Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Partograph Use
Partograph Use
Uploaded by
Julianne B. Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Intellectual RevolutionsDocument2 pagesIntellectual RevolutionsJulianne B. Dela Cruz89% (19)
- Essential Intrapartum and Newborn Care (EINC)Document26 pagesEssential Intrapartum and Newborn Care (EINC)Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Taking Anthropometric Measurements of NewbornDocument25 pagesTaking Anthropometric Measurements of NewbornClarissa MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Bag Technique ChecklistDocument2 pagesBag Technique ChecklistDanz KieNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingDocument47 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingBella OllieNo ratings yet
- Perineal Episiotomy Care Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesPerineal Episiotomy Care Teaching Planapi-3396685440% (1)
- Application of BindersDocument3 pagesApplication of BindersJayson Tom Briva Capaz100% (1)
- Acetic Acid TestDocument1 pageAcetic Acid Testlauriceannemarie100% (1)
- Health Teaching PlanDocument11 pagesHealth Teaching PlanVic Intia Paa100% (1)
- Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Home VisitDocument5 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Home VisitJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Clinic VisitDocument6 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Clinic VisitJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument12 pagesNursing Care During LaborJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practice in ObstetricsDocument17 pagesEvidence Based Practice in ObstetricsAnn Merlin JobinNo ratings yet
- Po No Breast RationaleDocument4 pagesPo No Breast Rationalearnold john boniteNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument5 pagesAbdominal ExaminationAnuradha MauryaNo ratings yet
- PartographDocument6 pagesPartographalyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- What Is Cord Care?Document2 pagesWhat Is Cord Care?Wenalyn Grace Abella LlavanNo ratings yet
- DR Instrument (Recovered)Document25 pagesDR Instrument (Recovered)Mayolianne DumayNo ratings yet
- Breast Care and Assisting in BreastfeedingDocument7 pagesBreast Care and Assisting in BreastfeedingBJ FernandezNo ratings yet
- 1-Significance and Purposes of Nursing ResearchDocument22 pages1-Significance and Purposes of Nursing ResearchPrincess Ivan Gayagoy100% (1)
- Maternity and Newborn MedicationsDocument38 pagesMaternity and Newborn MedicationsJaypee Fabros EdraNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dystocia NCPDocument6 pagesShoulder Dystocia NCPNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- MCN RLE Sitz Bath Procedure ChecklistDocument3 pagesMCN RLE Sitz Bath Procedure ChecklistHannah Angelu Cabading100% (1)
- Conducting Normal DeliveryDocument3 pagesConducting Normal DeliveryNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Breast Care ChecklistDocument3 pagesBreast Care ChecklistNeil Nette ReynaldoNo ratings yet
- Breast Care Means Care Given To The Breast by The Mother During Her Prenatal Period, Intranatal Period and Postnatal PeriodDocument6 pagesBreast Care Means Care Given To The Breast by The Mother During Her Prenatal Period, Intranatal Period and Postnatal PeriodCagabcab Canibel MelanyNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Labor As One of The Intrapartal ComplicationsDocument23 pagesDysfunctional Labor As One of The Intrapartal ComplicationsKenje Kate AgripoNo ratings yet
- Wiedenbach's TheoryDocument41 pagesWiedenbach's TheoryAnnaya KhanNo ratings yet
- NCP Fever 1Document11 pagesNCP Fever 1Deepak VermaNo ratings yet
- MCN NCPDocument6 pagesMCN NCPIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Finalrationale CAGABCABDocument9 pagesFinalrationale CAGABCABCagabcab Canibel MelanyNo ratings yet
- Thermometer TechniqueDocument6 pagesThermometer TechniqueJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Immediate Care of NewbornDocument21 pagesImmediate Care of NewbornRaida Marañon Ibrahim100% (2)
- Nursing Care of The NewbornDocument56 pagesNursing Care of The NewbornAngie Zimmerman DreilingNo ratings yet
- Apgar Score ChecklistDocument3 pagesApgar Score ChecklistAnnica Lozano100% (2)
- The PartographDocument65 pagesThe PartographAmyAgustinNo ratings yet
- Rubin's TheoryDocument3 pagesRubin's TheoryBeerna Grande50% (2)
- Individual ConferenceDocument19 pagesIndividual Conferencevincentsharon86% (7)
- Lumbar Puncture ReportDocument5 pagesLumbar Puncture ReportTweenie DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Baby BathDocument7 pagesBaby Bathavinash shindeNo ratings yet
- Skill 11 (1) ..Collection of Stool SpecimenDocument1 pageSkill 11 (1) ..Collection of Stool SpecimennetsquadNo ratings yet
- Kannaki (BREAST CARE)Document16 pagesKannaki (BREAST CARE)Jalajarani AridassNo ratings yet
- IV Meds in Volumetric Set C RationaleDocument2 pagesIV Meds in Volumetric Set C RationalePascal Marie IzhaqNo ratings yet
- Leopold's ManeuverDocument22 pagesLeopold's ManeuverArlene Cerdeña Salceda100% (1)
- English Ii Assignment: Midwifery Management in Cephalopelvic DisproportionDocument14 pagesEnglish Ii Assignment: Midwifery Management in Cephalopelvic DisproportionBintari Ancinonyx JubatusNo ratings yet
- Case Study..Care PlanDocument6 pagesCase Study..Care PlanPabhat Kumar0% (1)
- Clinical Objectives GuidelinesDocument11 pagesClinical Objectives GuidelinesprowritttersNo ratings yet
- Hot Sitz BathDocument10 pagesHot Sitz BathJohn Aladin ArcetaNo ratings yet
- RH Incompatibility Resource UnitDocument6 pagesRH Incompatibility Resource UnitJannah Marie A. DimaporoNo ratings yet
- Chapter24 PDFDocument43 pagesChapter24 PDFCindy MaslagNo ratings yet
- Obstetric & Gynaecological NursingDocument30 pagesObstetric & Gynaecological NursingSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- FAMILY PLanning FinalDocument23 pagesFAMILY PLanning FinalLebo Ramokolo100% (1)
- Role of The Head NurseDocument12 pagesRole of The Head Nurseمحمود على ما تفرج75% (4)
- Patient Assignment MethodDocument48 pagesPatient Assignment Methodsathya Arunkumar100% (1)
- Newborn Care ProcedureDocument6 pagesNewborn Care ProcedureHannah VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS Ectopic Pregnancy Part 1Document10 pagesCASE ANALYSIS Ectopic Pregnancy Part 1Diane Celine SantianoNo ratings yet
- Case Study NSVDDocument25 pagesCase Study NSVDLanju FerminNo ratings yet
- Partograph UseDocument8 pagesPartograph UseAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Cmca SLDocument17 pagesNCM 107 Cmca SLAshitaka100% (1)
- NFDN 2004 - Unit 4.3 - JLB StudentDocument43 pagesNFDN 2004 - Unit 4.3 - JLB StudentkendrabooboooNo ratings yet
- Management of First Stage of Labour: Prepared By: Nirsuba Gurung Assistant Lecturer MsonDocument55 pagesManagement of First Stage of Labour: Prepared By: Nirsuba Gurung Assistant Lecturer MsonBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Management of First Stage of LabourDocument55 pagesManagement of First Stage of LabourBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On Normal LaborDocument62 pagesCase Presentation On Normal LaborB34-YvesJethro ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Partograph & LCGDocument12 pagesThe Partograph & LCGعلي حسين خليلNo ratings yet
- Thermometer TechniqueDocument6 pagesThermometer TechniqueJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Bag Technique: Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1Document5 pagesBag Technique: Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Food AdvertisementDocument1 pageFood AdvertisementJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Notions of Development That May Evolve Into ScientismDocument2 pagesNotions of Development That May Evolve Into ScientismJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument12 pagesNursing Care During LaborJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Administering Opthalmic MedicationsDocument6 pagesAdministering Opthalmic MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument12 pagesNursing Care During LaborJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Historical Antecedents in The Course of Science and TechnologyDocument1 pageHistorical Antecedents in The Course of Science and TechnologyJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument10 pagesNursing Care During LaborAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- Administering Intradermal MedicationsDocument4 pagesAdministering Intradermal MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MMDST FormDocument3 pagesMMDST FormJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- APGAR Scoring and Ballard's Assessment ToolDocument2 pagesAPGAR Scoring and Ballard's Assessment ToolJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Basketball: Vision: Mission: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesBasketball: Vision: Mission: ObjectivesJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument1 pageHealth Teaching PlanJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of Systems: Involuntarily Blinking Pink ConjunctivaDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of Systems: Involuntarily Blinking Pink ConjunctivaJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Administering Opthalmic MedicationsDocument6 pagesAdministering Opthalmic MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument9 pagesHealth Teaching PlanJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Patient P / Room No. 415 - 1Document3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Patient P / Room No. 415 - 1Julianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- 1 Endorsement NotesDocument1 page1 Endorsement NotesJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Histolytica) Vaginalis) Brucei) Donovani)Document2 pagesHistolytica) Vaginalis) Brucei) Donovani)Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Postpartum CareDocument11 pagesOptimizing Postpartum Carengga.makasihNo ratings yet
- Antenatal CareDocument38 pagesAntenatal CareMominah MayamNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Breech DeliveryDocument34 pagesVaginal Breech Deliveryicursuii icursuiiNo ratings yet
- Antenatal and Intrapartum Prediction Dystocia ShoulderDocument7 pagesAntenatal and Intrapartum Prediction Dystocia ShoulderDewiDwipayantiGiriNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Flash On English in The HospitalDocument11 pagesUnit 3 Flash On English in The HospitalKartonoNo ratings yet
- The Use of Maternity Acupuncture Within A New Zealand Public Hospital: Integration Within An Outpatient ClinicDocument5 pagesThe Use of Maternity Acupuncture Within A New Zealand Public Hospital: Integration Within An Outpatient ClinicjjNo ratings yet
- Large For Gestational Age Baby - Feb21Document2 pagesLarge For Gestational Age Baby - Feb21saheemmirNo ratings yet
- Vasa Praevia RCOG GTGDocument13 pagesVasa Praevia RCOG GTGMariaBrincatNo ratings yet
- QMMC History - PE FormDocument1 pageQMMC History - PE FormPrisbert W. AlejoNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report FEBRUARYDocument14 pagesAccomplishment Report FEBRUARYYam Aba DianoNo ratings yet
- Miscarriage (Spontaneous Abortion) : Abnormal PregnancyDocument4 pagesMiscarriage (Spontaneous Abortion) : Abnormal PregnancyKyjoy Flores CstrNo ratings yet
- The Perinatal MortalityDocument38 pagesThe Perinatal MortalityMed PoxNo ratings yet
- Placental Accreta DayritDocument2 pagesPlacental Accreta DayritMb SumbadNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: and Problem Pregnancies. 5Document2 pagesDaftar Pustaka: and Problem Pregnancies. 5Iqbal HambaliNo ratings yet
- Management of Premature Rupture of The Fetal Membranes at TermDocument6 pagesManagement of Premature Rupture of The Fetal Membranes at TermFrancisco Javier Gayoso DhagaNo ratings yet
- The Using of Carbetosin in HPP - FINALDocument31 pagesThe Using of Carbetosin in HPP - FINALMahida El shafiNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy Risk Factors, Clinical Presentation and ManagementDocument6 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Risk Factors, Clinical Presentation and ManagementRizka AdiNo ratings yet
- Amniotic FluidDocument13 pagesAmniotic FluidSandhya SajiNo ratings yet
- DINOPROSTONEDocument2 pagesDINOPROSTONEWemslaiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental To Midwives Providing Labour Care in Freestanding Midwifery-Led UnitsDocument18 pagesFundamental To Midwives Providing Labour Care in Freestanding Midwifery-Led UnitsIntan Mustika SariNo ratings yet
- ASPIRE 2022 - Programme BookDocument102 pagesASPIRE 2022 - Programme BookpriyantoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Didik Fetal Urogenital Anomalies Fetal Urogenital Anomalies PDFDocument25 pagesDr. Didik Fetal Urogenital Anomalies Fetal Urogenital Anomalies PDFJTNo ratings yet
- Blom Et Al-2010-BJOG - An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument9 pagesBlom Et Al-2010-BJOG - An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyNeni RochmayatiNo ratings yet
- Mun Final ExamDocument7 pagesMun Final Examapi-278937794No ratings yet
- NLM Classification: Worldwide Source of Medical Library ClassificationDocument1 pageNLM Classification: Worldwide Source of Medical Library ClassificationFrancisca CuellarNo ratings yet
- Form BDocument2 pagesForm BDoctors QuizNo ratings yet
- Gupta2014 Article AmniopatchWayForwardForMid-triDocument4 pagesGupta2014 Article AmniopatchWayForwardForMid-triDewa Made Sucipta PutraNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Notes IconsDocument31 pagesMaternal and Child Notes IconsKSY JanedoeNo ratings yet
- Rhesus Isoimmunisation & Haemolytic Disease of The Newborn BriefDocument20 pagesRhesus Isoimmunisation & Haemolytic Disease of The Newborn BriefAnuradha RoopchandNo ratings yet
- Iec Obg CareDocument16 pagesIec Obg CareBlessy Madhuri100% (1)
Partograph Use
Partograph Use
Uploaded by
Julianne B. Dela CruzOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Partograph Use
Partograph Use
Uploaded by
Julianne B. Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
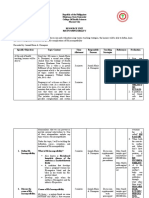
Name: ___Julianne B. dela Cruz_______________________________________________ Date: _Jan.
5, 2021_
Evaluator/Signature: ___Ms. Johanna Jiel S. Padogdog MN, RN_____________________ Grade: _____________
PARTOGRAPH USE
Definition: A partograph is a graphical record of a woman in labor and of fetal and maternal condition during labor on a labor record (partograph) on which, vital signs, fetal heart
rate, cervical dilation, descent of the fetal head, urine tests, and any drug administration can be recorded
Purposes:
1. To detect abnormal progress of labor as early as possible
2. To prevent prolonged labor
3. To recognize CPD long before obstructed labor
4. To assist in early decision on transfer, augmentation/ termination of labor
5. To increase the quality and regularity of all observations of mother and fetus
6. To recognize maternal or fetal problems as early as possible
Considerations:
1. A partograph should be started when a woman is in active labor (cervix dilated at 4cm/ more)
2. If there are any complications that require immediate attention, take appropriate actions before starting the partographh
3. All the recordings on the partograph should be done
4. Each rectangle of the time represents one hour
5. Record the number of hours passed since the partograph was started in the upper row
6. Record the actual time in the lower row
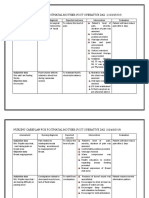
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING COMPETENCY WORKBOOK 41
PERFORMED
YES NO
ACTION RATIONALE REMARKS
1. Assess the woman in labor for any possible
complications that require immediate nursing For continuity of care
action.
2. Perform careful vaginal examination to determine The vaginal examination reveals whether the woman is in true labor
cervical dilatation and stage of labor. Succeeding and enables the examiner to determine whether the membranes have
vaginal examinations should then be done every 4 ruptured. Because this examination is often stressful and uncomfortable
hours. for the woman, it should be performed only when indicated by the
status of the woman and her fetus. Also, the only certain objective sign
that the second stage of labor has begun is the inability to feel the
cervix during the vaginal examination, indicating that the cervix is fully
dilated or effaced
I. Assessing Fetal Condition
3. Assessing the fetal condition involves assessing the Because labor is a period of physiologic stress for the fetus, frequent
Fetal Heart Rate (FHR), Amniotic Fluid, and Degree monitoring of fetal status is part of the nursing care during labor
of Moulding.
4. The first graph represents the FHR. Each vertical side Fetal well-being during labor can be measured by the response of the
of the rectangle represents the beats per minute in 10 fetal heart rate to uterine contractions
increments, while each horizontal side represents the
time by 30 minutes.
5. Monitor the heart rate for beats of less than 100 or A baseline FHR is 110 to 160 and must be checked. If the baseline rate
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING COMPETENCY WORKBOOK 41
beats of more than 180 beats per minute. This begins to slow or if deceleration patterns develop, prompt treatment
requires immediate attention. must be initiated
6. The next set of graph pertains to the status of Labor is initiated at term by SROM in approximately 25% of pregnant
amniotic fluid and membranes. If the membranes women. Membranes (the BOW) also can rupture spontaneously any
have not yet ruptured, write I on the box. time during labor, but most commonly in the transition phase of the
first stage of labor
PERFORMED
ACTION RATIONALE REMARKS
YES NO
7. If the membranes have ruptured, record the Amniotic fluid should be clear as water. Yellow- stained fluid suggests
characteristics of the amniotic fluid. Write C if Clear, a blood incompatibility between the mother and fetus (the amniotic
write B if bloody or red, write M if the fluid is green fluid is bilirubin stained from the breakdown of red blood cells). Green
or meconium stained, and write A if amniotic fluid is fluid suggests meconium staining
absent even after membranes ruptured.
8. If the amniotic fluid is absent after rupture of Because this may cause fetal distress. Assess FHR immediately to be
membranes, increase frequency of assessing the certain the umbilical cord hasn’t prolapsed and is now being
fetal heart rate. compressed against the cervix by the fetal head.
9. The last portion of fetal assessment is the moulding. Ensure normal, spontaneous vaginal delivery or if the mother needs CS
Moulding is an important indicator of how well the
pelvis can accommodate the fetal head.
10. Note and record moulding at each vaginal To monitor progress of labor
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING COMPETENCY WORKBOOK 41
examination.
11. Normally, in the early stage of labor, the fetal
sutures are separate and bones do not touch each To monitor progress of labor
other. This is recorded on the moulding graph as
(zero) 0.
12. On the later stage of labor, moulding will become If the presenting part is below the ischial spines, the distance is stated
prominent as the head fits on the pelvic inlet. If the as plus stations (+1 to +4 cm). at a +3 or +4 station, the presenting part
fetal bones are touching each other, record +, if they is at the perineum and can be seen if the vulva is separated
are overlapping moderately, record ++, and if the
bones are overlapping severely, record +++.
13. Watch out for severely overlapping skull bones To prevent head decapitation
which are non-reducible while the head is still
above the ischial spines. It is an ominous sign of
labor.
PERFORMED
ACTION RATIONALE REMARKS
YES NO
II. Assessing the Progress of Labor
14. This portion of the partograph assesses the degree of Dilation occurs first because uterine contractions gradually increase the
cervical dilatation against time. Cervical dilatation diameter of the cervical canal lumen by pulling the cervix upover the
is measured in cm. Time refers to the hours starting presenting part of the fetus
from the time the mother has entered the active
stage of labor (4cm) and has started using the
partograph. This is recorded as x on the graph.
15. The progress of labor graph features the Alert Line The form shows an “alert line”, which marks when 4 hours has passed.
and the Action Line. The goal of monitoring is to Four hours beyond that. An “action line” advises a primary care
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING COMPETENCY WORKBOOK 41
keep the progress line on the left side of the lines provider that cervical dilation is taking longer than usual and that an
and prevent or manage if the labor progress crosses intervention may be necessary to make the labor safe and effective
the alert or action line.
16. The alert line represents cervical dilatation rate of 1
cm per hour which is considered to the slowest rate To determine the normal progress of labor
of cervical dilatation in normal conditions both for
nullipara and multipara.
17. The normal progress of labor should be along the Maintaining an ongoing record and alerting the care provider that the
Alert Line or to the left of the alert line. If the rate alert line or action line is approaching are important nursing
of dilatation crosses the alert line (but before the responsibilities
action line) decisions to speed up the dilation such
as amniotomy can be considered.
PERFORMED
ACTION RATIONALE REMARKS
YES NO
18. If the rate of dilatation reaches or crosses the Action
Line, it indicates dangerously slow progress of To ensure safety and to have an effective labor
labor. Decision and action must be done to transfer
the mother to a hospital with equipment and
facilities that deal with obstetric emergencies.
19. Cervical dilatation should be accompanied with fetal
head descent. Head descent is plotted on the same
graph representing the cervical dilation on the To monitor the progress of labor
spaces from 0-5cm along the vertical line.
20. The assessment of head descent is done abdominally
and is represented by the examiners fingerbreadth To monitor fetal head descent
with each finger approximating 1cm.
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING COMPETENCY WORKBOOK 41
21. Head descent is plotted as O on the partograph and To demonstrate change along delivery and reflects the amount of
must be assessed and plotted the same time as the resistance that must be overcome
cervical dilatation.
22. It is important to remember that the direction of the To determine what are the resistance that must be overcome
dilatation and the fetal head descent must be in
opposite direction to represent a normal progress of
labor. As the dilatation goes up, the fetal head
simultaneously goes down in normal labor progress.
23. The third portion of labor progress monitoring is the Between contractions, the uterus relaxes. As labor progresses, the
labor contraction. Normally as the labor progresses, relaxation intervals decrease from 10 minutes early in labor to only 2 to
the uterine contractions become more frequent and 3 minutes.
last longer.
PERFORMED
ACTION RATIONALE REMARKS
YES NO
24. Uterine contraction should be assessed every 30 The duration of contractions also changes, increasing from 20 to 30
minutes, and is taken on a 10-minute period. The seconds at the beginning to a range of 60 to 70 seconds by the end of
technique is counting how many contraction within the first stage
10 minutes and recording the duration of each
contraction in seconds.
25. If contraction last for 20 seconds or less fill square To efficiently monitor the progress of labor and to obtain accurate
with dots. If between 20-40 seconds by diagonal results
line and >40 seconds fill the square completely by
shading.
III. Assessment of Maternal Condition
26. Assess maternal condition regularly by monitoring. To make labor safe and effective
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING COMPETENCY WORKBOOK 41
Drugs, IV fluids, Pulse are monitored every 30
minutes; Temperature and BP every 4 hours; and
urine volume, analysis for protein and acetones
every 2 to 4 hours.
27. When poor progress of labor is due to inadequate When labor contractions are ineffective, several interventions, such as
uterine activity, the use of amniotomy followed by induction and augmentation of labor with oxytocin or amniotomy
oxytocin infusion after may be considered. (artificial rupture of the membranes), may be initiated to strengthen
them
28. When oxytocin is used, record every 30 minutes the Oxytocin is an effective uterine stimulant, but there is a thin line
concentration per liter and the number of drops between adequate stimulation and hyperstimulation, so careful
infused to the patient. Always check the membranes observation during the entire infusion time is an important nursing
are ruptured before oxytocin is used. responsibility
28. Always observe that oxytocin infusion must result to
increased frequency and duration of uterine
contractions.
PERFORMED
ACTION RATIONALE REMARKS
YES NO
29. Drugs on IV infusions given during labor must be To keep track of what is happening
recorded on the portion of the partograph just below
the oxytocin infusion area. Record the name,
dosage, and route of administration. Make sure that
it is parallel on the exact time of the labor progress.
30. Record the mother’s pulse every 30 minutes and A side effect of oxytocin is that it causes peripheral vessel dilation, and
reflect as a dot connected with solid lines on each peripheral dilation can lead to extreme hypotension. To ensure safe
subsequent recordings. BP and temperature are induction, therefore, take the woman’s pulse and blood pressure
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING COMPETENCY WORKBOOK 41
recorded every 4 hours or more frequently if
indicated.
31. If ordered, obtain urine sample every 2 to 4 hours A second effect of oxytocin is that it can result in decreased urine flow,
and check for protein, volume, and acetone. possibly leading to water intoxication
32. Finally, do a written documentation of the outcome
of labor based on the observation obtained on the Ensure continuity of care
previous monitoring.
Learner’s Reflection: (What did you learn most of the activity? What is its impact to Instructor’s Comments:
you?)
I have learned about the importance of partograph and how to monitor the progress of
labor and identify and intervene in cases of abnormal labor.
Reference(s):
Maternal and Child Health Nursing(2014) Adele Pillitteri
Maternal-Neonatal Nursing (2008). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Maternal and Child Nursing (2007), Elsevier Inc.
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING COMPETENCY WORKBOOK 41
You might also like
- Intellectual RevolutionsDocument2 pagesIntellectual RevolutionsJulianne B. Dela Cruz89% (19)
- Essential Intrapartum and Newborn Care (EINC)Document26 pagesEssential Intrapartum and Newborn Care (EINC)Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Taking Anthropometric Measurements of NewbornDocument25 pagesTaking Anthropometric Measurements of NewbornClarissa MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Bag Technique ChecklistDocument2 pagesBag Technique ChecklistDanz KieNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingDocument47 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingBella OllieNo ratings yet
- Perineal Episiotomy Care Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesPerineal Episiotomy Care Teaching Planapi-3396685440% (1)
- Application of BindersDocument3 pagesApplication of BindersJayson Tom Briva Capaz100% (1)
- Acetic Acid TestDocument1 pageAcetic Acid Testlauriceannemarie100% (1)
- Health Teaching PlanDocument11 pagesHealth Teaching PlanVic Intia Paa100% (1)
- Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Home VisitDocument5 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Home VisitJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Clinic VisitDocument6 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1: Clinic VisitJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument12 pagesNursing Care During LaborJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practice in ObstetricsDocument17 pagesEvidence Based Practice in ObstetricsAnn Merlin JobinNo ratings yet
- Po No Breast RationaleDocument4 pagesPo No Breast Rationalearnold john boniteNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument5 pagesAbdominal ExaminationAnuradha MauryaNo ratings yet
- PartographDocument6 pagesPartographalyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- What Is Cord Care?Document2 pagesWhat Is Cord Care?Wenalyn Grace Abella LlavanNo ratings yet
- DR Instrument (Recovered)Document25 pagesDR Instrument (Recovered)Mayolianne DumayNo ratings yet
- Breast Care and Assisting in BreastfeedingDocument7 pagesBreast Care and Assisting in BreastfeedingBJ FernandezNo ratings yet
- 1-Significance and Purposes of Nursing ResearchDocument22 pages1-Significance and Purposes of Nursing ResearchPrincess Ivan Gayagoy100% (1)
- Maternity and Newborn MedicationsDocument38 pagesMaternity and Newborn MedicationsJaypee Fabros EdraNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dystocia NCPDocument6 pagesShoulder Dystocia NCPNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- MCN RLE Sitz Bath Procedure ChecklistDocument3 pagesMCN RLE Sitz Bath Procedure ChecklistHannah Angelu Cabading100% (1)
- Conducting Normal DeliveryDocument3 pagesConducting Normal DeliveryNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Breast Care ChecklistDocument3 pagesBreast Care ChecklistNeil Nette ReynaldoNo ratings yet
- Breast Care Means Care Given To The Breast by The Mother During Her Prenatal Period, Intranatal Period and Postnatal PeriodDocument6 pagesBreast Care Means Care Given To The Breast by The Mother During Her Prenatal Period, Intranatal Period and Postnatal PeriodCagabcab Canibel MelanyNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Labor As One of The Intrapartal ComplicationsDocument23 pagesDysfunctional Labor As One of The Intrapartal ComplicationsKenje Kate AgripoNo ratings yet
- Wiedenbach's TheoryDocument41 pagesWiedenbach's TheoryAnnaya KhanNo ratings yet
- NCP Fever 1Document11 pagesNCP Fever 1Deepak VermaNo ratings yet
- MCN NCPDocument6 pagesMCN NCPIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Finalrationale CAGABCABDocument9 pagesFinalrationale CAGABCABCagabcab Canibel MelanyNo ratings yet
- Thermometer TechniqueDocument6 pagesThermometer TechniqueJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Immediate Care of NewbornDocument21 pagesImmediate Care of NewbornRaida Marañon Ibrahim100% (2)
- Nursing Care of The NewbornDocument56 pagesNursing Care of The NewbornAngie Zimmerman DreilingNo ratings yet
- Apgar Score ChecklistDocument3 pagesApgar Score ChecklistAnnica Lozano100% (2)
- The PartographDocument65 pagesThe PartographAmyAgustinNo ratings yet
- Rubin's TheoryDocument3 pagesRubin's TheoryBeerna Grande50% (2)
- Individual ConferenceDocument19 pagesIndividual Conferencevincentsharon86% (7)
- Lumbar Puncture ReportDocument5 pagesLumbar Puncture ReportTweenie DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Baby BathDocument7 pagesBaby Bathavinash shindeNo ratings yet
- Skill 11 (1) ..Collection of Stool SpecimenDocument1 pageSkill 11 (1) ..Collection of Stool SpecimennetsquadNo ratings yet
- Kannaki (BREAST CARE)Document16 pagesKannaki (BREAST CARE)Jalajarani AridassNo ratings yet
- IV Meds in Volumetric Set C RationaleDocument2 pagesIV Meds in Volumetric Set C RationalePascal Marie IzhaqNo ratings yet
- Leopold's ManeuverDocument22 pagesLeopold's ManeuverArlene Cerdeña Salceda100% (1)
- English Ii Assignment: Midwifery Management in Cephalopelvic DisproportionDocument14 pagesEnglish Ii Assignment: Midwifery Management in Cephalopelvic DisproportionBintari Ancinonyx JubatusNo ratings yet
- Case Study..Care PlanDocument6 pagesCase Study..Care PlanPabhat Kumar0% (1)
- Clinical Objectives GuidelinesDocument11 pagesClinical Objectives GuidelinesprowritttersNo ratings yet
- Hot Sitz BathDocument10 pagesHot Sitz BathJohn Aladin ArcetaNo ratings yet
- RH Incompatibility Resource UnitDocument6 pagesRH Incompatibility Resource UnitJannah Marie A. DimaporoNo ratings yet
- Chapter24 PDFDocument43 pagesChapter24 PDFCindy MaslagNo ratings yet
- Obstetric & Gynaecological NursingDocument30 pagesObstetric & Gynaecological NursingSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- FAMILY PLanning FinalDocument23 pagesFAMILY PLanning FinalLebo Ramokolo100% (1)
- Role of The Head NurseDocument12 pagesRole of The Head Nurseمحمود على ما تفرج75% (4)
- Patient Assignment MethodDocument48 pagesPatient Assignment Methodsathya Arunkumar100% (1)
- Newborn Care ProcedureDocument6 pagesNewborn Care ProcedureHannah VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS Ectopic Pregnancy Part 1Document10 pagesCASE ANALYSIS Ectopic Pregnancy Part 1Diane Celine SantianoNo ratings yet
- Case Study NSVDDocument25 pagesCase Study NSVDLanju FerminNo ratings yet
- Partograph UseDocument8 pagesPartograph UseAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Cmca SLDocument17 pagesNCM 107 Cmca SLAshitaka100% (1)
- NFDN 2004 - Unit 4.3 - JLB StudentDocument43 pagesNFDN 2004 - Unit 4.3 - JLB StudentkendrabooboooNo ratings yet
- Management of First Stage of Labour: Prepared By: Nirsuba Gurung Assistant Lecturer MsonDocument55 pagesManagement of First Stage of Labour: Prepared By: Nirsuba Gurung Assistant Lecturer MsonBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Management of First Stage of LabourDocument55 pagesManagement of First Stage of LabourBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On Normal LaborDocument62 pagesCase Presentation On Normal LaborB34-YvesJethro ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Partograph & LCGDocument12 pagesThe Partograph & LCGعلي حسين خليلNo ratings yet
- Thermometer TechniqueDocument6 pagesThermometer TechniqueJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Bag Technique: Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1Document5 pagesBag Technique: Community Health Nursing Competency Workbook 1Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Food AdvertisementDocument1 pageFood AdvertisementJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Notions of Development That May Evolve Into ScientismDocument2 pagesNotions of Development That May Evolve Into ScientismJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument12 pagesNursing Care During LaborJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Administering Opthalmic MedicationsDocument6 pagesAdministering Opthalmic MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument12 pagesNursing Care During LaborJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Historical Antecedents in The Course of Science and TechnologyDocument1 pageHistorical Antecedents in The Course of Science and TechnologyJulianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument10 pagesNursing Care During LaborAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- Administering Intradermal MedicationsDocument4 pagesAdministering Intradermal MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MMDST FormDocument3 pagesMMDST FormJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- APGAR Scoring and Ballard's Assessment ToolDocument2 pagesAPGAR Scoring and Ballard's Assessment ToolJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Basketball: Vision: Mission: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesBasketball: Vision: Mission: ObjectivesJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument1 pageHealth Teaching PlanJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of Systems: Involuntarily Blinking Pink ConjunctivaDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of Systems: Involuntarily Blinking Pink ConjunctivaJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Administering Opthalmic MedicationsDocument6 pagesAdministering Opthalmic MedicationsJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument9 pagesHealth Teaching PlanJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Patient P / Room No. 415 - 1Document3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Patient P / Room No. 415 - 1Julianne B. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- 1 Endorsement NotesDocument1 page1 Endorsement NotesJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Histolytica) Vaginalis) Brucei) Donovani)Document2 pagesHistolytica) Vaginalis) Brucei) Donovani)Julianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Postpartum CareDocument11 pagesOptimizing Postpartum Carengga.makasihNo ratings yet
- Antenatal CareDocument38 pagesAntenatal CareMominah MayamNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Breech DeliveryDocument34 pagesVaginal Breech Deliveryicursuii icursuiiNo ratings yet
- Antenatal and Intrapartum Prediction Dystocia ShoulderDocument7 pagesAntenatal and Intrapartum Prediction Dystocia ShoulderDewiDwipayantiGiriNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Flash On English in The HospitalDocument11 pagesUnit 3 Flash On English in The HospitalKartonoNo ratings yet
- The Use of Maternity Acupuncture Within A New Zealand Public Hospital: Integration Within An Outpatient ClinicDocument5 pagesThe Use of Maternity Acupuncture Within A New Zealand Public Hospital: Integration Within An Outpatient ClinicjjNo ratings yet
- Large For Gestational Age Baby - Feb21Document2 pagesLarge For Gestational Age Baby - Feb21saheemmirNo ratings yet
- Vasa Praevia RCOG GTGDocument13 pagesVasa Praevia RCOG GTGMariaBrincatNo ratings yet
- QMMC History - PE FormDocument1 pageQMMC History - PE FormPrisbert W. AlejoNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report FEBRUARYDocument14 pagesAccomplishment Report FEBRUARYYam Aba DianoNo ratings yet
- Miscarriage (Spontaneous Abortion) : Abnormal PregnancyDocument4 pagesMiscarriage (Spontaneous Abortion) : Abnormal PregnancyKyjoy Flores CstrNo ratings yet
- The Perinatal MortalityDocument38 pagesThe Perinatal MortalityMed PoxNo ratings yet
- Placental Accreta DayritDocument2 pagesPlacental Accreta DayritMb SumbadNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: and Problem Pregnancies. 5Document2 pagesDaftar Pustaka: and Problem Pregnancies. 5Iqbal HambaliNo ratings yet
- Management of Premature Rupture of The Fetal Membranes at TermDocument6 pagesManagement of Premature Rupture of The Fetal Membranes at TermFrancisco Javier Gayoso DhagaNo ratings yet
- The Using of Carbetosin in HPP - FINALDocument31 pagesThe Using of Carbetosin in HPP - FINALMahida El shafiNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy Risk Factors, Clinical Presentation and ManagementDocument6 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Risk Factors, Clinical Presentation and ManagementRizka AdiNo ratings yet
- Amniotic FluidDocument13 pagesAmniotic FluidSandhya SajiNo ratings yet
- DINOPROSTONEDocument2 pagesDINOPROSTONEWemslaiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental To Midwives Providing Labour Care in Freestanding Midwifery-Led UnitsDocument18 pagesFundamental To Midwives Providing Labour Care in Freestanding Midwifery-Led UnitsIntan Mustika SariNo ratings yet
- ASPIRE 2022 - Programme BookDocument102 pagesASPIRE 2022 - Programme BookpriyantoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Didik Fetal Urogenital Anomalies Fetal Urogenital Anomalies PDFDocument25 pagesDr. Didik Fetal Urogenital Anomalies Fetal Urogenital Anomalies PDFJTNo ratings yet
- Blom Et Al-2010-BJOG - An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument9 pagesBlom Et Al-2010-BJOG - An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyNeni RochmayatiNo ratings yet
- Mun Final ExamDocument7 pagesMun Final Examapi-278937794No ratings yet
- NLM Classification: Worldwide Source of Medical Library ClassificationDocument1 pageNLM Classification: Worldwide Source of Medical Library ClassificationFrancisca CuellarNo ratings yet
- Form BDocument2 pagesForm BDoctors QuizNo ratings yet
- Gupta2014 Article AmniopatchWayForwardForMid-triDocument4 pagesGupta2014 Article AmniopatchWayForwardForMid-triDewa Made Sucipta PutraNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Notes IconsDocument31 pagesMaternal and Child Notes IconsKSY JanedoeNo ratings yet
- Rhesus Isoimmunisation & Haemolytic Disease of The Newborn BriefDocument20 pagesRhesus Isoimmunisation & Haemolytic Disease of The Newborn BriefAnuradha RoopchandNo ratings yet
- Iec Obg CareDocument16 pagesIec Obg CareBlessy Madhuri100% (1)