Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FATE Mindmap
FATE Mindmap
Uploaded by
ameenallyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Grossman Baims Cardiac Catheterization Angiography and Intervention 8th Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesGrossman Baims Cardiac Catheterization Angiography and Intervention 8th Edition Ebook PDFjeffrey.nevarez629100% (46)
- Veterinary AnatomyDocument13 pagesVeterinary AnatomyKenneth ShayNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical 1: Johdel CabalunaDocument235 pagesMedical Surgical 1: Johdel CabalunaAlthea Marie C. Mado100% (4)
- Sitema Steel Frame Prescient-Typical-Assemblies - 6.0sys PDFDocument3 pagesSitema Steel Frame Prescient-Typical-Assemblies - 6.0sys PDFalfa27No ratings yet
- Perevod Natalya VasilevnaDocument186 pagesPerevod Natalya Vasilevnamohammad farooque razaa71% (7)
- 07D4 YSR DS 007 Rev09 - Control Valves ListDocument2 pages07D4 YSR DS 007 Rev09 - Control Valves ListAli JameelNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument21 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- Annexure 3 - Vendor ComparisonDocument1 pageAnnexure 3 - Vendor ComparisonNikhil KarkeraNo ratings yet
- 3.1.07 Schedule of Components: L D SD S PIR DN L/P P Rtls Code Description TotalDocument1 page3.1.07 Schedule of Components: L D SD S PIR DN L/P P Rtls Code Description TotalVinay PallivalppilNo ratings yet
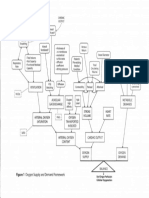
- O2 Supply and Demand FrameworkDocument1 pageO2 Supply and Demand FrameworkrachelweinhardtNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument23 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument21 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument22 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument18 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document6 pagesBook 1chinna_p_123No ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument19 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- UL Canon Transducers I-Series, Aplio Platinum Series, Xario Platinum Series, Viamo c100Document8 pagesUL Canon Transducers I-Series, Aplio Platinum Series, Xario Platinum Series, Viamo c100Gleb PolianovskyiNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument17 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument53 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument22 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- TOE For FCA2: Depth: From The ME Ascending Aortic SAX, Advance Probe and Turn Clockwise To Centre The TVDocument25 pagesTOE For FCA2: Depth: From The ME Ascending Aortic SAX, Advance Probe and Turn Clockwise To Centre The TVameenallyNo ratings yet
- DP Transmitter Range Vs Maximum Working Pressure - Automation & Control Engineering Forum PDFDocument1 pageDP Transmitter Range Vs Maximum Working Pressure - Automation & Control Engineering Forum PDFnboulegrouneNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument35 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- Summary Split Duct Bontang 08.01.2021 AgungDocument1 pageSummary Split Duct Bontang 08.01.2021 AgungCitimall BontangNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument51 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- AAF Filter Omega AirDocument2 pagesAAF Filter Omega AirMột Lằn Quang0% (1)
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument28 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- Sunlight RES SOPzS PDFDocument4 pagesSunlight RES SOPzS PDFAnonymous AnonyNo ratings yet
- Vessel Volume & Area CalcDocument5 pagesVessel Volume & Area CalcgagilamNo ratings yet
- 2015 Camera Comparison ChartDocument2 pages2015 Camera Comparison ChartAbhinandan PhapaleNo ratings yet
- Vitros Especificacion de PruebasDocument4 pagesVitros Especificacion de PruebasGeovanna Paola Lagarda MendezNo ratings yet
- 06.Tll With NCR Report June-23Document31 pages06.Tll With NCR Report June-23vishnuNo ratings yet
- Combi SC Straddle Carrier PDFDocument2 pagesCombi SC Straddle Carrier PDFjakeNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument23 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- R1 YankbDocument2 pagesR1 Yankbvivia sustrianaNo ratings yet
- E360 Operating ManualDocument180 pagesE360 Operating Manualpablo_ramirez_32No ratings yet
- Avalus Interactive Deck - Version 2Document60 pagesAvalus Interactive Deck - Version 2irmelodyNo ratings yet
- WEG 10004278046 13617810 r01 CFW700 Adenddum H1as1 en Es PTDocument2 pagesWEG 10004278046 13617810 r01 CFW700 Adenddum H1as1 en Es PTLuanNo ratings yet
- Stripper Bolt, Coil Spring, Dowel PinDocument3 pagesStripper Bolt, Coil Spring, Dowel Pinmuhamad laaliNo ratings yet
- 1118393872-61Document3 pages1118393872-61amirkhd8No ratings yet
- Ancon EdjPro Edge LifterDocument2 pagesAncon EdjPro Edge LifterBarrasons Engineers TeamNo ratings yet
- References: Chapter 3 - Sec - Ons 3-6, 3-7, 3-8Document1 pageReferences: Chapter 3 - Sec - Ons 3-6, 3-7, 3-8nickNo ratings yet
- Master Table: General Energy Conservation Special NotesDocument1 pageMaster Table: General Energy Conservation Special NotesSiyad p salamNo ratings yet
- Performance Reactivos A BordoDocument2 pagesPerformance Reactivos A Bordorocio1330No ratings yet
- Modulate Action Catalog EN PDFDocument59 pagesModulate Action Catalog EN PDFjesus casas garayNo ratings yet
- Manage Customer Engagements (Retail)Document1 pageManage Customer Engagements (Retail)Ram Mohan MishraNo ratings yet
- Freudenberg Xpress - Standard MaterialsDocument1 pageFreudenberg Xpress - Standard MaterialsAndrewFranciscoNo ratings yet
- 7 SAP Core Modules (SDMM, FICO, PP, PS, HR) Mindmaps - All-in-One Deck!Document7 pages7 SAP Core Modules (SDMM, FICO, PP, PS, HR) Mindmaps - All-in-One Deck!Yong Benedict100% (1)
- Atellica Solution CH Analyzer Assay Chart, 11484427 Rev 04, EN DXDCM 09017fe9807b250b-1676056852193Document26 pagesAtellica Solution CH Analyzer Assay Chart, 11484427 Rev 04, EN DXDCM 09017fe9807b250b-1676056852193chinuswami100% (3)
- Usaid An Icn Hemocue Population 2022Document1 pageUsaid An Icn Hemocue Population 2022Samson DesieNo ratings yet
- SB7300 051Document1 pageSB7300 051Md MasumNo ratings yet
- Sitema Steel Frame Prescient-Typical-Assemblies - 6.0sysDocument3 pagesSitema Steel Frame Prescient-Typical-Assemblies - 6.0sysalfa27100% (1)
- OISD-129 GAP AnalysisDocument1 pageOISD-129 GAP AnalysisNayan AhmedNo ratings yet
- P843 GEM Poster - JK CiDocument1 pageP843 GEM Poster - JK CiTsubasa OozoraNo ratings yet
- Middle Side Revisi 2bsjsDocument1 pageMiddle Side Revisi 2bsjsJOTA BLUEESSNo ratings yet
- C8051F38x-pages-17Document1 pageC8051F38x-pages-17lingeshtjNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology - AnatomyDocument5 pagesOphthalmology - AnatomyOscar Daniel MendezNo ratings yet
- 18 - Management of Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors 2Document18 pages18 - Management of Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors 2reeem1 alshehri2No ratings yet
- Table of Specifications: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesTable of Specifications: Objectivewanieramlie98No ratings yet
- Products Found: Transmissive Photo InterruptersDocument1 pageProducts Found: Transmissive Photo InterrupterswatteaucarNo ratings yet
- Straumann Dental System Map BoneLevelProstheticsDocument1 pageStraumann Dental System Map BoneLevelProstheticscarla1315No ratings yet
- Surgery StomachDocument31 pagesSurgery StomachAnnie HadassahNo ratings yet
- General Roof Plan Notes: Reflected Ceiling Plan LegendDocument10 pagesGeneral Roof Plan Notes: Reflected Ceiling Plan LegenddawitgggNo ratings yet
- TOE For FCA2: Depth: From The ME Ascending Aortic SAX, Advance Probe and Turn Clockwise To Centre The TVDocument25 pagesTOE For FCA2: Depth: From The ME Ascending Aortic SAX, Advance Probe and Turn Clockwise To Centre The TVameenallyNo ratings yet
- Radiography: S. Moore, E. GardinerDocument6 pagesRadiography: S. Moore, E. GardinerameenallyNo ratings yet
- FCA 2 Trials MindmapDocument1 pageFCA 2 Trials MindmapameenallyNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Electrons Between Atoms With ADocument1 pageTransfer of Electrons Between Atoms With AameenallyNo ratings yet
- Aortic Aneurysm Classification: SL No Time Specific Objective Content Av Aids EvaluationDocument2 pagesAortic Aneurysm Classification: SL No Time Specific Objective Content Av Aids EvaluationArunNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Forum Thorax DoneDocument8 pagesAnatomy Forum Thorax DoneMedShareNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Supertable PDFDocument14 pagesAnatomy Supertable PDFAlex Ondevilla100% (1)
- DAY: 4 I. Objectives: S9LT-lab-26Document6 pagesDAY: 4 I. Objectives: S9LT-lab-26GinalynMaacNo ratings yet
- Chest TraumaDocument28 pagesChest TraumaGitaAmeliaTurnipNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Digestive Glands. Alimentary CanalDocument27 pagesDigestive System: Digestive Glands. Alimentary CanalAnkit NariyaNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischemia and Claudication Unisba 2017Document65 pagesAcute Limb Ischemia and Claudication Unisba 2017nobi nobiNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of Chest Xray A Hands On GuideDocument209 pagesMaking Sense of Chest Xray A Hands On GuideAli Al-Ghamdi100% (2)
- Neet Iv-Test Body Fluids and CirculationDocument8 pagesNeet Iv-Test Body Fluids and CirculationYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Acquired Bronchiectasis: AbcessDocument14 pagesAcquired Bronchiectasis: AbcessAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Quiz 2Document45 pagesAnatomy Quiz 2Upscaled100% (1)
- Hilton Hotema Salt Eating DangerousDocument7 pagesHilton Hotema Salt Eating Dangeroushilly8100% (2)
- Kool Medic Golden 2Document406 pagesKool Medic Golden 2DijattxNo ratings yet
- Surgery PackratDocument46 pagesSurgery PackratRicardo Nelson100% (4)
- Blood Pressure.Document49 pagesBlood Pressure.Sally PujaNo ratings yet
- Neet PG 2012Document361 pagesNeet PG 2012Dhruvi PatelNo ratings yet
- CVSDocument58 pagesCVSDoina SvetNo ratings yet
- AneurysmDocument11 pagesAneurysmNashrah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Medical Mnemonics 4 PrintDocument65 pagesMedical Mnemonics 4 Printanne0521100% (1)
- Reviewer For Zoology LabDocument18 pagesReviewer For Zoology LabayeyedumpNo ratings yet
- Intra Aortic Balloon CounterpulsationDocument39 pagesIntra Aortic Balloon Counterpulsationmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Ebook Diagnostic Imaging Interventional Radiology PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Diagnostic Imaging Interventional Radiology PDF Full Chapter PDFjade.burrow118100% (37)
- Englesko Nemacki Medicinski RecnikDocument312 pagesEnglesko Nemacki Medicinski RecnikMilan Lukic50% (2)
- ANTY 1401 - Week 1 - : AnswersDocument3 pagesANTY 1401 - Week 1 - : AnswersCarina LattoNo ratings yet
- IVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesDocument151 pagesIVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (2)
- ICSE Class 8 Biology Selina Solution Chapter 6 The Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesICSE Class 8 Biology Selina Solution Chapter 6 The Circulatory SystemAmmolh MahajanNo ratings yet
FATE Mindmap
FATE Mindmap
Uploaded by
ameenallyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FATE Mindmap
FATE Mindmap
Uploaded by
ameenallyCopyright:
Available Formats
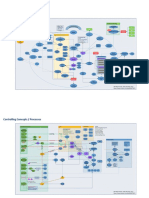
Blood Supply (all views)
Labeled
The anterior wall
The inferior-medial wall
The LV as a supplement to the 4 chamber and
long axis views
Quick
Wall thickness
Chamber dimensions
Apical 2-Ch
What good for
Valve function together with the apical 4
chamber and long axis views
Mitra! inflow and diastolic function
MR / MS
Comprehensive
Regional quantitative LV function
Global quantitative left ventricle function in
conjunction with other cardiac views
Labeled
Pathology
SC 4-Ch Wall thickness
Labeled What can be assessed
Chamber dimensions
The anterior-medial wall (anterior part of the
interventricular septum) Bi-ventricular function
The inferior-lateral wall
The LV supplementary to the 4 chamber and 2
chamber views
Quick Labelled
Wall thickness
The subcostal IVC view is obtained by placing
the transducer in the subcostal position,
Chamber dimensions slightly to the right of the mid line
How to obtain
Apical LAX
Valve function together with the apical 4 What good for The orientation marker on the transducer
chamber and 2 chamber views should be directed cranially
MitraI inflow and diastolic function IVC dimension
Cardiac output in the LVOT IVC dynamics with respiration
What can be assessed
Regional quantitative left ventricular function Placement of umbilical catheter in neonates
Comprehensive
Global quantitative left ventricle function in IVC dynamics for the optimization of fluid responsiveness
conjunction with other cardiac views
IVC IVC diameter (1-3cm from atrial junction)
MS / MR / AS / AR How is it assessed?
Collapsibility
IVC diameter <2.1 cm and >50% collapse
(inspiratory sniff) suggests normal RA
pressure (0-5 mm Hg)
Labeled IVC diameter >2.1 cm and <50% collapse
Volume responsiveness
RA P° (inspiratory sniff) suggests high RA pressure
(1 0-20 mmHg)
Left ventricular outflow tract How is it interpreted?
IVC diameter and collapse that do no.t fit in to
Aortic valve these two scenarios indicate intermediate RA
pressure increase (5-10 mm Hg)
Ascending aorta (proximal part)
Quick
Wall thickness Volume Responsiveness
Chamber dimensions
Apical 5-Ch
Global myocardial function in conjunction with
other cardiac views What good for
Blood flow in the LVOT Apical 4-Ch Labeled
Cardiac output in the LV outflow tract What good for: Same as S4Ch
Regional quantitative left ventricular function
Comprehensive
Global quantitative left ventricular function in
conjunction with other cardiac views
Labeled
MS / MR / AS / AR
Pathology
Wall thickness (M-mode)
PLAX
What good for Chamber dimensions (M-mode)
Labeled Mitra! septa! separation (M-mode)
←ADVANCED
Papillary muscle rupture Parasternal SAX (Mitral)
Aortic and mitral valves
What good for
MV vegetations FATE
BASIC→
Labeled
Pathology
Labeled
Parasternal SAX (Aortic)
Dimensions of cavities: Left and right ventricle
Central PE What good for
PSAX
Myocardium: Left and right ventricle
What good for
Global
Left ventricular function:
Regional (Myocardium with blood supply from
all three coronary arteries represented)
↔
Labeled
The ascending aorta
The aortic arch
Suprasternal
The proximal part of the descending aorta Labeled (L R)
What good for
Vessels to the neck Pleural effusion
Aortic valve stenosis and insufficiency with Pleural Atelectasis/lung parenchyma
Doppler
What good for Pneumothorax
Aortic dissection
Pulmonary edema
Done by selecting "Simpson's Biplane", then
tracing diastolic images of the atrium and
ventricle on the A4Ch and A2Ch Correct intubation confirmed by bi-lateral lung sliding
Modified Simpsons Biplane
Used for LV / RV volume estimation
EF (eyeballing)
FS
Views: A5Ch / ALAX (CWD)
Aortic P° gradient
Used for AR / AS → P° gradient is measured MSS (Normally < 1cm)
and peak velocity → should be > 3 m/s
Measures of LV function on PLAX
End stage P° gradient may not indicate
severity due to LV failure ∴ always Other considerations
assess LV function in conjunction with LA Dimension
Calculations
P° drop
What view: A4Ch (CWD)
Used for MR / MS
MAPSE (Normally > 11mm)
Atrial P° has to be added → convert to EF using FATE card
to the estimated P° drop
What other considerations
Tricuspid P° gradient
Easy to misinterpret trivial MR as severe AS
Premises
TAPSE (Normally > 16-20mm)
→ convert to EF using FATE card
CSA is taken from the diameter
just under the Aortic cusps (inner CSA
edge to inner edge) in mid systole
PLAX or Apical LAX Calculations
Views Cardiac Output
Pathologies
VTI using PWD (Apical 5-Ch) Dont forget POC lung ultrasound (not
FATE) - B-lines, sand on the beach, etc
CO = VTI x HR x CSA
E = Transmitral PWD early filling
A = Transmitral PWD atrial contraction Normal
E/A (Transmitral PWD)
Abnormalities
S = systolic velocity, normal value around 5m/s
with the myocardium moving towards the
transducer
Diastolic function
E' = Mitra! annulus TDI early filling
A' = Mitra! annulus TDI atrial contraction Normal
Tissue Doppler (A4Ch)
Normally < 8 for TDI measured at the
interventricular septum
Normally < 10 for TDI measured in the lateral
wall
Abnormalities
/ ←ADVANCED / SC 4-Ch
/ ←ADVANCED / SC 4-Ch / Labeled
/ ←ADVANCED / IVC
/ ←ADVANCED / IVC / Labelled
/ ←ADVANCED / IVC / Volume responsiveness / How is it interpreted? / Volume Responsiveness
/ ←ADVANCED / Apical 4-Ch
/ ←ADVANCED / Apical 4-Ch / Labeled
/ ←ADVANCED / PLAX
/ ←ADVANCED / PLAX / Labeled
/ ←ADVANCED / PSAX
/ ←ADVANCED / PSAX / Labeled
/ ←ADVANCED / Pleural
/ ←ADVANCED / Pleural / Labeled (L ↔ R)
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / EF (eyeballing)
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Measures of LV function on PLAX
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Measures of LV function on PLAX / FS
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Measures of LV function on PLAX / FS
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Measures of LV function on PLAX / MSS (Normally < 1cm)
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Measures of LV function on PLAX / LA Dimension
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / MAPSE (Normally > 11mm)
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / TAPSE (Normally > 16-20mm)
/ ←ADVANCED / Pathologies
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Aortic P° gradient / Views: A5Ch / ALAX (CWD)
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Tricuspid P° gradient
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Cardiac Output / Views / CSA / PLAX or Apical LAX
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Cardiac Output / Views / VTI using PWD (Apical 5-Ch)
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Diastolic function
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Diastolic function / E/A (Transmitral PWD)
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Diastolic function / E/A (Transmitral PWD) / Normal
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Diastolic function / E/A (Transmitral PWD) / Abnormalities
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Diastolic function / Tissue Doppler (A4Ch)
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Diastolic function / Tissue Doppler (A4Ch) / Normal
/ ←ADVANCED / Calculations / Diastolic function / Tissue Doppler (A4Ch) / Abnormalities
/ ←ADVANCED / Suprasternal
/ ←ADVANCED / Suprasternal / Labeled
/ ←ADVANCED / Parasternal SAX (Aortic)
/ ←ADVANCED / Parasternal SAX (Aortic) / Labeled
/ ←ADVANCED / Parasternal SAX (Mitral)
/ ←ADVANCED / Parasternal SAX (Mitral) / Labeled
/ ←ADVANCED / Apical 5-Ch
/ ←ADVANCED / Apical 5-Ch / Labeled
/ ←ADVANCED / Apical LAX
/ ←ADVANCED / Apical LAX / Labeled
/ ←ADVANCED / Apical 2-Ch
/ ←ADVANCED / Apical 2-Ch / Labeled
/ ←ADVANCED / Blood Supply (all views)
You might also like
- Grossman Baims Cardiac Catheterization Angiography and Intervention 8th Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesGrossman Baims Cardiac Catheterization Angiography and Intervention 8th Edition Ebook PDFjeffrey.nevarez629100% (46)
- Veterinary AnatomyDocument13 pagesVeterinary AnatomyKenneth ShayNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical 1: Johdel CabalunaDocument235 pagesMedical Surgical 1: Johdel CabalunaAlthea Marie C. Mado100% (4)
- Sitema Steel Frame Prescient-Typical-Assemblies - 6.0sys PDFDocument3 pagesSitema Steel Frame Prescient-Typical-Assemblies - 6.0sys PDFalfa27No ratings yet
- Perevod Natalya VasilevnaDocument186 pagesPerevod Natalya Vasilevnamohammad farooque razaa71% (7)
- 07D4 YSR DS 007 Rev09 - Control Valves ListDocument2 pages07D4 YSR DS 007 Rev09 - Control Valves ListAli JameelNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument21 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- Annexure 3 - Vendor ComparisonDocument1 pageAnnexure 3 - Vendor ComparisonNikhil KarkeraNo ratings yet
- 3.1.07 Schedule of Components: L D SD S PIR DN L/P P Rtls Code Description TotalDocument1 page3.1.07 Schedule of Components: L D SD S PIR DN L/P P Rtls Code Description TotalVinay PallivalppilNo ratings yet
- O2 Supply and Demand FrameworkDocument1 pageO2 Supply and Demand FrameworkrachelweinhardtNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument23 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument21 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument22 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument18 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document6 pagesBook 1chinna_p_123No ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument19 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- UL Canon Transducers I-Series, Aplio Platinum Series, Xario Platinum Series, Viamo c100Document8 pagesUL Canon Transducers I-Series, Aplio Platinum Series, Xario Platinum Series, Viamo c100Gleb PolianovskyiNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument17 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument53 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument22 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- TOE For FCA2: Depth: From The ME Ascending Aortic SAX, Advance Probe and Turn Clockwise To Centre The TVDocument25 pagesTOE For FCA2: Depth: From The ME Ascending Aortic SAX, Advance Probe and Turn Clockwise To Centre The TVameenallyNo ratings yet
- DP Transmitter Range Vs Maximum Working Pressure - Automation & Control Engineering Forum PDFDocument1 pageDP Transmitter Range Vs Maximum Working Pressure - Automation & Control Engineering Forum PDFnboulegrouneNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument35 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- Summary Split Duct Bontang 08.01.2021 AgungDocument1 pageSummary Split Duct Bontang 08.01.2021 AgungCitimall BontangNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument51 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- AAF Filter Omega AirDocument2 pagesAAF Filter Omega AirMột Lằn Quang0% (1)
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument28 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- Sunlight RES SOPzS PDFDocument4 pagesSunlight RES SOPzS PDFAnonymous AnonyNo ratings yet
- Vessel Volume & Area CalcDocument5 pagesVessel Volume & Area CalcgagilamNo ratings yet
- 2015 Camera Comparison ChartDocument2 pages2015 Camera Comparison ChartAbhinandan PhapaleNo ratings yet
- Vitros Especificacion de PruebasDocument4 pagesVitros Especificacion de PruebasGeovanna Paola Lagarda MendezNo ratings yet
- 06.Tll With NCR Report June-23Document31 pages06.Tll With NCR Report June-23vishnuNo ratings yet
- Combi SC Straddle Carrier PDFDocument2 pagesCombi SC Straddle Carrier PDFjakeNo ratings yet
- KTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelDocument23 pagesKTM Mühendislik Ltd. Şti.: Kabul Mall Project LV PanelTolgahan KaradagNo ratings yet
- R1 YankbDocument2 pagesR1 Yankbvivia sustrianaNo ratings yet
- E360 Operating ManualDocument180 pagesE360 Operating Manualpablo_ramirez_32No ratings yet
- Avalus Interactive Deck - Version 2Document60 pagesAvalus Interactive Deck - Version 2irmelodyNo ratings yet
- WEG 10004278046 13617810 r01 CFW700 Adenddum H1as1 en Es PTDocument2 pagesWEG 10004278046 13617810 r01 CFW700 Adenddum H1as1 en Es PTLuanNo ratings yet
- Stripper Bolt, Coil Spring, Dowel PinDocument3 pagesStripper Bolt, Coil Spring, Dowel Pinmuhamad laaliNo ratings yet
- 1118393872-61Document3 pages1118393872-61amirkhd8No ratings yet
- Ancon EdjPro Edge LifterDocument2 pagesAncon EdjPro Edge LifterBarrasons Engineers TeamNo ratings yet
- References: Chapter 3 - Sec - Ons 3-6, 3-7, 3-8Document1 pageReferences: Chapter 3 - Sec - Ons 3-6, 3-7, 3-8nickNo ratings yet
- Master Table: General Energy Conservation Special NotesDocument1 pageMaster Table: General Energy Conservation Special NotesSiyad p salamNo ratings yet
- Performance Reactivos A BordoDocument2 pagesPerformance Reactivos A Bordorocio1330No ratings yet
- Modulate Action Catalog EN PDFDocument59 pagesModulate Action Catalog EN PDFjesus casas garayNo ratings yet
- Manage Customer Engagements (Retail)Document1 pageManage Customer Engagements (Retail)Ram Mohan MishraNo ratings yet
- Freudenberg Xpress - Standard MaterialsDocument1 pageFreudenberg Xpress - Standard MaterialsAndrewFranciscoNo ratings yet
- 7 SAP Core Modules (SDMM, FICO, PP, PS, HR) Mindmaps - All-in-One Deck!Document7 pages7 SAP Core Modules (SDMM, FICO, PP, PS, HR) Mindmaps - All-in-One Deck!Yong Benedict100% (1)
- Atellica Solution CH Analyzer Assay Chart, 11484427 Rev 04, EN DXDCM 09017fe9807b250b-1676056852193Document26 pagesAtellica Solution CH Analyzer Assay Chart, 11484427 Rev 04, EN DXDCM 09017fe9807b250b-1676056852193chinuswami100% (3)
- Usaid An Icn Hemocue Population 2022Document1 pageUsaid An Icn Hemocue Population 2022Samson DesieNo ratings yet
- SB7300 051Document1 pageSB7300 051Md MasumNo ratings yet
- Sitema Steel Frame Prescient-Typical-Assemblies - 6.0sysDocument3 pagesSitema Steel Frame Prescient-Typical-Assemblies - 6.0sysalfa27100% (1)
- OISD-129 GAP AnalysisDocument1 pageOISD-129 GAP AnalysisNayan AhmedNo ratings yet
- P843 GEM Poster - JK CiDocument1 pageP843 GEM Poster - JK CiTsubasa OozoraNo ratings yet
- Middle Side Revisi 2bsjsDocument1 pageMiddle Side Revisi 2bsjsJOTA BLUEESSNo ratings yet
- C8051F38x-pages-17Document1 pageC8051F38x-pages-17lingeshtjNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology - AnatomyDocument5 pagesOphthalmology - AnatomyOscar Daniel MendezNo ratings yet
- 18 - Management of Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors 2Document18 pages18 - Management of Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors 2reeem1 alshehri2No ratings yet
- Table of Specifications: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesTable of Specifications: Objectivewanieramlie98No ratings yet
- Products Found: Transmissive Photo InterruptersDocument1 pageProducts Found: Transmissive Photo InterrupterswatteaucarNo ratings yet
- Straumann Dental System Map BoneLevelProstheticsDocument1 pageStraumann Dental System Map BoneLevelProstheticscarla1315No ratings yet
- Surgery StomachDocument31 pagesSurgery StomachAnnie HadassahNo ratings yet
- General Roof Plan Notes: Reflected Ceiling Plan LegendDocument10 pagesGeneral Roof Plan Notes: Reflected Ceiling Plan LegenddawitgggNo ratings yet
- TOE For FCA2: Depth: From The ME Ascending Aortic SAX, Advance Probe and Turn Clockwise To Centre The TVDocument25 pagesTOE For FCA2: Depth: From The ME Ascending Aortic SAX, Advance Probe and Turn Clockwise To Centre The TVameenallyNo ratings yet
- Radiography: S. Moore, E. GardinerDocument6 pagesRadiography: S. Moore, E. GardinerameenallyNo ratings yet
- FCA 2 Trials MindmapDocument1 pageFCA 2 Trials MindmapameenallyNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Electrons Between Atoms With ADocument1 pageTransfer of Electrons Between Atoms With AameenallyNo ratings yet
- Aortic Aneurysm Classification: SL No Time Specific Objective Content Av Aids EvaluationDocument2 pagesAortic Aneurysm Classification: SL No Time Specific Objective Content Av Aids EvaluationArunNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Forum Thorax DoneDocument8 pagesAnatomy Forum Thorax DoneMedShareNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Supertable PDFDocument14 pagesAnatomy Supertable PDFAlex Ondevilla100% (1)
- DAY: 4 I. Objectives: S9LT-lab-26Document6 pagesDAY: 4 I. Objectives: S9LT-lab-26GinalynMaacNo ratings yet
- Chest TraumaDocument28 pagesChest TraumaGitaAmeliaTurnipNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Digestive Glands. Alimentary CanalDocument27 pagesDigestive System: Digestive Glands. Alimentary CanalAnkit NariyaNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischemia and Claudication Unisba 2017Document65 pagesAcute Limb Ischemia and Claudication Unisba 2017nobi nobiNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of Chest Xray A Hands On GuideDocument209 pagesMaking Sense of Chest Xray A Hands On GuideAli Al-Ghamdi100% (2)
- Neet Iv-Test Body Fluids and CirculationDocument8 pagesNeet Iv-Test Body Fluids and CirculationYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Acquired Bronchiectasis: AbcessDocument14 pagesAcquired Bronchiectasis: AbcessAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Quiz 2Document45 pagesAnatomy Quiz 2Upscaled100% (1)
- Hilton Hotema Salt Eating DangerousDocument7 pagesHilton Hotema Salt Eating Dangeroushilly8100% (2)
- Kool Medic Golden 2Document406 pagesKool Medic Golden 2DijattxNo ratings yet
- Surgery PackratDocument46 pagesSurgery PackratRicardo Nelson100% (4)
- Blood Pressure.Document49 pagesBlood Pressure.Sally PujaNo ratings yet
- Neet PG 2012Document361 pagesNeet PG 2012Dhruvi PatelNo ratings yet
- CVSDocument58 pagesCVSDoina SvetNo ratings yet
- AneurysmDocument11 pagesAneurysmNashrah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Medical Mnemonics 4 PrintDocument65 pagesMedical Mnemonics 4 Printanne0521100% (1)
- Reviewer For Zoology LabDocument18 pagesReviewer For Zoology LabayeyedumpNo ratings yet
- Intra Aortic Balloon CounterpulsationDocument39 pagesIntra Aortic Balloon Counterpulsationmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Ebook Diagnostic Imaging Interventional Radiology PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Diagnostic Imaging Interventional Radiology PDF Full Chapter PDFjade.burrow118100% (37)
- Englesko Nemacki Medicinski RecnikDocument312 pagesEnglesko Nemacki Medicinski RecnikMilan Lukic50% (2)
- ANTY 1401 - Week 1 - : AnswersDocument3 pagesANTY 1401 - Week 1 - : AnswersCarina LattoNo ratings yet
- IVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesDocument151 pagesIVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (2)
- ICSE Class 8 Biology Selina Solution Chapter 6 The Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesICSE Class 8 Biology Selina Solution Chapter 6 The Circulatory SystemAmmolh MahajanNo ratings yet