H.H. Abdellatif, Mohamed S. Hasanin, Mohamed M. AbdellatifZackkNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution: B. Senthil Rathi, P. Senthil KumarDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Pollution: B. Senthil Rathi, P. Senthil KumarMd.Aminul IslamNo ratings yet
- Potential Application of Orange Peel (OP) As An Eco-Friendly Adsorbent For Textile Dyeing EffluentsDocument13 pagesPotential Application of Orange Peel (OP) As An Eco-Friendly Adsorbent For Textile Dyeing EffluentsAnoif Naputo AidnamNo ratings yet
- Investigation On Ef Uent Characteristics of Organic Cotton Fabric Dyeing With Eco-Friendly Remazol Reactive DyesDocument8 pagesInvestigation On Ef Uent Characteristics of Organic Cotton Fabric Dyeing With Eco-Friendly Remazol Reactive DyesVishnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Fenvs 10 872514Document29 pagesFenvs 10 872514ali abdulrahman al-ezziNo ratings yet
- Studies On Biological Treatment of Textile Effluent From CETP (2017)Document7 pagesStudies On Biological Treatment of Textile Effluent From CETP (2017)DHANARAJA D FOOD TECH (RESEARCH SCHOLAR)No ratings yet
- 65434-1 Jem PDFDocument15 pages65434-1 Jem PDFariefNo ratings yet
- A04 - 23-RESB-Waste AdsorbentDocument18 pagesA04 - 23-RESB-Waste AdsorbentCarol HernándezNo ratings yet
- Industrial Water Treatment and Industrial Marine Outfalls: Achieving The Right BalanceDocument11 pagesIndustrial Water Treatment and Industrial Marine Outfalls: Achieving The Right BalanceJeanOscorimaCelisNo ratings yet
- Removal of Dye From Textile Waste Water Using B-1Document31 pagesRemoval of Dye From Textile Waste Water Using B-1CHANDU DAS100% (1)
- Water 12 02032Document32 pagesWater 12 02032protea2222No ratings yet
- Bhatia Et Al. 2023 - Int J Environ Sci TechDocument16 pagesBhatia Et Al. 2023 - Int J Environ Sci TechRahul KhandareNo ratings yet
- Costa 2018Document35 pagesCosta 2018uthraNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Landfill Leachate With Different Techniques - An OverviewDocument31 pagesTreatment of Landfill Leachate With Different Techniques - An OverviewMatías YáñezNo ratings yet
- BBRC Vol 14 No 04 2021-30Document7 pagesBBRC Vol 14 No 04 2021-30Dr Sharique AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides (Week 8) - Final VersionDocument33 pagesLecture Slides (Week 8) - Final VersionWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Reading 3 - MBRs For Operators (2005)Document4 pagesWeek 7 - Reading 3 - MBRs For Operators (2005)Weixuan Zhang100% (1)
- Microbial Growth Kinetics: Prof MJ ManefieldDocument10 pagesMicrobial Growth Kinetics: Prof MJ ManefieldWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides (Week 3) - Final VersionDocument45 pagesLecture Slides (Week 3) - Final VersionWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides (Week 7) - Final VersionDocument35 pagesLecture Slides (Week 7) - Final VersionWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides (Week 1) - Final VersionDocument42 pagesLecture Slides (Week 1) - Final VersionWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- CVEN4102 - Quizzes Declaration Form-Z5092352Document1 pageCVEN4102 - Quizzes Declaration Form-Z5092352Weixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- F CVEN9857 - Biological Nutrient Removal MMDocument80 pagesF CVEN9857 - Biological Nutrient Removal MMWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Reading 1 - MBRs in Wastewater Treatment (2010)Document10 pagesWeek 7 - Reading 1 - MBRs in Wastewater Treatment (2010)Weixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- 55924-Article Text-94180-1-10-20100628Document5 pages55924-Article Text-94180-1-10-20100628Weixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
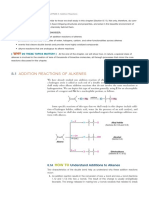
- Electrophilic Addition Reaction of Alkenes PDFDocument8 pagesElectrophilic Addition Reaction of Alkenes PDFRAAHEELNo ratings yet
- RotothermDocument2 pagesRotothermLee HaagNo ratings yet
- Flexible Temperature Sensors A ReviewDocument16 pagesFlexible Temperature Sensors A ReviewMicu CristiNo ratings yet
- Resin Fouling and CleaningDocument33 pagesResin Fouling and CleaningFareedNo ratings yet
- Different Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Document25 pagesDifferent Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Belaro JennyNo ratings yet
- 811 Disha Challenger ChemDocument21 pages811 Disha Challenger ChemVijay Kajolu100% (1)
- Solutions Anilkumar HssliveDocument3 pagesSolutions Anilkumar HssliveMathew YoyakkyNo ratings yet
- Isolation, Screening and Optimization of Production Medium For Thermostable Laccase Production From Ganoderma SPDocument9 pagesIsolation, Screening and Optimization of Production Medium For Thermostable Laccase Production From Ganoderma SPRajeshKumarNo ratings yet
- 3500-As ArsenicDocument3 pages3500-As ArsenicDavid AmayaNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Soap Manufacture 1000885989Document178 pagesThe Handbook of Soap Manufacture 1000885989adiseif100% (1)
- BioconcreteDocument12 pagesBioconcreteMoeesha KenkreNo ratings yet
- Getting To Understand: Euro MouldersDocument56 pagesGetting To Understand: Euro MouldersDiego Marangoni VicenteNo ratings yet
- Bakzid 10N - Product - Information - EN - PDSDocument2 pagesBakzid 10N - Product - Information - EN - PDSgaloisliu2020No ratings yet
- 3 - Defects in Crystals ExeDocument11 pages3 - Defects in Crystals Exeomar salahNo ratings yet
- 12 Pericyclic Rxns 2 PDFDocument13 pages12 Pericyclic Rxns 2 PDFPrasanth BitlaNo ratings yet
- Major Project E-Logbook Samuel Siow Updated 170712Document16 pagesMajor Project E-Logbook Samuel Siow Updated 170712Samuel Siow Wei JianNo ratings yet
- Green ChemistryDocument89 pagesGreen ChemistryAleena KanwalNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Total Free Amino AcidDocument6 pagesEstimation of Total Free Amino AcidSOUMITA MITRANo ratings yet
- Ch.7 ChemistryDocument34 pagesCh.7 ChemistryZeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Oxide DangersDocument6 pagesAluminum Oxide Dangersraguila00No ratings yet
- Ethane-1,2-Diol (Ethylene Glycol) PDFDocument1 pageEthane-1,2-Diol (Ethylene Glycol) PDFkrishna kumar bhardwaj100% (1)
- Care Chemicals & Formulators: Lutensol TO TypesDocument12 pagesCare Chemicals & Formulators: Lutensol TO TypesalaminNo ratings yet
- (Career Endeavour) MOLECULAR COMPOUNDSDocument15 pages(Career Endeavour) MOLECULAR COMPOUNDSVaibhav NikharNo ratings yet
- Chem 315 - Lab 7 - Gas ChromatographyDocument18 pagesChem 315 - Lab 7 - Gas ChromatographykNo ratings yet
- HPMC CelluloseDocument32 pagesHPMC Cellulosemailtorubal2573No ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Fortnightly Assessment QuizDocument6 pagesFiitjee: Fortnightly Assessment QuizYash ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Self-Healing PolymersDocument6 pagesSelf-Healing Polymersirvan syahmilNo ratings yet
- Ginplate Electroless Nickel 422: Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesGinplate Electroless Nickel 422: Technical Data SheetLuuThiThuyDuongNo ratings yet
Effluent Treatment in The Textile Industry
Effluent Treatment in The Textile Industry
Uploaded by
Weixuan ZhangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Effluent Treatment in The Textile Industry
Effluent Treatment in The Textile Industry
Uploaded by
Weixuan ZhangCopyright:
Available Formats
EFFLUENT TREATMENT IN THE ZHANG WEIXUAN
TEXTILE INDUSTRY z5092352
INTRODUCTION TO THE TEXTILE OPERATIONS TEXTILE EFFLUENTS AND ITS IMPACT
Textile industries prepare and transform fibers into yarn, convert the Textile effluents exhibit high values
yarn into fabric, and then these fabrics are manufactured through wet
processing into garments.Refer to figure 1.
of BOD, COD, total suspended
solids, and low dissolved oxygen
(DO) concentrations, and strong
color. Table 1 presents the
contaminants generated at this
stage.
Figure 1.A flow diagram fo textile processing.
Table 1. Wet processing and wastewater contaminants
CONVENTIONAL TREATMENTS
Wastewater discharged from the industries undergo
multiple physical and chemical treatments, such as ADVANCED OXIDATION PROCESS (AOP)
flocculation, coagulation, and ozonation. Organic
matter, nitrogen and, some metals can be removed
The fundamental principle of this
based on biological treatment. There are three
treatment processes involved: primary, secondary, and process is to crash the components
tertiary treatments, which refer to Figure 2.
which are difficult to oxidize by
generated OH0 radicals. Fentons
reagent is an appropriate chemical
that improves the ability of the
oxidation of organic contaminants by
decomposition of H2O2. One
disadvantage is the generation
of iron sludge.
Figure 2. Conventional Treatment processes in textile plants
REFERENCE
Babu, B.R.,
Parande, A., Raghu, S. and Kumar, T.P., 2007. Textile technology. The Journal of Cotton Science, 11. pp. 141-153.
Srebrenkoska,
COMPARISON
V., Zhezhova, S., Risteski, S., & Golomeova, S., 2014. Methods for waste waters treatment in textile industry.
García Montaño,
J., 2007. Combination of advanced oxidation processes and biological treatments for commercial reactive azo dyes
removal. Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona,.
Wang, C.,
Yediler, A., Lienert, D., Wang, Z., & Kettrup, A., 2002. Toxicity evaluation of reactive dyestuffs, auxiliaries and selected
effluents in textile finishing industry to luminescent bacteria Vibrio fischeri. Chemosphere, 46(2), 339-344.
Holkar, C. R.,
Jadhav, A. J., Pinjari, D. V., Mahamuni, N. M., & Pandit, A. B., 2016. A
critical review on textile wastewater treatments: possible approaches. Journal
of environmental management, 182, 351-366.
You might also like
- SK07.I.2013 Halal Positive List of Materials (English)Document10 pagesSK07.I.2013 Halal Positive List of Materials (English)FinaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry McqsDocument5 pagesAnalytical Chemistry McqsAll For U100% (3)
- A Review of Textile Industry: Wet Processing, Environmental Impacts, and Effluent Treatment MethodsDocument11 pagesA Review of Textile Industry: Wet Processing, Environmental Impacts, and Effluent Treatment MethodsShantoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Fenton Process On Treatment of Simulated Textile Wastewater: Optimization Using Response Surface MethodologyDocument14 pagesEffect of Fenton Process On Treatment of Simulated Textile Wastewater: Optimization Using Response Surface MethodologyMuhammad Hidayat Bin MazlanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Research: Shubham Sutar, Prasanna Patil, Jyoti JadhavDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Research: Shubham Sutar, Prasanna Patil, Jyoti JadhavKristina FilipovićNo ratings yet
- Cytotoxicity Reduction of Wastewater Treated by Advanced Oxidation ProcessDocument7 pagesCytotoxicity Reduction of Wastewater Treated by Advanced Oxidation ProcessilhamNo ratings yet
- Study of Environmental Issues in TeDocument12 pagesStudy of Environmental Issues in TeSimoni KhetaniNo ratings yet
- Mycoremediation For The Treatment of Dye Containing EffluentsDocument5 pagesMycoremediation For The Treatment of Dye Containing EffluentsiirNo ratings yet
- High-Performance Photocatalytic Membranes For Water PurificationDocument20 pagesHigh-Performance Photocatalytic Membranes For Water PurificationMihaiNo ratings yet
- Textile Dye Wastewater Characteristics and Constituents of Synthetic Effluents: A Critical ReviewDocument34 pagesTextile Dye Wastewater Characteristics and Constituents of Synthetic Effluents: A Critical ReviewAli HassanNo ratings yet
- Metagenomic Insight of A Full Scale Eco-Friendly Treatment System of Textile Dye Wastewater 2Document19 pagesMetagenomic Insight of A Full Scale Eco-Friendly Treatment System of Textile Dye Wastewater 2Tai Ning ZhangNo ratings yet
- Degradation of AzoDocument12 pagesDegradation of AzoANGELICA RAMOS RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Heliyon: R. Venkataraghavan, R. Thiruchelvi, D. SharmilaDocument15 pagesHeliyon: R. Venkataraghavan, R. Thiruchelvi, D. SharmilaVenkatNo ratings yet
- Biological Removal of Impurities From Textile Industry Wastewaters: An AssessmentDocument5 pagesBiological Removal of Impurities From Textile Industry Wastewaters: An Assessmentcsk909No ratings yet
- SaeefM 2022Document20 pagesSaeefM 2022josias vitorNo ratings yet
- Impact of Textile Wastewater On Water QualityDocument11 pagesImpact of Textile Wastewater On Water QualityCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Journal of Hazardous MaterialsDocument13 pagesJournal of Hazardous MaterialsRahul MandalNo ratings yet
- 1-s2.0-S221334372030049X-mainDocument9 pages1-s2.0-S221334372030049X-mainAbderrahim JbelNo ratings yet
- Removal of Dyes From Textile Industry Effluent: A ReviewDocument5 pagesRemoval of Dyes From Textile Industry Effluent: A ReviewBinu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- 71 76 PJAEC 12112014 16 OkDocument6 pages71 76 PJAEC 12112014 16 OkBhaskar BethiNo ratings yet
- Al Buriahi 2022Document14 pagesAl Buriahi 2022shipraNo ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: SciencedirectDocument17 pagesJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: SciencedirectNicholas YeohNo ratings yet
- Biological Ways of Water FiltrationDocument1 pageBiological Ways of Water FiltrationKe ShaneNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Ashfaq and Amna Khatoon2Document8 pagesAhmad Ashfaq and Amna Khatoon2Dian PiresNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0013935121014377 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0013935121014377 MainHassan juttNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0959652621019764 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0959652621019764 Mainmarcus_2009No ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles, Bioactivity Profiling and Assessment of Photocatalytic Dye Degradation Activity in Punica Granatum JuiceDocument16 pagesBiosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles, Bioactivity Profiling and Assessment of Photocatalytic Dye Degradation Activity in Punica Granatum JuiceIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- 5.5. Newly Isolated Ligninolytic Bacteria and Its Applications For Multiple Dye Degradation - CSDocument13 pages5.5. Newly Isolated Ligninolytic Bacteria and Its Applications For Multiple Dye Degradation - CSFarida RahayuNo ratings yet
- s11270 023 06217 8Document18 pagess11270 023 06217 8Vân VuNo ratings yet
- Gnest 03201 PublishedDocument7 pagesGnest 03201 Publishedshelbylevine1No ratings yet
- Ozonation Pre and Post Treatment of Denim Textile Mill Effluents Effect of Cleaner Production MeasuresDocument9 pagesOzonation Pre and Post Treatment of Denim Textile Mill Effluents Effect of Cleaner Production MeasuresGizem D.No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0013935122005539 Main 1Document11 pages1 s2.0 S0013935122005539 Main 1Rita karen Pacheco CabañasNo ratings yet
- Samia Asif XXXDocument60 pagesSamia Asif XXXAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- Azo Dyes Degradation by Microorganisms PDFDocument9 pagesAzo Dyes Degradation by Microorganisms PDFANGELICA RAMOS RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Reports: Selvaraj Barathi, K.N. Aruljothi, Chinnannan Karthik, Indra Arulselvi PadikasanDocument7 pagesBiotechnology Reports: Selvaraj Barathi, K.N. Aruljothi, Chinnannan Karthik, Indra Arulselvi PadikasanMrmc CovidNo ratings yet
- Investigation of The Removal Kinetics ThermodynamiDocument14 pagesInvestigation of The Removal Kinetics ThermodynamiRachid MakhloufiNo ratings yet
- South African Journal of Chemical Engineering: Kamal Sukla Baidya, Upendra KumarDocument11 pagesSouth African Journal of Chemical Engineering: Kamal Sukla Baidya, Upendra KumarCici refieyanaNo ratings yet
- Asgher 2010Document6 pagesAsgher 2010Finoana niainaNo ratings yet
- The Degradation of Textile Industry Dyes Using The EffectiveDocument10 pagesThe Degradation of Textile Industry Dyes Using The EffectiveShirley ramosNo ratings yet
- Applied Catalysis B: Environmental: SciencedirectDocument12 pagesApplied Catalysis B: Environmental: Sciencedirectapriya_ninaniNo ratings yet
- EvaluationoftheefficacyofupflowanaerobicsludgeblanketreactorinremovalofcolourandreductionofCODinrealtextilewastewater1Document9 pagesEvaluationoftheefficacyofupflowanaerobicsludgeblanketreactorinremovalofcolourandreductionofCODinrealtextilewastewater1ThereNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2773111123000086 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S2773111123000086 MainRavindu AriyarathneNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Ozonation Process For Industrial Wastewater TreatmentDocument21 pagesHybrid Ozonation Process For Industrial Wastewater Treatmentfrank2593No ratings yet
- Water Environment Research - 2018 - Deng - Textiles Wastewater TreatmentDocument15 pagesWater Environment Research - 2018 - Deng - Textiles Wastewater TreatmentShirley ramosNo ratings yet
- Cleaner Engineering and Technology: A.M. Elgarahy, K.Z. Elwakeel, S.H. Mohammad, G.A. ElshoubakyDocument15 pagesCleaner Engineering and Technology: A.M. Elgarahy, K.Z. Elwakeel, S.H. Mohammad, G.A. ElshoubakyPriya Vijay kumaarNo ratings yet
- Biodegradation of Synthetic Dyes of Textile Effluent by Microorganisms 1Document5 pagesBiodegradation of Synthetic Dyes of Textile Effluent by Microorganisms 1Tai Ning ZhangNo ratings yet
- Journal of Cleaner Production: Nabil A. Ibrahim, Faten H.H. Abdellatif, Mohamed S. Hasanin, Mohamed M. AbdellatifDocument12 pagesJournal of Cleaner Production: Nabil A. Ibrahim, Faten H.H. Abdellatif, Mohamed S. Hasanin, Mohamed M. AbdellatifZackkNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution: B. Senthil Rathi, P. Senthil KumarDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Pollution: B. Senthil Rathi, P. Senthil KumarMd.Aminul IslamNo ratings yet
- Potential Application of Orange Peel (OP) As An Eco-Friendly Adsorbent For Textile Dyeing EffluentsDocument13 pagesPotential Application of Orange Peel (OP) As An Eco-Friendly Adsorbent For Textile Dyeing EffluentsAnoif Naputo AidnamNo ratings yet
- Investigation On Ef Uent Characteristics of Organic Cotton Fabric Dyeing With Eco-Friendly Remazol Reactive DyesDocument8 pagesInvestigation On Ef Uent Characteristics of Organic Cotton Fabric Dyeing With Eco-Friendly Remazol Reactive DyesVishnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Fenvs 10 872514Document29 pagesFenvs 10 872514ali abdulrahman al-ezziNo ratings yet
- Studies On Biological Treatment of Textile Effluent From CETP (2017)Document7 pagesStudies On Biological Treatment of Textile Effluent From CETP (2017)DHANARAJA D FOOD TECH (RESEARCH SCHOLAR)No ratings yet
- 65434-1 Jem PDFDocument15 pages65434-1 Jem PDFariefNo ratings yet
- A04 - 23-RESB-Waste AdsorbentDocument18 pagesA04 - 23-RESB-Waste AdsorbentCarol HernándezNo ratings yet
- Industrial Water Treatment and Industrial Marine Outfalls: Achieving The Right BalanceDocument11 pagesIndustrial Water Treatment and Industrial Marine Outfalls: Achieving The Right BalanceJeanOscorimaCelisNo ratings yet
- Removal of Dye From Textile Waste Water Using B-1Document31 pagesRemoval of Dye From Textile Waste Water Using B-1CHANDU DAS100% (1)
- Water 12 02032Document32 pagesWater 12 02032protea2222No ratings yet
- Bhatia Et Al. 2023 - Int J Environ Sci TechDocument16 pagesBhatia Et Al. 2023 - Int J Environ Sci TechRahul KhandareNo ratings yet
- Costa 2018Document35 pagesCosta 2018uthraNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Landfill Leachate With Different Techniques - An OverviewDocument31 pagesTreatment of Landfill Leachate With Different Techniques - An OverviewMatías YáñezNo ratings yet
- BBRC Vol 14 No 04 2021-30Document7 pagesBBRC Vol 14 No 04 2021-30Dr Sharique AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides (Week 8) - Final VersionDocument33 pagesLecture Slides (Week 8) - Final VersionWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Reading 3 - MBRs For Operators (2005)Document4 pagesWeek 7 - Reading 3 - MBRs For Operators (2005)Weixuan Zhang100% (1)
- Microbial Growth Kinetics: Prof MJ ManefieldDocument10 pagesMicrobial Growth Kinetics: Prof MJ ManefieldWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides (Week 3) - Final VersionDocument45 pagesLecture Slides (Week 3) - Final VersionWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides (Week 7) - Final VersionDocument35 pagesLecture Slides (Week 7) - Final VersionWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides (Week 1) - Final VersionDocument42 pagesLecture Slides (Week 1) - Final VersionWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- CVEN4102 - Quizzes Declaration Form-Z5092352Document1 pageCVEN4102 - Quizzes Declaration Form-Z5092352Weixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- F CVEN9857 - Biological Nutrient Removal MMDocument80 pagesF CVEN9857 - Biological Nutrient Removal MMWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Reading 1 - MBRs in Wastewater Treatment (2010)Document10 pagesWeek 7 - Reading 1 - MBRs in Wastewater Treatment (2010)Weixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- 55924-Article Text-94180-1-10-20100628Document5 pages55924-Article Text-94180-1-10-20100628Weixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Electrophilic Addition Reaction of Alkenes PDFDocument8 pagesElectrophilic Addition Reaction of Alkenes PDFRAAHEELNo ratings yet
- RotothermDocument2 pagesRotothermLee HaagNo ratings yet
- Flexible Temperature Sensors A ReviewDocument16 pagesFlexible Temperature Sensors A ReviewMicu CristiNo ratings yet
- Resin Fouling and CleaningDocument33 pagesResin Fouling and CleaningFareedNo ratings yet
- Different Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Document25 pagesDifferent Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Belaro JennyNo ratings yet
- 811 Disha Challenger ChemDocument21 pages811 Disha Challenger ChemVijay Kajolu100% (1)
- Solutions Anilkumar HssliveDocument3 pagesSolutions Anilkumar HssliveMathew YoyakkyNo ratings yet
- Isolation, Screening and Optimization of Production Medium For Thermostable Laccase Production From Ganoderma SPDocument9 pagesIsolation, Screening and Optimization of Production Medium For Thermostable Laccase Production From Ganoderma SPRajeshKumarNo ratings yet
- 3500-As ArsenicDocument3 pages3500-As ArsenicDavid AmayaNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Soap Manufacture 1000885989Document178 pagesThe Handbook of Soap Manufacture 1000885989adiseif100% (1)
- BioconcreteDocument12 pagesBioconcreteMoeesha KenkreNo ratings yet
- Getting To Understand: Euro MouldersDocument56 pagesGetting To Understand: Euro MouldersDiego Marangoni VicenteNo ratings yet
- Bakzid 10N - Product - Information - EN - PDSDocument2 pagesBakzid 10N - Product - Information - EN - PDSgaloisliu2020No ratings yet
- 3 - Defects in Crystals ExeDocument11 pages3 - Defects in Crystals Exeomar salahNo ratings yet
- 12 Pericyclic Rxns 2 PDFDocument13 pages12 Pericyclic Rxns 2 PDFPrasanth BitlaNo ratings yet
- Major Project E-Logbook Samuel Siow Updated 170712Document16 pagesMajor Project E-Logbook Samuel Siow Updated 170712Samuel Siow Wei JianNo ratings yet
- Green ChemistryDocument89 pagesGreen ChemistryAleena KanwalNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Total Free Amino AcidDocument6 pagesEstimation of Total Free Amino AcidSOUMITA MITRANo ratings yet
- Ch.7 ChemistryDocument34 pagesCh.7 ChemistryZeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Oxide DangersDocument6 pagesAluminum Oxide Dangersraguila00No ratings yet
- Ethane-1,2-Diol (Ethylene Glycol) PDFDocument1 pageEthane-1,2-Diol (Ethylene Glycol) PDFkrishna kumar bhardwaj100% (1)
- Care Chemicals & Formulators: Lutensol TO TypesDocument12 pagesCare Chemicals & Formulators: Lutensol TO TypesalaminNo ratings yet
- (Career Endeavour) MOLECULAR COMPOUNDSDocument15 pages(Career Endeavour) MOLECULAR COMPOUNDSVaibhav NikharNo ratings yet
- Chem 315 - Lab 7 - Gas ChromatographyDocument18 pagesChem 315 - Lab 7 - Gas ChromatographykNo ratings yet
- HPMC CelluloseDocument32 pagesHPMC Cellulosemailtorubal2573No ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Fortnightly Assessment QuizDocument6 pagesFiitjee: Fortnightly Assessment QuizYash ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Self-Healing PolymersDocument6 pagesSelf-Healing Polymersirvan syahmilNo ratings yet
- Ginplate Electroless Nickel 422: Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesGinplate Electroless Nickel 422: Technical Data SheetLuuThiThuyDuongNo ratings yet