Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adaptation and Competition All Levels Q MS
Adaptation and Competition All Levels Q MS
Uploaded by
ForCounter OsasCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- New PiRA Assessment MapsDocument12 pagesNew PiRA Assessment MapsToqa osamaNo ratings yet
- Glow in The Dark QuizDocument3 pagesGlow in The Dark QuizJaime PDNo ratings yet
- The Arrogant Rose StorytellingDocument3 pagesThe Arrogant Rose StorytellingAshna Haron67% (3)
- Mixed Stoichiometry PracticeDocument4 pagesMixed Stoichiometry PracticeJonathan RuizNo ratings yet
- Maths Assessment Year 3 Term 3: Measurement: NameDocument7 pagesMaths Assessment Year 3 Term 3: Measurement: NamebayaNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science 2009 T5-7 Paper 2Document28 pagesKS3 Science 2009 T5-7 Paper 2박찬우No ratings yet
- 1819 Suli PPP Term 3 Final Grade 6 Science Revision Sheet Answer KeyDocument38 pages1819 Suli PPP Term 3 Final Grade 6 Science Revision Sheet Answer KeyLana100% (2)
- Rocks Revision Worksheet PDFDocument6 pagesRocks Revision Worksheet PDFnoeme tolentinoNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheet GR 6Document13 pagesScience Worksheet GR 6Abdelrhman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnets: The Around A Is Very - A Can Be Made by The Around A Piece ofDocument4 pagesElectromagnets: The Around A Is Very - A Can Be Made by The Around A Piece ofkaylonNo ratings yet
- Acids and Alkalis Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument3 pagesAcids and Alkalis Worksheet: Name: . DateCally ChewNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Sample Exam Questions On Energy Transfer and Food WebsDocument6 pagesLesson 2 Sample Exam Questions On Energy Transfer and Food WebsBalachandran Palaniandy0% (1)
- Holiday Assignment-Grade 7Document3 pagesHoliday Assignment-Grade 7aryan10No ratings yet
- Year - 9 Photosynthesis - Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesYear - 9 Photosynthesis - Mark SchemeChuanthing TeeNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 SCIENCE QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesGrade 9 SCIENCE QUESTIONSSharreah LimNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Reactivity of Metals QPDocument29 pages4.1 Reactivity of Metals QPTosyn AriyoNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits Related Questions (CH 12)Document50 pagesElectricity and Circuits Related Questions (CH 12)Srijan MauryaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Water CycleDocument5 pagesGrade 6 Water Cycletripti aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet ChemDocument8 pagesRevision Worksheet ChemJean StephenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Unit Test - QuizizzDocument4 pagesChemical Reaction Unit Test - QuizizzAngkita KiranaNo ratings yet
- Pearson - Science - 8 - SB - ENERGY Chapter - 5 - Unit - 5.1Document8 pagesPearson - Science - 8 - SB - ENERGY Chapter - 5 - Unit - 5.1loupoo80No ratings yet
- Sats QuestionsDocument9 pagesSats Questionsapi-3800318No ratings yet
- AE.23072022.Potential Difference, Resistance and Current AnswersDocument2 pagesAE.23072022.Potential Difference, Resistance and Current AnswersĐặng Thái Nhật100% (1)
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism QuestionsDocument17 pagesMagnetism and Electromagnetism QuestionseNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Reported Speech Exercise 2023-24Document10 pagesGrammar - Reported Speech Exercise 2023-24Subalakshmi Raja100% (1)
- Quiz - G9 Forces & Motion EoTA 2020Document14 pagesQuiz - G9 Forces & Motion EoTA 2020Jeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Physics Test Grade9!1!2023Document10 pagesPhysics Test Grade9!1!2023Mahmod YaishNo ratings yet
- Booklet Year 7 Space ActivityDocument7 pagesBooklet Year 7 Space Activityapi-222503660No ratings yet
- Grade 2 States of Matter DDocument4 pagesGrade 2 States of Matter DJehan MisenasNo ratings yet
- T2 S 183 Dissolving Worksheet - Ver - 1Document2 pagesT2 S 183 Dissolving Worksheet - Ver - 1Nazima MunirNo ratings yet
- Rastrick School ElectromagneticDocument37 pagesRastrick School Electromagneticathmi SNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Science Y7 Workbook + Worksheet Unit 9-10-11 StudentDocument50 pagesCambridge Science Y7 Workbook + Worksheet Unit 9-10-11 StudentpettagscoNo ratings yet
- Geog 123 KerboodlesampleDocument44 pagesGeog 123 KerboodlesampleSumathy0% (1)
- English Check Point Paper 2 Sample 2012Document8 pagesEnglish Check Point Paper 2 Sample 2012Thien Kim DoNo ratings yet
- Test & AnswersDocument24 pagesTest & AnswersHaziraAzly0% (1)
- Booklet 3Document10 pagesBooklet 3Elegbede AnthoniaNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Test - Igcse - ChemistryDocument11 pagesStoichiometry Test - Igcse - ChemistryhasiniNo ratings yet
- KS3 States of Matter Practice Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesKS3 States of Matter Practice Exam Questionsgzm yldz0% (1)
- 2023 IGCSE GIC O Level Entrance Test (May-June Intake) Science QuestionsDocument32 pages2023 IGCSE GIC O Level Entrance Test (May-June Intake) Science QuestionsIngyin SanNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Cells and Reproduction - Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesYear 7 Cells and Reproduction - Mark SchemeAnonymous tc7XPINo ratings yet
- Science Paper Section B and C Class VII 2019-10Document1 pageScience Paper Section B and C Class VII 2019-10Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- 1 Electricity Test QuestionsDocument5 pages1 Electricity Test QuestionsSandileVilaneNo ratings yet
- Ks3 Chem 9e Eq Q1to10 54marks 4students Metals and Corrosion 11pgsDocument11 pagesKs3 Chem 9e Eq Q1to10 54marks 4students Metals and Corrosion 11pgsmatthewansell6977No ratings yet
- Key Stage 3 Ks3 Science 57P2 2005Document14 pagesKey Stage 3 Ks3 Science 57P2 2005odysseym1No ratings yet
- Worksheet IG 2Document6 pagesWorksheet IG 2rekhaNo ratings yet
- Si-Fi, Horror Example Narrative For IgcseDocument2 pagesSi-Fi, Horror Example Narrative For IgcseOjaswin AVSNo ratings yet
- Limiting Factors 6Document7 pagesLimiting Factors 6Khadija AhmedNo ratings yet
- Food Tests Exam QsDocument8 pagesFood Tests Exam QsAleNo ratings yet
- G9 Metals and Reactivity TESTDocument4 pagesG9 Metals and Reactivity TESTMiral AlasbahiNo ratings yet
- S9 Unit 5 WorksheetsDocument2 pagesS9 Unit 5 WorksheetsChamika T100% (1)
- Crokscrew Rule WS PDFDocument2 pagesCrokscrew Rule WS PDFRosario diamondNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 1Document4 pagesGCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 1Mr. Suit100% (1)
- Key Stage 3 Ks3 Science MarkScheme 2005Document56 pagesKey Stage 3 Ks3 Science MarkScheme 2005odysseym1No ratings yet
- Review Worksheet No. 2 "Forces and Movement": Habib Public School Junior Section 2020 - 2021Document1 pageReview Worksheet No. 2 "Forces and Movement": Habib Public School Junior Section 2020 - 2021Noman Kulachi50% (2)
- Lesson 2 WorksheetsDocument11 pagesLesson 2 WorksheetsyuiNo ratings yet
- Specialised-Cells-Worksheet - Combined ScienceDocument3 pagesSpecialised-Cells-Worksheet - Combined ScienceBachittar SinghNo ratings yet
- 9701 Example Candidate Responses Paper 4 (For Examination From 2022)Document36 pages9701 Example Candidate Responses Paper 4 (For Examination From 2022)thiruveleyudhamNo ratings yet
- Collective Nouns Worksheet 1Document2 pagesCollective Nouns Worksheet 1DineshNo ratings yet
- B2 Questions and AnswersDocument24 pagesB2 Questions and AnswersalkachauhanNo ratings yet
- B2 Questions and AnswersDocument22 pagesB2 Questions and Answersinaayairshad.17No ratings yet
- Year 9 ScienceDocument28 pagesYear 9 Sciencesanctus.nirmalaNo ratings yet
- IMSO 2014 SCIENCE Theoretical 2Document7 pagesIMSO 2014 SCIENCE Theoretical 2Murni0% (1)
- AGRI-CROP G-9 (Nursery Facility)Document55 pagesAGRI-CROP G-9 (Nursery Facility)Clyde Lyndon RasayNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Some Mosses in Nainital, Almora and Pithoragarh District of Kumaon Region, IndiaDocument5 pagesDistribution of Some Mosses in Nainital, Almora and Pithoragarh District of Kumaon Region, IndiaA Lavate RajendraNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Plants - 5 Stages + Fun Facts - Science4FunDocument8 pagesLife Cycle of Plants - 5 Stages + Fun Facts - Science4FunMasthankhan PatanNo ratings yet
- Kudinkula BiologyDocument113 pagesKudinkula BiologylufeyocliftonNo ratings yet
- Cotton Cultivation in PakistanDocument18 pagesCotton Cultivation in PakistanHamid RazaNo ratings yet
- And Embryo Sac: 2.2.2 The Pistil, Megasporangium (Ovule)Document12 pagesAnd Embryo Sac: 2.2.2 The Pistil, Megasporangium (Ovule)ChandanNo ratings yet
- Major and Minor Cellulosic FibresDocument127 pagesMajor and Minor Cellulosic FibresYou Kno WhoNo ratings yet
- Dơnload Religion in Tudor England An Anthology of Primary Sources 1st Edition Ethan H Shagan Debora Shuger Full ChapterDocument24 pagesDơnload Religion in Tudor England An Anthology of Primary Sources 1st Edition Ethan H Shagan Debora Shuger Full Chapterbacaduaia100% (7)
- Brassica Carinata Biology and Agronomy As A Biofuel CropDocument18 pagesBrassica Carinata Biology and Agronomy As A Biofuel CropRamdeo SeepaulNo ratings yet
- Botany 3.4 DoneDocument3 pagesBotany 3.4 DoneLeslie Ann Potenciano100% (1)
- Janka Hardness TestDocument8 pagesJanka Hardness TestLuiz ImprovizzaNo ratings yet
- Biology XII (12th Grade/Class) MCQs KEYDocument268 pagesBiology XII (12th Grade/Class) MCQs KEYInni CallmeinniNo ratings yet
- Science - Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesScience - Levels of OrganizationAlexNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones - DR - FQDocument47 pagesPlant Hormones - DR - FQUmarNo ratings yet
- Ganga Aquatic Plants PDFDocument48 pagesGanga Aquatic Plants PDFDipakNo ratings yet
- Indoor Orchid Care - How Do I Take Care of An Orchid FlowerDocument13 pagesIndoor Orchid Care - How Do I Take Care of An Orchid Flowerjaz andersonNo ratings yet
- Safety s40 IntDocument2 pagesSafety s40 IntLos Laureles UrbanaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life 2Q ExamDocument5 pagesEarth and Life 2Q ExamImmanuel GranadaNo ratings yet
- Transpiration Diagram-Based QuestionsDocument9 pagesTranspiration Diagram-Based Questionsthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Till Saxby Electric Pallet Truck Egv 10-12-0240 0242 0300 0302 Workshop ManualDocument22 pagesTill Saxby Electric Pallet Truck Egv 10-12-0240 0242 0300 0302 Workshop Manualmichaelfisher030690fgaNo ratings yet
- Agr232 - c5 Principles and Techniques of Propagation by CuttingsDocument38 pagesAgr232 - c5 Principles and Techniques of Propagation by Cuttingsmohamad afifNo ratings yet
- Reading Unit 17:: Bees TextDocument2 pagesReading Unit 17:: Bees Textnaziroh herliaNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants of Pondoland 2012Document82 pagesMedicinal Plants of Pondoland 2012thaboNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy Sheet 2Document1 pageTaxonomy Sheet 2lettresaccelerer.0eNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Part 2A Organisation of Living Things - Nutrient and Gas RequirementsDocument94 pagesMODULE 2 Part 2A Organisation of Living Things - Nutrient and Gas RequirementsZenaNo ratings yet
- Plant Science Today: Genus Notoscyphus Mitt. - New To The Liverwort Flora of The Eastern GhatsDocument3 pagesPlant Science Today: Genus Notoscyphus Mitt. - New To The Liverwort Flora of The Eastern Ghatsmendal sciNo ratings yet
- Botanicon Sinicum, 1895 PDFDocument641 pagesBotanicon Sinicum, 1895 PDFadamtate137483No ratings yet
- 3625 Why Do Bees BuzzDocument17 pages3625 Why Do Bees BuzzSakshi GoelNo ratings yet
Adaptation and Competition All Levels Q MS
Adaptation and Competition All Levels Q MS
Uploaded by
ForCounter OsasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adaptation and Competition All Levels Q MS
Adaptation and Competition All Levels Q MS
Uploaded by
ForCounter OsasCopyright:
Available Formats
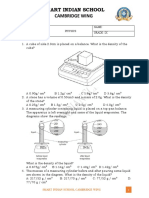
(a) Alex poured some pond water into three beakers.
She then put waterweed into
1. each beaker. She put the beakers in different places.
(i) In which beaker did the waterweed grow best? Give the correct letter.
… … … …
1 mark
(ii) The waterweed in the box changed from dark green to pale yellow.
Why did this happen?
… … … … … … … … … … … … … … … . … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
1 mark
(b) In the school pond there were lots of water lilies with large leaves covering the surface.
There were not many plants growing below the surface.
Suggest a reason for this.
… … … … … . . … … … … … … … … … … … … . … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
… … … … … . . … … … … … … … … … … … … . … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
1 mark
British School in Baku Page 1 of 13
(c) In another experiment, Alex put similar pieces of waterweed into two more beakers of pond
water.
She added fertiliser to one of them.
She kept them both by a window.
(i) Alex added fertiliser to beaker E. Suggest the results of this experiment.
… … … … … . . … … … … … … … … … … … … . … … … … … … … . . … … … … …
… … … … … . . … … … … … … … … … … … … . … … … … … … … . . … … … … …
1 mark
(ii) What do fertilisers contain to help plants grow?
Tick the correct box.
fat minerals
sand sugar
1 mark
Maximum 5 marks
British School in Baku Page 2 of 13
Plants take in water from the soil. Lisa did an experiment to find out if there is anything else in
2. soil that plants need for growth.
The diagrams below show the results of Lisa’s experiment.
Lisa made the clear, brown solution in flask B by shaking a mixture of soil and water and
then separating the solution from the soil particles.
(a) How could Lisa separate the brown solution from the soil particles?
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(b) Explain why Lisa grew one plant in distilled water.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(c) (i) What type of substance, dissolved in the water in flask B, is used by the plant
for growth?
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(ii) How are roots adapted for taking in water?
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
British School in Baku Page 3 of 13
(d) Lisa set up a second experiment using three similar plants. The solution in flasks C, D
and E was the same. She put all three flasks in a sunny position. The diagrams below
show the results of Lisa’s second experiment.
The plant in flask C was the only one which grew well in this experiment.
Explain why.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 5 marks
(a) The drawings below show a stoat in summer and in winter.
3.
stoat in summer stoat in winter
British School in Baku Page 4 of 13
In winter the ground is often covered by snow or frost. During this part of the year a
stoat’s fur is white.
Suggest two ways its white coat helps a stoat to survive in the winter.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
2 marks
(b) The diagram shows the family tree for a family of rabbits.
Use words from the list below to complete the sentences.
adapt cytoplasm genes grow inherit
letters membrane mutate nuclei
Rabbits have the same fur colour all year round.
Young rabbits ............................................ fur colour from their parents.
Information about fur colour is passed on from one generation to
the next in the form of ................................... in the ..................................... of
an egg and sperm.
3 marks
Maximum 5 marks
British School in Baku Page 5 of 13
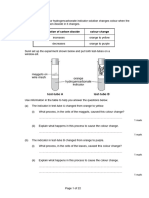
Codling moths lay eggs on apple trees. The caterpillars of the codling moth feed on apples.
4. The diagram below shows the life cycle of codling moths.
not to scale
Apple growers use special traps to catch male codling moths.
The traps contain a chemical which female moths produce to attract male moths.
(a) (i) Explain why trapping male moths may result in fewer caterpillars the next year.
… … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
… … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
1 mark
(ii) Some apple growers spray their trees with insecticide to kill moths.
Other apple growers disagree with this method of control.
Suggest two reasons for not using insecticides.
1 . … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
… … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
2 . … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
… … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
2 marks
British School in Baku Page 6 of 13
(b) The female moth lays large numbers of eggs.
Suggest why this is necessary.
… … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
… … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
1 mark
(c) When the caterpillars are fully grown, they crawl into tiny spaces under the bark of the
trees. The caterpillars stay under the bark during the winter and then change into pupae.
(i) Suggest why more caterpillars and pupae survive when they are under the bark.
… … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
… … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
1 mark
(ii) Some apple growers wrap bands of folded cardboard around the trunks of
apple trees, as shown below. Caterpillars crawl into the folds. The cardboard is
removed during the winter and destroyed.
Suggest one way in which this helps to protect the next year’s apples from
damage by caterpillars of codling moths.
… … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
… … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
1 mark
Maximum 6 marks
British School in Baku Page 7 of 13
Bats hibernate during the winter. While they are hibernating, their hearts beat more
5. slowly and they go into a deep sleep.
(a) Towards the end of the summer, bats build up a store of fat in a layer beneath the skin.
Give one reason why fat is a useful storage substance.
1 mark
(b) While bats are hibernating their body temperature falls.
What is the advantage of having a low body temperature during the winter?
… … … . … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
… … … . … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
1 mark
(c) Suggest one disadvantage of hibernating.
… … … . … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
… … … . … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
1 mark
(d) Sometimes bats wake up too early from hibernation.
These bats are unlikely to survive the cold weather.
Give one reason for their low survival rate as a result of waking too early.
… … … . … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
… … … . … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
1 mark
Maximum 4 marks
British School in Baku Page 8 of 13
Mark schemes
(a) (i) C
1. 1 (L3)
(ii) any one from
• no light
accept ‘no Sun’
• it was in the dark
do not accept ‘it was in the box’
1 (L3)
(b) any one from
• less light reached the lower plants
• plants need light to grow
accept ‘plants need light’
accept ‘no photosynthesis could take place’
• the water lilies blocked the light
accept ‘no light’
accept ‘lilies prevented
or reduced the air getting into the water’
accept ‘plants need carbon dioxide’
do not accept ‘the water lilies used the minerals’
1 (L3)
(c) (i) any one from
• the waterweed in E will grow bigger than in D
accept ‘it will grow more or faster or better in E’
• the waterweed in E will have more leaves than in D
accept ‘it will have more leaves in E’
do not accept ‘it grew fast in E’
1 (L3)
(ii) minerals
if more than one box is ticked, award no mark
1 (L4)
[5]
(a) by filtration or she filtered it
2.
accept ‘let it settle then pour off the liquid’
or ‘decant’
1 (L5)
British School in Baku Page 9 of 13
(b) any one from
• as a control
do not accept ‘to make it a fair test’
• to show that the dissolved substances affect the growth of the plant
• to see if they grow differently
do not accept ‘to see if it grows in distilled water’
• to see if they grow normally or well without the dissolved substances
do not accept ‘to see if it grows normally
without soil particles’
1 (L5)
(c) (i) mineral salts or minerals or salts or nutrients
accept ‘nitrates’ or ‘phosphates’
do not accept ‘fertiliser’
1 (L5)
(ii) any one from
• they are spread out
accept ‘they are long’
• they are branched
• they have a large surface area
• they have root hairs
accept ‘they have hairs’
accept ‘they are permeable’
do not accept ‘they can take in water’
1 (L5)
(d) the leaves need light for photosynthesis
accept ‘photosynthesis takes place in the leaves’
or ‘plants need light for photosynthesis’
do not accept ‘the leaves need light’
1 (L6)
[5]
(a) it helps it to hide from its prey
3. 1 (L6)
it helps it to hide from predators
answers may be in either order
accept ‘hides it from rabbits or from animals it eats’
accept ‘hides it from animals which eat or hunt it’
accept ‘to camouflage it’
for one mark only accept ‘it is an insulator’
or ‘it keeps them warm’
1 (L6)
British School in Baku Page 10 of 13
(b) inherit
1 (L6)
genes
1 (L6)
nuclei
accept ‘nucleus’
1 (L6)
[5]
(a) (i) Answers must refer to mating or breeding or reproduction.
4.
any one from
• fewer males to mate
do not accept ‘there are no males to mate’
or ‘there are fewer males’
• fewer moths to breed
do not accept ‘fewer moths’
accept ‘there will be fewer eggs’
1 (L5)
(ii) any two from
• insecticide might enter food chains
• other useful or harmless insects might be killed
accept ‘other insects or bees might be killed’
do not accept ‘other animals are killed’
• predators of pests might be killed
• people might eat the insecticide
accept ‘people might be poisoned’
accept ‘people might breathe it in’
accept ‘so that the apples are organic’
2 (L6)
(b) any one from
• some eggs or caterpillars or pupae or moths
accept ‘caterpillars get eaten’ may be eaten
• some might not hatch
• some might die
accept ‘so that as many as possible survive’
1 (L5)
British School in Baku Page 11 of 13
(c) (i) any one from
• they cannot be seen by predators or birds
accept ‘they are not eaten’ or ‘to hide’
accept a named predator such as blue-tit
• for shelter
accept ‘to keep warm’
• to protect them from the cold
accept ‘to protect them’
1 (L5)
(ii) any one from
• caterpillars are removed or killed
accept ‘pupae can be removed or killed’
accept ‘there are fewer pupae’
• fewer pupae change into moths
• fewer moths produce caterpillars
• there will be fewer caterpillars to eat the apples
1 (L6)
[6]
(a) any one from
5.
• it is a good source or store of energy
do not accept ‘it is a good store of food’
do not accept ‘it is a source of energy’
• it insulates the body
accept ‘it keeps the heat in’
accept ‘it stops them getting too cold’
do not accept ‘it keeps the body warm’
• it is insoluble
1 (L6)
(b) any one from
• less heat loss
• less energy needed
• food reserves or fat lasts longer
1 (L7)
British School in Baku Page 12 of 13
(c) any one from
• predators can catch them easily
• habitat or roosts could be damaged
• the food reserve may run out
1 (L7)
(d) any one from
• food in short supply
accept ‘no food’
• they lose too much heat
1 (L7)
[4]
British School in Baku Page 13 of 13
You might also like
- New PiRA Assessment MapsDocument12 pagesNew PiRA Assessment MapsToqa osamaNo ratings yet
- Glow in The Dark QuizDocument3 pagesGlow in The Dark QuizJaime PDNo ratings yet
- The Arrogant Rose StorytellingDocument3 pagesThe Arrogant Rose StorytellingAshna Haron67% (3)
- Mixed Stoichiometry PracticeDocument4 pagesMixed Stoichiometry PracticeJonathan RuizNo ratings yet
- Maths Assessment Year 3 Term 3: Measurement: NameDocument7 pagesMaths Assessment Year 3 Term 3: Measurement: NamebayaNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science 2009 T5-7 Paper 2Document28 pagesKS3 Science 2009 T5-7 Paper 2박찬우No ratings yet
- 1819 Suli PPP Term 3 Final Grade 6 Science Revision Sheet Answer KeyDocument38 pages1819 Suli PPP Term 3 Final Grade 6 Science Revision Sheet Answer KeyLana100% (2)
- Rocks Revision Worksheet PDFDocument6 pagesRocks Revision Worksheet PDFnoeme tolentinoNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheet GR 6Document13 pagesScience Worksheet GR 6Abdelrhman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnets: The Around A Is Very - A Can Be Made by The Around A Piece ofDocument4 pagesElectromagnets: The Around A Is Very - A Can Be Made by The Around A Piece ofkaylonNo ratings yet
- Acids and Alkalis Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument3 pagesAcids and Alkalis Worksheet: Name: . DateCally ChewNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Sample Exam Questions On Energy Transfer and Food WebsDocument6 pagesLesson 2 Sample Exam Questions On Energy Transfer and Food WebsBalachandran Palaniandy0% (1)
- Holiday Assignment-Grade 7Document3 pagesHoliday Assignment-Grade 7aryan10No ratings yet
- Year - 9 Photosynthesis - Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesYear - 9 Photosynthesis - Mark SchemeChuanthing TeeNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 SCIENCE QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesGrade 9 SCIENCE QUESTIONSSharreah LimNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Reactivity of Metals QPDocument29 pages4.1 Reactivity of Metals QPTosyn AriyoNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits Related Questions (CH 12)Document50 pagesElectricity and Circuits Related Questions (CH 12)Srijan MauryaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Water CycleDocument5 pagesGrade 6 Water Cycletripti aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet ChemDocument8 pagesRevision Worksheet ChemJean StephenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Unit Test - QuizizzDocument4 pagesChemical Reaction Unit Test - QuizizzAngkita KiranaNo ratings yet
- Pearson - Science - 8 - SB - ENERGY Chapter - 5 - Unit - 5.1Document8 pagesPearson - Science - 8 - SB - ENERGY Chapter - 5 - Unit - 5.1loupoo80No ratings yet
- Sats QuestionsDocument9 pagesSats Questionsapi-3800318No ratings yet
- AE.23072022.Potential Difference, Resistance and Current AnswersDocument2 pagesAE.23072022.Potential Difference, Resistance and Current AnswersĐặng Thái Nhật100% (1)
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism QuestionsDocument17 pagesMagnetism and Electromagnetism QuestionseNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Reported Speech Exercise 2023-24Document10 pagesGrammar - Reported Speech Exercise 2023-24Subalakshmi Raja100% (1)
- Quiz - G9 Forces & Motion EoTA 2020Document14 pagesQuiz - G9 Forces & Motion EoTA 2020Jeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Physics Test Grade9!1!2023Document10 pagesPhysics Test Grade9!1!2023Mahmod YaishNo ratings yet
- Booklet Year 7 Space ActivityDocument7 pagesBooklet Year 7 Space Activityapi-222503660No ratings yet
- Grade 2 States of Matter DDocument4 pagesGrade 2 States of Matter DJehan MisenasNo ratings yet
- T2 S 183 Dissolving Worksheet - Ver - 1Document2 pagesT2 S 183 Dissolving Worksheet - Ver - 1Nazima MunirNo ratings yet
- Rastrick School ElectromagneticDocument37 pagesRastrick School Electromagneticathmi SNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Science Y7 Workbook + Worksheet Unit 9-10-11 StudentDocument50 pagesCambridge Science Y7 Workbook + Worksheet Unit 9-10-11 StudentpettagscoNo ratings yet
- Geog 123 KerboodlesampleDocument44 pagesGeog 123 KerboodlesampleSumathy0% (1)
- English Check Point Paper 2 Sample 2012Document8 pagesEnglish Check Point Paper 2 Sample 2012Thien Kim DoNo ratings yet
- Test & AnswersDocument24 pagesTest & AnswersHaziraAzly0% (1)
- Booklet 3Document10 pagesBooklet 3Elegbede AnthoniaNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Test - Igcse - ChemistryDocument11 pagesStoichiometry Test - Igcse - ChemistryhasiniNo ratings yet
- KS3 States of Matter Practice Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesKS3 States of Matter Practice Exam Questionsgzm yldz0% (1)
- 2023 IGCSE GIC O Level Entrance Test (May-June Intake) Science QuestionsDocument32 pages2023 IGCSE GIC O Level Entrance Test (May-June Intake) Science QuestionsIngyin SanNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Cells and Reproduction - Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesYear 7 Cells and Reproduction - Mark SchemeAnonymous tc7XPINo ratings yet
- Science Paper Section B and C Class VII 2019-10Document1 pageScience Paper Section B and C Class VII 2019-10Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- 1 Electricity Test QuestionsDocument5 pages1 Electricity Test QuestionsSandileVilaneNo ratings yet
- Ks3 Chem 9e Eq Q1to10 54marks 4students Metals and Corrosion 11pgsDocument11 pagesKs3 Chem 9e Eq Q1to10 54marks 4students Metals and Corrosion 11pgsmatthewansell6977No ratings yet
- Key Stage 3 Ks3 Science 57P2 2005Document14 pagesKey Stage 3 Ks3 Science 57P2 2005odysseym1No ratings yet
- Worksheet IG 2Document6 pagesWorksheet IG 2rekhaNo ratings yet
- Si-Fi, Horror Example Narrative For IgcseDocument2 pagesSi-Fi, Horror Example Narrative For IgcseOjaswin AVSNo ratings yet
- Limiting Factors 6Document7 pagesLimiting Factors 6Khadija AhmedNo ratings yet
- Food Tests Exam QsDocument8 pagesFood Tests Exam QsAleNo ratings yet
- G9 Metals and Reactivity TESTDocument4 pagesG9 Metals and Reactivity TESTMiral AlasbahiNo ratings yet
- S9 Unit 5 WorksheetsDocument2 pagesS9 Unit 5 WorksheetsChamika T100% (1)
- Crokscrew Rule WS PDFDocument2 pagesCrokscrew Rule WS PDFRosario diamondNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 1Document4 pagesGCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 1Mr. Suit100% (1)
- Key Stage 3 Ks3 Science MarkScheme 2005Document56 pagesKey Stage 3 Ks3 Science MarkScheme 2005odysseym1No ratings yet
- Review Worksheet No. 2 "Forces and Movement": Habib Public School Junior Section 2020 - 2021Document1 pageReview Worksheet No. 2 "Forces and Movement": Habib Public School Junior Section 2020 - 2021Noman Kulachi50% (2)
- Lesson 2 WorksheetsDocument11 pagesLesson 2 WorksheetsyuiNo ratings yet
- Specialised-Cells-Worksheet - Combined ScienceDocument3 pagesSpecialised-Cells-Worksheet - Combined ScienceBachittar SinghNo ratings yet
- 9701 Example Candidate Responses Paper 4 (For Examination From 2022)Document36 pages9701 Example Candidate Responses Paper 4 (For Examination From 2022)thiruveleyudhamNo ratings yet
- Collective Nouns Worksheet 1Document2 pagesCollective Nouns Worksheet 1DineshNo ratings yet
- B2 Questions and AnswersDocument24 pagesB2 Questions and AnswersalkachauhanNo ratings yet
- B2 Questions and AnswersDocument22 pagesB2 Questions and Answersinaayairshad.17No ratings yet
- Year 9 ScienceDocument28 pagesYear 9 Sciencesanctus.nirmalaNo ratings yet
- IMSO 2014 SCIENCE Theoretical 2Document7 pagesIMSO 2014 SCIENCE Theoretical 2Murni0% (1)
- AGRI-CROP G-9 (Nursery Facility)Document55 pagesAGRI-CROP G-9 (Nursery Facility)Clyde Lyndon RasayNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Some Mosses in Nainital, Almora and Pithoragarh District of Kumaon Region, IndiaDocument5 pagesDistribution of Some Mosses in Nainital, Almora and Pithoragarh District of Kumaon Region, IndiaA Lavate RajendraNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Plants - 5 Stages + Fun Facts - Science4FunDocument8 pagesLife Cycle of Plants - 5 Stages + Fun Facts - Science4FunMasthankhan PatanNo ratings yet
- Kudinkula BiologyDocument113 pagesKudinkula BiologylufeyocliftonNo ratings yet
- Cotton Cultivation in PakistanDocument18 pagesCotton Cultivation in PakistanHamid RazaNo ratings yet
- And Embryo Sac: 2.2.2 The Pistil, Megasporangium (Ovule)Document12 pagesAnd Embryo Sac: 2.2.2 The Pistil, Megasporangium (Ovule)ChandanNo ratings yet
- Major and Minor Cellulosic FibresDocument127 pagesMajor and Minor Cellulosic FibresYou Kno WhoNo ratings yet
- Dơnload Religion in Tudor England An Anthology of Primary Sources 1st Edition Ethan H Shagan Debora Shuger Full ChapterDocument24 pagesDơnload Religion in Tudor England An Anthology of Primary Sources 1st Edition Ethan H Shagan Debora Shuger Full Chapterbacaduaia100% (7)
- Brassica Carinata Biology and Agronomy As A Biofuel CropDocument18 pagesBrassica Carinata Biology and Agronomy As A Biofuel CropRamdeo SeepaulNo ratings yet
- Botany 3.4 DoneDocument3 pagesBotany 3.4 DoneLeslie Ann Potenciano100% (1)
- Janka Hardness TestDocument8 pagesJanka Hardness TestLuiz ImprovizzaNo ratings yet
- Biology XII (12th Grade/Class) MCQs KEYDocument268 pagesBiology XII (12th Grade/Class) MCQs KEYInni CallmeinniNo ratings yet
- Science - Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesScience - Levels of OrganizationAlexNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones - DR - FQDocument47 pagesPlant Hormones - DR - FQUmarNo ratings yet
- Ganga Aquatic Plants PDFDocument48 pagesGanga Aquatic Plants PDFDipakNo ratings yet
- Indoor Orchid Care - How Do I Take Care of An Orchid FlowerDocument13 pagesIndoor Orchid Care - How Do I Take Care of An Orchid Flowerjaz andersonNo ratings yet
- Safety s40 IntDocument2 pagesSafety s40 IntLos Laureles UrbanaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life 2Q ExamDocument5 pagesEarth and Life 2Q ExamImmanuel GranadaNo ratings yet
- Transpiration Diagram-Based QuestionsDocument9 pagesTranspiration Diagram-Based Questionsthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Till Saxby Electric Pallet Truck Egv 10-12-0240 0242 0300 0302 Workshop ManualDocument22 pagesTill Saxby Electric Pallet Truck Egv 10-12-0240 0242 0300 0302 Workshop Manualmichaelfisher030690fgaNo ratings yet
- Agr232 - c5 Principles and Techniques of Propagation by CuttingsDocument38 pagesAgr232 - c5 Principles and Techniques of Propagation by Cuttingsmohamad afifNo ratings yet
- Reading Unit 17:: Bees TextDocument2 pagesReading Unit 17:: Bees Textnaziroh herliaNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants of Pondoland 2012Document82 pagesMedicinal Plants of Pondoland 2012thaboNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy Sheet 2Document1 pageTaxonomy Sheet 2lettresaccelerer.0eNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Part 2A Organisation of Living Things - Nutrient and Gas RequirementsDocument94 pagesMODULE 2 Part 2A Organisation of Living Things - Nutrient and Gas RequirementsZenaNo ratings yet
- Plant Science Today: Genus Notoscyphus Mitt. - New To The Liverwort Flora of The Eastern GhatsDocument3 pagesPlant Science Today: Genus Notoscyphus Mitt. - New To The Liverwort Flora of The Eastern Ghatsmendal sciNo ratings yet
- Botanicon Sinicum, 1895 PDFDocument641 pagesBotanicon Sinicum, 1895 PDFadamtate137483No ratings yet
- 3625 Why Do Bees BuzzDocument17 pages3625 Why Do Bees BuzzSakshi GoelNo ratings yet