Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Risk of Aspiration
NCP Risk of Aspiration
Uploaded by
Nura Zein100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views2 pagesThis document provides an assessment, intervention, and evaluation plan for a patient with multiple sclerosis who is at risk of aspiration due to impaired swallowing. The short term goal is to monitor the patient for 20 minutes for signs of aspiration and decrease their risk. The long term goal is for the patient to be able to swallow and digest food without aspiration after 1 day of nursing interventions like positioning, feeding techniques, and oral care. The intervention and evaluation sections outline specific actions like monitoring respiration and consciousness, assessing nausea, feeding positioning and timing, and encouraging oral hygiene to meet these goals and decrease aspiration risk.
Original Description:
ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an assessment, intervention, and evaluation plan for a patient with multiple sclerosis who is at risk of aspiration due to impaired swallowing. The short term goal is to monitor the patient for 20 minutes for signs of aspiration and decrease their risk. The long term goal is for the patient to be able to swallow and digest food without aspiration after 1 day of nursing interventions like positioning, feeding techniques, and oral care. The intervention and evaluation sections outline specific actions like monitoring respiration and consciousness, assessing nausea, feeding positioning and timing, and encouraging oral hygiene to meet these goals and decrease aspiration risk.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views2 pagesNCP Risk of Aspiration
NCP Risk of Aspiration
Uploaded by
Nura ZeinThis document provides an assessment, intervention, and evaluation plan for a patient with multiple sclerosis who is at risk of aspiration due to impaired swallowing. The short term goal is to monitor the patient for 20 minutes for signs of aspiration and decrease their risk. The long term goal is for the patient to be able to swallow and digest food without aspiration after 1 day of nursing interventions like positioning, feeding techniques, and oral care. The intervention and evaluation sections outline specific actions like monitoring respiration and consciousness, assessing nausea, feeding positioning and timing, and encouraging oral hygiene to meet these goals and decrease aspiration risk.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
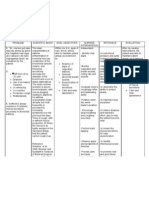
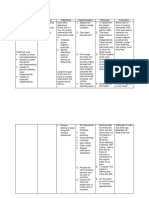
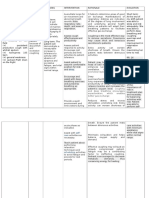
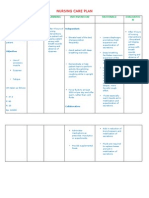
Assessment Explanation of Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation
the problem /Expected outcome
S:Non Short term TX: TX: Goals met if
Patient with After 20 mint of Signs of aspiration should be
O: multiple sclerosis nursing Monitor respiratory identified as soon as possible to Short term After 20
difficulty in have a high risk intervention: rate, depth, and prevent further aspiration and to mint of nursing
chewing and of aspiration both effort. Note any initiate treatment that can be life- intervention:
swallowing chewing and The patient is signs of aspiration saving.
swallowing free of signs of such as dyspnea, The patient is
A: require a number aspiration and cough, cyanosis, The primary risk factor of free of signs of
Risk of of muscles in the the risk of wheezing, or fever. aspiration is decreased level of aspiration and
aspiration mouth and throat aspiration is consciousness. the risk of
related to to work in a decreased. Assess the level of aspiration is
impaired coordinated way. consciousness. Nausea or vomiting places decreased.
swallowing In MS, the nerves patients at great risk for
that control these Long term Assess for presence aspiration, especially if the level
muscles can After1days Of of nausea or of consciousness is Goals met if
become damaged nursing vomiting compromised. Antiemetics may
causing weakness intervention: be required to prevent aspiration Long term
and of regurgitated gastric contents. After1days Of
incoordination nursing intervention:
that can provoke The patient DX: DX:
swallowing swallows and Auscultate bowel Reduced gastrointestinal motility The patient
problems. digests oral, sounds to assess for increases the risk of aspiration as swallows and
nasogastric, or gastrointestinal fluids and food build up in the digests oral,
gastric feeding motility. stomach. Further, elderly patients nasogastric, or
without have a decrease in esophageal gastric feeding
aspiration. motility, which delays without
Position patients esophageal emptying. When aspiration.
with a decreased combined with the weaker gag
level of reflex of older patients, aspiration
consciousness on is at higher risk.
their side.
secretions out of the mouth
instead of down the pharynx,
Keep head of the where they could be aspirated.
bed elevated when
feeding and for at Maintaining a sitting position
least a half-hour after meals may help decrease
afterward. aspiration pneumonia in the
elderly
EDX: EDX:
Encourage patients Oral care before meals reduces
to Provide oral care bacterial counts in the oral cavity.
before and after Oral care after eating removes
meals. residual food that could be
aspirated at a later time.
Instruct the patient
to have liquids after Ingesting food and fluids together
food is eaten. increases swallowing difficulties
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPaudreyNo ratings yet
- Risk For AspirationDocument2 pagesRisk For AspirationGly Mtg100% (6)
- Planning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byDocument10 pagesPlanning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byNicole Anne TungolNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearancejomerdalonaNo ratings yet
- Viii. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument1 pageViii. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationJohn Linero100% (2)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance (Retained Secretions)Document1 pageIneffective Airway Clearance (Retained Secretions)Danna Tan50% (2)
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 pageBody Weakness NCPArnold Christian QuilonNo ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument1 pageNCP DobsarahAcristobalNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- NCP Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Self Care Deficitnor ain b. odingNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument2 pagesConcept Mapjunifer laynoNo ratings yet
- FNCP TB As A Health DeficitDocument5 pagesFNCP TB As A Health Deficitkuu faalNo ratings yet
- NCP ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP ConstipationRoseben Somido100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationeihjay-bravo-8041No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired ComfortDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Impaired ComfortgmindalanoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Document1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Jamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Navidas-Hearing Impairnent Act.Document2 pagesNavidas-Hearing Impairnent Act.Fran Lan100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BAngela Mae DiestroNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAngela Neri0% (1)
- Drug Study of Mannitol RMCDocument1 pageDrug Study of Mannitol RMCAdrian Ardamil0% (1)
- NCP Fracture Risk For InfectionDocument3 pagesNCP Fracture Risk For InfectionMiggsNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPWendy Escalante100% (1)
- NCP For HemorrhoidsDocument3 pagesNCP For HemorrhoidsTADURAN RENE MAE ANGELLI F.No ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaNo ratings yet
- DeficientDocument2 pagesDeficientVANNEZA TRIXZY TAMPARONGNo ratings yet
- Risk For InjuryDocument1 pageRisk For Injuryandycamille7No ratings yet
- NCP SeratroDocument2 pagesNCP SeratroKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleeping PatternDocument5 pagesDisturbed Sleeping PatternEllenare RacionNo ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument3 pagesActivity Intolerance NCPGen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Document4 pagesFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain R/T Injuring AgentsDocument4 pagesNCP Acute Pain R/T Injuring AgentsKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- NCP For Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesNCP For Impaired Skin IntegrityAemz Alacasnap Ainegud100% (1)
- Risk For FallsDocument1 pageRisk For FallsEugene UCNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Imbalance Body TemperatureDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For Imbalance Body TemperatureCarl J.No ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument2 pagesNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoNo ratings yet
- NCP - CapDocument4 pagesNCP - CapSherryNo ratings yet
- NCP LocDocument2 pagesNCP LocMel RodolfoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocument3 pagesDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJashtine JingcoNo ratings yet
- NCP PryllDocument6 pagesNCP PryllpjcolitaNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing Care Plan (ACTUAL) Patient's Name: Alvarez, Marcelo Age: 59y.o. Sex: M Address: Bacolod CityDocument6 pagesIncomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing Care Plan (ACTUAL) Patient's Name: Alvarez, Marcelo Age: 59y.o. Sex: M Address: Bacolod CityTherese MargaretNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAnn AquinoNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternNecheal BaayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Duavent.Document1 pageDrug Study Duavent.Clariss AlotaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Gastric RefluxDocument6 pagesAcute Pain Related To Gastric RefluxRYAN SAPLADNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesImpaired Physical Mobilityvidagurl0% (1)
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- NCP: Impaired Physical Immobility Related To Loss of A Limb (Amputation)Document5 pagesNCP: Impaired Physical Immobility Related To Loss of A Limb (Amputation)RazelAnneValinoNo ratings yet
- NCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T SecretionDocument3 pagesNCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T Secretionherscentasiascribd50% (8)
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired MobilityDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired MobilityLouis LazaroNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To InjuryDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Related To InjuryErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermChi SabbalucaNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedZharm MayNo ratings yet
- Achalasia NCPDocument6 pagesAchalasia NCPkarl davidNo ratings yet
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermDocument3 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE TEST 1 - SECE StudentDocument17 pagesPRACTICE TEST 1 - SECE StudentAlex OlivarNo ratings yet
- Gastro Endo Neuro - AlmenDocument12 pagesGastro Endo Neuro - AlmenAlmen Pandangan Adjul100% (1)
- Performance Evaluation Checklist: Republic of The Philippines Isabela State University Echague, IsabelaDocument20 pagesPerformance Evaluation Checklist: Republic of The Philippines Isabela State University Echague, IsabelaAngel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity N3A & N3BDocument3 pagesLearning Activity N3A & N3BMikaela JosonNo ratings yet
- Nursing ProceduresDocument23 pagesNursing ProceduresMeeKo Videña100% (1)
- Module 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (A)Document18 pagesModule 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (A)Nashebah A. BatuganNo ratings yet
- Insertion and Confirmation of Position of Nasogastric Tubes For Adults and ChildrenDocument28 pagesInsertion and Confirmation of Position of Nasogastric Tubes For Adults and ChildrenMatt Q0% (1)
- Gastric Tube IrrigationDocument3 pagesGastric Tube IrrigationRitika TandonNo ratings yet
- Fluid Replacement For Gastric/Stoma Losses: Setting For Staff PatientsDocument4 pagesFluid Replacement For Gastric/Stoma Losses: Setting For Staff PatientsjuaoNo ratings yet
- NGT LavageDocument16 pagesNGT LavageTina Alteran100% (1)
- Best, 2019 - Selection and Management of Commonly Used Enteral Feeding TubesDocument5 pagesBest, 2019 - Selection and Management of Commonly Used Enteral Feeding TubesThuane SalesNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube InsertionDocument12 pagesNasogastric Tube Insertionmemon_bilqeesNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube InsertionDocument11 pagesNasogastric Tube InsertionDiane Kate Tobias Magno100% (1)
- NGT FeedingDocument2 pagesNGT FeedingValones BeaNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric+Tube+Insertion+and+Removal 2Document24 pagesNasogastric+Tube+Insertion+and+Removal 2Anonymous 4OJslWE1No ratings yet
- Form RKO Unit, Program, Jaringan 2024Document38 pagesForm RKO Unit, Program, Jaringan 2024farmasi.puskesmasgantungNo ratings yet
- Tube Insertion - NGT, Ogt (RM2021)Document2 pagesTube Insertion - NGT, Ogt (RM2021)Ray Emmanuel Enriquez DomingoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Inctruments KM RDocument33 pages1 - Inctruments KM RHelene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- RN Review NuggetsDocument32 pagesRN Review Nuggetsr.a.g.No ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPJoni Lyn Ba-as BayengNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills Checklist: InstructionsDocument7 pagesNursing Skills Checklist: Instructionsapi-539758088No ratings yet
- Adult Nasogastric Tube Insertion Procedure & Management PolicyDocument0 pagesAdult Nasogastric Tube Insertion Procedure & Management PolicyRubelyn Joy LazarteNo ratings yet
- Rotation Plan For Ward DutyDocument9 pagesRotation Plan For Ward DutyMarj Herrera0% (1)
- COnsumption JanuaryDocument11 pagesCOnsumption JanuaryKirby C. CatulinNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube: - Insertion - FeedingDocument61 pagesNasogastric Tube: - Insertion - FeedingJustine Cagatan75% (4)
- Gastric GavageDocument8 pagesGastric Gavageoxidalaj100% (15)
- TPN Total Parenteral Nutrition Recovered..Document17 pagesTPN Total Parenteral Nutrition Recovered..sakhawatNo ratings yet
- Oral Nutrition Support NotesDocument28 pagesOral Nutrition Support Notesleemon.mary.alipao8695No ratings yet
- Enteral FeedingDocument11 pagesEnteral Feedingنعمة حسنىNo ratings yet
- ICU Lines TubesDocument7 pagesICU Lines TubesCindy MurphyNo ratings yet