Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Calvin Cycle: Light Independent Reactions
The Calvin Cycle: Light Independent Reactions
Uploaded by
sintapuspitaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Calvin Cycle: Light Independent Reactions
The Calvin Cycle: Light Independent Reactions
Uploaded by
sintapuspitaCopyright:
Available Formats
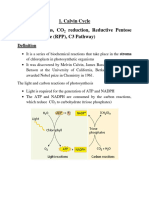
THE CALVIN CYCLE
Light independent reactions or the calvin
cycle known as second stage of photosynthesis.
The calvin cycle needs carbon dioxide to
synthesizing sugar. In plants carbon dioxide
enters the interior of a leaf via pores called
stomata and diffuses into the stroma –the site of
the calvin cycle reaction. The reactions are also
called light independent reactions because the
reaction are not directly driven by light.
The calvin cycle takes ATP and NADPH from the light reactions to convert carbon
dioxide and used to build three-carbon sugars. It takes place in the stroma unlike the light
reaction take place in thylakoid membrane.
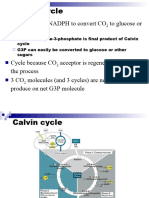
The calvin cycle have three main
steps, they are carbon fixation, reduction,
and regeneration of the staring molecule.
Carbon fixation, three molecules of
carbon dioxide is fixed by the enzyme
RuBisCo that catalyzes the carboxylation
and deavage of Rubp (ribulose – 1,5
biphosphate) into two molecules of a
three carbon compound (3 –
phosphoglyceric acid). Reduction is the
second step, ATP and NADPH are used
to convert the 3–PGA into a three carbon
sugars (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphat /
G3P), in this step reduction gets name because NADPH donates electrons or reduces a three
carbon intermediate to make G3P. The last, regeneration. Some G3P molecules go to make
glucose, while others must be recycled to regenerate the Rubp acceptor. Regeneration requires
ATP and involves a complex network of reactions.
You might also like
- The Calvin CycleDocument4 pagesThe Calvin CycleVerena Raga100% (1)
- 5.12C The Calvin CycleDocument2 pages5.12C The Calvin Cyclemadeline macalaladNo ratings yet
- The Krebs CycleDocument4 pagesThe Krebs CycleAliaNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesCalvin Cycleela ravenaNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle Reaction of Photosynthesis Reflection PaperDocument1 pageCalvin Cycle Reaction of Photosynthesis Reflection PaperMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Independent Reactions Because They Are Not Directly Driven by LightDocument3 pagesIndependent Reactions Because They Are Not Directly Driven by LightPauline TayabanNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument3 pagesCalvin Cyclekumarscribd5482No ratings yet
- Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)Document1 pageLight-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)Xavier Guell ParadisNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument5 pagesCalvin CycleSaman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument21 pagesCalvin Cyclejadenikomariano2132No ratings yet
- Just Like As Miss Aldana SaidDocument1 pageJust Like As Miss Aldana SaidGliane, Adrie Ann C.No ratings yet
- Light IndepDocument19 pagesLight IndepiasdfasfsfasfsNo ratings yet
- The Calvin Cycle - Dark ReactionDocument2 pagesThe Calvin Cycle - Dark ReactionVanna Shane MadejaNo ratings yet
- Calvin-Cycle ReviewerDocument2 pagesCalvin-Cycle Reviewer2JoshDaveTernedaNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 Biosynthetic PhaseDocument14 pagesPresentation1 Biosynthetic PhaseKalyani SreejithNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5. (Photosynthesis 3)Document3 pagesLesson 5. (Photosynthesis 3)Cristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Document3 pagesPhotosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Althea EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument5 pagesCalvin Cyclemingibabie2025No ratings yet
- The Light Reaction Events and Calvin Cycle of PhotosynthesisDocument17 pagesThe Light Reaction Events and Calvin Cycle of PhotosynthesisAngel Mae Masa FloresNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Photosynthesis in Plants Educational Presentation in Green and Yellow Illustrative StyleDocument53 pagesThe Basics of Photosynthesis in Plants Educational Presentation in Green and Yellow Illustrative Styleefesonbantillo18No ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument7 pagesCalvin CycleJoshua AguilaNo ratings yet
- Significant Events of The Calvin CycleDocument15 pagesSignificant Events of The Calvin CycleClaire MNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle Steps and DiagramDocument12 pagesCalvin Cycle Steps and Diagrammaria genio100% (1)
- The Calvin Cycle Dark Reaction G1Document15 pagesThe Calvin Cycle Dark Reaction G1GeminiNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument2 pagesCalvin CycleJoyce Anne Mae AdorioNo ratings yet
- Calvi CycleDocument16 pagesCalvi CycleLenor TunacNo ratings yet
- CALVIN CycleDocument13 pagesCALVIN CycleDaphne CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle General Biology Short SummaryDocument1 pageCarbon Cycle General Biology Short SummaryANO BYNOUUSNo ratings yet
- Light IndependentDocument31 pagesLight IndependentMadame UrsulaNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument1 pageThe Calvin CyclepeachyskizNo ratings yet
- Reactions of The Calvin CycleDocument1 pageReactions of The Calvin CycleFred CanamaNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument7 pagesCalvin Cyclehasan jamiNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument8 pagesThe Calvin CycleAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- Function of Carbon Dioxide in PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesFunction of Carbon Dioxide in Photosynthesisapi-310095373No ratings yet
- Biology ReviwerDocument7 pagesBiology Reviwerapi-709918261No ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument4 pagesGeneral BiologyCIANO, Dellaney Joy A.No ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesCalvin CycleELVIRA L. ABULOKNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceDocument39 pagesFundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceAlthea DoradoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer: Lesson 6.3: "Photosynthesis"Document4 pagesReviewer: Lesson 6.3: "Photosynthesis"Blair CaguioaNo ratings yet
- Q2Week-2 PhotosynthesisDocument36 pagesQ2Week-2 Photosynthesisjustin charles jerimy raymundoNo ratings yet
- Notes Calvin CycleDocument2 pagesNotes Calvin Cycleneelp331No ratings yet
- Bio 11 c4 and CAMDocument15 pagesBio 11 c4 and CAMBik WodeNo ratings yet
- Labador, Wenyl B. Bs-CriminologyDocument5 pagesLabador, Wenyl B. Bs-CriminologyBon TikNo ratings yet
- Light Independent Reaction - BiologyDocument3 pagesLight Independent Reaction - BiologyHidayah SakinahNo ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Carbohydrate synthesis (Calvin Cycle) : Lectured by Dr. Qin Yongmei (秦咏梅) :Nov. 28, 2007Document55 pagesPhotosynthetic Carbohydrate synthesis (Calvin Cycle) : Lectured by Dr. Qin Yongmei (秦咏梅) :Nov. 28, 2007bbaaddaarrNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesThe Calvin CycleNeha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 206 L6 Photosynthesis C3Document48 pages206 L6 Photosynthesis C3craigNo ratings yet
- Light Independent ReactionDocument10 pagesLight Independent ReactionazwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- Akshya PDFDocument13 pagesAkshya PDFSarvesh RautNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Reading Questions-1-1Document2 pagesChapter 7 Reading Questions-1-1Default AccountNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument21 pagesCalvin CycleBelac ZepolNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle UpdatedDocument31 pagesCalvin Cycle UpdatedClipNo ratings yet
- Division of Cebu Lilo-An National High School - Senior High: Department of Education (Deped)Document5 pagesDivision of Cebu Lilo-An National High School - Senior High: Department of Education (Deped)Jeston Mar BayogNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Document5 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Maria Bettina DizonNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument6 pagesCalvin CycleAtika ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle 2023Document12 pagesCalvin Cycle 2023Luisa Antonia F. MaligNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Reading QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Reading QuestionsDefault AccountNo ratings yet
- GB1 Q2 Week-3Document7 pagesGB1 Q2 Week-3Ian JamesNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument26 pagesPhotosynthesisAdithya RajeshNo ratings yet
- Nanoporous Catalysts for Biomass ConversionFrom EverandNanoporous Catalysts for Biomass ConversionFeng-Shou XiaoNo ratings yet