Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 viewsCommon Abbreviation Part 2
Common Abbreviation Part 2
Uploaded by
Stephanie Aira LumberaThis document provides definitions for common medical abbreviations and acronyms used in healthcare documentation. Some abbreviations refer to medical conditions, body parts, diagnostic tests, or medications. For example, FBOA refers to a foreign body obstructed airway, hCG is human chorionic gonadotropin hormone, and IVP stands for intravenous pyelogram imaging test. Other abbreviations are used as shorthand for terms like per hour (hr), family history (FH), or past medical history (PHx). Taking up medical terminology and common abbreviations is important for understanding clinical documentation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
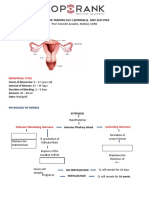
- Massey Ferguson MF 1200 Tractor Service Parts Catalogue ManualDocument14 pagesMassey Ferguson MF 1200 Tractor Service Parts Catalogue Manualqlb898316No ratings yet
- Revised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherDocument15 pagesRevised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- Eclampsia Pre EclampsiaDocument3 pagesEclampsia Pre EclampsiaOona Nicole Diorico100% (2)
- NCM 109 Prelims ReviewerDocument2 pagesNCM 109 Prelims ReviewerReyna Chame GarcinezNo ratings yet
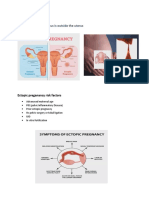
- Ectopic, Preterm, PIHDocument17 pagesEctopic, Preterm, PIHdanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
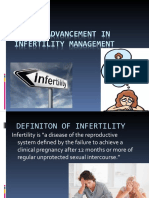
- InfertilityDocument12 pagesInfertilityMuhammad HamadNo ratings yet
- 107 Lec Prelim TopicsDocument22 pages107 Lec Prelim TopicsMary Ann SacramentoNo ratings yet
- Sistem Reproduksi Pria IkrDocument141 pagesSistem Reproduksi Pria IkrNidiyamilhaNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 1 1. Immediate ManagementDocument5 pagesCase Scenario 1 1. Immediate ManagementArtika MalaNo ratings yet
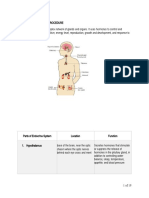
- Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesReproductive SystemEdwin OkonNo ratings yet
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument6 pagesHydatidiform MoleEspiritu, ChriscelNo ratings yet
- LM 3 Physiologic Adaptation of The MotherDocument8 pagesLM 3 Physiologic Adaptation of The MotherKiminatsu SyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes AnatomyDocument18 pagesLecture Notes AnatomyFau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE NURSING-FINAL HDDocument15 pagesENDOCRINE NURSING-FINAL HDJayvee Novenario Casaljay100% (1)
- History & Physical Exam in Ob/Gyn: By: - DR AmanuDocument75 pagesHistory & Physical Exam in Ob/Gyn: By: - DR AmanuKåbåñå TürüñåNo ratings yet
- Week 16 Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 16 Endocrine Systemrichard respetoNo ratings yet
- Task IncomingDocument14 pagesTask Incomingmonica mittiamNo ratings yet
- OB Cases ORV ReviewerDocument8 pagesOB Cases ORV Reviewerashley salangaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Animal ScienceDocument15 pagesEndocrine System Animal ScienceJairus LampanoNo ratings yet
- Medical Case Write UpDocument11 pagesMedical Case Write UpJang Abd MutalibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- CABITAC Histology (Digestive) FinalDocument9 pagesCABITAC Histology (Digestive) FinalZhon CabitacNo ratings yet
- Placenta InsufficiencyDocument39 pagesPlacenta InsufficiencyslyfoxkittyNo ratings yet
- RSVDocument15 pagesRSVbtheresakNo ratings yet
- VIVAO - G هاد الملف مهم اجا لبعض الجروبات من سنوات اورال قديمةDocument41 pagesVIVAO - G هاد الملف مهم اجا لبعض الجروبات من سنوات اورال قديمةbasharswork99No ratings yet
- Female Pelvis & Pregnancy 247Document22 pagesFemale Pelvis & Pregnancy 247INTHRESHH RAMASUBRAMANINo ratings yet
- 123 PDFDocument14 pages123 PDFSachin SinghNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - Anaphy Reproductive System: Maternal Lec QuizzesDocument7 pagesQuiz 1 - Anaphy Reproductive System: Maternal Lec QuizzesJana MendozaNo ratings yet
- OBGyn Endof Rotation OutlineDocument35 pagesOBGyn Endof Rotation OutlinehevinpatelNo ratings yet
- Ncm107 Summarization of MCNDocument40 pagesNcm107 Summarization of MCNArlyn Faith AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 1 4 4 Uterine Atony Group 3 PDFDocument53 pages1 4 4 Uterine Atony Group 3 PDFAlvin CruzNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (POS)Document3 pagesPolycystic Ovarian Syndrome (POS)Pirasan Traditional Medicine CenterNo ratings yet
- PBL Endocrine Week 1 Jason Leonard Wijaya 01071180063Document8 pagesPBL Endocrine Week 1 Jason Leonard Wijaya 01071180063Jason LeonardNo ratings yet
- The Pituitary GlandDocument2 pagesThe Pituitary GlandGerelNo ratings yet
- UMS Short and Long CaseDocument116 pagesUMS Short and Long CaseRosniza RosliNo ratings yet
- Therio NotesDocument7 pagesTherio NotesAsh-Lee HugginsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 SummaryDocument8 pagesChapter 20 SummaryNoreen B. BañagadoNo ratings yet
- GynecologyDocument18 pagesGynecologyLuai Tuma KhouryNo ratings yet
- NCM 107Document83 pagesNCM 107Jan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Feotal Measure: Presented by Sandhya Gupta M.SC - Nursing Previous YearDocument35 pagesFeotal Measure: Presented by Sandhya Gupta M.SC - Nursing Previous Yearsuman guptaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument31 pagesEndocrine SystemPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Recent Advancement in Infertility Management and Adoption ProcessDocument160 pagesRecent Advancement in Infertility Management and Adoption ProcessBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Menstrual History and Determining Ovulation: Prepared By: Danmar C. Yepez, RM, BSM Cp101-InstructorDocument23 pagesMenstrual History and Determining Ovulation: Prepared By: Danmar C. Yepez, RM, BSM Cp101-InstructorlaarnieNo ratings yet
- OB/GYNDocument58 pagesOB/GYNpaulineNo ratings yet
- DONE - NCM 116 RLE Week 9.docx ROXASDocument19 pagesDONE - NCM 116 RLE Week 9.docx ROXASBatiao Camille ClaireNo ratings yet
- InfertilityDocument29 pagesInfertilityCristina StanleeNo ratings yet
- Placenta FunctionsDocument46 pagesPlacenta Functionsvenkata sryanamala50% (2)
- ARTDocument36 pagesARTTtyyfff Fyyu89-No ratings yet
- Fetal Measures PresentationDocument6 pagesFetal Measures Presentationjeelani saima100% (1)
- Pcos NotesDocument24 pagesPcos NotesPreet RayatNo ratings yet
- Case Study Mastectomy RevisedDocument13 pagesCase Study Mastectomy RevisedJessa BorreNo ratings yet
- 2023 Med SurgDocument87 pages2023 Med Surgkhaidkhan0609No ratings yet
- Origin and Development Organ System: MCN ARL: 11619Document5 pagesOrigin and Development Organ System: MCN ARL: 11619JacobNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument34 pagesEndocrineBahareh SanabakhshNo ratings yet
- 2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Document75 pages2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Mary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- Infertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingDocument37 pagesInfertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingvincentsharonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Reproductive Physiology 2021Document10 pagesLecture 1 - Reproductive Physiology 2021Winnie PillyNo ratings yet
- NCP For Intranatal MotherDocument12 pagesNCP For Intranatal Motherpriyanka67% (6)
- Large, Solitary, Luteinized Follicle Cyst of Pregnancy and PuerperiumDocument5 pagesLarge, Solitary, Luteinized Follicle Cyst of Pregnancy and PuerperiumMade RusmanaNo ratings yet
- Leptin: Regulation and Clinical ApplicationsFrom EverandLeptin: Regulation and Clinical ApplicationsSam Dagogo-Jack, MDNo ratings yet
- Effective CommunicationDocument50 pagesEffective CommunicationStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- B1. SFTS 2020 - Chapter 1 - Introduction To SabreDocument15 pagesB1. SFTS 2020 - Chapter 1 - Introduction To SabreStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Purposive CommunicationDocument17 pagesWeek 1 Purposive CommunicationStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - CM17 - March 4, 2021 BSTM201A - 2nd Term AY 20-21Document14 pagesWeek 11 - CM17 - March 4, 2021 BSTM201A - 2nd Term AY 20-21Stephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- Course Material - MathematicsDocument20 pagesCourse Material - MathematicsStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- Course Material - ReasoningDocument16 pagesCourse Material - ReasoningStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of The Affordability of The Foods and Global Strategies at The Jollibee Foods CorporationDocument8 pagesAn Analysis of The Affordability of The Foods and Global Strategies at The Jollibee Foods CorporationStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- Westcott 2013Document13 pagesWestcott 2013Jose ManuelNo ratings yet
- TP. 2 REVISION PTE SIMPLE - Grammar ExcercisesDocument3 pagesTP. 2 REVISION PTE SIMPLE - Grammar ExcercisesgabyNo ratings yet
- LL. B. I Term: Paper - LB - 103 - Law of TortsDocument10 pagesLL. B. I Term: Paper - LB - 103 - Law of TortsFaisal ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Ipsative Personality TestsDocument10 pagesIpsative Personality Testseman_tenan2220No ratings yet
- BilcoDocument16 pagesBilcoruloNo ratings yet
- Vibrant Yet Under-Resourced: The State of Lesbian, Bisexual, and Queer MovementsDocument44 pagesVibrant Yet Under-Resourced: The State of Lesbian, Bisexual, and Queer MovementsSeres KozmicNo ratings yet
- Nurse's Assistant NotesDocument3 pagesNurse's Assistant NotesLonefallen DarkNo ratings yet
- Appendix 66 Rpci Updated Ues JehanDocument58 pagesAppendix 66 Rpci Updated Ues JehanOmar Gulam JrNo ratings yet
- Focus Level 3 Table of Contents PDFDocument2 pagesFocus Level 3 Table of Contents PDFDaria KudosLamNo ratings yet
- Application FormDocument8 pagesApplication FormCrystal KleistNo ratings yet
- The Employees' Compensation Act, 1923Document23 pagesThe Employees' Compensation Act, 1923Charan Kamal SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 21 Animals That Live On LandDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 21 Animals That Live On LandRoxan S. Pumphrey0% (1)
- Liabilities and EquityDocument23 pagesLiabilities and Equityadmiral spongebobNo ratings yet
- 2022 Tucson Plug in Hybrid Emergency Response Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pages2022 Tucson Plug in Hybrid Emergency Response Quick Reference GuideForum PompieriiNo ratings yet
- Gen 017 - Sas Lesson #4Document5 pagesGen 017 - Sas Lesson #4ABM - Villanueva, Jaimee Lyn C.No ratings yet
- 2 2 Bioaivers ExperienceDocument80 pages2 2 Bioaivers Experienceblashyrkh_79No ratings yet
- Billie Joe Armstrong: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesBillie Joe Armstrong: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJovz BumohyaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Dyes and PigmentsDocument5 pagesDifference Between Dyes and PigmentsHameedullah Ansari100% (1)
- NitrocelluloseDocument17 pagesNitrocelluloseAtif MehfoozNo ratings yet
- 2-BP-3.5K-5K 220v ManualDocument42 pages2-BP-3.5K-5K 220v ManualEcosenseTechnologies GreenenergyNo ratings yet
- ASIYADocument3 pagesASIYASOFIKUL HUUSAINNo ratings yet
- 2-Subject Verb Agreement CWDocument2 pages2-Subject Verb Agreement CWAmir NagyNo ratings yet
- Olea Europaea A Phyto-Pharmacological ReviewDocument5 pagesOlea Europaea A Phyto-Pharmacological ReviewyigalbyNo ratings yet
- TEST(s) Normal UNIT(s)Document1 pageTEST(s) Normal UNIT(s)HarisNo ratings yet
- The Science Behind AspirinDocument14 pagesThe Science Behind AspirindipetNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ibdp Exam Syle QuestionsDocument37 pagesChemistry Ibdp Exam Syle QuestionsGEORGE MATTHEWNo ratings yet
- Thermostats,: Type KPDocument12 pagesThermostats,: Type KPEvandro Jva compressoresNo ratings yet
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document13 pagesInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768maquinariakypcon100% (2)
- G6RNDocument3 pagesG6RNValeri Luht Eurocargo FinlandNo ratings yet
Common Abbreviation Part 2
Common Abbreviation Part 2
Uploaded by
Stephanie Aira Lumbera0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views4 pagesThis document provides definitions for common medical abbreviations and acronyms used in healthcare documentation. Some abbreviations refer to medical conditions, body parts, diagnostic tests, or medications. For example, FBOA refers to a foreign body obstructed airway, hCG is human chorionic gonadotropin hormone, and IVP stands for intravenous pyelogram imaging test. Other abbreviations are used as shorthand for terms like per hour (hr), family history (FH), or past medical history (PHx). Taking up medical terminology and common abbreviations is important for understanding clinical documentation.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides definitions for common medical abbreviations and acronyms used in healthcare documentation. Some abbreviations refer to medical conditions, body parts, diagnostic tests, or medications. For example, FBOA refers to a foreign body obstructed airway, hCG is human chorionic gonadotropin hormone, and IVP stands for intravenous pyelogram imaging test. Other abbreviations are used as shorthand for terms like per hour (hr), family history (FH), or past medical history (PHx). Taking up medical terminology and common abbreviations is important for understanding clinical documentation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views4 pagesCommon Abbreviation Part 2
Common Abbreviation Part 2
Uploaded by
Stephanie Aira LumberaThis document provides definitions for common medical abbreviations and acronyms used in healthcare documentation. Some abbreviations refer to medical conditions, body parts, diagnostic tests, or medications. For example, FBOA refers to a foreign body obstructed airway, hCG is human chorionic gonadotropin hormone, and IVP stands for intravenous pyelogram imaging test. Other abbreviations are used as shorthand for terms like per hour (hr), family history (FH), or past medical history (PHx). Taking up medical terminology and common abbreviations is important for understanding clinical documentation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
FBOA—foreign body obstructed airway stimulates the corpus luteum to produce
-a partial or complete blockage of the progesterone to maintain the pregnancy.
breathing tubes to the lungs due to a foreign Smaller amounts of hCG are also
body (for example, food, a bead, toy, etc.). The onset produced in the pituitary gland, the liver,
of respiratory distress may be sudden with cough. and the colon
FBS—fasting blood sugar hct—hematocrit
FBW—fasting blood work HDL—high-density lipoprotein
FF (F. Fl)—force fluids hgb—hemoglobin
FH—family history HOB—head of bed
FHS—fetal heart sounds hr (h)—hour
FHT—fetal heart tone HIV—human immunodeficiency virus
FIFO—first in, first out H&P—history and physical
FSH—follicle-stimulating hormone HR—heart rate
- one of the hormones essential to pubertal hs—hour of sleep, bedtime
development and the function of ht—height
women's ovaries and men's testes. In Hx—history
women, this hormone stimulates the hypo—hypodermic injection
growth of ovarian follicles in the ovary hyst—hysterectomy
before the release of an egg from
one follicle at ovulation. It also increases IBS—irritable bowel syndrome
oestradiol production. - common disorder that affects the large
ft—foot intestine. Signs and symptoms include
FUO—fever of undetermined origin cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, gas,
Fx—fracture and diarrhea or constipation, or
both. IBS is a chronic condition that you'll
GB—gallbladder need to manage long term.
GI—gastrointestinal I & D—incision and drainage
GU—genitourinary I & O—intake and output
GTT—glucose tolerance test (pancreas test) ICP—intracranial pressure
- One common protocol is the 2- ICU—intensive care unit
hour glucose tolerance test (GTT). For IM—intramuscular
this test, you may have a fasting glucose ing—inguinal
test done, then you drink a 75- inj—injection
gram glucose drink (or 1.75 grams per IPPB—intermittent positive pressure breathing
kilogram of body weight if you are a - a technique used to provide short term
child). Another blood sample is drawn 2 or intermittent mechanical ventilation via
hours after you begin to drink mouthpiece or mask for the purpose of
the glucose drink. augmenting lung expansion and delivering
gtt(s)—drop(s) aerosol medication.
gyn—gynecology irrig—irrigation
- medical practice dealing with the health IS—intercostal space
of the female reproductive system. isol—isolation
IT—inhalation therapy
H & H—hemoglobin and hematocrit IUD—intrauterine device
HCG—human chorionic gonadotrophin - small plastic T-shaped device used for
- Human chorionic gonadotropin is a birth control. It is inserted into the uterus
hormone produced primarily by where it stays to prevent pregnancy
syncytiotrophoblastic cells of the placenta IV—intravenous
during pregnancy. The hormone IVF—in vitro fertilization
- method of assisted reproduction in which MAST—medical antishock trousers
a man's sperm and a woman's eggs are - have been used to increase venous return
combined outside of the body in a to the heart until definitive care could be
laboratory dish. One or given. This, combined with compression
more fertilized eggs (embryos) may be of blood vessels, is believed to cause the
transferred to the woman's uterus, where movement of blood from the lower body
they may implant in the uterine lining and to the brain, heart and lungs.
develop. MCI—mass casualty incident
IVP—intravenous pyelogram meds—medications
- an x-ray exam that uses an injection of MI—myocardial infarction
contrast material to evaluate your MICU—mobile intensive care unit
kidneys, ureters and bladder and help min—minute
diagnose blood in the urine or pain in MN—midnight
your side or lower back. An IVP may MOM—milk of magnesia
provide enough information to allow your - indicated as an antacid for the
doctor to treat you with medication and symptomatic relief of stomach
avoid surgery. discomfort, indigestion, hyperacidity,
heartburn and flatulence; and as a
K+—potassium laxative for constipation. Use a 5 ml spoon
KCl—potassuim chloride or the dosing cup provided. Doses may be
KUB—kidney, ureter, bladder taken with milk or water if desired.
- X-ray may be performed to assess the MRI—magnetic resonance imagery
abdominal area for causes of abdominal MS—morphine sulfate, multiple sclerosis
pain, or to assess the organs and - Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a potentially
structures of the urinary and/or disabling disease of the brain and spinal cord (central
gastrointestinal (GI) system. A KUB X-ray nervous system). In MS , the immune system attacks
may be the first diagnostic procedure the protective sheath (myelin) that covers nerve fibers
used to assess the urinary system. and causes communication problems between your
brain and the rest of your body.
L—lumbar MVA—motor vehicle accident
L & D—labor and delivery
lac—laceration NVD—nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
lab—laboratory Na+—sodium
lap—laparotomy NaCl—sodium chloride
lat—lateral N/C—nasal cannula
LD—lethal dose no—complaints
LDH—lactic dehydrogenase neg—negative
- enzyme required during the process of neuro—neurology
turning sugar into energy for your cells. NG—nasogastric
LDL—low-density lipoprotein NGT—nasogastric tube
liq—liquid nitro—nitroglycerine
LLQ, LLL—left lower quadrant (abdomen), lobe (lung) - is a vasodilator, a medicine that opens
LMP—last menstrual period blood vessels to improve blood flow. It is
LOC—level of consciousness used to treat angina symptoms, such as
LP—lumbar puncture chest pain or pressure, that happens
lt—left when there is not enough blood flowing
LUQ, LUL—left upper quadrant (abdomen), lobe (lung) to the heart.
NKA—no known allergies
MA—mental age noc (t)—night
NPO—nothing by mouth States. Although not exactly
NS—normal saline recommended fare for bedtime reading,
nsg—nursing the PDR is the most
NSR—normal sinus rhythm commonly used drug reference.
NVS—neurological vital sign PE—physical exam, pulmonary embolism
PEDS—pediatrics
O—oxygen per—by or through
OB—obstetrics PERL(A)—pupils equal and reactive to light (and
OD—right eye, overdose accommodation)
oint—ointment PET—positron emission tomography
OOB—out of bed PH—past history
OPD—outpatient department pH—hydrogen ion concentration
OR—operating room PID—pelvic inflammatory disease
ord—orderly PKU—phenylketonuria
ORTH—orthopedics - is an inborn error of metabolism that
ortho—correct, right (bones) results in decreased metabolism of the
os—mouth amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated, PKU
OS—left eye can lead to intellectual disability, seizures,
OT—occupational therapy behavioral problems, and mental
OU—both eyes disorders. It may also result in a musty
oz—ounce smell and lighter skin.
pm—between noon and midnight
p—after PNS—peripheral nervous system
P—pulse po—by mouth
P & A—percussion and auscultation post (pos)—posterior postop,
PAC—premature atrial contraction PostOp—–postoperative
palp—palpation pp (p.p.)—postprandial (after eating)
PAR—post-anesthesia room pO2—partial pressure of oxygen
PAT—paroxysmal atrial tachycardia PPD—purified protein derivative (TB test) preop,
- is a type of arrhythmia, or irregular PreOp—before surgery
heartbeat. Paroxysmal means that the prn—as needed, whenever necessary
episode of arrhythmia begins and ends pro time—prothrombin time
abruptly. Atrial means that arrhythmia pt—patient, pint
starts in the upper chambers of the heart PT—physical therapy
(atria). Tachycardia means that the heart PTT—partial prothrombaplastin time
is beating abnormally fast. PVC—premature ventricular contraction
pc—after meals Px—physical exam, prognosis
pCO2—partial pressure of carbon dioxide
- The partial pressure of carbon dioxide q—every
(PCO2) is the measure of carbon dioxide qd—every day
within arterial or venous blood. It often qh—every hour
serves as a marker of sufficient alveolar q2h, q3h, ...—every two hours, every three hours, ...
ventilation within the lungs. Generally, qhs—every night at bedtime
under normal physiologic conditions, the qid—four times a day
value of PCO2 ranges between 35 to qns—quantity not sufficient
45 mmHg qod—every other day
PDR—physician’s desk reference qs—quantity sufficient
- A thick volume that provides a guide to
prescription drugs available in the United r (R)—rectal
R (resp)—respirations, rectal tachy—–tachycardic
RAIU—radioactive iodine uptake study TAH—total abdominal hysterectomy
RBC—red blood cell/count TB—tuberculosis
reg—regular TCDB—turn, cough, deep breath
Rh—rhesus temp (T)—temperature
RK—radial keratomy TH—thyroid hormone
RL—ringer’s lactate TIA—transient ischemic attack
RLQ, RLL—right lower quadrant (abdomen), lobe tid—three times a day
(lung) RML—right middle lobe (lung) TMJ—temporomandibular joint
RO—reality orientation tol—tolerated
R/O—rule out TPN—total parenteral nutrition
ROM—range of motion TPR—temperature, pulse, respirations
R.R.—recovery room tr—tincture
RUQ, RLL—right upper quadrant, lobe trach—tracheotomy, tracheostomy
rt—right TSH—thyroid-stimulating hormone
RV—residual volume TT—tetanus toxiod
Rx—take (prescription) TUR—transurethral resection
TV—tidal volume
s—without TVH—total vaginal hysterectomy
S & S—signs and symptoms TX—traction
ss—1/2
Sats—oxygen/blood saturation level UA—urinalysis
SA—sinoatrial umb—umbilicus
SB—small bowel unc.—unconscious
sc—subcutaneous ung—ointment
SGOT—serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase unk—unknown
- An enzyme that is normally present in liver ur—urine
and heart cells. SGOT is released into blood URC—usual, reasonable, customary
when the liver or heart is damaged. URI—upper respiratory infection
SGPT—serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase US—ultrasonic
SIDS—sudden infant death syndrome UTI—urinary tract infection
Sig:—label/write
SL—sublingual V fib—ventricular fibrillation
SMAC—sequential multiple analysis computer V tach—ventricular tachycardia
SOB—shortness of breath vag—vaginal
spec—specimen VC—vital capacity
sp. gr.—specific gravity VD—venereal disease
SQ, sub q—subcutaneous vit—vitamin
SSE—soap suds enema vo—verbal order
stat—immediately vol—volume
STD—sexually transmitted disease V/S—vital signs
STH—somatotropic hormone
SVD—spontaneous vaginal delivery WA—while awake
SVN—small volume nebulizer WBC—white blood cell/count
SVT—supraventricular tachycardia w/c—wheelchair
Sx—symptoms WNL—within normal limits
wt—weight
T—temperature, thoracic
T & A—tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy y/o—year(s) ol
tab—tablet
You might also like
- Massey Ferguson MF 1200 Tractor Service Parts Catalogue ManualDocument14 pagesMassey Ferguson MF 1200 Tractor Service Parts Catalogue Manualqlb898316No ratings yet
- Revised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherDocument15 pagesRevised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- Eclampsia Pre EclampsiaDocument3 pagesEclampsia Pre EclampsiaOona Nicole Diorico100% (2)
- NCM 109 Prelims ReviewerDocument2 pagesNCM 109 Prelims ReviewerReyna Chame GarcinezNo ratings yet
- Ectopic, Preterm, PIHDocument17 pagesEctopic, Preterm, PIHdanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- InfertilityDocument12 pagesInfertilityMuhammad HamadNo ratings yet
- 107 Lec Prelim TopicsDocument22 pages107 Lec Prelim TopicsMary Ann SacramentoNo ratings yet
- Sistem Reproduksi Pria IkrDocument141 pagesSistem Reproduksi Pria IkrNidiyamilhaNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 1 1. Immediate ManagementDocument5 pagesCase Scenario 1 1. Immediate ManagementArtika MalaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesReproductive SystemEdwin OkonNo ratings yet
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument6 pagesHydatidiform MoleEspiritu, ChriscelNo ratings yet
- LM 3 Physiologic Adaptation of The MotherDocument8 pagesLM 3 Physiologic Adaptation of The MotherKiminatsu SyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes AnatomyDocument18 pagesLecture Notes AnatomyFau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE NURSING-FINAL HDDocument15 pagesENDOCRINE NURSING-FINAL HDJayvee Novenario Casaljay100% (1)
- History & Physical Exam in Ob/Gyn: By: - DR AmanuDocument75 pagesHistory & Physical Exam in Ob/Gyn: By: - DR AmanuKåbåñå TürüñåNo ratings yet
- Week 16 Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 16 Endocrine Systemrichard respetoNo ratings yet
- Task IncomingDocument14 pagesTask Incomingmonica mittiamNo ratings yet
- OB Cases ORV ReviewerDocument8 pagesOB Cases ORV Reviewerashley salangaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Animal ScienceDocument15 pagesEndocrine System Animal ScienceJairus LampanoNo ratings yet
- Medical Case Write UpDocument11 pagesMedical Case Write UpJang Abd MutalibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- CABITAC Histology (Digestive) FinalDocument9 pagesCABITAC Histology (Digestive) FinalZhon CabitacNo ratings yet
- Placenta InsufficiencyDocument39 pagesPlacenta InsufficiencyslyfoxkittyNo ratings yet
- RSVDocument15 pagesRSVbtheresakNo ratings yet
- VIVAO - G هاد الملف مهم اجا لبعض الجروبات من سنوات اورال قديمةDocument41 pagesVIVAO - G هاد الملف مهم اجا لبعض الجروبات من سنوات اورال قديمةbasharswork99No ratings yet
- Female Pelvis & Pregnancy 247Document22 pagesFemale Pelvis & Pregnancy 247INTHRESHH RAMASUBRAMANINo ratings yet
- 123 PDFDocument14 pages123 PDFSachin SinghNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - Anaphy Reproductive System: Maternal Lec QuizzesDocument7 pagesQuiz 1 - Anaphy Reproductive System: Maternal Lec QuizzesJana MendozaNo ratings yet
- OBGyn Endof Rotation OutlineDocument35 pagesOBGyn Endof Rotation OutlinehevinpatelNo ratings yet
- Ncm107 Summarization of MCNDocument40 pagesNcm107 Summarization of MCNArlyn Faith AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 1 4 4 Uterine Atony Group 3 PDFDocument53 pages1 4 4 Uterine Atony Group 3 PDFAlvin CruzNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (POS)Document3 pagesPolycystic Ovarian Syndrome (POS)Pirasan Traditional Medicine CenterNo ratings yet
- PBL Endocrine Week 1 Jason Leonard Wijaya 01071180063Document8 pagesPBL Endocrine Week 1 Jason Leonard Wijaya 01071180063Jason LeonardNo ratings yet
- The Pituitary GlandDocument2 pagesThe Pituitary GlandGerelNo ratings yet
- UMS Short and Long CaseDocument116 pagesUMS Short and Long CaseRosniza RosliNo ratings yet
- Therio NotesDocument7 pagesTherio NotesAsh-Lee HugginsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 SummaryDocument8 pagesChapter 20 SummaryNoreen B. BañagadoNo ratings yet
- GynecologyDocument18 pagesGynecologyLuai Tuma KhouryNo ratings yet
- NCM 107Document83 pagesNCM 107Jan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Feotal Measure: Presented by Sandhya Gupta M.SC - Nursing Previous YearDocument35 pagesFeotal Measure: Presented by Sandhya Gupta M.SC - Nursing Previous Yearsuman guptaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument31 pagesEndocrine SystemPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Recent Advancement in Infertility Management and Adoption ProcessDocument160 pagesRecent Advancement in Infertility Management and Adoption ProcessBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Menstrual History and Determining Ovulation: Prepared By: Danmar C. Yepez, RM, BSM Cp101-InstructorDocument23 pagesMenstrual History and Determining Ovulation: Prepared By: Danmar C. Yepez, RM, BSM Cp101-InstructorlaarnieNo ratings yet
- OB/GYNDocument58 pagesOB/GYNpaulineNo ratings yet
- DONE - NCM 116 RLE Week 9.docx ROXASDocument19 pagesDONE - NCM 116 RLE Week 9.docx ROXASBatiao Camille ClaireNo ratings yet
- InfertilityDocument29 pagesInfertilityCristina StanleeNo ratings yet
- Placenta FunctionsDocument46 pagesPlacenta Functionsvenkata sryanamala50% (2)
- ARTDocument36 pagesARTTtyyfff Fyyu89-No ratings yet
- Fetal Measures PresentationDocument6 pagesFetal Measures Presentationjeelani saima100% (1)
- Pcos NotesDocument24 pagesPcos NotesPreet RayatNo ratings yet
- Case Study Mastectomy RevisedDocument13 pagesCase Study Mastectomy RevisedJessa BorreNo ratings yet
- 2023 Med SurgDocument87 pages2023 Med Surgkhaidkhan0609No ratings yet
- Origin and Development Organ System: MCN ARL: 11619Document5 pagesOrigin and Development Organ System: MCN ARL: 11619JacobNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument34 pagesEndocrineBahareh SanabakhshNo ratings yet
- 2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Document75 pages2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Mary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- Infertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingDocument37 pagesInfertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingvincentsharonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Reproductive Physiology 2021Document10 pagesLecture 1 - Reproductive Physiology 2021Winnie PillyNo ratings yet
- NCP For Intranatal MotherDocument12 pagesNCP For Intranatal Motherpriyanka67% (6)
- Large, Solitary, Luteinized Follicle Cyst of Pregnancy and PuerperiumDocument5 pagesLarge, Solitary, Luteinized Follicle Cyst of Pregnancy and PuerperiumMade RusmanaNo ratings yet
- Leptin: Regulation and Clinical ApplicationsFrom EverandLeptin: Regulation and Clinical ApplicationsSam Dagogo-Jack, MDNo ratings yet
- Effective CommunicationDocument50 pagesEffective CommunicationStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- B1. SFTS 2020 - Chapter 1 - Introduction To SabreDocument15 pagesB1. SFTS 2020 - Chapter 1 - Introduction To SabreStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Purposive CommunicationDocument17 pagesWeek 1 Purposive CommunicationStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - CM17 - March 4, 2021 BSTM201A - 2nd Term AY 20-21Document14 pagesWeek 11 - CM17 - March 4, 2021 BSTM201A - 2nd Term AY 20-21Stephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- Course Material - MathematicsDocument20 pagesCourse Material - MathematicsStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- Course Material - ReasoningDocument16 pagesCourse Material - ReasoningStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of The Affordability of The Foods and Global Strategies at The Jollibee Foods CorporationDocument8 pagesAn Analysis of The Affordability of The Foods and Global Strategies at The Jollibee Foods CorporationStephanie Aira LumberaNo ratings yet
- Westcott 2013Document13 pagesWestcott 2013Jose ManuelNo ratings yet
- TP. 2 REVISION PTE SIMPLE - Grammar ExcercisesDocument3 pagesTP. 2 REVISION PTE SIMPLE - Grammar ExcercisesgabyNo ratings yet
- LL. B. I Term: Paper - LB - 103 - Law of TortsDocument10 pagesLL. B. I Term: Paper - LB - 103 - Law of TortsFaisal ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Ipsative Personality TestsDocument10 pagesIpsative Personality Testseman_tenan2220No ratings yet
- BilcoDocument16 pagesBilcoruloNo ratings yet
- Vibrant Yet Under-Resourced: The State of Lesbian, Bisexual, and Queer MovementsDocument44 pagesVibrant Yet Under-Resourced: The State of Lesbian, Bisexual, and Queer MovementsSeres KozmicNo ratings yet
- Nurse's Assistant NotesDocument3 pagesNurse's Assistant NotesLonefallen DarkNo ratings yet
- Appendix 66 Rpci Updated Ues JehanDocument58 pagesAppendix 66 Rpci Updated Ues JehanOmar Gulam JrNo ratings yet
- Focus Level 3 Table of Contents PDFDocument2 pagesFocus Level 3 Table of Contents PDFDaria KudosLamNo ratings yet
- Application FormDocument8 pagesApplication FormCrystal KleistNo ratings yet
- The Employees' Compensation Act, 1923Document23 pagesThe Employees' Compensation Act, 1923Charan Kamal SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 21 Animals That Live On LandDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 21 Animals That Live On LandRoxan S. Pumphrey0% (1)
- Liabilities and EquityDocument23 pagesLiabilities and Equityadmiral spongebobNo ratings yet
- 2022 Tucson Plug in Hybrid Emergency Response Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pages2022 Tucson Plug in Hybrid Emergency Response Quick Reference GuideForum PompieriiNo ratings yet
- Gen 017 - Sas Lesson #4Document5 pagesGen 017 - Sas Lesson #4ABM - Villanueva, Jaimee Lyn C.No ratings yet
- 2 2 Bioaivers ExperienceDocument80 pages2 2 Bioaivers Experienceblashyrkh_79No ratings yet
- Billie Joe Armstrong: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesBillie Joe Armstrong: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJovz BumohyaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Dyes and PigmentsDocument5 pagesDifference Between Dyes and PigmentsHameedullah Ansari100% (1)
- NitrocelluloseDocument17 pagesNitrocelluloseAtif MehfoozNo ratings yet
- 2-BP-3.5K-5K 220v ManualDocument42 pages2-BP-3.5K-5K 220v ManualEcosenseTechnologies GreenenergyNo ratings yet
- ASIYADocument3 pagesASIYASOFIKUL HUUSAINNo ratings yet
- 2-Subject Verb Agreement CWDocument2 pages2-Subject Verb Agreement CWAmir NagyNo ratings yet
- Olea Europaea A Phyto-Pharmacological ReviewDocument5 pagesOlea Europaea A Phyto-Pharmacological ReviewyigalbyNo ratings yet
- TEST(s) Normal UNIT(s)Document1 pageTEST(s) Normal UNIT(s)HarisNo ratings yet
- The Science Behind AspirinDocument14 pagesThe Science Behind AspirindipetNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ibdp Exam Syle QuestionsDocument37 pagesChemistry Ibdp Exam Syle QuestionsGEORGE MATTHEWNo ratings yet
- Thermostats,: Type KPDocument12 pagesThermostats,: Type KPEvandro Jva compressoresNo ratings yet
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document13 pagesInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768maquinariakypcon100% (2)
- G6RNDocument3 pagesG6RNValeri Luht Eurocargo FinlandNo ratings yet