Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculating Gravitational Force Formula
Calculating Gravitational Force Formula
Uploaded by
Jhie BautistaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculating Gravitational Force Formula
Calculating Gravitational Force Formula
Uploaded by
Jhie BautistaCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculating Gravitational Force Formula
What holds us to the ground? Why we don't float around in the air? The answer lies in one word: gravitational force. Newton's law on universal
gravitation explains this force. When the apple fell to the ground from the tree, Newton analyzed that the force that had caused apple's fall had
to be dependent on the mass of the apple. And he further deduced that the force which had caused the apple to fall was also dependent on
mass of the earth. So as per Newton, the force of gravity acting between the earth and the apple was directly proportional to the mass of both
the entities and inversely proportional to the square of distance between the centers of the entities. So gravitational force formula can be
represented as:
Fgav ~ (product of masses of the objects) / (square of the distance between the center of the objects)
Formulating the above equation, we obtain with the magnitude of gravitational force:
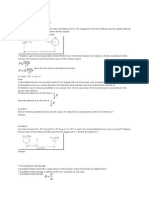
Fgav = G x (m1x m2)/d2
where
G: Gravitational constant
m1: Mass of object 1
m2: Mass of object 2
d: Distance between centers of the masses of objects
(G here is the constant of proportionality and has been calculated to be about 6.673 x 10-11 Newton meter2/Kg2. It is often known as the
universal gravitation constant.)
Let's understand this formula better with an example:
Sample Problem:
A 70 Kg student is traveling in a plane which is flying about 40000 feet above earth's surface. Earth's mass is about 5.98 x 10 24 Kg. So what
would be the gravitational force of attraction?
Solution:
40000 feet ~ 6.39 x 106 meters.
G = 6.673 x 10-11 Newton meter2/Kg2
So Fgav = G x (m1x m2)/d2
= 6.673 x 10-11 x (5.98 x 1024 x 70) / (6.39 x 106)2
= 684 N
So the amount of gravitational force between the earth and the passenger is 684 Newtons (N). (Force is always measured in Newtons).
The other fundamental forces of nature apart from the force of gravitation are electromagnetic force (force that causes repulsion between like
electric charges), weak forces (the forces responsible for radioactive decay) and strong forces (which are the forces that hold the nuclei of
atoms together).
Calculating Centripetal Force Formula
Have you ever sat on rides that contain swings? I bet, you must have enjoyed them in fairs. But have you ever wondered the feeling you
experience in those rides is caused by what? You feel the spinning in your head, right? Well the answer lies in the term: centripetal force. So
what is centripetal force? This is an unbalanced form of force that allows the object to move in a circular path towards the instantaneous center
of curvature of the path traveled. The word "centripetal" itself originates from the Latin word - centrum (center) and petere (towards). So how
to calculate the formula for force (centripetal force)?
Fcentripetal = (m x v2) / r
where
m: mass of the object
v: velocity with which the object is moving
r: radius of the path of curvature
You might also like
- Q1 Week 2 - Module 3 Uniform Circular MotionDocument21 pagesQ1 Week 2 - Module 3 Uniform Circular MotionLullaby GomaNo ratings yet
- POGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSDocument3 pagesPOGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSSharmet SolarzNo ratings yet
- Cheman AzizDocument7 pagesCheman AzizAmeen KamaranNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 - Gravitation and GPEDocument57 pagesTOPIC 2 - Gravitation and GPELuke kenneth MacalawaNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document49 pagesCH 10al hNo ratings yet
- Universal Law of Gravitation Preparation Grade 11Document9 pagesUniversal Law of Gravitation Preparation Grade 11Reitumetse MolefeNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week 2 LAS No.1 Newtons Law of Universal GravitationDocument5 pagesQ2 Week 2 LAS No.1 Newtons Law of Universal GravitationKrisha Mae Arbo EspinasNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Gravitational: Background Information For The Learners (BIL)Document32 pagesNewton's Law of Gravitational: Background Information For The Learners (BIL)Charlie CezarNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 GravityDocument16 pagesGrade 12 GravityRe Zi LeNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Quarter 2: Module 2Document9 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Quarter 2: Module 2Maria Kriselle ApuhinNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Basic Principles of PhysicsDocument18 pagesChapter One: Basic Principles of Physicsm46960580No ratings yet
- A2 Gravitational FieldDocument57 pagesA2 Gravitational Fieldincorrect37No ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Universal GravitationDocument4 pagesNewton's Law of Universal GravitationLeon MathaiosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GravitationDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Gravitationzair aliNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - Science - Ch10 - Gravitation: What Is Centripetal ForceDocument7 pagesClass 9 - Science - Ch10 - Gravitation: What Is Centripetal ForceLulun NeithamNo ratings yet
- Gravitational ForceDocument40 pagesGravitational Forcethunder32xNo ratings yet
- There Are Four Known Fundamental Forces in Nature.: Gravity Weak Nuclear Electromagnetic Strong NuclearDocument54 pagesThere Are Four Known Fundamental Forces in Nature.: Gravity Weak Nuclear Electromagnetic Strong Nuclearapi-19790880No ratings yet
- Gravity Notes PhysicsDocument44 pagesGravity Notes PhysicsCash Cash CashNo ratings yet
- Class 11 CH 8Document21 pagesClass 11 CH 8Freddy Joe VargheseNo ratings yet
- Force (Full)Document41 pagesForce (Full)Sumit ShahNo ratings yet
- Gravity Teacher Guide PDFDocument56 pagesGravity Teacher Guide PDFThuran Nathan100% (1)
- Gravitational FieldDocument30 pagesGravitational FieldAng Yu LongNo ratings yet
- A2 42 GravitationDocument45 pagesA2 42 GravitationJeffreyNo ratings yet
- Me 20111108 On SiteDocument54 pagesMe 20111108 On SiteyashuNo ratings yet
- Physics CHP 3 (E)Document10 pagesPhysics CHP 3 (E)Omkar PawarNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 2Document5 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 2Normal Fan100% (1)
- Work, Energy, & Power: Chapter 6 (C&J) Chapter 10 (Glencoe)Document29 pagesWork, Energy, & Power: Chapter 6 (C&J) Chapter 10 (Glencoe)Emieleah Lorenzo PauigNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion 3EDocument13 pagesLaws of Motion 3EAditya VijayNo ratings yet
- 9th Gravitation 2014 45 Solved QuestionsDocument9 pages9th Gravitation 2014 45 Solved Questionsapi-242227794No ratings yet
- Universal Law of GravitationDocument17 pagesUniversal Law of GravitationScionNo ratings yet
- 7750 - Gravitational Field Wk6Document7 pages7750 - Gravitational Field Wk6leonnelpremiereNo ratings yet
- Calculate Gravity ForceDocument2 pagesCalculate Gravity ForceJohn MalonesNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument10 pagesForceengmun80No ratings yet
- Circular Motion (Chap.7) :: Physics (A-Level)Document18 pagesCircular Motion (Chap.7) :: Physics (A-Level)Major warriorNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Gravitation v1Document15 pagesWeek 9 Gravitation v1KarQunNo ratings yet
- 3786 FdocDocument3 pages3786 FdocThandanani MdakaneNo ratings yet
- Universal Law of MotionDocument6 pagesUniversal Law of Motionooglaboogla81No ratings yet
- 1 Force Stress IDocument13 pages1 Force Stress Iaravind grandhiNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law of Universal GravitationDocument25 pagesNewtons Law of Universal Gravitationaurhonjuliocelso0707No ratings yet
- ForceDocument19 pagesForcePrashant sapkotaNo ratings yet
- CH 9 GravitationDocument5 pagesCH 9 GravitationBhovwtik ShahNo ratings yet
- HSC Physics in MonthDocument162 pagesHSC Physics in MonthZarina100% (2)
- Lecture-1 Scalars and Vectors: 1 Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)Document4 pagesLecture-1 Scalars and Vectors: 1 Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)Raef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 GravitationDocument71 pagesChapter 7 GravitationWendy TangNo ratings yet
- q2wk2 gp1 Module2Document3 pagesq2wk2 gp1 Module2STEM A - CalusinNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: PreviewDocument23 pagesForces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: PreviewAnonymous m8oCtJBNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3E-GravitationDocument7 pagesChapter 3E-Gravitationben martinNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument24 pagesPhysicsMayra FlorNo ratings yet
- Repaso MecanicaDocument58 pagesRepaso MecanicaHeimer Dario Lopez MinaNo ratings yet
- EN3: Introduction To Engineering and Statics: 2. ForcesDocument24 pagesEN3: Introduction To Engineering and Statics: 2. ForceskarthikaNo ratings yet
- GRAVITATIONDocument30 pagesGRAVITATIONRajendra RathNo ratings yet
- Work Done by A Frictional Force: Name(s)Document7 pagesWork Done by A Frictional Force: Name(s)Estefania Delgado ArdilaNo ratings yet
- SSPHY1.PPT - Law of Universal Gravitation - Sy1920Document28 pagesSSPHY1.PPT - Law of Universal Gravitation - Sy1920Analyn Ensano0% (1)
- Newton and GravityDocument40 pagesNewton and GravityRica ChavezNo ratings yet
- IS - Reviewer 3 - Netwon's Law of Universal GravitationDocument3 pagesIS - Reviewer 3 - Netwon's Law of Universal Gravitationajuj jerNo ratings yet
- SS3 Physics GRAVITATIONAL FIELD AND LAW - PassnownowDocument9 pagesSS3 Physics GRAVITATIONAL FIELD AND LAW - Passnownowsunlias0% (1)
- Chapter 3 Newton's Law of Motion: 3.1 The Important StuffDocument19 pagesChapter 3 Newton's Law of Motion: 3.1 The Important StuffNoppadol EGATNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: PreviewDocument24 pagesForces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: Previewnanio_7No ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Newtons Laws PDFDocument5 pagesChapter-3 Newtons Laws PDFMohammad Fuad HasanNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Lo.1Document40 pagesPhysics 2 Lo.1Mohamed KilanyNo ratings yet
- Free Download Physics I 501 Practice Problems For Dummies The Experts at Dummies Full Chapter PDFDocument51 pagesFree Download Physics I 501 Practice Problems For Dummies The Experts at Dummies Full Chapter PDFroger.leavell785100% (22)
- 2.2 Newton'S Laws of Motion: Bridge Course - Phy - I PUC - 40Document7 pages2.2 Newton'S Laws of Motion: Bridge Course - Phy - I PUC - 40Jit AggNo ratings yet
- Whirlz of MotionDocument18 pagesWhirlz of MotionLanah Krizten AsperoNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument184 pagesPhysicsPiyush BhaskarNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - Plus One Phy Questions Bank 2023 HssreporterDocument98 pagesHSSRPTR - Plus One Phy Questions Bank 2023 HssreporterShimi BasheerNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two Dimensions: Onceptual UestionsDocument40 pagesMotion in Two Dimensions: Onceptual UestionsranahajNo ratings yet
- Lesson 33: Horizontal & Vertical Circular ProblemsDocument5 pagesLesson 33: Horizontal & Vertical Circular Problemsclaimstudent3515No ratings yet
- Engineeringmcqs Blogspot in 2014-08-154 Top Theory of MachinDocument27 pagesEngineeringmcqs Blogspot in 2014-08-154 Top Theory of Machinstuart ashrafNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6: Solutions: U A Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 106-4 / Leclair Fall 2008Document8 pagesProblem Set 6: Solutions: U A Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 106-4 / Leclair Fall 2008Nicolás KozakNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam 608Document9 pagesPhysics Exam 608joseftrihandokoNo ratings yet
- Physics 11Document5 pagesPhysics 11Kabeer SananNo ratings yet
- Test Paper - 3 Pattern: Mht-Cet: Please Read The Following Instructions CarefullyDocument16 pagesTest Paper - 3 Pattern: Mht-Cet: Please Read The Following Instructions CarefullyThe mind SetterNo ratings yet
- Study Material Force & Laws of Motion For AIEEEDocument46 pagesStudy Material Force & Laws of Motion For AIEEEApex Institute100% (1)
- Very Important IOE Practice Set 1Document29 pagesVery Important IOE Practice Set 1Ayush KarkiNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion Worksheet 3Document1 pageCircular Motion Worksheet 3Nipun Fernando100% (1)
- Jerome S. Santos - Science Week 2 - Module 1Document3 pagesJerome S. Santos - Science Week 2 - Module 1Jelyne santosNo ratings yet
- XI (2018-19) Physics Quarterly Exam QPDocument7 pagesXI (2018-19) Physics Quarterly Exam QPD SamyNo ratings yet
- Physics SBAsDocument7 pagesPhysics SBAsGrace JosephNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics English 2013Document241 pages11 Physics English 2013Bibek Kumar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Physics Definitions and ExplanationsDocument22 pagesPhysics Definitions and ExplanationsOwen ZhaoNo ratings yet
- BSF Head Constable Previous Year Papers RO 22 September 2019 - EnglishDocument77 pagesBSF Head Constable Previous Year Papers RO 22 September 2019 - EnglishKrishan SainiNo ratings yet
- PHY130 Exam#2 StudyGuideDocument2 pagesPHY130 Exam#2 StudyGuideSagar GogiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document38 pagesChapter 11NikhilSaxenaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 First Semester Review SheetDocument14 pagesAP Physics 1 First Semester Review Sheet이정빈No ratings yet
- The Dynamics'' of Leibnizian Relationism: Reference Frames and Force in Leibniz's PlenumDocument18 pagesThe Dynamics'' of Leibnizian Relationism: Reference Frames and Force in Leibniz's Plenumrebe53No ratings yet
- Mapeh GR.7Document3 pagesMapeh GR.7Unibelle Joy LachicaNo ratings yet
- Power Transfer: 2.2 Velocity Ratio, Belt Tension 2.1 Belt Drive SystemDocument25 pagesPower Transfer: 2.2 Velocity Ratio, Belt Tension 2.1 Belt Drive SystemHamizan AzliNo ratings yet
- hw06 SolutionsDocument6 pageshw06 SolutionsChristina Ish SpeshNo ratings yet
- Unlock Chapter4Document9 pagesUnlock Chapter4altwirqiNo ratings yet