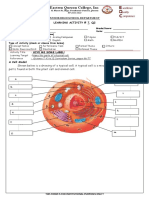
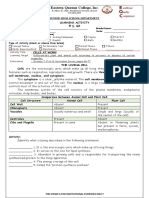
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration Others
Concept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration Others
Uploaded by
Shmaira Ghulam RejanoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- UCSP Module 1 Quarter 1Document21 pagesUCSP Module 1 Quarter 1Jd Anadon86% (194)
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument62 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsTeds TV89% (84)
- Lesson Plan InstitutionsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan InstitutionsNeil Geraldizo Dagohoy100% (2)
- Learning Activity # 15: A Virtue Is An Excellent Trait of CharacterDocument1 pageLearning Activity # 15: A Virtue Is An Excellent Trait of CharacterShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration OthersDocument1 pageConcept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration OthersShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity # 11Document2 pagesLearning Activity # 11Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- 754cfa5fe555 PRELIM LASDocument13 pages754cfa5fe555 PRELIM LASJasper PelicanoNo ratings yet
- Bsed Las Pe101 Gymnastics PrelimDocument10 pagesBsed Las Pe101 Gymnastics PrelimDump LenseNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self OBEDocument16 pagesUnderstanding The Self OBEFranckkMnster91% (11)
- Grading Rubric: Ethnographic Observation TSL 4520Document10 pagesGrading Rubric: Ethnographic Observation TSL 4520galilleagalilleeNo ratings yet
- DLP Module1 AnthroDocument3 pagesDLP Module1 AnthroMaymay AuauNo ratings yet
- Markee Module 1 Session 1 Activity 2Document4 pagesMarkee Module 1 Session 1 Activity 2Markee JoyceNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Course OutlineDocument2 pagesUnderstanding The Self Course OutlineFluffyhaji100% (1)
- Module 1Document6 pagesModule 1pretzqtpogiNo ratings yet
- Module 1introduction About The Course Diagnostic TestDocument7 pagesModule 1introduction About The Course Diagnostic TestJobelle JuanNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Psy3331.001.11s Taught by Karen Huxtable-Jester (kxh014900)Document11 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Psy3331.001.11s Taught by Karen Huxtable-Jester (kxh014900)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1-Module 2 Perspectives of Anthropology, Sociology and Sociology and Political ScienceDocument10 pagesQuarter 1-Module 2 Perspectives of Anthropology, Sociology and Sociology and Political ScienceFranzine Kisha De MesaNo ratings yet
- Q1, Week 1 (Sept 1, 2023)Document3 pagesQ1, Week 1 (Sept 1, 2023)Jenny Vhie S. VinagreraNo ratings yet
- Gen 002 SasDocument143 pagesGen 002 Saszyyw.abello.uiNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument69 pagesUCSPAlexandria Loren Lozano PerezNo ratings yet
- Psychodrama SWK 6114Document16 pagesPsychodrama SWK 6114Hector OrgenaneroNo ratings yet
- Module 2 UcspDocument16 pagesModule 2 UcspBenice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 8 DLLDocument6 pagesMapeh 8 DLLTeodi alden TegioNo ratings yet
- Material SelfDocument5 pagesMaterial SelfDarioz Basanez Lucero100% (3)
- Module 3 UTSDocument23 pagesModule 3 UTSAlexandre QuintoNo ratings yet
- Cesc (Week 1)Document4 pagesCesc (Week 1)Airen AvellanedaNo ratings yet
- TG Iphp - Deontological & Teleological EthicsDocument3 pagesTG Iphp - Deontological & Teleological EthicsGlecyl R.No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Philosophy DLLDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Philosophy DLLKevzz EspirituNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Quarter 1Document20 pagesModule 1 Quarter 1Alex Abonales Dumandan100% (6)
- Title of Book: and Tango Makes Three - Author(s) : Justin Richardson and Peter ParnellDocument1 pageTitle of Book: and Tango Makes Three - Author(s) : Justin Richardson and Peter Parnellapi-261280845No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level District Learning Area Personal Development Name of Teacher/Position Head Teacher School Year Quarter Date WeekDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Plan School Grade Level District Learning Area Personal Development Name of Teacher/Position Head Teacher School Year Quarter Date WeekAdrian CastilloNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 UCSPDocument14 pagesQuarter 1 UCSPWindyl Camarillo76% (41)
- Psy 101 - TopacioDocument15 pagesPsy 101 - TopacioBiancaNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Exemplars in Understanding Culture Society and Politics Using The IDEA Instructional ProcessDocument4 pagesSample Lesson Exemplars in Understanding Culture Society and Politics Using The IDEA Instructional ProcessJen Jeciel PenusNo ratings yet
- Reflective Personal Diary - Part ADocument5 pagesReflective Personal Diary - Part ASeng Yieng100% (1)
- Jenniferhorne Learning Styles Do Matter 050414Document5 pagesJenniferhorne Learning Styles Do Matter 050414api-252669940No ratings yet
- DLL Week 8 PhiloDocument5 pagesDLL Week 8 Philokathryn sorianoNo ratings yet
- Guidance & Counselling Assignment: BY P.Esakkiammal 19BDMT06Document11 pagesGuidance & Counselling Assignment: BY P.Esakkiammal 19BDMT06AntoNo ratings yet
- GROUP1Document3 pagesGROUP1nhfdbhddhsdeyterhguyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Philosophy DLLDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Philosophy DLLJan Andrew FajardoNo ratings yet
- UCSP Module1Document8 pagesUCSP Module1Pablo EraNo ratings yet
- OBE Course Plan SA 2Document15 pagesOBE Course Plan SA 2Ryan M. MungcalNo ratings yet
- LP Intro 1STQDocument16 pagesLP Intro 1STQJomark RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Aug 23Document3 pagesAug 23Jonathan OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document9 pagesModule 1Camille Joves EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- DLP Homeroom-GuidanceDocument4 pagesDLP Homeroom-GuidanceMichelle BorromeoNo ratings yet
- 2 6C Kinds of Qualitative Research PDFDocument15 pages2 6C Kinds of Qualitative Research PDFPhansyNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Syllabus 1st Sem 2013-2014Document7 pagesGeneral Psychology Syllabus 1st Sem 2013-2014api-224281496No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet 11: Immaculate Conception Cathedral SchoolDocument8 pagesLearning Activity Sheet 11: Immaculate Conception Cathedral SchoolPaul Fajardo CanoyNo ratings yet
- Book in A Bag Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesBook in A Bag Lesson Planapi-509266258No ratings yet
- PerDev July 2, 2019Document2 pagesPerDev July 2, 2019LornaNo ratings yet
- Iligan City National High SchoolDocument10 pagesIligan City National High SchoolNoor Yassin H. JamelNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Gabriel Arcangel: Learning ActivityDocument22 pagesColegio de San Gabriel Arcangel: Learning ActivityMarlon GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide Catchup UCSPDocument2 pagesTeaching Guide Catchup UCSPSabel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan Reading & Writing Skills (RWS)Document4 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan Reading & Writing Skills (RWS)Senior High E-ClassNo ratings yet
- Ge1 Handouts - 2 - For Bsba1 - SumalpongDocument5 pagesGe1 Handouts - 2 - For Bsba1 - SumalpongIres YuloNo ratings yet
- Unpack Standards and Competencies SeminarDocument18 pagesUnpack Standards and Competencies SeminarShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Midterm AttachmentsDocument16 pagesMidterm AttachmentsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- 10745-Article Text-41358-1-10-20200314Document13 pages10745-Article Text-41358-1-10-20200314Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- PRELIMINARYDocument2 pagesPRELIMINARYShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMDocument4 pagesMIDTERMShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- PRELIMDocument2 pagesPRELIMShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #1 AttachmentDocument4 pagesLas #1 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las 3 AttachmentsDocument6 pagesLas 3 AttachmentsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las 3Document1 pageLas 3Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las 2 AttachmentsDocument6 pagesLas 2 AttachmentsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #6 AttachmentDocument4 pagesLas #6 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las 1 AttachmentsDocument4 pagesLas 1 AttachmentsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- InstructionalmaterialsDocument5 pagesInstructionalmaterialsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration OthersDocument1 pageConcept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration OthersShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #7Document1 pageLas #7Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Southeast Asian Fabrics and AttireDocument5 pagesSoutheast Asian Fabrics and AttireShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #8 AttachmentDocument3 pagesLas #8 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Performance TaskDocument1 pagePerformance TaskShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #7Document1 pageLas #7Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #6Document1 pageLas #6Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity # 15: A Virtue Is An Excellent Trait of CharacterDocument1 pageLearning Activity # 15: A Virtue Is An Excellent Trait of CharacterShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science-Module 5 Quarter 3Document3 pagesPhysical Science-Module 5 Quarter 3Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Art 8 Q1 TransferDocument7 pagesArt 8 Q1 TransferShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Eastern Quezon College, Inc: (See The Attachment LAS# 1 and Read It)Document4 pagesEastern Quezon College, Inc: (See The Attachment LAS# 1 and Read It)Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Gr. 11 Module 1Document4 pagesEarth Science Gr. 11 Module 1Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Gr. 11 Module 5Document3 pagesEarth Science Gr. 11 Module 5Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity # 11Document2 pagesLearning Activity # 11Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Gr. 11 Module 4Document3 pagesEarth Science Gr. 11 Module 4Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Gr. 11 Module 2Document4 pagesEarth Science Gr. 11 Module 2Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Gr. 11 Module 3Document3 pagesEarth Science Gr. 11 Module 3Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
Concept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration Others
Concept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration Others
Uploaded by
Shmaira Ghulam RejanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration Others
Concept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration Others
Uploaded by
Shmaira Ghulam RejanoCopyright:
Available Formats
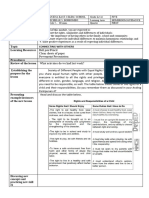
LEARNING ACTIVITY # 16
Name: Score
Program / Course: GE 8- ETHICS Class Schedule: Mon- Tues 7:30- 9:00
Year & Section: 1st yr- Eng Contact No. / FB Account:
Residential Address: Instructor: Angelica F. Nullan, RPm
Type of Activity (check or choose from below)
Concept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio
Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration Others:___________________
Activity Title : Ethical Schools of Thought
Learning Target : Explain the basic premise of Existentialism.
References (Author, Title, Pages) : Bulaong Jr. O. G.,et. Al (2018). Ethics. Foundation of Moral Valuation. Rex Bookstore, Inc.
Montemayor, F.M. (2004) Ethics, The Philosophy of Life. National Book Store.,
Nabor- Nery, M. P. (2003) Ethics, Katha Publishing Co., Inc.
Existentialism
• Is the philosophical belief we are each responsible for creating purpose or meaning in our own lives. Our
individual purpose and meaning is not given to us by Gods, governments, teachers or other authorities.
• Existentialists believe that “existence precedes essence” meaning, man, unlike natural things, objects,
organisms, does not have his essential nature given to him as an already realized possibility.
• Human nature is made, not inborn.
Proponent
The considered founding figures or original giants were: Søren Kierkegaard (1813-1855), Friedrich
Nietzsche (1844-1900), Fyodor Dostoevsky. It became more prominent and widely- known after WWII due to
the following figures: Martin Heidegger (1889-1976), Jean-Paul Sartre (1905-1980).
Criticism
• It is hard to choose your own existence when we are dependent on outside stimuli like money and survival.
THIS FORM IS FOR INSTITUTIONAL PURPOSES ONLY
You might also like
- UCSP Module 1 Quarter 1Document21 pagesUCSP Module 1 Quarter 1Jd Anadon86% (194)
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument62 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsTeds TV89% (84)
- Lesson Plan InstitutionsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan InstitutionsNeil Geraldizo Dagohoy100% (2)
- Learning Activity # 15: A Virtue Is An Excellent Trait of CharacterDocument1 pageLearning Activity # 15: A Virtue Is An Excellent Trait of CharacterShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration OthersDocument1 pageConcept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration OthersShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity # 11Document2 pagesLearning Activity # 11Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- 754cfa5fe555 PRELIM LASDocument13 pages754cfa5fe555 PRELIM LASJasper PelicanoNo ratings yet
- Bsed Las Pe101 Gymnastics PrelimDocument10 pagesBsed Las Pe101 Gymnastics PrelimDump LenseNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self OBEDocument16 pagesUnderstanding The Self OBEFranckkMnster91% (11)
- Grading Rubric: Ethnographic Observation TSL 4520Document10 pagesGrading Rubric: Ethnographic Observation TSL 4520galilleagalilleeNo ratings yet
- DLP Module1 AnthroDocument3 pagesDLP Module1 AnthroMaymay AuauNo ratings yet
- Markee Module 1 Session 1 Activity 2Document4 pagesMarkee Module 1 Session 1 Activity 2Markee JoyceNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Course OutlineDocument2 pagesUnderstanding The Self Course OutlineFluffyhaji100% (1)
- Module 1Document6 pagesModule 1pretzqtpogiNo ratings yet
- Module 1introduction About The Course Diagnostic TestDocument7 pagesModule 1introduction About The Course Diagnostic TestJobelle JuanNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Psy3331.001.11s Taught by Karen Huxtable-Jester (kxh014900)Document11 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Psy3331.001.11s Taught by Karen Huxtable-Jester (kxh014900)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1-Module 2 Perspectives of Anthropology, Sociology and Sociology and Political ScienceDocument10 pagesQuarter 1-Module 2 Perspectives of Anthropology, Sociology and Sociology and Political ScienceFranzine Kisha De MesaNo ratings yet
- Q1, Week 1 (Sept 1, 2023)Document3 pagesQ1, Week 1 (Sept 1, 2023)Jenny Vhie S. VinagreraNo ratings yet
- Gen 002 SasDocument143 pagesGen 002 Saszyyw.abello.uiNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument69 pagesUCSPAlexandria Loren Lozano PerezNo ratings yet
- Psychodrama SWK 6114Document16 pagesPsychodrama SWK 6114Hector OrgenaneroNo ratings yet
- Module 2 UcspDocument16 pagesModule 2 UcspBenice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 8 DLLDocument6 pagesMapeh 8 DLLTeodi alden TegioNo ratings yet
- Material SelfDocument5 pagesMaterial SelfDarioz Basanez Lucero100% (3)
- Module 3 UTSDocument23 pagesModule 3 UTSAlexandre QuintoNo ratings yet
- Cesc (Week 1)Document4 pagesCesc (Week 1)Airen AvellanedaNo ratings yet
- TG Iphp - Deontological & Teleological EthicsDocument3 pagesTG Iphp - Deontological & Teleological EthicsGlecyl R.No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Philosophy DLLDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Philosophy DLLKevzz EspirituNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Quarter 1Document20 pagesModule 1 Quarter 1Alex Abonales Dumandan100% (6)
- Title of Book: and Tango Makes Three - Author(s) : Justin Richardson and Peter ParnellDocument1 pageTitle of Book: and Tango Makes Three - Author(s) : Justin Richardson and Peter Parnellapi-261280845No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level District Learning Area Personal Development Name of Teacher/Position Head Teacher School Year Quarter Date WeekDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Plan School Grade Level District Learning Area Personal Development Name of Teacher/Position Head Teacher School Year Quarter Date WeekAdrian CastilloNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 UCSPDocument14 pagesQuarter 1 UCSPWindyl Camarillo76% (41)
- Psy 101 - TopacioDocument15 pagesPsy 101 - TopacioBiancaNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Exemplars in Understanding Culture Society and Politics Using The IDEA Instructional ProcessDocument4 pagesSample Lesson Exemplars in Understanding Culture Society and Politics Using The IDEA Instructional ProcessJen Jeciel PenusNo ratings yet
- Reflective Personal Diary - Part ADocument5 pagesReflective Personal Diary - Part ASeng Yieng100% (1)
- Jenniferhorne Learning Styles Do Matter 050414Document5 pagesJenniferhorne Learning Styles Do Matter 050414api-252669940No ratings yet
- DLL Week 8 PhiloDocument5 pagesDLL Week 8 Philokathryn sorianoNo ratings yet
- Guidance & Counselling Assignment: BY P.Esakkiammal 19BDMT06Document11 pagesGuidance & Counselling Assignment: BY P.Esakkiammal 19BDMT06AntoNo ratings yet
- GROUP1Document3 pagesGROUP1nhfdbhddhsdeyterhguyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Philosophy DLLDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Philosophy DLLJan Andrew FajardoNo ratings yet
- UCSP Module1Document8 pagesUCSP Module1Pablo EraNo ratings yet
- OBE Course Plan SA 2Document15 pagesOBE Course Plan SA 2Ryan M. MungcalNo ratings yet
- LP Intro 1STQDocument16 pagesLP Intro 1STQJomark RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Aug 23Document3 pagesAug 23Jonathan OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document9 pagesModule 1Camille Joves EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- DLP Homeroom-GuidanceDocument4 pagesDLP Homeroom-GuidanceMichelle BorromeoNo ratings yet
- 2 6C Kinds of Qualitative Research PDFDocument15 pages2 6C Kinds of Qualitative Research PDFPhansyNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Syllabus 1st Sem 2013-2014Document7 pagesGeneral Psychology Syllabus 1st Sem 2013-2014api-224281496No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet 11: Immaculate Conception Cathedral SchoolDocument8 pagesLearning Activity Sheet 11: Immaculate Conception Cathedral SchoolPaul Fajardo CanoyNo ratings yet
- Book in A Bag Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesBook in A Bag Lesson Planapi-509266258No ratings yet
- PerDev July 2, 2019Document2 pagesPerDev July 2, 2019LornaNo ratings yet
- Iligan City National High SchoolDocument10 pagesIligan City National High SchoolNoor Yassin H. JamelNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Gabriel Arcangel: Learning ActivityDocument22 pagesColegio de San Gabriel Arcangel: Learning ActivityMarlon GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide Catchup UCSPDocument2 pagesTeaching Guide Catchup UCSPSabel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan Reading & Writing Skills (RWS)Document4 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan Reading & Writing Skills (RWS)Senior High E-ClassNo ratings yet
- Ge1 Handouts - 2 - For Bsba1 - SumalpongDocument5 pagesGe1 Handouts - 2 - For Bsba1 - SumalpongIres YuloNo ratings yet
- Unpack Standards and Competencies SeminarDocument18 pagesUnpack Standards and Competencies SeminarShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Midterm AttachmentsDocument16 pagesMidterm AttachmentsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- 10745-Article Text-41358-1-10-20200314Document13 pages10745-Article Text-41358-1-10-20200314Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- PRELIMINARYDocument2 pagesPRELIMINARYShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMDocument4 pagesMIDTERMShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- PRELIMDocument2 pagesPRELIMShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #1 AttachmentDocument4 pagesLas #1 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las 3 AttachmentsDocument6 pagesLas 3 AttachmentsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las 3Document1 pageLas 3Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las 2 AttachmentsDocument6 pagesLas 2 AttachmentsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #6 AttachmentDocument4 pagesLas #6 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las 1 AttachmentsDocument4 pagesLas 1 AttachmentsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- InstructionalmaterialsDocument5 pagesInstructionalmaterialsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration OthersDocument1 pageConcept Notes Laboratory Report Portfolio Skills: Exercise / Drill Illustration OthersShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #7Document1 pageLas #7Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Southeast Asian Fabrics and AttireDocument5 pagesSoutheast Asian Fabrics and AttireShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #8 AttachmentDocument3 pagesLas #8 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Performance TaskDocument1 pagePerformance TaskShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #7Document1 pageLas #7Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #6Document1 pageLas #6Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity # 15: A Virtue Is An Excellent Trait of CharacterDocument1 pageLearning Activity # 15: A Virtue Is An Excellent Trait of CharacterShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science-Module 5 Quarter 3Document3 pagesPhysical Science-Module 5 Quarter 3Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Art 8 Q1 TransferDocument7 pagesArt 8 Q1 TransferShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Eastern Quezon College, Inc: (See The Attachment LAS# 1 and Read It)Document4 pagesEastern Quezon College, Inc: (See The Attachment LAS# 1 and Read It)Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Gr. 11 Module 1Document4 pagesEarth Science Gr. 11 Module 1Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Gr. 11 Module 5Document3 pagesEarth Science Gr. 11 Module 5Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity # 11Document2 pagesLearning Activity # 11Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Gr. 11 Module 4Document3 pagesEarth Science Gr. 11 Module 4Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Gr. 11 Module 2Document4 pagesEarth Science Gr. 11 Module 2Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Gr. 11 Module 3Document3 pagesEarth Science Gr. 11 Module 3Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet