Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nucleic Acid: Genetic Code
Nucleic Acid: Genetic Code
Uploaded by
Angelica AycardoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 8 - Fire and ArsonDocument11 pagesChapter 8 - Fire and ArsonLJ Mermida100% (1)
- Soap Internship ReportDocument18 pagesSoap Internship ReportUmaarAliShiekhNo ratings yet
- K. J. Saunders (Auth.) - Organic Polymer Chemistry - An Introduction To The Organic Chemistry of Adhesives, Fibres, Paints, Plastics and Rubbers-Springer Netherlands (1988) PDFDocument508 pagesK. J. Saunders (Auth.) - Organic Polymer Chemistry - An Introduction To The Organic Chemistry of Adhesives, Fibres, Paints, Plastics and Rubbers-Springer Netherlands (1988) PDFCarlos Alberto Ararat BermudezNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Chemist Chapter 7Document7 pagesLab Report Chemist Chapter 7SPMUSER9A60% (10)
- ANSUL Manual Foam 2016.09 BackupDocument357 pagesANSUL Manual Foam 2016.09 BackupvengielNo ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTypes of Nucleic AcidsJomari Alipante100% (1)
- Biochemistry SemiDocument5 pagesBiochemistry SemiTsukishima RinNo ratings yet
- 04-Chemical Basis of HeredityDocument10 pages04-Chemical Basis of HeredityBen Abella100% (1)
- Heredity Inheritance and Variations PDFDocument56 pagesHeredity Inheritance and Variations PDFNoean LargoNo ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument33 pagesLesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologySherwin YenogacioNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody DNA Ebook Oct2021Document14 pagesVisibleBody DNA Ebook Oct2021Anjarika TripathyNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleDocument44 pagesStructure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleGxmini playsNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five GeneticsDocument28 pagesChapter Five GeneticsYahya AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxDocument2 pagesLESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxJedy IvoryNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument41 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular Biologyanmbeltran31No ratings yet
- Biochemistry FinalsDocument11 pagesBiochemistry FinalsKc CalderonNo ratings yet
- DNAto ProteinDocument41 pagesDNAto ProteinJimmy gogoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Biotech 2Document3 pagesQuarter 3 Biotech 2Hezekiah GatesNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument35 pagesProtein SynthesisDaryl GumacalNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument5 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyMartires, Vea Janela P.100% (1)
- 4.4 Nucleic AcidsDocument13 pages4.4 Nucleic Acidsrovicvaldenor97No ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer FinalsDocument18 pagesBiochem Reviewer Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Pre FinalsDocument31 pagesBiochemistry Pre FinalsArah Lyn ApiagNo ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiochem ReviewerKathleenNo ratings yet
- Simone PostersDocument1 pageSimone PostersMasr RedaNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides Nucleic Acids, and HeredityDocument15 pagesNucleotides Nucleic Acids, and Hereditycjolou100% (3)
- Rna & Protein SynthesisDocument41 pagesRna & Protein SynthesisJoeric CarinanNo ratings yet
- 456-Microbio-Topics - 3Document3 pages456-Microbio-Topics - 3Margot JonesNo ratings yet
- Biotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Document14 pagesBiotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Aileen Ocampo100% (1)
- Nucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesNucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis (1)Document1 pageProtein-Synthesis (1)Juan Carlo SamsonNo ratings yet
- Acidos Nucleicos (Nucleic Acids) : Ana Jimena González Perez Andrea Tatiana Tiedra Bayona Maria Fernanda Avila RubianoDocument11 pagesAcidos Nucleicos (Nucleic Acids) : Ana Jimena González Perez Andrea Tatiana Tiedra Bayona Maria Fernanda Avila RubianoJimena GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocument47 pagesNucleic Acid Chemistryjohn2001royNo ratings yet
- Reaya 3rd PeriodicalDocument16 pagesReaya 3rd PeriodicalRhenz San PedroNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes Lesson 4Document4 pagesGuided Notes Lesson 4Raine RagadioNo ratings yet
- Functions of Nucleic Acids Are:: Nucleic Acids Consist of Either One or Two Long Chains of Two Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesFunctions of Nucleic Acids Are:: Nucleic Acids Consist of Either One or Two Long Chains of Two Types of Nucleic AcidsveloNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument3 pagesGeneticsbonoo.santuchoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Genetic ControlDocument53 pagesChapter 3 Genetic ControlCor GuerreroNo ratings yet
- (SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and PhotosynthesisDocument2 pages(SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and Photosynthesisitz.jdv1694No ratings yet
- Lesson - Perpetu-Wps OfficeDocument6 pagesLesson - Perpetu-Wps OfficeAngelica Pardeño100% (1)
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument28 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologysannsannNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTSDocument3 pagesHANDOUTScareeseta bongcawilNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes - 35 Transcription TranslationDocument2 pagesIB Biology Notes - 35 Transcription TranslationJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument23 pagesNucleic AcidsShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- BacterialDocument2 pagesBacterialjulietaira quibilanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologySowmya PNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Document6 pagesLeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Tzuyu ChouNo ratings yet
- Genbio Lesson 1 4Document26 pagesGenbio Lesson 1 4Greenard Imperial GualbertoNo ratings yet
- BIO-5dll 3rdDocument15 pagesBIO-5dll 3rdarlene dioknoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3A - RNA Types and StructuresDocument3 pagesLesson 3A - RNA Types and Structureshannah CorpuzNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument20 pagesGeneticsMadaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument10 pagesNucleic Acidslovely carilloNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides,: Roles of RNA MoleculesDocument6 pagesNucleotides,: Roles of RNA MoleculesGizelle Mae Pasiol-MacayanNo ratings yet
- Types of RNA-Worksheet Omar IbrahimDocument5 pagesTypes of RNA-Worksheet Omar IbrahimOmar Ibrahim LNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument5 pagesBio ReviewerFaye Lianne MaderoNo ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectDocument18 pagesNucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectSakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3Nona PeriarceNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular Biology: Tapeshwar Yadav (Lecturer)Document69 pagesBasics of Molecular Biology: Tapeshwar Yadav (Lecturer)Nando NanginNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Genetic Control of Protein Synthesis, Cell Function, and Cell ReproductionDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 3: Genetic Control of Protein Synthesis, Cell Function, and Cell ReproductionMan DejeloNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidsAntonette SolaresNo ratings yet
- Act On Cheaper MedicineDocument2 pagesAct On Cheaper MedicineAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Fever DHF UnlikelyDocument1 pageFever DHF UnlikelyAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Family Assessment Tool: Obstetric HX Reproductive Life PlanningDocument2 pagesFamily Assessment Tool: Obstetric HX Reproductive Life PlanningAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Family Health Nursing Learning OutcomesDocument3 pagesFamily Health Nursing Learning OutcomesAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Bemonc Capable Facility or ProviderDocument1 pageBemonc Capable Facility or ProviderAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Angelica Aycardo Flores BSN 2ADocument2 pagesAngelica Aycardo Flores BSN 2AAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Competency Checklist: (Formative/Diagnotic Assessment) : Sherwin M. Calinao Bsit-Automotive 3BDocument3 pagesPre-Competency Checklist: (Formative/Diagnotic Assessment) : Sherwin M. Calinao Bsit-Automotive 3BAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Care of The Mother During PregnancyDocument4 pagesCare of The Mother During PregnancyAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Template - General Overview of The Law On PartnershipDocument1 pageTemplate - General Overview of The Law On PartnershipAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument4 pagesGeneticsAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Competency Checklist: (Formative/Diagnotic Assessment) : Sherwin M. Calinao Bsit-Automotive 3BDocument2 pagesPre-Competency Checklist: (Formative/Diagnotic Assessment) : Sherwin M. Calinao Bsit-Automotive 3BAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and ImplantationDocument2 pagesFertilization and ImplantationAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Lab Expts 3 To 4 ReviewDocument4 pagesLab Expts 3 To 4 ReviewKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Tricalcium Silicate Cement Sealers: Do The Potential Bene Fits of Bioactivity Justify The Drawbacks?Document11 pagesTricalcium Silicate Cement Sealers: Do The Potential Bene Fits of Bioactivity Justify The Drawbacks?sarmientocornejoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Mechanical PropertiesDocument237 pagesEvaluation of The Mechanical PropertiesGeorgiana IlincaNo ratings yet
- Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) : 3.1 Contextualization of and Introduction To MBBR ProcessDocument38 pagesMoving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) : 3.1 Contextualization of and Introduction To MBBR ProcessOscar Eduardo Manco CuevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, 3Document35 pagesChapter 2, 3silvanyangelliong2No ratings yet
- Vitec 5000Document1 pageVitec 5000eduardoNo ratings yet
- Redução. EFFICIENT PERIPHERAL FUNCTIONALIZATIONDocument8 pagesRedução. EFFICIENT PERIPHERAL FUNCTIONALIZATIONGivaldo Dos Santos AndradeNo ratings yet
- Iso 7366 1987Document8 pagesIso 7366 1987Juan OlivaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Systems and Management-71sDocument71 pagesEnvironmental Systems and Management-71salexborges50No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Classification of MatterDocument29 pagesChemistry: Classification of MatterRamzen Raphael DomingoNo ratings yet
- The Transformation of Cu (Oh) Into Cuo, Revisited: 2 Yannick Cudennec, André LecerfDocument4 pagesThe Transformation of Cu (Oh) Into Cuo, Revisited: 2 Yannick Cudennec, André LecerfJose David CastroNo ratings yet
- Econ5688 6900Document4 pagesEcon5688 6900lmao maoNo ratings yet
- research proposal (Hifza Maryam)Document3 pagesresearch proposal (Hifza Maryam)Hifza maryamNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and Related Compounds: Unit 3Document19 pagesCarbohydrates and Related Compounds: Unit 3Gerald AquinoNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials and Testing Apparatus & Equipment: Essential QuestionsDocument9 pagesConstruction Materials and Testing Apparatus & Equipment: Essential QuestionsDiane de OcampoNo ratings yet
- Patriot #16: Parkside Professional Products LTDDocument2 pagesPatriot #16: Parkside Professional Products LTDEmmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 - Thin Film From SolutionDocument41 pagesLecture - 2 - Thin Film From SolutionSam StideNo ratings yet
- Phenol Degradation and Genotypic Analysis of Dioxygenase Genes in Bacteria Isolated From SedimentsDocument9 pagesPhenol Degradation and Genotypic Analysis of Dioxygenase Genes in Bacteria Isolated From Sedimentsahmed salahNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry SyllabusDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry SyllabusAdityaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids, Anhydrides, Esters, and AmidesDocument35 pagesCarboxylic Acids, Anhydrides, Esters, and AmidesHarshwardhan PhatakNo ratings yet
- RPT 12 07Document118 pagesRPT 12 07CHRISTOS KALOUDISNo ratings yet
- Chemically Modified Polysaccharides For Hexavalent Chromium AdsorptionDocument31 pagesChemically Modified Polysaccharides For Hexavalent Chromium Adsorptiondwiki shandyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Secondary School Certificate Examination Syllabus Classes Ix-XDocument11 pagesChemistry: Secondary School Certificate Examination Syllabus Classes Ix-XUmme AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Study of Modern Artistic Materials Using Combined - PICASSO - RIPOLINDocument10 pagesStudy of Modern Artistic Materials Using Combined - PICASSO - RIPOLINJoão Henrique Ribeiro BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Short NotesDocument39 pagesInorganic Chemistry Short NotesPrakhar BishtNo ratings yet
Nucleic Acid: Genetic Code
Nucleic Acid: Genetic Code
Uploaded by
Angelica AycardoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nucleic Acid: Genetic Code
Nucleic Acid: Genetic Code
Uploaded by
Angelica AycardoCopyright:
Available Formats
Protein synthesis
is a process of
creating protein molecules.
STEP 1: TRANSCRIPTION
NUCLEIC ACID
.
DNA in the nucleus partially unwinds and
allows a strand of hnRNA that will turn into
mRNA Essential to all known forms of
life
STEP 2: TRANSLATION
Process by which mRNA codons are
deciphered and a particular protein
molecule is synthesized
GENETIC CODE
The genetic code is the set of
rules used by living cells to
translate information encoded
within genetic material (DNA
or mRNA sequences) into
proteins. ... The code defines
how sequences of nucleotide
triplets, called codons, specify
which amino acid will be
added next during protein
synthesis.
ANTICODON
Anticodons are found on
molecules of tRNA. Their Group 1:
function is to base pair with Marajas, Dwight Micheal
the codon on a strand of Balanoyos, Angeline
mRNA during translation. This Flores, Angelica
action ensures that the correct Agudos, Jonalyn
Cuartelon, Mencherryl
amino acid will be added to
Fernandez, Nicole Khaila
the growing polypeptide chain. Bautista, Shyrichna
A tRNA molecule will enter the
ribosome bound to an amino
acid.
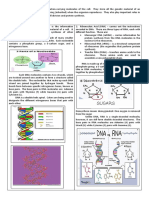
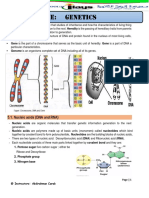
NUCLEIC ACID
-are the biopolymers, or DOUBLE HELIX Kinds of RNA
small biomolecules, essential to all
is the description of the structure of a 1. Transfer RNA – 10 tO 15% -small,
known forms of life. The term nucleic
DNA molecule. A DNA molecule about 80 nucleotides long. -transport
acid is the overall name for DNA and
consists of two strands that wind amino acids to site of protein synthesis.
RNA. They are composed of nucleotides,
around each other like a twisted -exhibits extensive inter chain of bonding
which are the monomers made of three
ladder. Each strand has a backbone represent by clover leaf structure.
components: a 5-carbon sugar,
a phosphate group and a nitrogenous made of alternating groups of sugar
2) Ribosomal RNA – 75 to 80% -several
base. If the sugar is a compound ribose, (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups.
kinds –variable in size -combines with
the polymer is RNA (ribonucleic acid); if proteins to form ribosome's, the site oh
the sugar is derived from ribose CHON synthesis. - molecules to be quite
as deoxyribose, the polymer large.
DNA ENZYMES
is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
3) Messenger RNA -variable size(its size
Helicases are enzymes that bind and may
TYPES OF NUCLEIC ACIDS varies with the size of CHON) -directs
even remodel nucleic acid or nucleic acid
amino acids sequence of proteins - extent
DNA( deoxyribonucleic acid) protein complexes.
of it bonding is very little. - in most cells
–found only inside the nucleus of Primase is an enzyme that synthesizes short it constitutes not more than 5% to 10% of
the cell. Contains the organism’s RNA sequences called primers. These the total cellular RNA
genetic information, including primers serve as a starting point for DNA
instructions for how to make synthesis
proteins.
RNA( ribonucleic acid) – DNA Polymerase is an enzyme that
found both inside and outside of synthesizes DNA molecules from
the nucleus. Directs the building deoxyribonucleotides, the building blocks
of proteins. -primarily concerned of DNA.
with the synthesis of protein. DNA Ligase is a specific type of enzyme,
POLYPEPTIDES are the a ligase, that facilitates the joining of DNA
building blocks of nucleic acids. strands together by catalyzing the formation
of a phosphodiester bond.
You might also like
- Chapter 8 - Fire and ArsonDocument11 pagesChapter 8 - Fire and ArsonLJ Mermida100% (1)
- Soap Internship ReportDocument18 pagesSoap Internship ReportUmaarAliShiekhNo ratings yet
- K. J. Saunders (Auth.) - Organic Polymer Chemistry - An Introduction To The Organic Chemistry of Adhesives, Fibres, Paints, Plastics and Rubbers-Springer Netherlands (1988) PDFDocument508 pagesK. J. Saunders (Auth.) - Organic Polymer Chemistry - An Introduction To The Organic Chemistry of Adhesives, Fibres, Paints, Plastics and Rubbers-Springer Netherlands (1988) PDFCarlos Alberto Ararat BermudezNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Chemist Chapter 7Document7 pagesLab Report Chemist Chapter 7SPMUSER9A60% (10)
- ANSUL Manual Foam 2016.09 BackupDocument357 pagesANSUL Manual Foam 2016.09 BackupvengielNo ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTypes of Nucleic AcidsJomari Alipante100% (1)
- Biochemistry SemiDocument5 pagesBiochemistry SemiTsukishima RinNo ratings yet
- 04-Chemical Basis of HeredityDocument10 pages04-Chemical Basis of HeredityBen Abella100% (1)
- Heredity Inheritance and Variations PDFDocument56 pagesHeredity Inheritance and Variations PDFNoean LargoNo ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument33 pagesLesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologySherwin YenogacioNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody DNA Ebook Oct2021Document14 pagesVisibleBody DNA Ebook Oct2021Anjarika TripathyNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleDocument44 pagesStructure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleGxmini playsNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five GeneticsDocument28 pagesChapter Five GeneticsYahya AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxDocument2 pagesLESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxJedy IvoryNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument41 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular Biologyanmbeltran31No ratings yet
- Biochemistry FinalsDocument11 pagesBiochemistry FinalsKc CalderonNo ratings yet
- DNAto ProteinDocument41 pagesDNAto ProteinJimmy gogoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Biotech 2Document3 pagesQuarter 3 Biotech 2Hezekiah GatesNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument35 pagesProtein SynthesisDaryl GumacalNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument5 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyMartires, Vea Janela P.100% (1)
- 4.4 Nucleic AcidsDocument13 pages4.4 Nucleic Acidsrovicvaldenor97No ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer FinalsDocument18 pagesBiochem Reviewer Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Pre FinalsDocument31 pagesBiochemistry Pre FinalsArah Lyn ApiagNo ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiochem ReviewerKathleenNo ratings yet
- Simone PostersDocument1 pageSimone PostersMasr RedaNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides Nucleic Acids, and HeredityDocument15 pagesNucleotides Nucleic Acids, and Hereditycjolou100% (3)
- Rna & Protein SynthesisDocument41 pagesRna & Protein SynthesisJoeric CarinanNo ratings yet
- 456-Microbio-Topics - 3Document3 pages456-Microbio-Topics - 3Margot JonesNo ratings yet
- Biotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Document14 pagesBiotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Aileen Ocampo100% (1)
- Nucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesNucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis (1)Document1 pageProtein-Synthesis (1)Juan Carlo SamsonNo ratings yet
- Acidos Nucleicos (Nucleic Acids) : Ana Jimena González Perez Andrea Tatiana Tiedra Bayona Maria Fernanda Avila RubianoDocument11 pagesAcidos Nucleicos (Nucleic Acids) : Ana Jimena González Perez Andrea Tatiana Tiedra Bayona Maria Fernanda Avila RubianoJimena GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocument47 pagesNucleic Acid Chemistryjohn2001royNo ratings yet
- Reaya 3rd PeriodicalDocument16 pagesReaya 3rd PeriodicalRhenz San PedroNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes Lesson 4Document4 pagesGuided Notes Lesson 4Raine RagadioNo ratings yet
- Functions of Nucleic Acids Are:: Nucleic Acids Consist of Either One or Two Long Chains of Two Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesFunctions of Nucleic Acids Are:: Nucleic Acids Consist of Either One or Two Long Chains of Two Types of Nucleic AcidsveloNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument3 pagesGeneticsbonoo.santuchoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Genetic ControlDocument53 pagesChapter 3 Genetic ControlCor GuerreroNo ratings yet
- (SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and PhotosynthesisDocument2 pages(SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and Photosynthesisitz.jdv1694No ratings yet
- Lesson - Perpetu-Wps OfficeDocument6 pagesLesson - Perpetu-Wps OfficeAngelica Pardeño100% (1)
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument28 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologysannsannNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTSDocument3 pagesHANDOUTScareeseta bongcawilNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes - 35 Transcription TranslationDocument2 pagesIB Biology Notes - 35 Transcription TranslationJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument23 pagesNucleic AcidsShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- BacterialDocument2 pagesBacterialjulietaira quibilanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologySowmya PNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Document6 pagesLeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Tzuyu ChouNo ratings yet
- Genbio Lesson 1 4Document26 pagesGenbio Lesson 1 4Greenard Imperial GualbertoNo ratings yet
- BIO-5dll 3rdDocument15 pagesBIO-5dll 3rdarlene dioknoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3A - RNA Types and StructuresDocument3 pagesLesson 3A - RNA Types and Structureshannah CorpuzNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument20 pagesGeneticsMadaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument10 pagesNucleic Acidslovely carilloNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides,: Roles of RNA MoleculesDocument6 pagesNucleotides,: Roles of RNA MoleculesGizelle Mae Pasiol-MacayanNo ratings yet
- Types of RNA-Worksheet Omar IbrahimDocument5 pagesTypes of RNA-Worksheet Omar IbrahimOmar Ibrahim LNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument5 pagesBio ReviewerFaye Lianne MaderoNo ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectDocument18 pagesNucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectSakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3Nona PeriarceNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular Biology: Tapeshwar Yadav (Lecturer)Document69 pagesBasics of Molecular Biology: Tapeshwar Yadav (Lecturer)Nando NanginNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Genetic Control of Protein Synthesis, Cell Function, and Cell ReproductionDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 3: Genetic Control of Protein Synthesis, Cell Function, and Cell ReproductionMan DejeloNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidsAntonette SolaresNo ratings yet
- Act On Cheaper MedicineDocument2 pagesAct On Cheaper MedicineAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Fever DHF UnlikelyDocument1 pageFever DHF UnlikelyAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Family Assessment Tool: Obstetric HX Reproductive Life PlanningDocument2 pagesFamily Assessment Tool: Obstetric HX Reproductive Life PlanningAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Family Health Nursing Learning OutcomesDocument3 pagesFamily Health Nursing Learning OutcomesAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Bemonc Capable Facility or ProviderDocument1 pageBemonc Capable Facility or ProviderAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Angelica Aycardo Flores BSN 2ADocument2 pagesAngelica Aycardo Flores BSN 2AAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Competency Checklist: (Formative/Diagnotic Assessment) : Sherwin M. Calinao Bsit-Automotive 3BDocument3 pagesPre-Competency Checklist: (Formative/Diagnotic Assessment) : Sherwin M. Calinao Bsit-Automotive 3BAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Care of The Mother During PregnancyDocument4 pagesCare of The Mother During PregnancyAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Template - General Overview of The Law On PartnershipDocument1 pageTemplate - General Overview of The Law On PartnershipAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument4 pagesGeneticsAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Competency Checklist: (Formative/Diagnotic Assessment) : Sherwin M. Calinao Bsit-Automotive 3BDocument2 pagesPre-Competency Checklist: (Formative/Diagnotic Assessment) : Sherwin M. Calinao Bsit-Automotive 3BAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and ImplantationDocument2 pagesFertilization and ImplantationAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Lab Expts 3 To 4 ReviewDocument4 pagesLab Expts 3 To 4 ReviewKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Tricalcium Silicate Cement Sealers: Do The Potential Bene Fits of Bioactivity Justify The Drawbacks?Document11 pagesTricalcium Silicate Cement Sealers: Do The Potential Bene Fits of Bioactivity Justify The Drawbacks?sarmientocornejoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Mechanical PropertiesDocument237 pagesEvaluation of The Mechanical PropertiesGeorgiana IlincaNo ratings yet
- Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) : 3.1 Contextualization of and Introduction To MBBR ProcessDocument38 pagesMoving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) : 3.1 Contextualization of and Introduction To MBBR ProcessOscar Eduardo Manco CuevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, 3Document35 pagesChapter 2, 3silvanyangelliong2No ratings yet
- Vitec 5000Document1 pageVitec 5000eduardoNo ratings yet
- Redução. EFFICIENT PERIPHERAL FUNCTIONALIZATIONDocument8 pagesRedução. EFFICIENT PERIPHERAL FUNCTIONALIZATIONGivaldo Dos Santos AndradeNo ratings yet
- Iso 7366 1987Document8 pagesIso 7366 1987Juan OlivaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Systems and Management-71sDocument71 pagesEnvironmental Systems and Management-71salexborges50No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Classification of MatterDocument29 pagesChemistry: Classification of MatterRamzen Raphael DomingoNo ratings yet
- The Transformation of Cu (Oh) Into Cuo, Revisited: 2 Yannick Cudennec, André LecerfDocument4 pagesThe Transformation of Cu (Oh) Into Cuo, Revisited: 2 Yannick Cudennec, André LecerfJose David CastroNo ratings yet
- Econ5688 6900Document4 pagesEcon5688 6900lmao maoNo ratings yet
- research proposal (Hifza Maryam)Document3 pagesresearch proposal (Hifza Maryam)Hifza maryamNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and Related Compounds: Unit 3Document19 pagesCarbohydrates and Related Compounds: Unit 3Gerald AquinoNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials and Testing Apparatus & Equipment: Essential QuestionsDocument9 pagesConstruction Materials and Testing Apparatus & Equipment: Essential QuestionsDiane de OcampoNo ratings yet
- Patriot #16: Parkside Professional Products LTDDocument2 pagesPatriot #16: Parkside Professional Products LTDEmmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 - Thin Film From SolutionDocument41 pagesLecture - 2 - Thin Film From SolutionSam StideNo ratings yet
- Phenol Degradation and Genotypic Analysis of Dioxygenase Genes in Bacteria Isolated From SedimentsDocument9 pagesPhenol Degradation and Genotypic Analysis of Dioxygenase Genes in Bacteria Isolated From Sedimentsahmed salahNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry SyllabusDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry SyllabusAdityaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids, Anhydrides, Esters, and AmidesDocument35 pagesCarboxylic Acids, Anhydrides, Esters, and AmidesHarshwardhan PhatakNo ratings yet
- RPT 12 07Document118 pagesRPT 12 07CHRISTOS KALOUDISNo ratings yet
- Chemically Modified Polysaccharides For Hexavalent Chromium AdsorptionDocument31 pagesChemically Modified Polysaccharides For Hexavalent Chromium Adsorptiondwiki shandyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Secondary School Certificate Examination Syllabus Classes Ix-XDocument11 pagesChemistry: Secondary School Certificate Examination Syllabus Classes Ix-XUmme AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Study of Modern Artistic Materials Using Combined - PICASSO - RIPOLINDocument10 pagesStudy of Modern Artistic Materials Using Combined - PICASSO - RIPOLINJoão Henrique Ribeiro BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Short NotesDocument39 pagesInorganic Chemistry Short NotesPrakhar BishtNo ratings yet