Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson: Setting Up Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)
Lesson: Setting Up Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)
Uploaded by
Tanmoy KarmakarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson: Setting Up Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)
Lesson: Setting Up Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)
Uploaded by
Tanmoy KarmakarCopyright:
Available Formats
7/9/2019 SAP e-book
Lesson: Setting Up Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)
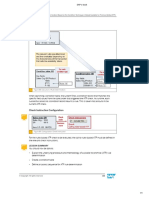
Rule Control: Combination of Substitution Lists (2)
Figure 75: Rule Control: Combination of Substitution Lists (2)
To combine substitution lists in rule control, the following sets of parameters need to be
defined:
● Qualified products and locations: The qualified product or location is used to restrict the
substitution list. You can qualify an element in a substitution list (product or location). The
relevant substitution list is then restricted to this element for the combination.
● Combined lists of product and location: You define how the lists generated by the
combination sequence should be combined.
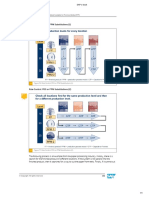
When you apply the combination sequence to the substitution lists, the system always
generates two ordered lists from location products.
For example, when you select the Combine qualified location with all products, then
qualified prod. w. all locs radio button, the first list consists of locations with products and
the second list consists of products with locations.
For the substitution lists, there are two combination options:
- Union: This is the standard setting. If an element from the second list that is not
contained in the first list, then it is appended to the first list.
- Intersection: If an element is not in the second list, then the system deletes it from the
first list.
The Complement of the combination of the product and location list indicator controls whether
the system returns the results list or its complement. The results list is the location product
list generated by the system after combining the location and product lists. If you have set the
indicator, the system returns the complement of the results list.
If a level does not exist for a specific location product, then this location product is not
evaluated.
© Copyright. All rights reserved. 119
1/1
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Rule of Ethics: Organizations in EquilibriumDocument11 pagesThe Rule of Ethics: Organizations in EquilibriumAlzan ZanderNo ratings yet
- 5thGr Sci Bundle 4Document7 pages5thGr Sci Bundle 4Emma YulionoNo ratings yet
- S4hana 2021 UdemyDocument79 pagesS4hana 2021 UdemyTanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageUnit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Available-To-Promise (Atp) Time Series in The LivecacheDocument1 pageAvailable-To-Promise (Atp) Time Series in The LivecacheTanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageUnit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Rule DeterminationDocument1 pageRule DeterminationTanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageUnit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageUnit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Access SequenceDocument1 pageAccess SequenceTanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Lesson 2Document1 pageUnit 7 Lesson 2Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageUnit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Calculation Profile: Unit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageCalculation Profile: Unit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Setting Up Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageLesson: Setting Up Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageUnit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageUnit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageUnit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Planning and Optimization, Choose Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP) General Settings Maintain Check InstructionsDocument1 pageAdvanced Planning and Optimization, Choose Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP) General Settings Maintain Check InstructionsTanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Setting Up Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageLesson: Setting Up Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Document1 pageUnit 7: Rules-Based Availability Check in Global Available-to-Promise (Global ATP)Tanmoy KarmakarNo ratings yet
- PEST AnalysisDocument3 pagesPEST Analysisgekk0No ratings yet
- Vishal PanwarDocument4 pagesVishal Panwarvishaldeep9219No ratings yet
- 1-Sentence-Summary: The Unexpected Joy of Being Sober Will Help You Have ADocument4 pages1-Sentence-Summary: The Unexpected Joy of Being Sober Will Help You Have ASainolzii GanboldNo ratings yet
- Ly Tieu Long - 1 Thoi Vang BongDocument4 pagesLy Tieu Long - 1 Thoi Vang Bonghoaitrung796969No ratings yet
- Indian Maritime University: Section-A (12x 1 12 Marks) (Answer All Questions) Choose The Correct AnswerDocument4 pagesIndian Maritime University: Section-A (12x 1 12 Marks) (Answer All Questions) Choose The Correct AnswerAmitrajeet kumarNo ratings yet
- MMC Questions For Division Finals Grade 5 - 2Document2 pagesMMC Questions For Division Finals Grade 5 - 2Rocelia Abelardo100% (1)
- Gravograph MachinesDocument2 pagesGravograph MachinesIndranil ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Trimble R8s GNSS Receiver: User GuideDocument71 pagesTrimble R8s GNSS Receiver: User GuideSilvio Vuolo NetoNo ratings yet
- Study ThisDocument83 pagesStudy Thispavithiran subramaniNo ratings yet
- MS2A - Ch7 - Practice and Answers With MC Ans Update-1Document56 pagesMS2A - Ch7 - Practice and Answers With MC Ans Update-1s200522No ratings yet
- A Rite of The WerewolfDocument15 pagesA Rite of The WerewolfRAVINDER BSINGH100% (1)
- 5-6 Chapter QSTN AnswerDocument28 pages5-6 Chapter QSTN Answer02 - CM Ankita AdamNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Anilao, Carlos Emmanuel G., G-SOSC002 - Kursong Rizal. Jumel G. Estrañero, DLSUDDocument2 pages(PDF) Anilao, Carlos Emmanuel G., G-SOSC002 - Kursong Rizal. Jumel G. Estrañero, DLSUDcarlos anilaoNo ratings yet
- EmpTech - Multimedia and Its SourcesDocument48 pagesEmpTech - Multimedia and Its SourcesEllisha Mae Sorra MacabentaNo ratings yet
- WTanksDocument26 pagesWTanksestebanosorionovaNo ratings yet
- Gestetner MP C3001/4501 Gestetner MP C3002/ 3502: High PerformanceDocument2 pagesGestetner MP C3001/4501 Gestetner MP C3002/ 3502: High PerformanceDipa Nusantara ArthaNo ratings yet
- Homework Font DownloadDocument5 pagesHomework Font Downloader9rz5b2100% (1)
- Listeria Monocytogenes and Other Listeria Species PDFDocument27 pagesListeria Monocytogenes and Other Listeria Species PDFkurniawan0031No ratings yet
- Multi Touch TrademarkDocument18 pagesMulti Touch TrademarkJordan GolsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Social Science and Applied Social ScienceDocument51 pagesLesson 1 Social Science and Applied Social ScienceGERALDINE ROBLESNo ratings yet
- Final Fnis Assignment 3Document6 pagesFinal Fnis Assignment 3api-521537122No ratings yet
- A B C - S of Hoodoo - Tina HarrisDocument152 pagesA B C - S of Hoodoo - Tina HarrisDarío Ol100% (11)
- 4Document6 pages4nikko candaNo ratings yet
- EXTER T150-st: Installation ManualDocument24 pagesEXTER T150-st: Installation ManualdwdawadNo ratings yet
- Rough Surface Scattering ModelsDocument11 pagesRough Surface Scattering ModelshakimNo ratings yet
- Year 6 Mco Lesson PlanDocument25 pagesYear 6 Mco Lesson PlanVanitha ThiagarajNo ratings yet
- Damper 140613085442 Phpapp01Document22 pagesDamper 140613085442 Phpapp01Andre Luis Fontes FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Blanchard Ch12 2011 1 C. GROTHDocument54 pagesBlanchard Ch12 2011 1 C. GROTHikakkosNo ratings yet