Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsWKSHT-prok Euk
WKSHT-prok Euk
Uploaded by
erika alzateCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Complete TB Essential Cell Biology by Alberts 3rd Ed PDFDocument346 pagesComplete TB Essential Cell Biology by Alberts 3rd Ed PDFHusein Dharas95% (19)
- Activity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument8 pagesActivity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAdrian NenengNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesAmoeba Sisters Video Recap: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cellseric wyatt33% (3)
- SLM Number 4-Grade 7 Science - 2nd-Quarter - Plant - and - Animalcell-2Document16 pagesSLM Number 4-Grade 7 Science - 2nd-Quarter - Plant - and - Animalcell-2Maria Fe Vibar100% (5)
- Practice With Taxonomy and ClassificationDocument2 pagesPractice With Taxonomy and Classificationerika alzateNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: LessonDocument4 pagesProkaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: Lessonjoshiah glennNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet: Read The Passage Below. Then Answer The Questions That FollowDocument2 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet: Read The Passage Below. Then Answer The Questions That Followapi-242868690100% (1)
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheetDocument2 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheetAra Hella JordasNo ratings yet
- GenBio SMILE LP2 Q1 WEEK2Document14 pagesGenBio SMILE LP2 Q1 WEEK2jeknendoNo ratings yet
- Organize Your Organelles WKSTDocument2 pagesOrganize Your Organelles WKSTAdvaith SureshNo ratings yet
- IGCSE BiologyDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biologytee sooyeeNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 - 11/12: I. Introductory ConceptDocument17 pagesBiology 1 - 11/12: I. Introductory ConceptBlack CombatNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function CW2Document5 pagesCell Structure and Function CW2areej salimNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsDocument2 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsJanelle ArañaNo ratings yet
- A104 Biology Problem 1: Blocks of Life? Student Resources (Access March 2020) : 1. Factsheet and History of The Cell TheoryDocument6 pagesA104 Biology Problem 1: Blocks of Life? Student Resources (Access March 2020) : 1. Factsheet and History of The Cell Theoryjaswanth sriramNo ratings yet
- PRESTON HOLT - Cells Investigation LEXILE 610Document6 pagesPRESTON HOLT - Cells Investigation LEXILE 610Brian HoltNo ratings yet
- 2.3: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsDocument3 pages2.3: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsJubaer UtshobNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. EukaryoticDocument3 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryoticdomelub.jNo ratings yet
- Cells Introduction SHODocument5 pagesCells Introduction SHOshamshadNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic Cells: There Are Two Types of CellsDocument15 pagesProkaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic Cells: There Are Two Types of CellsgAARaNo ratings yet
- Two Types of Cells:: Prokaryote Cells and Eukaryote CellsDocument18 pagesTwo Types of Cells:: Prokaryote Cells and Eukaryote CellsShahrat Farsim ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Module-2 (Without Edits)Document27 pagesModule-2 (Without Edits)Jennie SoloNo ratings yet
- General Biology q1 w2 Mod2Document40 pagesGeneral Biology q1 w2 Mod2Karen Mae CastilloNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument10 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumChristopher PhilipNo ratings yet
- AY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Document7 pagesAY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Lim Liang XuanNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: Shs Stem - Biology 1Document17 pagesProkaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: Shs Stem - Biology 1Dette Dominic BallanoNo ratings yet
- Neil Hubilla - Gen Bio 1 q1 Las 3Document5 pagesNeil Hubilla - Gen Bio 1 q1 Las 3Neil Jhon HubillaNo ratings yet
- Biology Worksheet Activity 2 The CellDocument9 pagesBiology Worksheet Activity 2 The CellAaron Lance LopezNo ratings yet
- ds45 Intro To Cellular OrganellesDocument10 pagesds45 Intro To Cellular Organellesapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Eukaryotes Topic BuilderDocument2 pagesEukaryotes Topic Builderapi-281171147No ratings yet
- Biology: Cells: Date Topics/Activities Objectives HW DueDocument18 pagesBiology: Cells: Date Topics/Activities Objectives HW DueMarie Pearl F. AdamosNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Module 4Document13 pagesGen Bio 1 Module 4Ante,Glainry Rose Basan100% (1)
- Prokaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmDocument3 pagesProkaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmErvin WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Tyler Mckee, Adam Johnston, Hannah Williams 55 Minute Lesson Plan October 5Th, 2016 Biology: Grade 9-10Document5 pagesTyler Mckee, Adam Johnston, Hannah Williams 55 Minute Lesson Plan October 5Th, 2016 Biology: Grade 9-10api-340017879No ratings yet
- Real Mod 305Document9 pagesReal Mod 305api-332834916No ratings yet
- Biology: Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument5 pagesBiology: Cell Organelles WorksheetАлександър Антоан НиколовNo ratings yet
- 1st 9 WeekreviewDocument5 pages1st 9 Weekreviewapi-262368188No ratings yet
- Introduction To Cells WorksheetDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Cells WorksheetChristalhyne MendozaNo ratings yet
- Objectives::: Ultrastructure Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Comaprtmentalisation Binary Fission PiliDocument25 pagesObjectives::: Ultrastructure Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Comaprtmentalisation Binary Fission PiliAli MakiNo ratings yet
- 2016 Prokaytoes and Eukaryotes Station PDFDocument3 pages2016 Prokaytoes and Eukaryotes Station PDFsushantNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes Vs EukaryotesDocument17 pagesProkaryotes Vs EukaryotesJermaine Barnett-WeeksNo ratings yet
- North Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideDocument38 pagesNorth Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideRaquel Galdamez-GaldamezNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2Document6 pagesWorksheet 2rapNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Document12 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Farman MunawarNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheeetDocument3 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheeetsomeone swagNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes - EukaryotesDocument15 pagesProkaryotes - Eukaryotes24milesunderNo ratings yet
- Ds108-Intro To EcologyDocument5 pagesDs108-Intro To Ecologyapi-110789702No ratings yet
- The World of The Cell: General Biology 1Document8 pagesThe World of The Cell: General Biology 1Patrixia MiclatNo ratings yet
- Activity Worksheets: BiotechnologyDocument15 pagesActivity Worksheets: BiotechnologyTrinity MarieNo ratings yet
- EOC Review Packet 2013Document25 pagesEOC Review Packet 2013Danielle WiltseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biologi Sel Molekuler-1Document18 pagesIntroduction To Biologi Sel Molekuler-1arista purnama sariNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Document12 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017ufaysa gensaNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life EditedDocument22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life EditedQuerubin SalesNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Web QuestDocument4 pagesCell Organelle Web Questyadhugulanravendran5No ratings yet
- Prokaryotes Topic BuilderDocument3 pagesProkaryotes Topic Builderapi-281171147No ratings yet
- ScribdDocument4 pagesScribdam9792251No ratings yet
- AP BIO Animal Kingdom AssignmentDocument21 pagesAP BIO Animal Kingdom AssignmentHelen HeNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Scientists Types Reinforcement WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Theory Scientists Types Reinforcement Worksheetapi-165869000No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Sexual and Asexual HandoutDocument3 pagesSexual and Asexual Handouterika alzateNo ratings yet
- WS - Prokaryotic - Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesWS - Prokaryotic - Eukaryotic Cellserika alzateNo ratings yet
- Domain and Kingdom Worksheet BlankDocument2 pagesDomain and Kingdom Worksheet Blankerika alzateNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (6th Grade)Document26 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (6th Grade)erika alzateNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Metabolism Seventh GradeDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Metabolism Seventh Gradeerika alzateNo ratings yet
WKSHT-prok Euk
WKSHT-prok Euk
Uploaded by
erika alzate0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesOriginal Title
WKSHT-prok_euk_ (4)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesWKSHT-prok Euk
WKSHT-prok Euk
Uploaded by
erika alzateCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Name _______________________
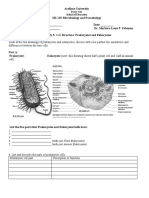
Cell Structure: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
What’s the Difference?
Look at the two drawings of prokaryotes and eukaryotes; discuss with your partner the similarities and
differences between the two cells.
Prokaryote: Eukaryote (note: this drawing shows half a plant cell and half an animal cell):
List the five parts that Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes both have:
1. ___________________________
2. ___________________________
3. ___________________________
4. ___________________________ (with just Plant Eukaryotes)
5. ___________________________ (with just Animal Eukaryotes)
6. List and describe 8 part of prokaryote cells.
Prokaryote cell part Description or function
7. Do Prokaryotes have a nucleus? ________
8. Which is more complex, Eukaryotes or Prokaryotes? _______________________
9. Which is larger? ____________________
Why are cells named that way?
From Greek words…
EU means __________________. PRO means __________________. KARY means __________________.
Eukaryote = ____________________; Prokaryote = ____________________.
All cells have ____________________, in eukaryotes it is stored in the ____________________. Prokaryotes
don’t have a nucleus, and it floats around in the cytoplasm in an area called a ____________________. Only
eukaryotes have ____________________.
Label each as prokaryotic or eukaryotic (circle one)
Plant cell Prokaryote Eukaryote Yeast cell P E
Staphylococcus cell Prokaryote Eukaryote E. coli cell P E
Fungus cell Prokaryote Eukaryote mouse cell P E
Animal cell Prokaryote Eukaryote strep germ cell P E
Bacterial cell Prokaryote Eukaryote flu virus P E
Blood cell Prokaryote Eukaryote sperm cell P E
10. Describe one advantage prokaryote cells have over eukaryote cells.
11. Describe one advantage eukaryote cells have over prokaryote cells.
You might also like
- Complete TB Essential Cell Biology by Alberts 3rd Ed PDFDocument346 pagesComplete TB Essential Cell Biology by Alberts 3rd Ed PDFHusein Dharas95% (19)
- Activity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument8 pagesActivity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAdrian NenengNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesAmoeba Sisters Video Recap: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cellseric wyatt33% (3)
- SLM Number 4-Grade 7 Science - 2nd-Quarter - Plant - and - Animalcell-2Document16 pagesSLM Number 4-Grade 7 Science - 2nd-Quarter - Plant - and - Animalcell-2Maria Fe Vibar100% (5)
- Practice With Taxonomy and ClassificationDocument2 pagesPractice With Taxonomy and Classificationerika alzateNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: LessonDocument4 pagesProkaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: Lessonjoshiah glennNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet: Read The Passage Below. Then Answer The Questions That FollowDocument2 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet: Read The Passage Below. Then Answer The Questions That Followapi-242868690100% (1)
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheetDocument2 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheetAra Hella JordasNo ratings yet
- GenBio SMILE LP2 Q1 WEEK2Document14 pagesGenBio SMILE LP2 Q1 WEEK2jeknendoNo ratings yet
- Organize Your Organelles WKSTDocument2 pagesOrganize Your Organelles WKSTAdvaith SureshNo ratings yet
- IGCSE BiologyDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biologytee sooyeeNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 - 11/12: I. Introductory ConceptDocument17 pagesBiology 1 - 11/12: I. Introductory ConceptBlack CombatNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function CW2Document5 pagesCell Structure and Function CW2areej salimNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsDocument2 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsJanelle ArañaNo ratings yet
- A104 Biology Problem 1: Blocks of Life? Student Resources (Access March 2020) : 1. Factsheet and History of The Cell TheoryDocument6 pagesA104 Biology Problem 1: Blocks of Life? Student Resources (Access March 2020) : 1. Factsheet and History of The Cell Theoryjaswanth sriramNo ratings yet
- PRESTON HOLT - Cells Investigation LEXILE 610Document6 pagesPRESTON HOLT - Cells Investigation LEXILE 610Brian HoltNo ratings yet
- 2.3: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsDocument3 pages2.3: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsJubaer UtshobNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. EukaryoticDocument3 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryoticdomelub.jNo ratings yet
- Cells Introduction SHODocument5 pagesCells Introduction SHOshamshadNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic Cells: There Are Two Types of CellsDocument15 pagesProkaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic Cells: There Are Two Types of CellsgAARaNo ratings yet
- Two Types of Cells:: Prokaryote Cells and Eukaryote CellsDocument18 pagesTwo Types of Cells:: Prokaryote Cells and Eukaryote CellsShahrat Farsim ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Module-2 (Without Edits)Document27 pagesModule-2 (Without Edits)Jennie SoloNo ratings yet
- General Biology q1 w2 Mod2Document40 pagesGeneral Biology q1 w2 Mod2Karen Mae CastilloNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument10 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumChristopher PhilipNo ratings yet
- AY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Document7 pagesAY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Lim Liang XuanNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: Shs Stem - Biology 1Document17 pagesProkaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: Shs Stem - Biology 1Dette Dominic BallanoNo ratings yet
- Neil Hubilla - Gen Bio 1 q1 Las 3Document5 pagesNeil Hubilla - Gen Bio 1 q1 Las 3Neil Jhon HubillaNo ratings yet
- Biology Worksheet Activity 2 The CellDocument9 pagesBiology Worksheet Activity 2 The CellAaron Lance LopezNo ratings yet
- ds45 Intro To Cellular OrganellesDocument10 pagesds45 Intro To Cellular Organellesapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Eukaryotes Topic BuilderDocument2 pagesEukaryotes Topic Builderapi-281171147No ratings yet
- Biology: Cells: Date Topics/Activities Objectives HW DueDocument18 pagesBiology: Cells: Date Topics/Activities Objectives HW DueMarie Pearl F. AdamosNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Module 4Document13 pagesGen Bio 1 Module 4Ante,Glainry Rose Basan100% (1)
- Prokaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmDocument3 pagesProkaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmErvin WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Tyler Mckee, Adam Johnston, Hannah Williams 55 Minute Lesson Plan October 5Th, 2016 Biology: Grade 9-10Document5 pagesTyler Mckee, Adam Johnston, Hannah Williams 55 Minute Lesson Plan October 5Th, 2016 Biology: Grade 9-10api-340017879No ratings yet
- Real Mod 305Document9 pagesReal Mod 305api-332834916No ratings yet
- Biology: Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument5 pagesBiology: Cell Organelles WorksheetАлександър Антоан НиколовNo ratings yet
- 1st 9 WeekreviewDocument5 pages1st 9 Weekreviewapi-262368188No ratings yet
- Introduction To Cells WorksheetDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Cells WorksheetChristalhyne MendozaNo ratings yet
- Objectives::: Ultrastructure Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Comaprtmentalisation Binary Fission PiliDocument25 pagesObjectives::: Ultrastructure Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Comaprtmentalisation Binary Fission PiliAli MakiNo ratings yet
- 2016 Prokaytoes and Eukaryotes Station PDFDocument3 pages2016 Prokaytoes and Eukaryotes Station PDFsushantNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes Vs EukaryotesDocument17 pagesProkaryotes Vs EukaryotesJermaine Barnett-WeeksNo ratings yet
- North Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideDocument38 pagesNorth Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideRaquel Galdamez-GaldamezNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2Document6 pagesWorksheet 2rapNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Document12 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Farman MunawarNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheeetDocument3 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheeetsomeone swagNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes - EukaryotesDocument15 pagesProkaryotes - Eukaryotes24milesunderNo ratings yet
- Ds108-Intro To EcologyDocument5 pagesDs108-Intro To Ecologyapi-110789702No ratings yet
- The World of The Cell: General Biology 1Document8 pagesThe World of The Cell: General Biology 1Patrixia MiclatNo ratings yet
- Activity Worksheets: BiotechnologyDocument15 pagesActivity Worksheets: BiotechnologyTrinity MarieNo ratings yet
- EOC Review Packet 2013Document25 pagesEOC Review Packet 2013Danielle WiltseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biologi Sel Molekuler-1Document18 pagesIntroduction To Biologi Sel Molekuler-1arista purnama sariNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Document12 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017ufaysa gensaNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life EditedDocument22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life EditedQuerubin SalesNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Web QuestDocument4 pagesCell Organelle Web Questyadhugulanravendran5No ratings yet
- Prokaryotes Topic BuilderDocument3 pagesProkaryotes Topic Builderapi-281171147No ratings yet
- ScribdDocument4 pagesScribdam9792251No ratings yet
- AP BIO Animal Kingdom AssignmentDocument21 pagesAP BIO Animal Kingdom AssignmentHelen HeNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Scientists Types Reinforcement WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Theory Scientists Types Reinforcement Worksheetapi-165869000No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Sexual and Asexual HandoutDocument3 pagesSexual and Asexual Handouterika alzateNo ratings yet
- WS - Prokaryotic - Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesWS - Prokaryotic - Eukaryotic Cellserika alzateNo ratings yet
- Domain and Kingdom Worksheet BlankDocument2 pagesDomain and Kingdom Worksheet Blankerika alzateNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (6th Grade)Document26 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (6th Grade)erika alzateNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Metabolism Seventh GradeDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Metabolism Seventh Gradeerika alzateNo ratings yet