Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Roperties of Waves: (1 Mark)
Roperties of Waves: (1 Mark)
Uploaded by
Mr. SuitOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Roperties of Waves: (1 Mark)
Roperties of Waves: (1 Mark)
Uploaded by
Mr. SuitCopyright:
Available Formats
1
0 1 A sound engineer is preparing for a rock concert. They are investigating
the sound produced by a particular speaker. The below graph shows how
the change in air pressure produced by the speaker varies with time.
0.03
Change in air pressure / Pa
0.02
0.01
-0.01
-0.02
-0.03
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Time / ms
0 1 . 1 State the amplitude of the sound produced.
Amplitude = 0.02 Pa
[1 mark]
0 1 . 2 Calculate the frequency of the sound produced.
Include an appropriate unit with your answer.
Time period, T = 2 ms = 0.002 s (time for one full oscillation/wave/cycle)
f = 1 ÷ T = 1 ÷ 0.002 = 500 Hz
0 1 . 3 The sound engineer then changes the uses the same equipment to
produce a sound which has half the frequency and half the amplitude of
the original sound.
Sketch the graph which would be obtained for this new sound wave on
the above axes.
Red line above.
Maximum/minimum y-values of +0.01 and –0.01 Pa [1].
Time period of 4 ms (so half the number of waves passing a given point
per second) [1].
PROPERTIES OF WAVES © my-gcsescience.com
2
0 2 Imelda is relaxing on the beach. She starts counting as soon as a
particular wave crest reaches the shore, and notices that twelve more
wave crests reach the shore in two minutes.
0 2 . 1 Show that the waves are striking the shore at a frequency of 0.1 Hz.
Number of waves = 12
Total time = 2 minutes = 120 seconds
Time period, T = total time ÷ number of waves = 120 ÷ 12 = 10 s
f = 1 ÷ T = 1 ÷ 10 = 0.1 Hz
0 2 . 2 A pilot in a light plane which is flying overhead estimates that the
distance between the wave crests which are striking the shore is
approximately 40 m.
Use this information to estimate the speed at which the waves are
striking the shore.
Wavelength, λ = 40 m
Frequency, f = 0.1 Hz
Speed, v = f λ = 0.1 × 40 = 4 m/s
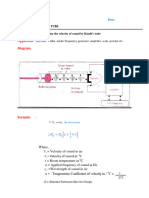
0 3 A student is using the below setup to measure the speed of sound.
The millisecond timer measures how long it takes for the sound they
produce to travel from the first microphone to the second.
They obtain the following times: 3.0 ms, 2.9 ms, 3.1 ms.
0 3 . 1 State the name given to the type of error which is present in these
measurements.
Random error [1]
0 3 . 2 Use the above information to calculate an accurate value for the speed of
sound in air.
Average time (for greatest accuracy) = (3.0 + 2.9 + 3.1) ÷ 3 = 3.0 ms
Time, t = 3.0 ms = 0.003 s
v = s ÷ t = 1 ÷ 0.003 = 333 m/s (to nearest whole number)
PROPERTIES OF WAVES © my-gcsescience.com
You might also like
- JBL Audio Engineering for Sound ReinforcementFrom EverandJBL Audio Engineering for Sound ReinforcementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Pass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewFrom EverandPass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Acoustics PresentationDocument133 pagesAcoustics Presentationpunksot_kawNo ratings yet
- VNX5700 Unified Power Up ProcedureDocument5 pagesVNX5700 Unified Power Up ProcedurerobertwegnerNo ratings yet
- PCS Lab 3Document8 pagesPCS Lab 3Dhruv VaspateNo ratings yet
- L9 - Acoustic Phonetics I-1Document71 pagesL9 - Acoustic Phonetics I-1Just NickNo ratings yet
- 1Document57 pages1Vansh Mehta100% (1)
- ExercicesDocument3 pagesExercicesEmma ArnouldNo ratings yet
- Sound Primer 2020 - v1Document28 pagesSound Primer 2020 - v1High ManwichNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Phy Target-6 Level-1 Chapter-14 PDFDocument31 pagesCLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Phy Target-6 Level-1 Chapter-14 PDFA JNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Principle of SoundDocument44 pagesTopic 9 Principle of SoundSurie AiniezaNo ratings yet
- TP1-Fernandez-Iturburu-Venezia-2023 2C-V1Document20 pagesTP1-Fernandez-Iturburu-Venezia-2023 2C-V1iturburu48593No ratings yet
- 12 - Radiated and Internal NoisesDocument25 pages12 - Radiated and Internal NoisesJuan SilvaNo ratings yet
- Sound PhysicsDocument6 pagesSound Physicssreepranad DevarakondaNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Sound WavesDocument14 pages1.6 Sound Wavespanitiafiziksmkb100% (1)
- Waves 1Document22 pagesWaves 1iamrushabhshethNo ratings yet
- Presentation: Classical ControlDocument10 pagesPresentation: Classical Controlİbrahim KayğanNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XI Physics ResonanceColumn1Document1 pageHsslive XI Physics ResonanceColumn1Saajan MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Fan Sound Sound Ratings FE 300 PDFDocument8 pagesFan Sound Sound Ratings FE 300 PDFM. v.d. WielNo ratings yet
- 3.4 SoundDocument25 pages3.4 SoundMadiha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sound NumericalsDocument1 pageSound NumericalsArmaan MehtaniNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Distance Measurement and Ultrasonic Doppler EffectDocument4 pagesUltrasound Distance Measurement and Ultrasonic Doppler EffectA N ArunkumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of SoundDocument59 pagesFundamentals of SoundDigambar ZomanNo ratings yet
- MASONEILAN 2005 Noise Control ManualDocument24 pagesMASONEILAN 2005 Noise Control ManualhamzaNo ratings yet
- Noise Control Manual (Masoneilan) PDFDocument24 pagesNoise Control Manual (Masoneilan) PDFtxagusNo ratings yet
- Physics - WavesDocument21 pagesPhysics - WavesMemory SitambuliNo ratings yet
- Part1 PDFDocument117 pagesPart1 PDFHussein AliNo ratings yet
- CH 15Document65 pagesCH 15Pathshala SrsecschoolNo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument44 pagesAcousticsLuiza HarutyunyanNo ratings yet
- Lab G With PendulumDocument5 pagesLab G With PendulumzhanartrdwNo ratings yet
- Grade-9 Science Chapter12 SoundDocument10 pagesGrade-9 Science Chapter12 Soundobbyhobbyl4No ratings yet
- 09 Scip 12 Sound ArvindDocument12 pages09 Scip 12 Sound ArvindMAX GAMERNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Basics Principles: Resident Physics LecturesDocument71 pagesUltrasound Basics Principles: Resident Physics LecturesRolianisa LianiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 15 WavesDocument7 pagesCBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 15 Wavesanshbhatnagar002No ratings yet
- Acoustic Plane Waves: Julian WeathersbyDocument11 pagesAcoustic Plane Waves: Julian WeathersbyFaizan AlyNo ratings yet
- Lab1 Acoustics 331Document14 pagesLab1 Acoustics 331Mengistu AberaNo ratings yet
- Expt No 3 Kundt's TubeDocument2 pagesExpt No 3 Kundt's TubeShravanNo ratings yet
- Determining The Speed of Sound Invoking The Phenomenon of Wave Interference in A Close-Ended PipeDocument4 pagesDetermining The Speed of Sound Invoking The Phenomenon of Wave Interference in A Close-Ended PipeJesse CenizaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 - Solutions - (EPH105C) - August - 2023Document5 pagesTutorial 9 - Solutions - (EPH105C) - August - 2023Charity ChazNo ratings yet
- Lecture Version 2.oDocument33 pagesLecture Version 2.oludaid muhammedNo ratings yet
- Ida SoundDocument24 pagesIda Soundameerul_hazeeqNo ratings yet
- ResonanceDocument8 pagesResonanceDavid BenjamingNo ratings yet
- Sound Quality Analysis of CymbalsDocument9 pagesSound Quality Analysis of Cymbalsapi-643891443No ratings yet
- Unit6-Lab - Part2 - Velocity of The SoundDocument3 pagesUnit6-Lab - Part2 - Velocity of The Soundfarooq pervezNo ratings yet
- Subject:: Audio, Video & TV EngineeringDocument71 pagesSubject:: Audio, Video & TV EngineeringNilesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Ebook 2 Sound and VibrationDocument28 pagesEbook 2 Sound and Vibrationshriramana100% (4)
- Fundamental of NoiseDocument70 pagesFundamental of NoiseajaykumarparikhNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic FormulaDocument12 pagesUltrasonic FormulaAbdalla Mohamed Abdalla50% (2)
- QUEST - Unit 07.1 - Waves and Sound - QuestionsDocument5 pagesQUEST - Unit 07.1 - Waves and Sound - Questionsdarshi joshiNo ratings yet
- Physics Module 2 ProjectDocument23 pagesPhysics Module 2 ProjectNikki LirioNo ratings yet
- Fluent 6.1 Acoustics Module Manual: February 2003Document21 pagesFluent 6.1 Acoustics Module Manual: February 2003Alex JuastinNo ratings yet
- SPM Vibration AnalysisDocument74 pagesSPM Vibration Analysissyarafunnisa85No ratings yet
- ECE 356 Acoustics F22 DS 1 ST X360 1 AfterDocument40 pagesECE 356 Acoustics F22 DS 1 ST X360 1 Aftermariam hanyNo ratings yet
- ECE 356 Acoustics F23 DS 1 ST X360 1 AfterDocument40 pagesECE 356 Acoustics F23 DS 1 ST X360 1 AfterMariam MaherNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions - Sound, Class 9, Science - EduRevDocument4 pagesPractice Questions - Sound, Class 9, Science - EduRevArsi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Principle of SoundDocument49 pagesTopic 9 Principle of SoundAizat ZameerNo ratings yet
- Navigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsFrom EverandNavigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsNo ratings yet
- Physics: Momentum 1 Questions (A + E)Document3 pagesPhysics: Momentum 1 Questions (A + E)Mr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Forces and Elasticity 1 MSDocument2 pagesForces and Elasticity 1 MSMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- GCSE Physics: EnergyDocument5 pagesGCSE Physics: EnergyMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Forces and Elasticity 1 QSDocument6 pagesForces and Elasticity 1 QSMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Moments Levers and Gears Exam Style QuestionsDocument2 pagesMoments Levers and Gears Exam Style QuestionsMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Momentum 2 Exam Style QuestionsDocument2 pagesMomentum 2 Exam Style QuestionsMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Momentum-1-Exam Style QuestionsDocument2 pagesMomentum-1-Exam Style QuestionsMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- GCSE Physics: Forces and MotionDocument6 pagesGCSE Physics: Forces and MotionMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- GCSE Physics: Electromagnetic Waves - 1Document4 pagesGCSE Physics: Electromagnetic Waves - 1Mr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Forces - Motion Questions 1 MSDocument3 pagesForces - Motion Questions 1 MSMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Falling Objects Answer SchemeDocument3 pagesFalling Objects Answer SchemeMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Falling Objects Exam Style QuestionsDocument3 pagesFalling Objects Exam Style QuestionsMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- GCSE Physics: Electromagnetic Waves - 1 MsDocument3 pagesGCSE Physics: Electromagnetic Waves - 1 MsMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Distance and Displacement Speed and Velocity Answer SchemeDocument2 pagesDistance and Displacement Speed and Velocity Answer SchemeMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Distance and Displacement Speed and Velocity Exam Style QuestionsDocument2 pagesDistance and Displacement Speed and Velocity Exam Style QuestionsMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Acids and Alkali - 1 QSDocument4 pagesAcids and Alkali - 1 QSMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- June 2018 QP - Paper 1 (H) AQA Biology GCSEDocument32 pagesJune 2018 QP - Paper 1 (H) AQA Biology GCSEMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 1Document4 pagesGCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 1Mr. Suit100% (1)
- GCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 3Document4 pagesGCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 3Mr. SuitNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry: Acids and Alkali - 2Document3 pagesGCSE Chemistry: Acids and Alkali - 2Mr. SuitNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry: Acids and Alkali - 1 MSDocument3 pagesGCSE Chemistry: Acids and Alkali - 1 MSMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 2Document5 pagesGCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 2Mr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Technical Guide Vitomax 200 HS M75A PDFDocument152 pagesTechnical Guide Vitomax 200 HS M75A PDFAdhi candra irawanNo ratings yet
- TPC AC - DC Ground Detector Fault DetectorDocument6 pagesTPC AC - DC Ground Detector Fault DetectorIrfan Ari PNo ratings yet
- Spohn FerencDocument29 pagesSpohn Ferencemy1188No ratings yet
- Comparison of Arching Profiles of Golden Age Cremonese Violins and Some Mathematically Generated CurvesDocument18 pagesComparison of Arching Profiles of Golden Age Cremonese Violins and Some Mathematically Generated Curvesnostromo1979No ratings yet
- Assessment 1 - Introduction To An Organization: "We Deliver With Quality"Document15 pagesAssessment 1 - Introduction To An Organization: "We Deliver With Quality"Ar-Rayyan AshNo ratings yet
- Name SAP Technical Consultant Resume - 4+Document5 pagesName SAP Technical Consultant Resume - 4+Vinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Letter of InternshipDocument69 pagesLetter of InternshipZain Afzal67% (3)
- Mesa MK2C+ SLOCLONEDocument4 pagesMesa MK2C+ SLOCLONEedi spenkNo ratings yet
- Runway UsaDocument150 pagesRunway UsakyoobumNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Deh-2100ib SMDocument68 pagesPioneer Deh-2100ib SMJuly DemariaNo ratings yet
- Binani Cement Limited, SirohiDocument47 pagesBinani Cement Limited, SirohivikassspaceNo ratings yet
- Achieving Massive MIMO Spectral Efficiency With A Not-so-Large Number of AntennasDocument14 pagesAchieving Massive MIMO Spectral Efficiency With A Not-so-Large Number of AntennasBruno AlvimNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Applications For Cello TrackDocument2 pagesTop 10 Applications For Cello TrackMạnh LêNo ratings yet
- Datasheet VS18-2D5450 6011849 enDocument4 pagesDatasheet VS18-2D5450 6011849 enGabriel MtzNo ratings yet
- Smith ChartDocument28 pagesSmith ChartsniyaNo ratings yet
- Liferay 6.x Portal Enterprise Intranets Cookbook - Sample ChapterDocument23 pagesLiferay 6.x Portal Enterprise Intranets Cookbook - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Self-Assessment Checks: Core CompetenciesDocument9 pagesForm 1 Self-Assessment Checks: Core CompetenciesLyka ollerasNo ratings yet
- Mini Milling MachineDocument4 pagesMini Milling Machinekrisbhaskar22No ratings yet
- Analysis Bharti AirtelDocument70 pagesAnalysis Bharti Airtelshweta_4666450% (2)
- Company ListDocument6 pagesCompany ListengvaithyNo ratings yet
- Br Nồi hấp SJ-RTDocument3 pagesBr Nồi hấp SJ-RTVật Tư Lab Đức Dương Như Nguyễn (AS ONE JAPAN)No ratings yet
- Brand Management of HULDocument76 pagesBrand Management of HULMohammed Yunus100% (1)
- Mechanical Seals PDFDocument14 pagesMechanical Seals PDFZeeshan SajidNo ratings yet
- Create BAPIDocument7 pagesCreate BAPImathurjitendraNo ratings yet
- Spatial ResolutionDocument14 pagesSpatial ResolutionMuhammad Hammad AzharNo ratings yet
- User's Manual: Thermal Printer Mechanical Control Lsi CBM-202PC-04Document88 pagesUser's Manual: Thermal Printer Mechanical Control Lsi CBM-202PC-04gadacz111No ratings yet
- Innovation Culture The Big Elephant in The RoomDocument13 pagesInnovation Culture The Big Elephant in The RoomkreatosNo ratings yet
- Asha Sharma ResumeDocument3 pagesAsha Sharma ResumeRachit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solo User Manual v1Document57 pagesSolo User Manual v1mohx0001No ratings yet