Professional Documents
Culture Documents
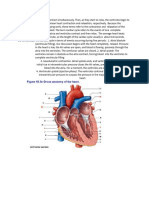
List The Chambers/vessels That The Four Valves Connect:: The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Cycle
List The Chambers/vessels That The Four Valves Connect:: The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Cycle
Uploaded by
KathiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
List The Chambers/vessels That The Four Valves Connect:: The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Cycle
List The Chambers/vessels That The Four Valves Connect:: The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Cycle
Uploaded by
KathiCopyright:
Available Formats
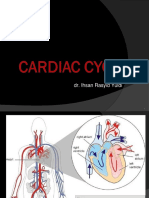
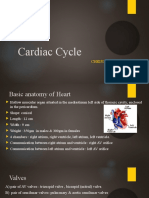
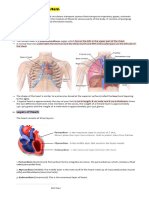
The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Cycle
1. Valves open in response to difference in blood pressure on their two sides.
2. List the chambers/vessels that the four valves connect:
Chamber Chamber/Vessel
Right ventricle Pulmonary Semilunar Pulmonary trunk
Left ventricle Aortic Semilunar Semilunar aorta
Left atrium Left AV Left ventricle
Right atrium Right AV Right ventricle
3. a. Ventricular filling occurs during mid to late ventricular diastole .
b. Blood flows through the AV or mitral/tricuspid valves into the ventricles.
4. During Ventricular Systole, what closes the AV valves?
Intraventricular pressure is greater than atrial pressure
5. During Ventricular Systole, what opens the semilunar valves?
Intraventricular pressure is greater than pressure in the pulmonary trunk and aorta
6. During Isovolumetric Relaxation, what closes the semilunar valves?
Bloodflow back toward the heart- due to aortic pressure being greater than intraventricular pressure
7. During Isovolumetric Relaxation, what opens the AV valves?
Atrial pressure is greater than intraventricular pressure
8. Why is hypertension hard on the heart? Is it increased preload or afterload?
With hypertension, the ventricular pressure must rise higher to open the semilunar valves. For the same
increase in pressure in a normotensive person, less blood is ejected in a hypertensive person. Thus, the
heart of someone with hypertension must work harder to eject the same stroke volume due to an increased
afterload.
9. How can stroke volume be calculated?
STROKE VOLUME = (End-diastolic volume)-(End-systolic volume)
10. During the four phases listed below, state whether the AV and semilunar
valves are opened or closed:
AV valves Semilunar valves
Ventricular Filling Opened Closed
Isovolumetric Contraction Closed Closed
Ventricular Ejection Closed Opened
Isovolumetric Relaxation Closed Closed
You might also like
- Chem 1220 Assignment 3Document3 pagesChem 1220 Assignment 3Kathi100% (1)
- Chem 1220 Assignment 4Document5 pagesChem 1220 Assignment 4KathiNo ratings yet
- FIN 1050 - Final ExamDocument6 pagesFIN 1050 - Final ExamKathi100% (1)
- Biology Class Note-Cardiac CycleDocument1 pageBiology Class Note-Cardiac CycleJack KowmanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle CardiodynamicsDocument29 pagesCardiac Cycle Cardiodynamicseverforyou2023No ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument4 pagesCardiac CyclefailinNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle 2Document7 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle 2Abigail ChristisnNo ratings yet
- Functions of Cardiovascular System:: The Gross AnatomyDocument6 pagesFunctions of Cardiovascular System:: The Gross AnatomyShreyasi PatankarNo ratings yet
- Module 13Document1 pageModule 13A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Lecture 1 - 2023 2024Document31 pagesCardiovascular Lecture 1 - 2023 2024inegbenosegideonNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument11 pagesCardiac Cyclemadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle - Atrial Contraction (Phase 1) : A-V Valves Open Semilunar Valves ClosedDocument10 pagesCardiac Cycle - Atrial Contraction (Phase 1) : A-V Valves Open Semilunar Valves ClosedFatima KhanNo ratings yet
- Blood Flow Through HeartDocument1 pageBlood Flow Through HeartMatthew Alan BrittonNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle - Atrial Contraction (Phase 1)Document10 pagesCardiac Cycle - Atrial Contraction (Phase 1)Fatima KhanNo ratings yet
- Animal Transport Revision NotesDocument19 pagesAnimal Transport Revision NotesNada Abu ShweimehNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle: Dr. Ahmed Al-Sayed HassanDocument29 pagesCardiac Cycle: Dr. Ahmed Al-Sayed HassanHussain GauharNo ratings yet
- 04-The Cardiac Cycle - Wigger's Diagram (J Swanevelder)Document6 pages04-The Cardiac Cycle - Wigger's Diagram (J Swanevelder)Patrick WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 4.4iii CardiacCycle SsDocument33 pages4.4iii CardiacCycle Sswashmaarshad11No ratings yet
- Heart PDFDocument67 pagesHeart PDFMuhammad Syafi'iNo ratings yet
- C8 (Transport System)Document26 pagesC8 (Transport System)nurhasinahabrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Card WPS OfficeDocument19 pagesChapter 12 Card WPS OfficeKaye CepedaNo ratings yet
- CARDIAC CYCLE New For StudentDocument54 pagesCARDIAC CYCLE New For StudentDavi DzikirianNo ratings yet
- Physiology (Code) - Year 2Document20 pagesPhysiology (Code) - Year 2bgj9cddvxhNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument4 pagesCardiac CycleDivya RanasariaNo ratings yet
- Heart PathophysiologyDocument20 pagesHeart PathophysiologyDoctorDrapion100% (2)
- CH 6 - The Circulatory System PDFDocument11 pagesCH 6 - The Circulatory System PDFAnonymous e6LINHNo ratings yet
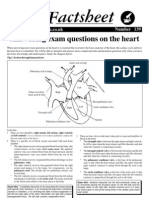
- Bio Factsheet: Answering Exam Questions On The HeartDocument5 pagesBio Factsheet: Answering Exam Questions On The Heartapi-213276898No ratings yet
- Riya Arya - 21msc1279 - Biology For ChemistsDocument13 pagesRiya Arya - 21msc1279 - Biology For ChemistsSwadesh SenNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument30 pagesCardiac CycleAdel100% (1)
- Embryology: HeartDocument46 pagesEmbryology: HeartRahul K. JagaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle ExplainedDocument5 pagesCardiac Cycle ExplainedCai Peng FeiNo ratings yet
- Wiki Heart ChamberDocument4 pagesWiki Heart Chamberdgina8800No ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument37 pagesCardiac CycleEltika utariNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The HeartHerman DjawaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular ReportDocument7 pagesCardiovascular ReportFaith MarfilNo ratings yet
- The Heart ValvesDocument7 pagesThe Heart ValvesJordan MosesNo ratings yet
- Valve SurgeriesDocument13 pagesValve SurgeriesShreeja SajitNo ratings yet
- 8.1 The Circulatory SystemDocument172 pages8.1 The Circulatory Systemnie20060301No ratings yet
- Maintenance of The Body: Cardiovascular SystemDocument74 pagesMaintenance of The Body: Cardiovascular Systemdania mauriyanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7b_Cardiovascular SystemDocument59 pagesLecture 7b_Cardiovascular SystemNathaniel GuirhemNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System - Part 2 4-8-14 For BBDocument23 pagesCirculatory System - Part 2 4-8-14 For BBroman7dbNo ratings yet
- The Heart of The MatterDocument33 pagesThe Heart of The MatterhuangsoulNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac CycleDocument19 pagesThe Cardiac CycleRebi NesroNo ratings yet
- 8.1b. Systole-Diastole & Cardiac CycleDocument34 pages8.1b. Systole-Diastole & Cardiac Cycleverysedatedx100% (1)
- Structure and Function of The HeartDocument5 pagesStructure and Function of The HeartThereseNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument2 pagesCardiac CyclevamshidhNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument31 pagesCardiac CycleAdwaitha KrNo ratings yet
- The Heart of The MatterDocument33 pagesThe Heart of The MatterSETH VILORIANo ratings yet
- Chapter 020Document54 pagesChapter 020Mar3RDi MusicNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac CycleDocument9 pagesThe Cardiac CycleKaylababy Hamilton BlackNo ratings yet
- مذكرة فرست الزمالة المجمعةDocument160 pagesمذكرة فرست الزمالة المجمعةmahi_elsemary7011100% (1)
- Heart ValveDocument3 pagesHeart ValveKhairunnisa InnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Heart and Neck VesselsDocument10 pagesChapter 20 Heart and Neck Vesselsannoja selvaNo ratings yet
- CARDIAC CYCLE New For StudentDocument54 pagesCARDIAC CYCLE New For StudentDavi DzikirianNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle - WikipediaDocument13 pagesCardiac Cycle - WikipediaHarshal GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartMikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- Cvsa 1Document5 pagesCvsa 1rosednova3No ratings yet
- CVS, Dr. Ahmad Alarabi 2016-17Document74 pagesCVS, Dr. Ahmad Alarabi 2016-17crad toNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Beating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartFrom EverandBeating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartNo ratings yet
- Chem 1220 Assignment 2Document4 pagesChem 1220 Assignment 2KathiNo ratings yet
- Chem 1220 Assignment 1Document2 pagesChem 1220 Assignment 1Kathi100% (1)