Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BreastCancer Pathophysiology
BreastCancer Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
ClaudineCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Breast Imaging - The RequisitesDocument513 pagesBreast Imaging - The RequisitesEvi Polideras100% (6)
- Breast Cancer PDFDocument37 pagesBreast Cancer PDFSanti Galang Guades50% (2)
- Pathophysiology Diagram: Breast Cancer: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Diagram: Breast Cancer: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsMarinill Soliman100% (1)
- CANCER ReportDocument135 pagesCANCER ReportEnzo TimbolNo ratings yet
- Beauty, Health, and Risk in Brazilian Plastic SurgeryDocument18 pagesBeauty, Health, and Risk in Brazilian Plastic SurgeryAlex EdmondsNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer: UnknownDocument3 pagesBreast Cancer: UnknownIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument6 pagesBreast Cancersarguss14No ratings yet
- Gynecology - Cancer IntroDocument1 pageGynecology - Cancer IntroAnsley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Cancer IntroDocument1 pageGynecology - Cancer IntroEugen MNo ratings yet
- Tumor Jinak Dan Ganas PayudaraDocument92 pagesTumor Jinak Dan Ganas PayudarasyerlypramaNo ratings yet
- ReproductiveSlides2020 FullSize 5 PDFDocument9 pagesReproductiveSlides2020 FullSize 5 PDFnaazaninrahat76No ratings yet
- Patho of Invasive Duct CarcinomaDocument3 pagesPatho of Invasive Duct CarcinomaBESA JERIC FLORESNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Case Study Presentation-2Document46 pagesBreast Cancer Case Study Presentation-2api-501121524No ratings yet
- Mary Rose S. Gargar Bsn-Iv Cancer of The Female ReproductiveDocument9 pagesMary Rose S. Gargar Bsn-Iv Cancer of The Female ReproductiveMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Cancer IntroDocument1 pageGynecology Cancer IntroHhaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-03-01 at 3.14.03 PMDocument17 pagesScreenshot 2023-03-01 at 3.14.03 PMmohameeedar1No ratings yet
- ASCP PC Breast CancerDocument6 pagesASCP PC Breast CancerTulsi KambleNo ratings yet
- Female GUDocument18 pagesFemale GULauren LaMonicaNo ratings yet
- CCSP - NewDocument69 pagesCCSP - NewasdfNo ratings yet
- Marnie and GidgetDocument33 pagesMarnie and GidgetMarnie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Tumours PresentationDocument49 pagesOvarian Tumours PresentationChoden JamyangNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma Breast - DR AKASHDocument78 pagesCarcinoma Breast - DR AKASH55 Akshya KNo ratings yet
- Female-Genital 2 PDFDocument16 pagesFemale-Genital 2 PDFMuhammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer: MembersDocument15 pagesBreast Cancer: MembersEstefany LopezNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument15 pagesCancerAficionadoNo ratings yet
- Mammo MidtermsDocument23 pagesMammo MidtermsCherie lou PizaNo ratings yet
- PHPS30020 Cancer Epidemiogy and Screening 2023 - Prof FitzpatrickDocument53 pagesPHPS30020 Cancer Epidemiogy and Screening 2023 - Prof FitzpatrickKatie NolanNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Pap Smear Test Result (Bethesda) : Adenocarcinoma, Growth ofDocument1 pageCervical Cancer Pap Smear Test Result (Bethesda) : Adenocarcinoma, Growth ofJeremiah JustoNo ratings yet
- CERVICAL-CANCER PaularDocument20 pagesCERVICAL-CANCER PaularRachel Julianne MoralesNo ratings yet
- Exposure Normal Cells Precursors Invasive Cancer: Natural History of Cervical CancerDocument6 pagesExposure Normal Cells Precursors Invasive Cancer: Natural History of Cervical CancerNalin AbeysingheNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument21 pagesBreast CancerAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - Natural History of CC - 2022Document15 pagesSession 3 - Natural History of CC - 2022Faraaz SokwalaNo ratings yet
- Newest Breast CancerDocument27 pagesNewest Breast CancerSAMMYNo ratings yet
- Sarcomas SurgeryDocument8 pagesSarcomas SurgeryJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- Cáncer Precoz, MastologíaDocument31 pagesCáncer Precoz, MastologíaDr. Pablo Maria Peralta LorcaNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis - Aaron Arce BSN 3 DDocument7 pagesCase Analysis - Aaron Arce BSN 3 DAaron ArceNo ratings yet
- Breast and Ovarian Cancer - PresentationDocument26 pagesBreast and Ovarian Cancer - PresentationRawa MuhsinNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer (Aka BR CA) : - Routine Screening For Genetic Abnormalities of A Strong Family HX of BR CA Is NOT NeededDocument6 pagesBreast Cancer (Aka BR CA) : - Routine Screening For Genetic Abnormalities of A Strong Family HX of BR CA Is NOT NeededChanthorn SokNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument5 pagesBreast CancerJohiarra Madanglog TabigneNo ratings yet
- Cancerscreeningand Preventionhighlightsin Gynecologiccancer: Jeanine N. Staples,, Linda R. DuskaDocument18 pagesCancerscreeningand Preventionhighlightsin Gynecologiccancer: Jeanine N. Staples,, Linda R. DuskaAndrea ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Screening Cancer GinecológicoDocument18 pagesScreening Cancer GinecológicoLeonardoCampanelliNo ratings yet
- The Breast - Part 2 Dr. Roberto B. Acuña: Hormonal Non-HormonalDocument14 pagesThe Breast - Part 2 Dr. Roberto B. Acuña: Hormonal Non-HormonalMaf BNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document4 pagesWeek 2AliceNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer: Medical-Surgial LectureDocument4 pagesBreast Cancer: Medical-Surgial LectureNoreen PadillaNo ratings yet
- CESA January 2009Document7 pagesCESA January 2009Anonymous rZdsbP67iXNo ratings yet
- DR Sagar Rathod Drddwagh: Presented by GuideDocument1 pageDR Sagar Rathod Drddwagh: Presented by GuideSagarRathodNo ratings yet
- Johnson Jerry Alan Chinese Medical Qigong Therapy Vol 5-121-140Document20 pagesJohnson Jerry Alan Chinese Medical Qigong Therapy Vol 5-121-140toanbauNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer - McMaster Pathophysiology Review PDFDocument8 pagesBreast Cancer - McMaster Pathophysiology Review PDFAprilla Ayu W.No ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument7 pagesBreast Cancermikhail juteNo ratings yet
- Profil Penderita Kanker Payudara Stadium 8499b5a2Document11 pagesProfil Penderita Kanker Payudara Stadium 8499b5a2mia amaliaNo ratings yet
- Dr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari, M.B.B.S.,D.C.P., Tutor in Pathology, MapimsDocument59 pagesDr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari, M.B.B.S.,D.C.P., Tutor in Pathology, MapimsIntan Eklesiana Napitupulu100% (1)
- Tumor Markers Common Manifestations Therapy/Treatment Others: Male CancersDocument9 pagesTumor Markers Common Manifestations Therapy/Treatment Others: Male CancersErica DagdagNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1083318821003247 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S1083318821003247 MainMeta ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument35 pagesFinals Reviewerimlookingforyou.03No ratings yet
- 18 - HPV Infection (Diapo)Document43 pages18 - HPV Infection (Diapo)Massouh AssouiNo ratings yet
- UP PGH 2019 Interns Review 4 Malignant GyneDocument82 pagesUP PGH 2019 Interns Review 4 Malignant GyneTrisNo ratings yet
- 4-Ovarian Cancer PPDocument28 pages4-Ovarian Cancer PPtaha obaidNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument42 pagesBreast CancerJumar ValdezNo ratings yet
- HPV Vaccine Cervical Cancer: AndrijonoDocument54 pagesHPV Vaccine Cervical Cancer: Andrijonosri PurwayantiNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For Breast Surgery: Andrew J Westbrook Fcarcsi Donal J Buggy MD MSC Dipmedeld Frcpi Fcarcsi FrcaDocument4 pagesAnaesthesia For Breast Surgery: Andrew J Westbrook Fcarcsi Donal J Buggy MD MSC Dipmedeld Frcpi Fcarcsi FrcajonathanNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 4Document26 pagesKelompok 4Marturia DrifanyNo ratings yet
- Pathology of TestesDocument4 pagesPathology of TestesGerardLum100% (1)
- How to Cook a Revolution: Recipes for Breast Cancer PreventionFrom EverandHow to Cook a Revolution: Recipes for Breast Cancer PreventionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Data Nursing Diagnoses Goals and Outcomes Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Data Nursing Diagnoses Goals and Outcomes Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationClaudineNo ratings yet
- MMHDocument8 pagesMMHClaudineNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Data NSG Diagnoses Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation Goal MetDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Data NSG Diagnoses Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation Goal MetClaudineNo ratings yet
- Data NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoDocument3 pagesData NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoClaudineNo ratings yet
- Rizal's Life: Higher Education and Life AbroadDocument2 pagesRizal's Life: Higher Education and Life AbroadClaudineNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Self Test 2Document5 pagesSpiritual Self Test 2ClaudineNo ratings yet
- Module 7: Communicable Diseases (Typhoid Fever) Case Analysis #1Document3 pagesModule 7: Communicable Diseases (Typhoid Fever) Case Analysis #1ClaudineNo ratings yet
- Baguio Cathedral Baguio Cathedral: "Sing To The Lord With All Your Heart"Document2 pagesBaguio Cathedral Baguio Cathedral: "Sing To The Lord With All Your Heart"ClaudineNo ratings yet
- Assessment NSG DX Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment NSG DX Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale EvaluationClaudineNo ratings yet
- UELS NIH Research Plan CompressedDocument36 pagesUELS NIH Research Plan CompressedKunal JaisinghaniNo ratings yet
- Reiser DBTDocument10 pagesReiser DBTMelanie DascăluNo ratings yet
- Community Based Assessment Checklist (CBAC) FormDocument3 pagesCommunity Based Assessment Checklist (CBAC) FormShubhaDavalgiNo ratings yet
- Breast Self ExaminationDocument40 pagesBreast Self ExaminationPrince Rener Velasco PeraNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Risks RecommendationsDocument2 pagesBreast Cancer Risks RecommendationsYohannes GirmawNo ratings yet
- 2.3.a DR Yadi Permana Whats New in Ovarian Function Suppression in Pre-MenopausalDocument36 pages2.3.a DR Yadi Permana Whats New in Ovarian Function Suppression in Pre-Menopausaltepat rshsNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and Depression After Cancer DiagnosisDocument26 pagesAnxiety and Depression After Cancer DiagnosisMesias PatricioNo ratings yet
- A Web-Based Self-Management Exercise and Diet Intervention PDFDocument11 pagesA Web-Based Self-Management Exercise and Diet Intervention PDFAsis muhammadNo ratings yet
- Speech by Her Excellency Margaret Kenyatta, First Lady of The Republic of Kenya During The Official Opening Ceremony of the 10th Stop Cervical, Breast and Prostate Cancer in Africa (SCCA) Conference in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia on 25th July, 2016.Document4 pagesSpeech by Her Excellency Margaret Kenyatta, First Lady of The Republic of Kenya During The Official Opening Ceremony of the 10th Stop Cervical, Breast and Prostate Cancer in Africa (SCCA) Conference in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia on 25th July, 2016.First Lady KenyaNo ratings yet
- Honey Wounds CancerDocument6 pagesHoney Wounds CancerburhanNo ratings yet
- Healthmedicinet I 2017 1Document676 pagesHealthmedicinet I 2017 1tuni santeNo ratings yet
- Norton Simon HypothesisDocument2 pagesNorton Simon HypothesissusdoctorNo ratings yet
- Promotion OBGYNDocument30 pagesPromotion OBGYNAloah122346No ratings yet
- Breast - Invasive 4.8.1.0.REL CAPCP (1) MDocument42 pagesBreast - Invasive 4.8.1.0.REL CAPCP (1) MPaulina GarcesNo ratings yet
- Granulomatous Mastitis: Review ArticleDocument3 pagesGranulomatous Mastitis: Review ArticledwiagusyuliantoNo ratings yet
- Sensors: Early Diagnosis of Breast CancerDocument20 pagesSensors: Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancerrizka hastariNo ratings yet
- The BreastDocument4,358 pagesThe BreastluficorNo ratings yet
- FDA Sientra Briefing PackageDocument50 pagesFDA Sientra Briefing PackageMaresNo ratings yet
- Program PrezentariDocument14 pagesProgram PrezentariRoxana Alexandra BogosNo ratings yet
- 50 Items HADocument7 pages50 Items HAToni Marie Buenconsejo PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Clinonc Assignment FinalDocument28 pagesClinonc Assignment Finalapi-633652323No ratings yet
- DOH Breast Cancer Guidelines FinalDocument123 pagesDOH Breast Cancer Guidelines Finalsupratimbiswas073380No ratings yet
- Pathology ofDocument114 pagesPathology ofRahul Audenesen BratNo ratings yet
- Soy Food GuideDocument24 pagesSoy Food Guideabhi_841No ratings yet
- Pe Notes 4Document28 pagesPe Notes 4Caleb FellowesNo ratings yet
- BREAST CANCER & TCM. DR Fatima Manesh PDFDocument140 pagesBREAST CANCER & TCM. DR Fatima Manesh PDFmehranerezvani50% (2)
- UntitledDocument327 pagesUntitledInes MartinhoNo ratings yet
BreastCancer Pathophysiology
BreastCancer Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
ClaudineOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BreastCancer Pathophysiology
BreastCancer Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
ClaudineCopyright:
Available Formats
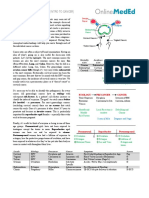
Mutation of - Genetics/Family
tumor Hx
Cannot suppressor - Demographics
genes -Prolonged Alcohol High Smoking Previous
repair (high risk= breast cancer
(BRCA1/ estrogen exposure
BMI
damaged 2-5 drinks/ or carcinoma
DNA or BRCA2) - Medical Hx
-Lifestyle day) in situ (CIS),
destroy radiation
affected
cells
Family hx Adipocy
of breast or other Old age, Nulliparity, tes Moderately
cancers, rare females early produce increased if
genetic syndromes (99%) menarche estroge high pack
(<12), late High n from years, early
menopause serum androge initiation,
(>55), older estrogen ns longer duration
Increased age at first
protoonco delivery
genes like (>30), etc.
HER2
Increased
tissue
growth, no
regulation
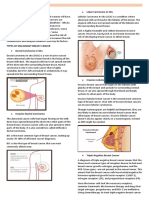
Breast
Cancer
Non-
Invasive invasive
Lobular Ductal
Rarer Paget’s Inflammatory Invasive Invasive carcinoma in carcinoma in
types: male disease carcinoma lobular ductal situ (LCIS) situ (DCIS)
breast (1-3%) (1-4%) carcinoma carcinoma
cancer, (8-15%) (80%)
lymphoma,
sarcoma
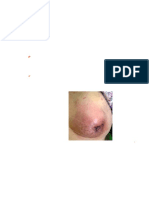
Ductal Infiltrates
Ductal carcinoma Infiltrates surrounding Malignant Malignant
carcinoma invading surrounding breast cells cells
Male breast invading dermal breast tissue, contained contained
cancer nipple
lymphatics tissue, 20% palpable if within breast within breast
usually , bilateral, large or lobule, ducts,
invasive Scaling, aggressive
diagnosed detected on detected on detected on
ductal eczema- microscopic mammogra biopsy done mammogram
carcinoma, like Tender, ally m for other
diagnosed at lesions on red, warm, indication
advanced nipple swollen
stage breast;
peas d’
orange=ad
vanced
You might also like
- Breast Imaging - The RequisitesDocument513 pagesBreast Imaging - The RequisitesEvi Polideras100% (6)
- Breast Cancer PDFDocument37 pagesBreast Cancer PDFSanti Galang Guades50% (2)
- Pathophysiology Diagram: Breast Cancer: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Diagram: Breast Cancer: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsMarinill Soliman100% (1)
- CANCER ReportDocument135 pagesCANCER ReportEnzo TimbolNo ratings yet
- Beauty, Health, and Risk in Brazilian Plastic SurgeryDocument18 pagesBeauty, Health, and Risk in Brazilian Plastic SurgeryAlex EdmondsNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer: UnknownDocument3 pagesBreast Cancer: UnknownIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument6 pagesBreast Cancersarguss14No ratings yet
- Gynecology - Cancer IntroDocument1 pageGynecology - Cancer IntroAnsley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Cancer IntroDocument1 pageGynecology - Cancer IntroEugen MNo ratings yet
- Tumor Jinak Dan Ganas PayudaraDocument92 pagesTumor Jinak Dan Ganas PayudarasyerlypramaNo ratings yet
- ReproductiveSlides2020 FullSize 5 PDFDocument9 pagesReproductiveSlides2020 FullSize 5 PDFnaazaninrahat76No ratings yet
- Patho of Invasive Duct CarcinomaDocument3 pagesPatho of Invasive Duct CarcinomaBESA JERIC FLORESNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Case Study Presentation-2Document46 pagesBreast Cancer Case Study Presentation-2api-501121524No ratings yet
- Mary Rose S. Gargar Bsn-Iv Cancer of The Female ReproductiveDocument9 pagesMary Rose S. Gargar Bsn-Iv Cancer of The Female ReproductiveMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Cancer IntroDocument1 pageGynecology Cancer IntroHhaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-03-01 at 3.14.03 PMDocument17 pagesScreenshot 2023-03-01 at 3.14.03 PMmohameeedar1No ratings yet
- ASCP PC Breast CancerDocument6 pagesASCP PC Breast CancerTulsi KambleNo ratings yet
- Female GUDocument18 pagesFemale GULauren LaMonicaNo ratings yet
- CCSP - NewDocument69 pagesCCSP - NewasdfNo ratings yet
- Marnie and GidgetDocument33 pagesMarnie and GidgetMarnie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Tumours PresentationDocument49 pagesOvarian Tumours PresentationChoden JamyangNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma Breast - DR AKASHDocument78 pagesCarcinoma Breast - DR AKASH55 Akshya KNo ratings yet
- Female-Genital 2 PDFDocument16 pagesFemale-Genital 2 PDFMuhammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer: MembersDocument15 pagesBreast Cancer: MembersEstefany LopezNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument15 pagesCancerAficionadoNo ratings yet
- Mammo MidtermsDocument23 pagesMammo MidtermsCherie lou PizaNo ratings yet
- PHPS30020 Cancer Epidemiogy and Screening 2023 - Prof FitzpatrickDocument53 pagesPHPS30020 Cancer Epidemiogy and Screening 2023 - Prof FitzpatrickKatie NolanNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Pap Smear Test Result (Bethesda) : Adenocarcinoma, Growth ofDocument1 pageCervical Cancer Pap Smear Test Result (Bethesda) : Adenocarcinoma, Growth ofJeremiah JustoNo ratings yet
- CERVICAL-CANCER PaularDocument20 pagesCERVICAL-CANCER PaularRachel Julianne MoralesNo ratings yet
- Exposure Normal Cells Precursors Invasive Cancer: Natural History of Cervical CancerDocument6 pagesExposure Normal Cells Precursors Invasive Cancer: Natural History of Cervical CancerNalin AbeysingheNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument21 pagesBreast CancerAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - Natural History of CC - 2022Document15 pagesSession 3 - Natural History of CC - 2022Faraaz SokwalaNo ratings yet
- Newest Breast CancerDocument27 pagesNewest Breast CancerSAMMYNo ratings yet
- Sarcomas SurgeryDocument8 pagesSarcomas SurgeryJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- Cáncer Precoz, MastologíaDocument31 pagesCáncer Precoz, MastologíaDr. Pablo Maria Peralta LorcaNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis - Aaron Arce BSN 3 DDocument7 pagesCase Analysis - Aaron Arce BSN 3 DAaron ArceNo ratings yet
- Breast and Ovarian Cancer - PresentationDocument26 pagesBreast and Ovarian Cancer - PresentationRawa MuhsinNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer (Aka BR CA) : - Routine Screening For Genetic Abnormalities of A Strong Family HX of BR CA Is NOT NeededDocument6 pagesBreast Cancer (Aka BR CA) : - Routine Screening For Genetic Abnormalities of A Strong Family HX of BR CA Is NOT NeededChanthorn SokNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument5 pagesBreast CancerJohiarra Madanglog TabigneNo ratings yet
- Cancerscreeningand Preventionhighlightsin Gynecologiccancer: Jeanine N. Staples,, Linda R. DuskaDocument18 pagesCancerscreeningand Preventionhighlightsin Gynecologiccancer: Jeanine N. Staples,, Linda R. DuskaAndrea ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Screening Cancer GinecológicoDocument18 pagesScreening Cancer GinecológicoLeonardoCampanelliNo ratings yet
- The Breast - Part 2 Dr. Roberto B. Acuña: Hormonal Non-HormonalDocument14 pagesThe Breast - Part 2 Dr. Roberto B. Acuña: Hormonal Non-HormonalMaf BNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document4 pagesWeek 2AliceNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer: Medical-Surgial LectureDocument4 pagesBreast Cancer: Medical-Surgial LectureNoreen PadillaNo ratings yet
- CESA January 2009Document7 pagesCESA January 2009Anonymous rZdsbP67iXNo ratings yet
- DR Sagar Rathod Drddwagh: Presented by GuideDocument1 pageDR Sagar Rathod Drddwagh: Presented by GuideSagarRathodNo ratings yet
- Johnson Jerry Alan Chinese Medical Qigong Therapy Vol 5-121-140Document20 pagesJohnson Jerry Alan Chinese Medical Qigong Therapy Vol 5-121-140toanbauNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer - McMaster Pathophysiology Review PDFDocument8 pagesBreast Cancer - McMaster Pathophysiology Review PDFAprilla Ayu W.No ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument7 pagesBreast Cancermikhail juteNo ratings yet
- Profil Penderita Kanker Payudara Stadium 8499b5a2Document11 pagesProfil Penderita Kanker Payudara Stadium 8499b5a2mia amaliaNo ratings yet
- Dr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari, M.B.B.S.,D.C.P., Tutor in Pathology, MapimsDocument59 pagesDr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari, M.B.B.S.,D.C.P., Tutor in Pathology, MapimsIntan Eklesiana Napitupulu100% (1)
- Tumor Markers Common Manifestations Therapy/Treatment Others: Male CancersDocument9 pagesTumor Markers Common Manifestations Therapy/Treatment Others: Male CancersErica DagdagNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1083318821003247 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S1083318821003247 MainMeta ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument35 pagesFinals Reviewerimlookingforyou.03No ratings yet
- 18 - HPV Infection (Diapo)Document43 pages18 - HPV Infection (Diapo)Massouh AssouiNo ratings yet
- UP PGH 2019 Interns Review 4 Malignant GyneDocument82 pagesUP PGH 2019 Interns Review 4 Malignant GyneTrisNo ratings yet
- 4-Ovarian Cancer PPDocument28 pages4-Ovarian Cancer PPtaha obaidNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument42 pagesBreast CancerJumar ValdezNo ratings yet
- HPV Vaccine Cervical Cancer: AndrijonoDocument54 pagesHPV Vaccine Cervical Cancer: Andrijonosri PurwayantiNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For Breast Surgery: Andrew J Westbrook Fcarcsi Donal J Buggy MD MSC Dipmedeld Frcpi Fcarcsi FrcaDocument4 pagesAnaesthesia For Breast Surgery: Andrew J Westbrook Fcarcsi Donal J Buggy MD MSC Dipmedeld Frcpi Fcarcsi FrcajonathanNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 4Document26 pagesKelompok 4Marturia DrifanyNo ratings yet
- Pathology of TestesDocument4 pagesPathology of TestesGerardLum100% (1)
- How to Cook a Revolution: Recipes for Breast Cancer PreventionFrom EverandHow to Cook a Revolution: Recipes for Breast Cancer PreventionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Data Nursing Diagnoses Goals and Outcomes Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Data Nursing Diagnoses Goals and Outcomes Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationClaudineNo ratings yet
- MMHDocument8 pagesMMHClaudineNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Data NSG Diagnoses Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation Goal MetDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Data NSG Diagnoses Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation Goal MetClaudineNo ratings yet
- Data NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoDocument3 pagesData NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoClaudineNo ratings yet
- Rizal's Life: Higher Education and Life AbroadDocument2 pagesRizal's Life: Higher Education and Life AbroadClaudineNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Self Test 2Document5 pagesSpiritual Self Test 2ClaudineNo ratings yet
- Module 7: Communicable Diseases (Typhoid Fever) Case Analysis #1Document3 pagesModule 7: Communicable Diseases (Typhoid Fever) Case Analysis #1ClaudineNo ratings yet
- Baguio Cathedral Baguio Cathedral: "Sing To The Lord With All Your Heart"Document2 pagesBaguio Cathedral Baguio Cathedral: "Sing To The Lord With All Your Heart"ClaudineNo ratings yet
- Assessment NSG DX Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment NSG DX Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale EvaluationClaudineNo ratings yet
- UELS NIH Research Plan CompressedDocument36 pagesUELS NIH Research Plan CompressedKunal JaisinghaniNo ratings yet
- Reiser DBTDocument10 pagesReiser DBTMelanie DascăluNo ratings yet
- Community Based Assessment Checklist (CBAC) FormDocument3 pagesCommunity Based Assessment Checklist (CBAC) FormShubhaDavalgiNo ratings yet
- Breast Self ExaminationDocument40 pagesBreast Self ExaminationPrince Rener Velasco PeraNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Risks RecommendationsDocument2 pagesBreast Cancer Risks RecommendationsYohannes GirmawNo ratings yet
- 2.3.a DR Yadi Permana Whats New in Ovarian Function Suppression in Pre-MenopausalDocument36 pages2.3.a DR Yadi Permana Whats New in Ovarian Function Suppression in Pre-Menopausaltepat rshsNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and Depression After Cancer DiagnosisDocument26 pagesAnxiety and Depression After Cancer DiagnosisMesias PatricioNo ratings yet
- A Web-Based Self-Management Exercise and Diet Intervention PDFDocument11 pagesA Web-Based Self-Management Exercise and Diet Intervention PDFAsis muhammadNo ratings yet
- Speech by Her Excellency Margaret Kenyatta, First Lady of The Republic of Kenya During The Official Opening Ceremony of the 10th Stop Cervical, Breast and Prostate Cancer in Africa (SCCA) Conference in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia on 25th July, 2016.Document4 pagesSpeech by Her Excellency Margaret Kenyatta, First Lady of The Republic of Kenya During The Official Opening Ceremony of the 10th Stop Cervical, Breast and Prostate Cancer in Africa (SCCA) Conference in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia on 25th July, 2016.First Lady KenyaNo ratings yet
- Honey Wounds CancerDocument6 pagesHoney Wounds CancerburhanNo ratings yet
- Healthmedicinet I 2017 1Document676 pagesHealthmedicinet I 2017 1tuni santeNo ratings yet
- Norton Simon HypothesisDocument2 pagesNorton Simon HypothesissusdoctorNo ratings yet
- Promotion OBGYNDocument30 pagesPromotion OBGYNAloah122346No ratings yet
- Breast - Invasive 4.8.1.0.REL CAPCP (1) MDocument42 pagesBreast - Invasive 4.8.1.0.REL CAPCP (1) MPaulina GarcesNo ratings yet
- Granulomatous Mastitis: Review ArticleDocument3 pagesGranulomatous Mastitis: Review ArticledwiagusyuliantoNo ratings yet
- Sensors: Early Diagnosis of Breast CancerDocument20 pagesSensors: Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancerrizka hastariNo ratings yet
- The BreastDocument4,358 pagesThe BreastluficorNo ratings yet
- FDA Sientra Briefing PackageDocument50 pagesFDA Sientra Briefing PackageMaresNo ratings yet
- Program PrezentariDocument14 pagesProgram PrezentariRoxana Alexandra BogosNo ratings yet
- 50 Items HADocument7 pages50 Items HAToni Marie Buenconsejo PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Clinonc Assignment FinalDocument28 pagesClinonc Assignment Finalapi-633652323No ratings yet
- DOH Breast Cancer Guidelines FinalDocument123 pagesDOH Breast Cancer Guidelines Finalsupratimbiswas073380No ratings yet
- Pathology ofDocument114 pagesPathology ofRahul Audenesen BratNo ratings yet
- Soy Food GuideDocument24 pagesSoy Food Guideabhi_841No ratings yet
- Pe Notes 4Document28 pagesPe Notes 4Caleb FellowesNo ratings yet
- BREAST CANCER & TCM. DR Fatima Manesh PDFDocument140 pagesBREAST CANCER & TCM. DR Fatima Manesh PDFmehranerezvani50% (2)
- UntitledDocument327 pagesUntitledInes MartinhoNo ratings yet