Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Education System in Poland
Education System in Poland
Uploaded by
api-466148385Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Education System in Poland
Education System in Poland
Uploaded by
api-466148385Copyright:
Available Formats
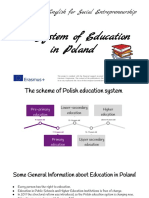
Compulsory education in Poland starts at the age of six from the
mandatory “0” reception class. The reception class is a part of
kindegarten/pre-school rather than school.
The actual school education, primary school (szkoła podstawowa),
starts at the age of 7 (earlier entry is possible on the condition of
receiving a positive opinion on emotional and intellectual school readiness
of the child).
żłobek – creche; przedszkole – kindergarten; szkoła podstawowa – primary school; liceum ogólnokształcące –
secondary general education school; technikum – technical (vocational) secondary school; szkoła branżowa I
stopnia – vocational school (I stage)
Primary school (szkoła podstawowa)
There are 8 years of education in primary school in Poland with a
division into:
• grades 1 – 3 – early education where teaching is delivered in the form of
teaching blocs rather than single subjects; the class teacher delivers classes in
literacy and numeracy as well as in musical education and art; the marks at
this stage are descriptive rather than numerical;
• grades 4 – 8 – there is a clear division into subjects (Polish language, English
language, Mathematics, Nature, History, Computing, PE, Music, Art, Practical
skills, Religion/Ethics, and from grade 7 also Chemistry, Biology and a foreign
language); students receive numerical marks for all subjects on a scale from 1
to 6 (1- failed, 6 – excellent).
The primary school ends with end-of-school exams the results of
which are taken into account when applying to a secondary
education school.
Secondary school (szkoła średnia)
At the age of 15 young people in Poland start secondary education which
can take a form of:
• 4-year general secondary school (high school),
• 5-year technical (vocational) secondary school,
• 3-year vocational school (stage I),
• 2-year vocational school (stage II)
Students of vocational schools – basic vocational schools and technical
secondary schools – may take exams confirming vocational qualifications
in a given occupation during the course of study or upon completion of
school to receive a diploma confirming their vocational qualifications.
Graduates of general upper secondary schools (liceum ogólnoształcące)
and technical secondary schools may take the school-leaving
examination (egzamin maturalny) to obtain the Matura certificate,
which gives access to higher education.
Compulsory education
In the Polish education system full-time compulsory education and part-
time compulsory education are defined. Full-time compulsory
education (obligation to attend primary and lower secondary school – old
structure, and primary school – new structure) applies to pupils aged
7-15 years while part-time compulsory education (obligation to be in
education) concerns pupils aged 15-18 and it may take place either in
school settings (a student attends an upper secondary school) or in non-
school settings (e.g. a student follows vocational training offered by
employers).
You might also like
- Jurisprudence and Legal Liabilities in NursingDocument32 pagesJurisprudence and Legal Liabilities in Nursingzade89080% (5)
- 2019 Education Council Member GuideDocument122 pages2019 Education Council Member GuidemariposanycNo ratings yet
- T.L.E 9 & 10 First Periodical Exam With Answer KeyDocument5 pagesT.L.E 9 & 10 First Periodical Exam With Answer KeyLudivert Solomon85% (52)
- The System of Education in PolandDocument10 pagesThe System of Education in PolandDaniela RotaruNo ratings yet
- Education in EuropeDocument3 pagesEducation in EuropeAdri DaswinNo ratings yet
- Ukrainian System of EducationDocument3 pagesUkrainian System of EducationЕлизавета Сахно100% (1)
- School System in SlovakiaDocument8 pagesSchool System in Slovakiakate0% (1)
- Education Czech RepublicDocument9 pagesEducation Czech RepublicRenata BockovaNo ratings yet
- Educational System in PolandDocument2 pagesEducational System in PolandagaboNo ratings yet
- EducationDocument2 pagesEducationVeronika SkorikovaNo ratings yet
- Oktatás MagyarországonDocument2 pagesOktatás MagyarországonannaszekerNo ratings yet
- EducationDocument3 pagesEducationZsuzsa TóthNo ratings yet
- The Educational System in Switzerland Vs in RomaniaDocument10 pagesThe Educational System in Switzerland Vs in RomaniaStefania NeacsuNo ratings yet
- In Ukraine Children Start Going To School at The Age of Six or SevenDocument2 pagesIn Ukraine Children Start Going To School at The Age of Six or SevenYana FishkaNo ratings yet
- Hungarian EduactionDocument1 pageHungarian EduactionPeti HorváthNo ratings yet
- Polish Education Marek SzymańskiDocument21 pagesPolish Education Marek SzymańskiMarek SzymańskiNo ratings yet
- Education in CroatiaDocument4 pagesEducation in CroatiaBibo MovaNo ratings yet
- Sekilas Pendidikan Di ItaliaDocument13 pagesSekilas Pendidikan Di ItaliaSiti ZakiahanimNo ratings yet
- Educational System in Slovakia-1Document10 pagesEducational System in Slovakia-1cscsabi109No ratings yet
- Theme 2 THE EDUCATIONAL - SYSTEM - OF GREAT - BRITAINDocument4 pagesTheme 2 THE EDUCATIONAL - SYSTEM - OF GREAT - BRITAINyulia lishNo ratings yet
- Belarus EducationDocument2 pagesBelarus EducationМария ИсаковаNo ratings yet
- Educational System in Great BritainDocument16 pagesEducational System in Great BritainНаталия ТурченкоNo ratings yet
- Sistemul Educational Din RomaniaDocument17 pagesSistemul Educational Din RomaniaLidia NistorNo ratings yet
- Education System in HungaryDocument2 pagesEducation System in HungaryMulholland Váradi EszterNo ratings yet
- Educational System in SpainDocument27 pagesEducational System in SpainEva Marie RaquelNo ratings yet
- Education in FranceDocument4 pagesEducation in FranceАлександрNo ratings yet
- EducationDocument2 pagesEducationFlora BartalosovaNo ratings yet
- JotkaDocument1 pageJotkatomášNo ratings yet
- Higher Education in The UK and UkraineDocument13 pagesHigher Education in The UK and UkraineЄлизавета ГалімськаNo ratings yet
- Education Czech RepublicDocument3 pagesEducation Czech RepublicMíša PihrtováNo ratings yet
- Education System SwedenDocument21 pagesEducation System SwedenZehan Syahrida hsb100% (1)
- Luxembourg's Education SystemDocument6 pagesLuxembourg's Education SystemaviNo ratings yet
- Europian Model of CurriculumDocument25 pagesEuropian Model of CurriculumFrances Diane Arnaiz SegurolaNo ratings yet
- Education in HungaryDocument2 pagesEducation in HungaryMartin HauserNo ratings yet
- Education in Ukraine IsDocument2 pagesEducation in Ukraine IsAliona PosnaNo ratings yet
- System Edukacji W PolsceDocument11 pagesSystem Edukacji W Polsceapi-305705553No ratings yet
- Education in RussiaDocument1 pageEducation in RussiaAlenaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Curriculum vs. Singaporean CurriculumDocument3 pagesPhilippine Curriculum vs. Singaporean CurriculumGracielle Mae MortejoNo ratings yet
- Education System in Poland 2017 2018 enDocument6 pagesEducation System in Poland 2017 2018 enJuan Pablo OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Type of School Providing This EducationDocument2 pagesType of School Providing This EducationDragana JovovNo ratings yet
- SalazarDocument7 pagesSalazarMaida Salazar - MicosaNo ratings yet
- Education in BritainDocument1 pageEducation in BritainMartin HauserNo ratings yet
- Education in Ukraine, Mulyk L., F-41Document7 pagesEducation in Ukraine, Mulyk L., F-41Леся МуликNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten To High SchoolDocument12 pagesKindergarten To High SchoolAlexander SőreNo ratings yet
- The Secondary Education System in Your CountryDocument1 pageThe Secondary Education System in Your CountryOrsi PagonyiNo ratings yet
- Educational Level of de Jure Population: Literate IlliterateDocument2 pagesEducational Level of de Jure Population: Literate Illiterate555miskoNo ratings yet
- Education DifferencesDocument3 pagesEducation Differencesdaniel delimarschiNo ratings yet
- Global TeachrDocument30 pagesGlobal TeachraldinetteNo ratings yet
- Education System in Europe: Worked By:fiona Mata Class:10-2Document4 pagesEducation System in Europe: Worked By:fiona Mata Class:10-2eem6577No ratings yet
- Education in KazakhstanDocument5 pagesEducation in KazakhstanИндира КойгелдиеваNo ratings yet
- EducationDocument1 pageEducationNoemiNo ratings yet
- Secondary SchoolDocument1 pageSecondary SchoolQuỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Education C1Document8 pagesEducation C1Bernadett TóthNo ratings yet
- Expo Inglés PDFDocument3 pagesExpo Inglés PDFValeria RobainaNo ratings yet
- Education in MoldovaDocument7 pagesEducation in MoldovaDragomir MariusNo ratings yet
- Education in The Philippines: Structure: ST NDDocument7 pagesEducation in The Philippines: Structure: ST NDJorenel FeriaNo ratings yet
- Bayerisches Schulsystem Englisch EnglishDocument2 pagesBayerisches Schulsystem Englisch EnglishMilan AvramovićNo ratings yet
- Difference Between The American and British: System of EducationDocument4 pagesDifference Between The American and British: System of EducationszuhiNo ratings yet
- Education C1Document16 pagesEducation C1Bernadett TóthNo ratings yet
- EducationDocument4 pagesEducationMivhelNo ratings yet
- 16 09c Slovenian Education System 1Document24 pages16 09c Slovenian Education System 1PixyorizaNo ratings yet
- English For Social Entrepreneurship: Presentation Prepared by Students FromDocument16 pagesEnglish For Social Entrepreneurship: Presentation Prepared by Students Fromapi-466148385No ratings yet
- Legal Requirements For A BakeryDocument8 pagesLegal Requirements For A Bakeryapi-466148385No ratings yet
- BrochureDocument26 pagesBrochureapi-466148385No ratings yet
- Social Entrepreneurship Survey Results - TurkeyDocument13 pagesSocial Entrepreneurship Survey Results - Turkeyapi-466148385No ratings yet
- Our Area - PLDocument9 pagesOur Area - PLapi-466148385No ratings yet
- Medical AdmissionsDocument3 pagesMedical AdmissionsPraneeth Reddy NimmaNo ratings yet
- Golden Bull 2001 JohnDocument256 pagesGolden Bull 2001 JohnClaudio PalincasNo ratings yet
- Obstacle Detection Robot Using Arduino Project ReportDocument6 pagesObstacle Detection Robot Using Arduino Project ReportjangiliNo ratings yet
- Civil-Eng-Jan-08-aboutcivil.comDocument56 pagesCivil-Eng-Jan-08-aboutcivil.comAyman MurrarNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument7 pagesDifferentiationapi-299191302No ratings yet
- IMT CDL Brochure PDFDocument40 pagesIMT CDL Brochure PDFSaumya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Flyer SDMDocument2 pagesFlyer SDMAnanda P MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuous Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous Lesson PlanMouradFilaliNo ratings yet
- Lesson mcd2 PDFDocument5 pagesLesson mcd2 PDFkoolNo ratings yet
- MagazineidDocument12 pagesMagazineidapi-338907264No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan - FERNANDEZDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan - FERNANDEZJoy AcodeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document27 pagesLesson 1Farah CarbonelNo ratings yet
- Stages in Micro TeachingDocument1 pageStages in Micro Teachingem_giesweet100% (1)
- Argentine U Libraries 1956Document8 pagesArgentine U Libraries 1956althegelNo ratings yet
- Forensic Accounting Research White PaperDocument34 pagesForensic Accounting Research White PaperIvy Lastimoso Sablon0% (1)
- Pride and Prejudice Unit 339Document30 pagesPride and Prejudice Unit 339api-508901716No ratings yet
- Fwlearningcontract sp17 Kan LiDocument4 pagesFwlearningcontract sp17 Kan Liapi-318952018No ratings yet
- The Contributions of Socrates and PlatoDocument1 pageThe Contributions of Socrates and Platoapi-340391876No ratings yet
- HLTH 5332 Spring 2023 Syllabus Revised 1 1Document14 pagesHLTH 5332 Spring 2023 Syllabus Revised 1 1api-522555065No ratings yet
- AppositiveDocument2 pagesAppositivewaqarali78692No ratings yet
- INED7211 Module ReaderDocument77 pagesINED7211 Module ReadernangamsoNo ratings yet
- Eng Y1 Module Thursday 15 JulyDocument9 pagesEng Y1 Module Thursday 15 JulyPRISCELLA SOFEA ANAK SUDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Note ReadingDocument3 pagesSample Lesson Note ReadingKz Kamal100% (1)
- Honda Job Electrical Aliston OntarioDocument4 pagesHonda Job Electrical Aliston OntariobarnamahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Nature and Characteristics of Language ResearchDocument11 pagesLesson 1 Nature and Characteristics of Language ResearchRoxanne MendezNo ratings yet
- 414947-2020-Syllabus Islamiat PDFDocument15 pages414947-2020-Syllabus Islamiat PDFRoshni HussainNo ratings yet
- Data Storytelling Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesData Storytelling Cheat SheetLisa Oberascher100% (3)