Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity Schizophrenia: I. Case Scenario
Activity Schizophrenia: I. Case Scenario
Uploaded by
Dan HizonCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationJulvica HeuwNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking ExerciseDocument1 pageCritical Thinking ExerciseMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Worksheet#2-Maintaining Asepsis: Medical Asepsis Includes All Practices Intended To Confine A SpecificDocument4 pagesWorksheet#2-Maintaining Asepsis: Medical Asepsis Includes All Practices Intended To Confine A SpecificCj MayoyoNo ratings yet
- DS KetosterilDocument1 pageDS KetosteriljessicamaysNo ratings yet
- Filipino Practices in Relation To Care of ClientsDocument7 pagesFilipino Practices in Relation To Care of ClientsTrixia AlmendralNo ratings yet
- Karen's Case StudyDocument12 pagesKaren's Case StudyShamini Subramaniam100% (1)
- Week 7Document2 pagesWeek 7Maria Carmela ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Hizon 2 NCP 1 Npi I Am SamDocument5 pagesHizon 2 NCP 1 Npi I Am SamDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Focus Diagnosis Action ResponseDocument2 pagesFocus Diagnosis Action ResponseGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Renea Joy Arruejo - Activity For LectureDocument2 pagesRenea Joy Arruejo - Activity For LectureRenea Joy Arruejo100% (1)
- NCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainDocument2 pagesNCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainAubrey RecierdoNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain NCPDocument2 pagesAcute Pain NCPCaren AntonioNo ratings yet
- Nurse Patient Themes Therapeutic Technique Rationale Defense Mechanisms Evaluation Verbal Non Verbal Verbal Non VerbalDocument9 pagesNurse Patient Themes Therapeutic Technique Rationale Defense Mechanisms Evaluation Verbal Non Verbal Verbal Non VerbalAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPeun kyung shinNo ratings yet
- Sheryl Ann B. Pedines Bsn-IvDocument2 pagesSheryl Ann B. Pedines Bsn-IvSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- NPI Mariano Psychiatric WardDocument4 pagesNPI Mariano Psychiatric WardAlessandra Dominique MarianoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For CamoxDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For CamoxRolena Johnette B. PiñeroNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPEve DelosoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveAngelaNo ratings yet
- Related Assessment and Provision of Care of Clients With Maladaptive Patterns of BehaviorDocument52 pagesRelated Assessment and Provision of Care of Clients With Maladaptive Patterns of Behaviorgabrielle magdaraogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorNo ratings yet
- Needs/ Problems/Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Nursing Actions RationaleDocument1 pageNeeds/ Problems/Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Nursing Actions RationaleHarold PeranduzNo ratings yet
- Problem PRIORITIZATION and NCP 1, 2, 3 of CataractDocument7 pagesProblem PRIORITIZATION and NCP 1, 2, 3 of CataractEries Lacanlale LumbaNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 Final Exam MamelDocument16 pagesNCM 117 Final Exam MamelJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- Care of Older PersonDocument3 pagesCare of Older PersonIt's EllaaaNo ratings yet
- NCP FoodDocument1 pageNCP FoodAdrian ArdamilNo ratings yet
- CUW5Document2 pagesCUW5Ericka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPjoyce_albertoNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument3 pagesNCP FormatAl Bhert Timbal MagbalotNo ratings yet
- BFC NCPDocument2 pagesBFC NCPMonica Melo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Exit Ticket - Beth Taylor's CaseDocument2 pagesExit Ticket - Beth Taylor's CaseGayle RavanchoNo ratings yet
- NCP For LeptospirosisDocument1 pageNCP For LeptospirosiskyawNo ratings yet
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Document4 pagesFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- N P I Sa M PleDocument1 pageN P I Sa M PleSkyeNo ratings yet
- Defient Fluid Volume Intake and Impaired Mobility NCPDocument6 pagesDefient Fluid Volume Intake and Impaired Mobility NCPjordan aguilarNo ratings yet
- NCP Ch31 p991-992Document2 pagesNCP Ch31 p991-992Ala'a Abd Mansor100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationlaehaaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter III Pathopysiology (Print!!!)Document3 pagesChapter III Pathopysiology (Print!!!)Kismet SummonsNo ratings yet
- NCP Actual and PotentialDocument4 pagesNCP Actual and PotentialKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Navidas-Hearing Impairnent Act.Document2 pagesNavidas-Hearing Impairnent Act.Fran Lan100% (1)
- Working PhaseDocument1 pageWorking PhaseJoan Parlan100% (1)
- Planning For Successful AgingDocument11 pagesPlanning For Successful AgingMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedZharm MayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanCaracel Cabrera SobionoNo ratings yet
- Pao NCPDocument3 pagesPao NCPJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- DeficientDocument2 pagesDeficientVANNEZA TRIXZY TAMPARONGNo ratings yet
- NCP - Altered ComfortDocument2 pagesNCP - Altered ComfortJhudiel Gabriel Go0% (1)
- NCP GoiterDocument1 pageNCP GoiterDavid Calalo67% (3)
- NCP 2Document3 pagesNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- NCP Sleep PatternDocument3 pagesNCP Sleep PatternRA Balaoing100% (1)
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanWilliam Oz CiferNo ratings yet
- D.A. DolcetDocument2 pagesD.A. DolcetSasha FongNo ratings yet
- NPIDocument12 pagesNPIJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- Orbital Trauma NCP and Drug StudyDocument5 pagesOrbital Trauma NCP and Drug StudyDersly LaneNo ratings yet
- Nurse Parient Interaction Thera-Communication and Defense Mechanism Rationale AnalysisDocument6 pagesNurse Parient Interaction Thera-Communication and Defense Mechanism Rationale AnalysisKim S GutierrezNo ratings yet
- NAME: Cañete, Princess Laira V. BSN 3-YB-18Document4 pagesNAME: Cañete, Princess Laira V. BSN 3-YB-18Laira CañeteNo ratings yet
- NAME: Cañete, Princess Laira V. BSN 3-YB-18Document3 pagesNAME: Cañete, Princess Laira V. BSN 3-YB-18Laira CañeteNo ratings yet
- Schiz NCPDocument5 pagesSchiz NCPCharisse LuteroNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 - Graded SeatworkDocument7 pagesNCM 117 - Graded SeatworkShamsa AfdalNo ratings yet
- NCP - Major Depressive DisorderDocument7 pagesNCP - Major Depressive DisorderJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Disturbed Thought Processes DescribeDocument2 pagesDisturbed Thought Processes DescribePRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Hizon, EndocrineDocument3 pagesHizon, EndocrineDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisorderDocument23 pagesThyroid DisorderDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Gulang Gulang National High School 3W-Ilm Q1 Week 1 & 2 Lesson 1 Inquiries, Investigation, and Immersions (3I'S) Grade 12Document22 pagesGulang Gulang National High School 3W-Ilm Q1 Week 1 & 2 Lesson 1 Inquiries, Investigation, and Immersions (3I'S) Grade 12Dan HizonNo ratings yet
- Southern Luzon State University College of Allied MedicineDocument6 pagesSouthern Luzon State University College of Allied MedicineDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Southern Luzon State University College of Allied MedicineDocument5 pagesSouthern Luzon State University College of Allied MedicineDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal and MetabolismDocument5 pagesGastrointestinal and MetabolismDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon, Research Lab Avtivity 2Document2 pagesHizon, Research Lab Avtivity 2Dan HizonNo ratings yet
- Assessme NT Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessme NT Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDan HizonNo ratings yet
- NCM 111 OverviewDocument3 pagesNCM 111 OverviewDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon, Physical AssessmentDocument3 pagesHizon, Physical AssessmentDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon, DrugsDocument4 pagesHizon, DrugsDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Activity Therapeutic Communication-HizonDocument3 pagesActivity Therapeutic Communication-HizonDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Alad Bihag Hizon Medicine Case StudyDocument103 pagesAlad Bihag Hizon Medicine Case StudyDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon Neuro TestDocument3 pagesHizon Neuro TestDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon Interview Group 2Document3 pagesHizon Interview Group 2Dan HizonNo ratings yet
- Activity Abuse and Violence-HizonDocument2 pagesActivity Abuse and Violence-HizonDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - NCM 118: College of Allied MedicineDocument3 pagesActivity 1 - NCM 118: College of Allied MedicineDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Bihag Quiz Medicine AreaDocument5 pagesBihag Quiz Medicine AreaDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Bihag Quiz Medicine AreaDocument5 pagesBihag Quiz Medicine AreaDan HizonNo ratings yet
- OR AppendixDocument9 pagesOR AppendixDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon For Validation 3Document7 pagesHizon For Validation 3Dan HizonNo ratings yet
- Standards For Nursing TerminologyDocument7 pagesStandards For Nursing TerminologyDan HizonNo ratings yet
- If You Are Given The Opportunity To Build A Nursing Home Facility, What Is Your Dream For The Older Person?Document1 pageIf You Are Given The Opportunity To Build A Nursing Home Facility, What Is Your Dream For The Older Person?Dan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon Module 5 QuizDocument2 pagesHizon Module 5 QuizDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 HypothesisDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 HypothesisDan HizonNo ratings yet
- ss9 Canadian Federal Government - Unit PlanDocument5 pagesss9 Canadian Federal Government - Unit Planapi-533354288No ratings yet
- Monitoring and EvaluationDocument22 pagesMonitoring and EvaluationHabibQayumi100% (1)
- Self HypnosisDocument26 pagesSelf HypnosisPoonamBhardwaj100% (2)
- Rogerian ArgumentDocument8 pagesRogerian Argumentapi-262580972100% (1)
- PSYDocument4 pagesPSYSaqib AkramNo ratings yet
- Angel E. Picazo Homeroom Guidance 12-STEM Module#2Document7 pagesAngel E. Picazo Homeroom Guidance 12-STEM Module#2Angel Picazo100% (1)
- RP CH 5 PresentationDocument10 pagesRP CH 5 Presentationapi-273543630No ratings yet
- The Leader HabitDocument5 pagesThe Leader Habitsaisaati2No ratings yet
- My K-F-D Profile: in Art AppreciationDocument3 pagesMy K-F-D Profile: in Art AppreciationJimuel Ace SarmientoNo ratings yet
- How Art Can HealDocument16 pagesHow Art Can HealNguyễn Phạm Minh NgọcNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Report 19 20Document10 pagesComprehensive Report 19 20api-461482219No ratings yet
- Chapter 09presentationsDocument41 pagesChapter 09presentationsAbhinav Suneeth100% (2)
- W 2Document4 pagesW 2Nurul HusnaNo ratings yet
- Williamssara IssuesDocument3 pagesWilliamssara Issuesapi-302192993No ratings yet
- Learners Weekly Home Learning Plan in Introduction To World Religion and Belief System Week 2Document2 pagesLearners Weekly Home Learning Plan in Introduction To World Religion and Belief System Week 2Rolando Corado Rama Gomez Jr.100% (1)
- Skillful LS4 Unit 4 Test - EditableDocument4 pagesSkillful LS4 Unit 4 Test - EditableHoa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Long Test in Practical Research IDocument3 pagesLong Test in Practical Research IJhullian Frederick Val VergaraNo ratings yet
- Elc590 PersuasiveDocument5 pagesElc590 PersuasiveFatien Zakaria50% (2)
- Mapc 001Document11 pagesMapc 001Swarnali MitraNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument5 pagesEthicsBenedict AcuñaNo ratings yet
- P 415 Lecture 021203Document20 pagesP 415 Lecture 021203Shanmugam BalasubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Task 2 - Defining EspDocument12 pagesTask 2 - Defining EspAlvaro Babilonia100% (1)
- Information Systems and NeuroscienceDocument201 pagesInformation Systems and NeuroscienceGavril HabaNo ratings yet
- BookDocument499 pagesBookapi-3813809100% (1)
- 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Lesson PlanDocument25 pages21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Lesson PlanCynthiaZuycoDelusoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document19 pagesChapter 4Ruthwik KolanuNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument17 pagesLearning StylesMariangelaNo ratings yet
- The Relation Between Tranquility and Insight Meditation PDFDocument26 pagesThe Relation Between Tranquility and Insight Meditation PDFjcap11No ratings yet
Activity Schizophrenia: I. Case Scenario
Activity Schizophrenia: I. Case Scenario
Uploaded by
Dan HizonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity Schizophrenia: I. Case Scenario
Activity Schizophrenia: I. Case Scenario
Uploaded by
Dan HizonCopyright:
Available Formats
Southern Luzon State University
College of Allied Medicine
Lucban, Quezon
Hizon, Dan Melton Anthony A
BSN3B
ACTIVITY SCHIZOPHRENIA
I. Case Scenario
John Jones, age 33 has been admitted to the hospital for the third time with a diagnosis of
paranoid schizophrenia. John had been taking haloperidol (Haldol) but stopped taking it weeks
ago, telling his wife it was “the poison that making me sick”. Yesterday, John was brought to the
hospital after neighbors reported him saying, “I can’t do it! They don’t deserve to die!”
John appears guarded and suspicious and has little to say to anyone. His hair is matted, he
has a strong body odor and he is dressed in several layers of heavy clothing even though the
weather is warm. So far, John has been refusing any offers of food or fluids. When the nurse
approached John with a dose of haloperidol, he said “Do you want me to die?”
1. What additional assessment data does the nurse need to plan care for John?
The nurse should assess the amount of sleep during the past few days.
Assess for positive symptoms that the client is manifesting.
Assess the client’s medical history, aside from the medication, the nurse can
assess if the client had been hospitalized previously.
Assess support system. Determine whether the family is well informed about the
disease.
Assess the reason why the client is no longer complying to medication.
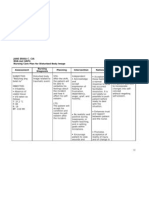
2. Identify the three priorities, nursing diagnosis and expected outcomes for John’s
care with your rationales for the choices.
PRIORITIES NURSING Dx EXPECTED RATIONALE
OUTCOMES
1. Risk for 1. Risk for 1. The client will 1. it would be a
imbalanced imbalanced start to verbalize major issue if
nutrition nutrition what food that he we do not
2. Risk for related to likely to eat stimulate the
insufficient psychological 2. The client will patient's
fluid volume disorder as take at least 3 appetite then
3. Disturbed manifested by glasses of water. the client will
thought insufficient 3. The client will not eat for an
processes interest in food have 5 minute extended period
2. Risk for interactions that of time. This
insufficient are based from might intensify
fluid volume reality his anxiety.
related to 2. Adequate oral
psychological fluid intake is
disorder as important and if
manifested by it is not
refusal of prioritized, it
water intake will have a
3. Disturbed significant
thought impact on his
processes body and
related to increase his
diagnosis of anxiety.
psychological 3. When the
disorder as client's thoughts
manifested by are focused on
inappropriate reality-based
non-reality- events, he or
based thinking she is free of
delusional
thinking. Helps
focus attention
externally.
3. Identify at least two nursing interventions for the three priorities listed in question
no. 2.
PRIORITIES INTERVENTION
1. Risk for imbalanced nutrition Assess the client preference for
food and why he is refusing to eat.
Emphasize importance of food
intake to the client and assure him
that the food to be offered will not
harm him
2. Risk for insufficient fluid volume Identify the cause of refusal of oral
fluid.
Assess skin turgor and administer
IV fluids as ordered
3. Disturbed thought processes Initially do not argue with the
client’s beliefs or try to
convince the client that the
delusions are false and
unreal.
Interact with clients on the
basis of things in the
environment. Try to distract
client from their delusions by
engaging in reality-based
activities.
4. Formulate a teaching plan for John and his family upon discharge.
1. Emphasize to the family the importance of social interaction to the patient.
2. Emphasize the importance of having adequate sleep to reduce the client’s
environment.
3. Emphasize importance of encouraging the patient’s compliance to treatment
regimen.
4. Educate and develop support networks for the families reduces the family's
anxiety, increases their physical and mental health.
5. Educate the family members about the disease and medications used to treat the
disease.
6. Provide information on disease and treatment strategies at the family’s level of
understanding.
7. Instruct the family to keep the patient from a lot of stimulus that might increase
his anxiety.
8. Instruct to report any violence behaviours that the client is manifesting.
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationJulvica HeuwNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking ExerciseDocument1 pageCritical Thinking ExerciseMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Worksheet#2-Maintaining Asepsis: Medical Asepsis Includes All Practices Intended To Confine A SpecificDocument4 pagesWorksheet#2-Maintaining Asepsis: Medical Asepsis Includes All Practices Intended To Confine A SpecificCj MayoyoNo ratings yet
- DS KetosterilDocument1 pageDS KetosteriljessicamaysNo ratings yet
- Filipino Practices in Relation To Care of ClientsDocument7 pagesFilipino Practices in Relation To Care of ClientsTrixia AlmendralNo ratings yet
- Karen's Case StudyDocument12 pagesKaren's Case StudyShamini Subramaniam100% (1)
- Week 7Document2 pagesWeek 7Maria Carmela ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Hizon 2 NCP 1 Npi I Am SamDocument5 pagesHizon 2 NCP 1 Npi I Am SamDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Focus Diagnosis Action ResponseDocument2 pagesFocus Diagnosis Action ResponseGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Renea Joy Arruejo - Activity For LectureDocument2 pagesRenea Joy Arruejo - Activity For LectureRenea Joy Arruejo100% (1)
- NCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainDocument2 pagesNCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainAubrey RecierdoNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain NCPDocument2 pagesAcute Pain NCPCaren AntonioNo ratings yet
- Nurse Patient Themes Therapeutic Technique Rationale Defense Mechanisms Evaluation Verbal Non Verbal Verbal Non VerbalDocument9 pagesNurse Patient Themes Therapeutic Technique Rationale Defense Mechanisms Evaluation Verbal Non Verbal Verbal Non VerbalAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPeun kyung shinNo ratings yet
- Sheryl Ann B. Pedines Bsn-IvDocument2 pagesSheryl Ann B. Pedines Bsn-IvSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- NPI Mariano Psychiatric WardDocument4 pagesNPI Mariano Psychiatric WardAlessandra Dominique MarianoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For CamoxDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For CamoxRolena Johnette B. PiñeroNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPEve DelosoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveAngelaNo ratings yet
- Related Assessment and Provision of Care of Clients With Maladaptive Patterns of BehaviorDocument52 pagesRelated Assessment and Provision of Care of Clients With Maladaptive Patterns of Behaviorgabrielle magdaraogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorNo ratings yet
- Needs/ Problems/Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Nursing Actions RationaleDocument1 pageNeeds/ Problems/Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Nursing Actions RationaleHarold PeranduzNo ratings yet
- Problem PRIORITIZATION and NCP 1, 2, 3 of CataractDocument7 pagesProblem PRIORITIZATION and NCP 1, 2, 3 of CataractEries Lacanlale LumbaNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 Final Exam MamelDocument16 pagesNCM 117 Final Exam MamelJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- Care of Older PersonDocument3 pagesCare of Older PersonIt's EllaaaNo ratings yet
- NCP FoodDocument1 pageNCP FoodAdrian ArdamilNo ratings yet
- CUW5Document2 pagesCUW5Ericka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPjoyce_albertoNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument3 pagesNCP FormatAl Bhert Timbal MagbalotNo ratings yet
- BFC NCPDocument2 pagesBFC NCPMonica Melo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Exit Ticket - Beth Taylor's CaseDocument2 pagesExit Ticket - Beth Taylor's CaseGayle RavanchoNo ratings yet
- NCP For LeptospirosisDocument1 pageNCP For LeptospirosiskyawNo ratings yet
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Document4 pagesFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- N P I Sa M PleDocument1 pageN P I Sa M PleSkyeNo ratings yet
- Defient Fluid Volume Intake and Impaired Mobility NCPDocument6 pagesDefient Fluid Volume Intake and Impaired Mobility NCPjordan aguilarNo ratings yet
- NCP Ch31 p991-992Document2 pagesNCP Ch31 p991-992Ala'a Abd Mansor100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationlaehaaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter III Pathopysiology (Print!!!)Document3 pagesChapter III Pathopysiology (Print!!!)Kismet SummonsNo ratings yet
- NCP Actual and PotentialDocument4 pagesNCP Actual and PotentialKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Navidas-Hearing Impairnent Act.Document2 pagesNavidas-Hearing Impairnent Act.Fran Lan100% (1)
- Working PhaseDocument1 pageWorking PhaseJoan Parlan100% (1)
- Planning For Successful AgingDocument11 pagesPlanning For Successful AgingMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedZharm MayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanCaracel Cabrera SobionoNo ratings yet
- Pao NCPDocument3 pagesPao NCPJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- DeficientDocument2 pagesDeficientVANNEZA TRIXZY TAMPARONGNo ratings yet
- NCP - Altered ComfortDocument2 pagesNCP - Altered ComfortJhudiel Gabriel Go0% (1)
- NCP GoiterDocument1 pageNCP GoiterDavid Calalo67% (3)
- NCP 2Document3 pagesNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- NCP Sleep PatternDocument3 pagesNCP Sleep PatternRA Balaoing100% (1)
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanWilliam Oz CiferNo ratings yet
- D.A. DolcetDocument2 pagesD.A. DolcetSasha FongNo ratings yet
- NPIDocument12 pagesNPIJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- Orbital Trauma NCP and Drug StudyDocument5 pagesOrbital Trauma NCP and Drug StudyDersly LaneNo ratings yet
- Nurse Parient Interaction Thera-Communication and Defense Mechanism Rationale AnalysisDocument6 pagesNurse Parient Interaction Thera-Communication and Defense Mechanism Rationale AnalysisKim S GutierrezNo ratings yet
- NAME: Cañete, Princess Laira V. BSN 3-YB-18Document4 pagesNAME: Cañete, Princess Laira V. BSN 3-YB-18Laira CañeteNo ratings yet
- NAME: Cañete, Princess Laira V. BSN 3-YB-18Document3 pagesNAME: Cañete, Princess Laira V. BSN 3-YB-18Laira CañeteNo ratings yet
- Schiz NCPDocument5 pagesSchiz NCPCharisse LuteroNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 - Graded SeatworkDocument7 pagesNCM 117 - Graded SeatworkShamsa AfdalNo ratings yet
- NCP - Major Depressive DisorderDocument7 pagesNCP - Major Depressive DisorderJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Disturbed Thought Processes DescribeDocument2 pagesDisturbed Thought Processes DescribePRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Hizon, EndocrineDocument3 pagesHizon, EndocrineDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisorderDocument23 pagesThyroid DisorderDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Gulang Gulang National High School 3W-Ilm Q1 Week 1 & 2 Lesson 1 Inquiries, Investigation, and Immersions (3I'S) Grade 12Document22 pagesGulang Gulang National High School 3W-Ilm Q1 Week 1 & 2 Lesson 1 Inquiries, Investigation, and Immersions (3I'S) Grade 12Dan HizonNo ratings yet
- Southern Luzon State University College of Allied MedicineDocument6 pagesSouthern Luzon State University College of Allied MedicineDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Southern Luzon State University College of Allied MedicineDocument5 pagesSouthern Luzon State University College of Allied MedicineDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal and MetabolismDocument5 pagesGastrointestinal and MetabolismDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon, Research Lab Avtivity 2Document2 pagesHizon, Research Lab Avtivity 2Dan HizonNo ratings yet
- Assessme NT Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessme NT Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDan HizonNo ratings yet
- NCM 111 OverviewDocument3 pagesNCM 111 OverviewDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon, Physical AssessmentDocument3 pagesHizon, Physical AssessmentDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon, DrugsDocument4 pagesHizon, DrugsDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Activity Therapeutic Communication-HizonDocument3 pagesActivity Therapeutic Communication-HizonDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Alad Bihag Hizon Medicine Case StudyDocument103 pagesAlad Bihag Hizon Medicine Case StudyDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon Neuro TestDocument3 pagesHizon Neuro TestDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon Interview Group 2Document3 pagesHizon Interview Group 2Dan HizonNo ratings yet
- Activity Abuse and Violence-HizonDocument2 pagesActivity Abuse and Violence-HizonDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - NCM 118: College of Allied MedicineDocument3 pagesActivity 1 - NCM 118: College of Allied MedicineDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Bihag Quiz Medicine AreaDocument5 pagesBihag Quiz Medicine AreaDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Bihag Quiz Medicine AreaDocument5 pagesBihag Quiz Medicine AreaDan HizonNo ratings yet
- OR AppendixDocument9 pagesOR AppendixDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon For Validation 3Document7 pagesHizon For Validation 3Dan HizonNo ratings yet
- Standards For Nursing TerminologyDocument7 pagesStandards For Nursing TerminologyDan HizonNo ratings yet
- If You Are Given The Opportunity To Build A Nursing Home Facility, What Is Your Dream For The Older Person?Document1 pageIf You Are Given The Opportunity To Build A Nursing Home Facility, What Is Your Dream For The Older Person?Dan HizonNo ratings yet
- Hizon Module 5 QuizDocument2 pagesHizon Module 5 QuizDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 HypothesisDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 HypothesisDan HizonNo ratings yet
- ss9 Canadian Federal Government - Unit PlanDocument5 pagesss9 Canadian Federal Government - Unit Planapi-533354288No ratings yet
- Monitoring and EvaluationDocument22 pagesMonitoring and EvaluationHabibQayumi100% (1)
- Self HypnosisDocument26 pagesSelf HypnosisPoonamBhardwaj100% (2)
- Rogerian ArgumentDocument8 pagesRogerian Argumentapi-262580972100% (1)
- PSYDocument4 pagesPSYSaqib AkramNo ratings yet
- Angel E. Picazo Homeroom Guidance 12-STEM Module#2Document7 pagesAngel E. Picazo Homeroom Guidance 12-STEM Module#2Angel Picazo100% (1)
- RP CH 5 PresentationDocument10 pagesRP CH 5 Presentationapi-273543630No ratings yet
- The Leader HabitDocument5 pagesThe Leader Habitsaisaati2No ratings yet
- My K-F-D Profile: in Art AppreciationDocument3 pagesMy K-F-D Profile: in Art AppreciationJimuel Ace SarmientoNo ratings yet
- How Art Can HealDocument16 pagesHow Art Can HealNguyễn Phạm Minh NgọcNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Report 19 20Document10 pagesComprehensive Report 19 20api-461482219No ratings yet
- Chapter 09presentationsDocument41 pagesChapter 09presentationsAbhinav Suneeth100% (2)
- W 2Document4 pagesW 2Nurul HusnaNo ratings yet
- Williamssara IssuesDocument3 pagesWilliamssara Issuesapi-302192993No ratings yet
- Learners Weekly Home Learning Plan in Introduction To World Religion and Belief System Week 2Document2 pagesLearners Weekly Home Learning Plan in Introduction To World Religion and Belief System Week 2Rolando Corado Rama Gomez Jr.100% (1)
- Skillful LS4 Unit 4 Test - EditableDocument4 pagesSkillful LS4 Unit 4 Test - EditableHoa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Long Test in Practical Research IDocument3 pagesLong Test in Practical Research IJhullian Frederick Val VergaraNo ratings yet
- Elc590 PersuasiveDocument5 pagesElc590 PersuasiveFatien Zakaria50% (2)
- Mapc 001Document11 pagesMapc 001Swarnali MitraNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument5 pagesEthicsBenedict AcuñaNo ratings yet
- P 415 Lecture 021203Document20 pagesP 415 Lecture 021203Shanmugam BalasubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Task 2 - Defining EspDocument12 pagesTask 2 - Defining EspAlvaro Babilonia100% (1)
- Information Systems and NeuroscienceDocument201 pagesInformation Systems and NeuroscienceGavril HabaNo ratings yet
- BookDocument499 pagesBookapi-3813809100% (1)
- 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Lesson PlanDocument25 pages21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Lesson PlanCynthiaZuycoDelusoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document19 pagesChapter 4Ruthwik KolanuNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument17 pagesLearning StylesMariangelaNo ratings yet
- The Relation Between Tranquility and Insight Meditation PDFDocument26 pagesThe Relation Between Tranquility and Insight Meditation PDFjcap11No ratings yet