Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ineffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of Dyspnea
Ineffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of Dyspnea
Uploaded by
Niel Minatozaki0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
235 views3 pagesThe nursing care process is used to address a client's ineffective breathing pattern. Short term goals include the client being able to express knowledge of the problem and make lifestyle changes after 30 minutes. Long term goals are proper breathing without effort, proper coping, and a normal respiratory rate after 7 days. Interventions like relaxation, posture, diet and rest are implemented. The client is assessed and interventions are tailored based on their history of heart failure weakening respiratory muscles. Progress is evaluated against goals.
Original Description:
NCP
Original Title
Ineffective breathing pattern as evidenced by use of accessory muscles and episodes of dyspnea
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nursing care process is used to address a client's ineffective breathing pattern. Short term goals include the client being able to express knowledge of the problem and make lifestyle changes after 30 minutes. Long term goals are proper breathing without effort, proper coping, and a normal respiratory rate after 7 days. Interventions like relaxation, posture, diet and rest are implemented. The client is assessed and interventions are tailored based on their history of heart failure weakening respiratory muscles. Progress is evaluated against goals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
235 views3 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of Dyspnea
Ineffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of Dyspnea
Uploaded by
Niel MinatozakiThe nursing care process is used to address a client's ineffective breathing pattern. Short term goals include the client being able to express knowledge of the problem and make lifestyle changes after 30 minutes. Long term goals are proper breathing without effort, proper coping, and a normal respiratory rate after 7 days. Interventions like relaxation, posture, diet and rest are implemented. The client is assessed and interventions are tailored based on their history of heart failure weakening respiratory muscles. Progress is evaluated against goals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
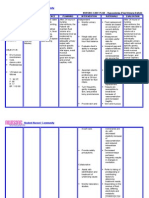
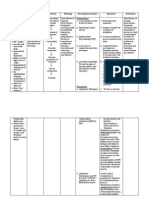
NURSING CARE PROCESS
Cues Nursing Analysis Goals and Implementation Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis Objective
Ineffective SCIENTIFIC Short-term Goal: Independent: Short-term Goal:
Subjective cues: breathing ANALYSIS: After 30 minutes of After 30 minutes of nursing
pattern as Ineffective nursing intervention, the 1. Note rate and depth 1. To help intervention, the client will
-The client evidenced by breathing pattern is client will be able to be of respirations and determine if the be able to be express her
verbalized that use of accessory also known as express her knowledge type of breathing respiratory status knowledge about the
she had a muscles and inspiration and/or about the nursing pattern of the client falls nursing problem, initiate
history of heart episodes of expiration that problem, initiate needed within the normal needed lifestyle changes,
failure dyspnea does not provide lifestyle changes, and range of and participate on the
adequate participate on the return respiratory rate in return demonstration
-Sometimes, ventilation demonstration activities older adult which activities in health
she experiences (Doenges et al., in health teaching. is 16-25 cpm teaching.
a hard time in 2019). (Meiner, 2019). __Met
breathing easily Meiner & Yeager Objectives: __Partially Met
(2019) asserted 2. Encourage 2. To help control __Unmet
Objective cues: that respiratory 1. After 10 minutes of slower/deeper shortness of
symptoms common nursing intervention, the respirations, use of breath, and Objectives:
- uses accessory in older adults client will be able to pursed-lip technique. provides a quick
muscle to include alterations verbalize the etiology of and easy way to 1. Was the client able to
support her in breathing respiratory distress and slow pace of verbalize the etiology of
breathing as she pattern, dyspnea, possible coping breathing, making respiratory distress and
exhibits and coughing. behaviors using their each breath more possible coping behaviors
shortness of Abnormal own words. effective using their own words after
breath breathing patterns ( American Lung 10 minutes of nursing
in the elderly may 2. After 10 minutes of Association, n.d.). intervention?
- Dyspnea was be indicative of nursing intervention, the __Met
noted other metabolic client will be able to 3. Assist the client in 3. To help slower __Partially Met
and respiratory verbalize the importance the use of relaxation heart rate and __Unmet
RR: 14 cpm illnesses. of good posture, proper techniques. lower blood
PR: 118 bpm Complaints of diet, coping behaviors, pressure which 2. Was the client be able to
dyspnea in older effective use of contributes to verbalize the importance of
adults may be accessory muscles, ineffective good posture, proper diet,
associated with pursed-lip breathing. breathing (Mayo coping behaviors, effective
underlying Clinic, n.d.). use of accessory muscles,
respiratory or 3. After 10 minutes of pursed-lip breathing?
cardiac disease. nursing intervention, the 4. Encourage a position 4. To promote __Met
client will be able to of comfort. physiological and __Partially Met
SITUATIONAL demonstrate good psychological ease __Unmet
ANALYSIS: posture, accessory of maximal
Upon client muscles, and pursed-lip inspiration 3. Was the client able to
assessment, usage breathing. (Doenges et al., demonstrate good posture,
of respiratory 2019). accessory muscles, and
muscles, especially Long-term Goal: pursed-lip breathing?
around the neck. After 7 days of nursing 5. Encourage client to 5. To avoid __Met
Also, only 14 cycles intervention, the client avoid overeating/gas- abdominal __Partially Met
per minutes was will be able to forming foods. distention and __Unmet
noted. According to demonstrate proper impair breathing
Meiner (2019), breathing without too efforts (Doenges Long-term Goal:
muscle strength much effort, et al., 2019). After 7 days of nursing
also weakens with demonstrate proper intervention, the client will
age, and as coping behavior, and 6. Review the etiology 6. To promote be able to demonstrate
respiratory muscles display respiratory rate of respiratory distress knowledge on the proper breathing without
weaken, it becomes within the normal range. and possible coping client and too much effort,
increasingly more behaviors. caregiver demonstrate proper coping
difficult to exert regarding etiology behavior, and display
inspiratory and of respiratory respiratory rate within the
expiratory forces, distress and normal range.
resulting to older possible coping __Met
adults making use behaviors __Partially Met
of accessory (Doenges et al., __Unmet
muscles of 2019).
respiration. The
client also had a 7. Emphasize the 7. To maximize
history of heart importance of good respiratory effort
failure, which can posture and effective (Doenges et al.,
be a factor why she use of accessory 2019).
is having ineffective muscles.
breathing patterns.
8. Encourage adequate 8. To limit fatigue
References: rest periods between (Doenges et al.,
Doenges, M., activities. 2019).
Moorhouse, M., &
Murr, A. (2016).
Nurse's Pocket
Guide: Diagnoses,
Prioritized
Interventions, and
Rationales.
F.A. Davis.
Meiner, S., &
Yeager, J. J. (2019).
Gerontologic
Nursing (6th ed.,
364-368). Elsevier.
References:
American Lung Association. Pursed Lip Breathing. https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/copd/patient-resources-and-videos/pursed-
lip-breathing-video#:~:text=Pursed%20lip%20breathing%20helps%20control,can%20better%20control%20your%20breath.
Doenges, M., Moorhouse, M., & Murr, A. (2016). Nurse's Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Prioritized Interventions, and Rationales. F.A. Davis.
Mayo Clinic. Relaxation techniques: Try these steps to reduce stress. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/stress-management/in-
depth/relaxation-technique/art-20045368.
Meiner, S., & Yeager, J. J. (2019). Gerontologic Nursing (6th ed., 364-368). Elsevier.
You might also like
- ARDS Concept MapDocument1 pageARDS Concept Mapadro100% (2)
- Newborn Exam Checklist PDFDocument2 pagesNewborn Exam Checklist PDFAnonymous Sfcml4GvZNo ratings yet
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument16 pagesBio ProjectKumar Prabhat Sinha89% (37)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- NCP For HemorrhoidsDocument3 pagesNCP For HemorrhoidsTADURAN RENE MAE ANGELLI F.No ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPYesha Mae MartinNo ratings yet
- SNU49Document2 pagesSNU49Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesTissue PerfusionMichael John LeandichoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleNo ratings yet
- AAAAA Altered-Body-Temp-NCPDocument2 pagesAAAAA Altered-Body-Temp-NCPMoi ValdozNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationDocument3 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationNur faizah bt azmiNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPMcmc Ryan Ferdinand GutierrezNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge DeficitPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Age NCPDocument4 pagesAge NCPnj_pink081794No ratings yet
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Document4 pagesAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonNo ratings yet
- NCP PSHDocument17 pagesNCP PSHMargareth OrtizNo ratings yet
- NCP For FeverDocument2 pagesNCP For FeverSherwin B. CaytapNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNo ratings yet
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDocument13 pagesNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BAngela Mae DiestroNo ratings yet
- NCP SeratroDocument2 pagesNCP SeratroKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- NCP - ERDocument5 pagesNCP - ERAnnelore ArcayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Document1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Jamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain DiarrheaDocument4 pagesNCP Acute Pain DiarrheaBARRISTERFLOWERSEAURCHIN6No ratings yet
- Cutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesCutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanYayin Pestaño100% (1)
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Document3 pagesNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPMichael John F. NatividadNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJames PajarilloNo ratings yet
- Deficit)Document2 pagesDeficit)Lee DeeNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationDocument1 pageCholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationJess GoNo ratings yet
- NCP, Ent, Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageNCP, Ent, Risk For InfectionGale DizonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy MalaiseDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy Malaise06eltianNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationastersisk1121No ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Document6 pagesIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.No ratings yet
- Developmental HistoryDocument2 pagesDevelopmental HistoryShulamaye VelascoNo ratings yet
- Baiae NCPDocument1 pageBaiae NCPreignyfayeNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain FractureDocument1 pageNCP Acute Pain FractureAi RouNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan FormDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan FormissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Hypertonic SolutionsDocument4 pagesHypertonic SolutionsVanessa PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Case CHFDocument10 pagesCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- Or NCP (Impaired Elimination)Document1 pageOr NCP (Impaired Elimination)Nikki M. ArapolNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- "Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument2 pages"Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientMussaib Mushtaq100% (1)
- Virtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsDocument7 pagesVirtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsEdgie FabreNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Tonsilitis NCPDocument2 pagesTonsilitis NCPFATIMA MARYAMA USMANNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCP-Septic Shock (Acute Pain)Document3 pagesNCP-Septic Shock (Acute Pain)Ted anadiloNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- NANDA Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To As Evidenced by NANDA DefinitionDocument3 pagesNANDA Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To As Evidenced by NANDA DefinitionTrisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pathology: General Pathology Is The Study of The Mechanisms of Disease (WithDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Pathology: General Pathology Is The Study of The Mechanisms of Disease (Withعلي الكوافيNo ratings yet
- Basic Immunology - 06032020Document30 pagesBasic Immunology - 06032020IchaNo ratings yet
- Herbs - Monograph On Marigold & DandelionDocument17 pagesHerbs - Monograph On Marigold & DandelionalbertofarmaNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Bipolar DisorderDocument4 pagesDissertation Bipolar DisorderWhereCanIFindSomeoneToWriteMyPaperSingapore100% (1)
- AidsDocument3 pagesAidsmehulj099No ratings yet
- Cross-Sectional Imaging of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Development, Growth, Spread, and PrognosisDocument12 pagesCross-Sectional Imaging of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Development, Growth, Spread, and PrognosisNikos SerifisNo ratings yet
- ParQ Plus Jan 2022 FillableDocument5 pagesParQ Plus Jan 2022 FillableRaechelle DizonNo ratings yet
- Child Protection - Dr. GarciaDocument55 pagesChild Protection - Dr. GarciaGio GelilangNo ratings yet
- Comparative Evaluation of Cell Block and Smear Sampling Techniques in FNACDocument72 pagesComparative Evaluation of Cell Block and Smear Sampling Techniques in FNACOwuda BenedictNo ratings yet
- History TakingDocument8 pagesHistory TakingMihraban OmerNo ratings yet
- Eular 2018Document1,986 pagesEular 2018Syed Ali Akbar100% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJoey PolicarNo ratings yet
- February, 26 2019 Group: 2 (Two) Member: - Ajisa UtamiDocument2 pagesFebruary, 26 2019 Group: 2 (Two) Member: - Ajisa UtamiNoor SalimahNo ratings yet
- Lectura Previa3-Approach To The Patient With Abnormal Vital SignsDocument7 pagesLectura Previa3-Approach To The Patient With Abnormal Vital SignsEdwin Robles NorabuenaNo ratings yet
- DS LosartanDocument1 pageDS LosartanYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Hashimoto ThyroiditisDocument19 pagesHashimoto ThyroiditisPaulina Maria PaciejNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic CancerDocument26 pagesPancreatic CancerJesus RFNo ratings yet
- MeaslesDocument14 pagesMeaslesCHALIE MEQUNo ratings yet
- Complications of Orthognathic SurgeryDocument39 pagesComplications of Orthognathic SurgeryAME DENTAL COLLEGE RAICHUR, KARNATAKANo ratings yet
- Down SyndromeDocument19 pagesDown SyndromeRiya LalchandaniNo ratings yet
- Client in Context Present State Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Patient History: Subjective Cues: IndependentDocument3 pagesClient in Context Present State Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Patient History: Subjective Cues: IndependentMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- Acute Complication of Diabetic MellitusDocument10 pagesAcute Complication of Diabetic MellitusNdzalama Freedom MakhuveleNo ratings yet
- CHN REVIEWER LESSON 1 and 2Document9 pagesCHN REVIEWER LESSON 1 and 2Imogen MasumiNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 - Epidemiology of HIAs PDFDocument12 pagesLecture - 1 - Epidemiology of HIAs PDFDr.SajalNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders: Disruptive Mood Dysregulation DisorderDocument12 pagesMood Disorders: Disruptive Mood Dysregulation DisorderAnna ClaroNo ratings yet
- ArciagaDocument5 pagesArciagaJerecho Ramon R. ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Ehy 339Document98 pagesEhy 339Xarisis IoannisNo ratings yet