Professional Documents
Culture Documents
T215B FINAL 2016-2017 Spring
T215B FINAL 2016-2017 Spring
Uploaded by
Christina FingtonCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CSE3482 Final Winter2016Document20 pagesCSE3482 Final Winter2016Joseph Wu100% (1)
- IT Revision QuestionsDocument5 pagesIT Revision QuestionsPatricia Ĉutie-Lil Princesŝ Green100% (2)
- Inside Reading Unit 9 UpDocument35 pagesInside Reading Unit 9 UpChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Economics Boom and BustDocument50 pagesUnit 6 Economics Boom and BustChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Business Searching For SuccessDocument48 pagesUnit 8 Business Searching For SuccessChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Sociology Decisions, DecisionsDocument47 pagesUnit 7 Sociology Decisions, DecisionsChristina Fington0% (1)
- Astone AP-300 Media PlayerDocument3 pagesAstone AP-300 Media Playerevodata5217No ratings yet
- Manual Camera IP AltecDocument50 pagesManual Camera IP AltecNoel Silva CostaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam-KEY: Faculty of Computer StudiesDocument9 pagesFinal Exam-KEY: Faculty of Computer StudiesChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- COA511S TEST2 MemoDocument6 pagesCOA511S TEST2 MemoLavinia DongwiNo ratings yet
- T215B FINAL 2015-2016 FallDocument8 pagesT215B FINAL 2015-2016 FallChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- T215B - MTA - Spring 2014-2015 AKDocument7 pagesT215B - MTA - Spring 2014-2015 AKChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Lebanon Branch Faculty of Computer StudiesDocument9 pagesLebanon Branch Faculty of Computer StudiesDima TahaNo ratings yet
- T325-Final Exam-MockDocument5 pagesT325-Final Exam-MockDima TahaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Document7 pagesMidterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Christina FingtonNo ratings yet
- FIT1047 S1 2019 Sample Exam SolutionsDocument18 pagesFIT1047 S1 2019 Sample Exam Solutionstwist mcgeeNo ratings yet
- T215B FINAL 2016-2017 FallDocument8 pagesT215B FINAL 2016-2017 FallChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- T324 200810Document8 pagesT324 200810marki-555No ratings yet
- 12 January 2011Document9 pages12 January 2011shaniahNo ratings yet
- Technology in Action Complete 12th Edition Evans Test BankDocument15 pagesTechnology in Action Complete 12th Edition Evans Test BankMrsKellyHammondqrejw100% (16)
- Introduction To Computing and Information Technology 2 Final ExaminationDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Computing and Information Technology 2 Final ExaminationKhalidNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Cardiff Cardiff University Examination PaperDocument15 pagesSolutions: Cardiff Cardiff University Examination PaperKhan Muhammad ZaidNo ratings yet
- Computer StudiesDocument7 pagesComputer Studiesanees shahidNo ratings yet
- Comp 7thDocument3 pagesComp 7thMohib AbbasiNo ratings yet
- CS - QP - XI - Set 2Document7 pagesCS - QP - XI - Set 2shauryamittal11acsNo ratings yet
- EXAMDec2012 SolutionDocument8 pagesEXAMDec2012 Solutionخالد ناهض نايف نجمNo ratings yet
- T215B - MTA Make Up - Spring 2014 - 2015 AKDocument8 pagesT215B - MTA Make Up - Spring 2014 - 2015 AKChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- عماد فاينلDocument17 pagesعماد فاينلChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Mid Seg3155 Ceg3185 2013w SolutionsDocument8 pagesMid Seg3155 Ceg3185 2013w SolutionsMoe Shanti100% (1)
- EECS 485, Fall 2013 Midterm ExamDocument11 pagesEECS 485, Fall 2013 Midterm Examkakazzz2No ratings yet
- Midterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Document7 pagesMidterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Christina FingtonNo ratings yet
- CSEC Info Tech 1993-2003 SolutionsDocument68 pagesCSEC Info Tech 1993-2003 SolutionsVernon WhiteNo ratings yet
- Midterm Solution - COSC 3213 - Computer Networks 1Document13 pagesMidterm Solution - COSC 3213 - Computer Networks 1faesalhasanNo ratings yet
- 2000-1653190315242-CT6054ES - NPS - Exam (1) NewwwwDocument24 pages2000-1653190315242-CT6054ES - NPS - Exam (1) Newwwwdinudee27No ratings yet
- Test 1: LKC Fes UEET2523 October 2016 Digital CommunicationDocument4 pagesTest 1: LKC Fes UEET2523 October 2016 Digital CommunicationYenlyn TanNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 8 SolutionDocument5 pagesAssignment - 8 SolutionGnaneswar reddyNo ratings yet
- PracticeExam 2016Document6 pagesPracticeExam 2016Ahmed Mahmoud YassinNo ratings yet
- Ecomms s07 MidtermDocument6 pagesEcomms s07 MidtermJos2No ratings yet
- Quiz2 Answers Rev3.3Document6 pagesQuiz2 Answers Rev3.3qiaochuma2No ratings yet
- MT0031 Basics of IT Model Question PaperDocument13 pagesMT0031 Basics of IT Model Question Papertiyara124No ratings yet
- CGR Map W22Document26 pagesCGR Map W22arya.murudkar22No ratings yet
- ToDocument14 pagesToyetsedawNo ratings yet
- 2000-1653191490997-NPS QPDocument13 pages2000-1653191490997-NPS QPdinudee27No ratings yet
- SIT202 Problem Solving Report 1Document5 pagesSIT202 Problem Solving Report 1Rakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing and Information Technology 2 Final ExaminationDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Computing and Information Technology 2 Final ExaminationKhalidNo ratings yet
- Keselamatan Teknologi Maklumat Information Technology SecurityDocument9 pagesKeselamatan Teknologi Maklumat Information Technology SecurityKiera ShakiraNo ratings yet
- Exam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1Document4 pagesExam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1svahidsNo ratings yet
- Insem 2017 18 30 Marks CNDocument9 pagesInsem 2017 18 30 Marks CNMUHAMMAD ABU ZAR TAMIMINo ratings yet
- 13imagecompression 120321055027 Phpapp02Document54 pages13imagecompression 120321055027 Phpapp02Tripathi VinaNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning Week 12Document3 pagesDeep Learning Week 1221atharvaghodekarNo ratings yet
- EC360 - Computer CommunicationDocument9 pagesEC360 - Computer CommunicationTtfcfgbbNo ratings yet
- Su 2011 Final SolDocument19 pagesSu 2011 Final SolmissionchocolateNo ratings yet
- Mount Kenya UniversityDocument4 pagesMount Kenya UniversitymosesNo ratings yet
- CSC 340 - Assignment 1Document10 pagesCSC 340 - Assignment 1Daniel sNo ratings yet
- Screening Test Dec 2023Document5 pagesScreening Test Dec 2023adeel hussainNo ratings yet
- Midterm: F B KeyDocument13 pagesMidterm: F B Keyapi-26050323No ratings yet
- Computer Science 2210 XI Worksheet - Mock 2015 Mark Scheme PDFDocument18 pagesComputer Science 2210 XI Worksheet - Mock 2015 Mark Scheme PDFsofia_baloch09No ratings yet
- Networking Mid-Semester Exam Marking Scheme - 2004-5 Semester 1Document7 pagesNetworking Mid-Semester Exam Marking Scheme - 2004-5 Semester 1abraha gebruNo ratings yet
- ADC Ousetion Solutions (BT17ECE067)Document6 pagesADC Ousetion Solutions (BT17ECE067)Ashok YadavNo ratings yet
- Ist 2010 Computer Organization and Programming MidsemexnmsDocument5 pagesIst 2010 Computer Organization and Programming MidsemexnmsAbbNo ratings yet
- Thapar Institute of Engineering & Technology, Patiala: End Semester Examination (May 2019)Document4 pagesThapar Institute of Engineering & Technology, Patiala: End Semester Examination (May 2019)Forza HorizonNo ratings yet
- Csi 3131 Midterm 2015Document10 pagesCsi 3131 Midterm 2015Carlos MorenoNo ratings yet
- Ece-Vii-dsp Algorithms & Architecture (10ec751) - SolutionDocument79 pagesEce-Vii-dsp Algorithms & Architecture (10ec751) - Solutionsanjay prasadNo ratings yet
- Standard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerFrom EverandStandard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerNo ratings yet
- C Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemFrom EverandC Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemNo ratings yet
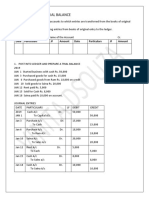
- Ledger Posting and Trial Balance: Date Particulars JF Amount Date Particulars JF AmountDocument4 pagesLedger Posting and Trial Balance: Date Particulars JF Amount Date Particulars JF AmountChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- The Portrait of A LadyDocument2 pagesThe Portrait of A LadyChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Psychology Your Attention, PleaseDocument65 pagesUnit 2 Psychology Your Attention, PleaseChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Physiology Movie MagicDocument44 pagesUnit 3 Physiology Movie MagicChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Anthropology The Mystery of Easter IslandDocument47 pagesUnit 10 Anthropology The Mystery of Easter IslandChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Music The Power of MusicDocument51 pagesUnit 4 Music The Power of MusicChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Neuroscience Sensory PerceptionDocument61 pagesUnit 5 Neuroscience Sensory PerceptionChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- ترجمة الدَّرْسُ السَّادسDocument8 pagesترجمة الدَّرْسُ السَّادسChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- session تعاريف + كلمات + رسماتDocument49 pagessession تعاريف + كلمات + رسماتChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Eat Right, Exercise and Get Plenty of RestDocument9 pagesEat Right, Exercise and Get Plenty of RestChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- ترجمة الدَّرْسُ السَّابعDocument7 pagesترجمة الدَّرْسُ السَّابعChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Midterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Document7 pagesMidterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Christina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Course Calendar: Week Course Book Reading Skills Homework and Self StudyDocument2 pagesCourse Calendar: Week Course Book Reading Skills Homework and Self StudyChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- ترجمة الدَّرْسُ الأوّلDocument12 pagesترجمة الدَّرْسُ الأوّلChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- ترجمة الدَّرْسُ الخامسDocument13 pagesترجمة الدَّرْسُ الخامسChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Revision On Session 1 & 2 MCQ: E-CountingDocument3 pagesRevision On Session 1 & 2 MCQ: E-CountingChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Approved KSA OU MTA Schedule 2018 2019 First 01-10-2018 v2Document1 pageApproved KSA OU MTA Schedule 2018 2019 First 01-10-2018 v2Christina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Midterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Document7 pagesMidterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Christina FingtonNo ratings yet
- MTA Makeup Spring 2014 PDFDocument8 pagesMTA Makeup Spring 2014 PDFChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Indigo DVR Quick Start GuideDocument28 pagesIndigo DVR Quick Start GuideSub ZeroNo ratings yet
- KNX Solutions enDocument32 pagesKNX Solutions enalexwongks6118No ratings yet
- AEO Light 2.2 Beta ManualDocument19 pagesAEO Light 2.2 Beta ManualzlovitchNo ratings yet
- Liveu Lu2000 Server User Guide: Part Number: Doc00076Document34 pagesLiveu Lu2000 Server User Guide: Part Number: Doc00076Javier Sanchez SanchezNo ratings yet
- List of MoviesDocument3 pagesList of MoviesTejaswi VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Lawo Compact ENDocument15 pagesLawo Compact ENEdilsn CruzNo ratings yet
- Skyworth 43 Inch Full HD Led TV - Led-43e3000, Price, Review and Buy in Dubai, ADocument8 pagesSkyworth 43 Inch Full HD Led TV - Led-43e3000, Price, Review and Buy in Dubai, AHer RiosNo ratings yet
- Stream Bitrate CalculatorDocument9 pagesStream Bitrate CalculatorRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Samsung TV UN-J6500Document62 pagesSamsung TV UN-J6500WilfredoRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lista ExtDocument3 pagesLista ExtAlekso GjakovskiNo ratings yet
- Extron MVX 1616 PDFDocument1 pageExtron MVX 1616 PDFBrianNo ratings yet
- Beko 28c723idw IbDocument37 pagesBeko 28c723idw Ibboki7777No ratings yet
- PeliculasasasDocument41 pagesPeliculasasasJose Armando SupoNo ratings yet
- DVB-T2: Digital Terrestrial Receiver WD-822T2Document21 pagesDVB-T2: Digital Terrestrial Receiver WD-822T2reza sajatNo ratings yet
- EC100 User ManualDocument43 pagesEC100 User Manualcristhian7cz356100% (1)
- Fourier - Traductori Si Stocare DateDocument113 pagesFourier - Traductori Si Stocare DateHanganu MariusNo ratings yet
- Specsheet XMR-X5Document2 pagesSpecsheet XMR-X5eduardoNo ratings yet
- Cine Tal MenusDocument18 pagesCine Tal MenusAbdelwahad LabiadNo ratings yet
- Lista Canale OROC TV Prin Cablu 24 Iunie 2022Document5 pagesLista Canale OROC TV Prin Cablu 24 Iunie 2022kukori143No ratings yet
- DM 50 Manual For Canon MicrophoneDocument2 pagesDM 50 Manual For Canon MicrophoneAnonymous 5EVS9avNo ratings yet
- Zoom Q4 ManualDocument32 pagesZoom Q4 ManualcoreymastNo ratings yet
- Comparison CCTV and IP CamerasDocument23 pagesComparison CCTV and IP Camerascommunicates100% (1)
- Audiovox Vme-9120tsDocument32 pagesAudiovox Vme-9120tsadrianNo ratings yet
- TP8 User Manual V009 1-25Document25 pagesTP8 User Manual V009 1-25William Orozco LópezNo ratings yet
- Kenwood DVF 3530 PDFDocument40 pagesKenwood DVF 3530 PDFEmil BlumeNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Pcam Wi2 Quick Install GuideDocument2 pagesHoneywell Pcam Wi2 Quick Install GuideAlarm Grid Home Security and Alarm MonitoringNo ratings yet
- Z7 TG N-Log (En) 01Document14 pagesZ7 TG N-Log (En) 01Zlatko OžanićNo ratings yet
- Philips Bds4241v Service ManualDocument204 pagesPhilips Bds4241v Service ManualopeninfNo ratings yet
T215B FINAL 2016-2017 Spring
T215B FINAL 2016-2017 Spring
Uploaded by
Christina FingtonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
T215B FINAL 2016-2017 Spring
T215B FINAL 2016-2017 Spring
Uploaded by
Christina FingtonCopyright:
Available Formats
Faculty Of Computer Studies
Course code: T215 B
Course Title: Communication and information Technologies- Part B
Final Exam_Key
Spring 2016/2017
T215B_ Final_Exam_Key_Spring_2016/2017 Page 1 of 10
Part 1
This part carries 15% of the total examination marks. You should attempt all questions in this
part by choosing the best answer for each question and write it on the external answer sheet.
Each question carries 1.5 marks. You are advised to dedicate approximately 20 minutes to this
part.
1. To align two fingerprints effectively in a matching process, a reference point known as
___________is often used.
a. Principle.
b. Vertex.
c. Core.
d. Edge.
2. ____________refers to incorrectly believing that two given sets of biometric data are not
matched.
a. False acceptance
b. False positive.
c. False non-match
d. False match.
3. Authentication of the server like the bank with the client like the client’s computer is
achieved using __________setup procedure between an HTTPS protected server and a client.
a. TCP/IP
b. TLS/SSL
c. WEP/WPA
d. SMTP/SOA
4. _____________that may include key-loggers and Trojans is generally downloaded from
compromised websites and email attachments. They can send “harvested” information to
fraudsters.
a. Skimming.
b. DOS attack.
c. Malware.
d. Eavesdropping.
5. One of attributes of the CRIAC framework which is related to a feature or service working as
expected, when expected and with acceptable accuracy is____________.
a. Acceptability
b. Reliability
c. Identity
d. Convenience
T215B_ Final_Exam_Key_Spring_2016/2017 Page 2 of 10
6. _________Consists of small rapid fluctuations of the atmospheric air pressure that surrounds
us.
a. Pixel
b. Sound
c. Image
d. Weight
7. The figure below shows two sinewaves, (a) and (b), that are _________________
a. Completely in phase.
b. Identical phase
c. Completely out of phase
d. Similar phase
8. The condenser microphone and the electret microphone are two types of microphone that
use the effect of_______________.
a. Electrostatic induction.
b. Electromagnetic induction
c. Electrodynamic induction
d. Optical induction.
9. When the minimum sampling rate is not respected, another sinewave with a lower frequency
can be drawn through these samples. This phenomenon is known as____________.
a. Amplification.
b. modulation
c. Aliasing
d. Boosting
10. __________is a tool for video production that provides ways of creating, editing and
processing videos.
a. Compiler
b. Interpreter.
c. Paintbrush
d. AviSynth
T215B_ Final_Exam_Key_Spring_2016/2017 Page 3 of 10
Part 2
This part carries 35% of the total examination marks. You should attempt only 5 out of 7
questions in this part. Each question carries 7 marks. You are advised to dedicate approximately
70 minutes to this part.
1. In the context of Cryptography, explain briefly the difference between a code and a cipher?
Solution:
A code replaces whole words, phrases or groups of symbols with alternatives (or code words).
The purpose of creating a code is not always for secrecy.
A code is used simply as an abbreviation.
A code is used to provide an alternative way of communicating information.
A code is the output of an encoding process (the reverse is decoding) and generally relies on sets
of look-up tables (codebooks) for the conversion processes. (3.5 marks)
Ciphers:
A cipher is the output of an encryption process that either replaces data symbols with alternative
symbols, or rearranges existing symbols.
The operation used to create a cipher is systematic (i.e. follows some set rules).
A cipher is almost always created for reasons of secrecy. (3.5 marks)
2. The level of security afforded during a TLS/SSL session depends on a number of factors. List
three of these factors.
Solution:
i. The browser application used at the client (2 marks)
ii. The version of TLS/SSL used to set up the connection (2 marks)
iii. Proper authentication of the digital certificate. (3 marks)
3. In fingerprint matching process, there are many reasons for intra-class variations. Explain
briefly, three of these reasons.
Solution: (any three from the list below are correct)
Reasons for intra-class variations:
• Displacement: different parts of the fingertip are presented to the sensor.
• Rotation: the fingertip is presented to the sensor at a different angle.
• Pressure of the impression: the finger is pressed on the sensor with a different force.
• Skin condition: on different occasions the fingertip may be dry, wet, scratched or
dirty.
• Condition of the sensor surface: on different occasions the surface may be clean,
dirty or greasy.
• Feature extraction accuracy.
T215B_ Final_Exam_Key_Spring_2016/2017 Page 4 of 10
(Award 2 marks for each of the first two items and 3 marks for the third one. Order is not
significant. Total marks=2x2+3=7 marks)
4. Automated teller machines (ATMs) are often referred as ‘cash machines’. What are the
services that can be provided by ATMs (at least four)? What are their benefits (at least three)?
Solution:
Modern ATMs allow many of the traditional over-the-counter services involving a bank teller to
be accessed through a machine. Some of these services are:
• withdraw cash
• check an account balance
• print out a summary or detailed statement
• pay in cheques, money orders and cash (4 marks)
ATM benefits:
• reduced costs (to banks)
• reduced delays (for customers)
• Extended availability outside normal banking hours. (3 marks)
5. Moving coil microphones is one type of microphones. What are its advantages and
disadvantages? What is its usage?
Solution:
Moving coil Microphones (electromagnetic induction):
Advantages:
Moving-coil microphones are typically quite rugged.
Moving-coil microphones are able to convert sounds more or less over the full range of audible
frequencies. (3 marks)
Disadvantage:
Moving-coil microphones tend not to be as sensitive as electrostatic microphone types.
(2 marks)
Usage:
Moving-coil microphones are most often used as handheld microphones for singers and
speakers, where ruggedness is more important than sensitivity. (2 marks)
T215B_ Final_Exam_Key_Spring_2016/2017 Page 5 of 10
6. Working with sound signal in its digital form has many advantages. Explain briefly, two of
these advantages.
Solution: (Any two items from the given below are correct. Award each item 3.5 marks):
1. Immunity from signal corruption brought about by extensive processing or through
transmission or storage.
2. Mixing and processing of sound comes down to a simple process of computation
(‘number crunching’) rather than involving complicated analogue electronic circuits and
devices.
3. Computer storage techniques can easily be used for storing sound in its digital form.
(Total marks=3.5x2=7 marks)
7. Provide briefly, the definitions for the following terms:
a- Digital video. (3 marks)
b- Frame. (2 marks)
c- Resolution of digital image. (2 marks)
Solution:
a. A digital video can be defined as a sequence of digital still images displayed in rapid
succession in order to simulate different types of animations and effects. (3 marks)
b. Each image in the video is known as a frame. (2 marks)
c. The resolution of the digital image is a measure of the amount of detail it can hold, and
is dependent on the number of pixels used to make up that image. (2 marks)
Part 3
This part carries 50% of the total examination marks. You should attempt all the problems in
this part. You are advised to dedicate approximately 90 minutes to this part.
Problem 1: (10 marks)
Part A:
Compute the decryption keys for the Caesar cipher (single coding) with encryption keys of: 8, 12
and 16? (Show calculation details) (6 marks)
Part B:
Consider that a fingerprint database contains 36 million records. If the identification system can
perform 12000 fingerprint comparisons per second, how long would it take to search through all
the records? Express time in minutes. (Show calculation details and formulas used) (4 marks)
T215B_ Final_Exam_Key_Spring_2016/2017 Page 6 of 10
Solution:
K=8 → K+ 𝐾̅ =26 → 𝐾
̅ =26 – K = 26 – 8 → 𝐾
̅ =18 (2 marks)
̅ ̅ ̅ =14
K=12 → K+ 𝐾 =26 → 𝐾 =26 – K = 26 – 12 → 𝐾 (2 marks)
̅ =26 → 𝐾
K=16 → K+ 𝐾 ̅ =26 – K = 26 – 16 → 𝐾
̅ =10 (2 marks)
Part B:
Time = number of records/processing speed. (1 mark)
6 3
Time = 36 x 10 / 12x10 = 3000 s (2 marks)
Time in minutes= 3000/60=50 minutes. (1 mark)
Problem 2: (10 marks)
Part A:
How many bytes are needed to store a single video frame with a RGB24 color model, and a
frame size of 1400 x 1000 pixels? Express your answer in bytes. At 24 frames per second what is
the data rate that will have to be handled by the video player software? (Express your answer in
megabytes per second.) (4 marks)
Solution:
• The RGB24 color model allocates 24 bits, or 3 bytes, to determine the color of each pixel.
• There are 1400×1000 pixels per frame giving a total of: 3×1400×1000 = 4 200 000 bytes.
(2 marks)
• In 1 second, 24 frames will be processed. The number of bytes per second is therefore:
24×4200000 = 100 800 000 bytes per second = 100.8 megabytes per second. (2 marks)
Part B:
Consider an audio CD that contains exactly one third of an hour of stereo sound. Ignoring any
additional requirements for format information and other data to ensure the integrity of the
sound samples, how many bytes of storage does the CD need to contain for both of the stereo
channels? Assume the sample rate is 44100 samples per second and each sample requires two
bytes of storage. (6 marks)
Solution:
Third of an hour = 20 x 60 = 1200 seconds. (2 marks)
Storage requirement = 1200 × 44100 × 2 = 105840000 bytes (2 marks)
For both of the stereo channels = 105840000 × 2 = 211680000 bytes. (2 marks)
T215B_ Final_Exam_Key_Spring_2016/2017 Page 7 of 10
Problem 3: (10 marks)
The figure below represents a sound signal propagates in air as medium, answer the following
questions:
a) Consider each square of the time axis represents 0.4 ms; calculate the period of signal in
seconds and milliseconds? (2 marks)
T = 5 x 0.4 = 2 ms (1 mark)
T = 2x0.001=0.002 s (1 mark)
b) Calculate the frequency of signal in Hz? (2 marks)
f = 1/T = 1/0.002 = 500 Hz
c) Calculate the wavelength of signal. Consider the speed of sound in air is 340 m/s? (2
marks)
λ = v x T = 340 x 0.002 = 0.68 m
d) What are the peak and root-mean square (r.m.s.) amplitudes? Consider each square of
the pressure axis represents 0.2 µPa? (4 marks)
Peak pressure = 7 squares x 0.2 = 1.4 µPa (2 marks)
r.m.s. = peak amplitude / √2 = 1.4 / √2 = 0.9899 µPa (2 marks)
T215B_ Final_Exam_Key_Spring_2016/2017 Page 8 of 10
Problem 4: (10 marks)
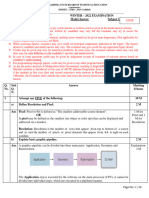
The system shown below consists of two subsystems: Face and fingerprint. Each subsystem
provides a decision (Match or Non-Match)
Finger Match/Non Match
Combined biometric
Fingerprint biometric
Subsystem
system Match/
AND Non Match
Face Facial biometric
Subsystem
Match/Non Match
Suppose that the subsystems decisions are combined as follows:
The outcome of the combined system will be a match only when the outcomes of both of the
subsystems are matches. When the outcome of either subsystem is a non-match, the outcome
of the combined system will be a non-match.
Assume that the following values have been obtained for the two systems separately,
The FMR for the face subsystem is 6%
The FNMR for the face subsystem is 12%
The FMR of the fingerprint subsystem is 2%
The FNMR of the fingerprint subsystem is 7%.
a. Calculate the FMR and FNMR of the combined system? (Show details). (6 marks)
b. What are your observations about the obtained values? (2 marks)
c. What is your conclusion about the combined system? (2 marks)
Solution:
a.
Combined FMR:
A false match can only occur if BOTH subsystems wrongly say there is a match.
FMR of the combined system: FMR = FMR x FMR
C 1 2
6 2 12
FMR = 100 × 100 = 10000 = 0.0012 = 0.12% (3 marks)
c
T215B_ Final_Exam_Key_Spring_2016/2017 Page 9 of 10
Combined FNMR:
A false non-match can occur if EITHER the face subsystem or the fingerprint subsystem gives a
false non-match.
FNMR of the combined system: FNMR = FNMR + FNMR – (FNMR x FNMR )
C 1 2 1 2
FNMR = 12% + 7% – (12% × 7%) = 19% – 0.84% = 18.16%. (3 marks)
C
b.
Observation about FMR: The FMR of the combined system is much smaller (at 0.12%) than is
C
the FMR of either subsystems (which are 6% and 2%). (1 mark)
Observation about FNMR: The FNMR of combined system has not gone down, it has gone up!
(1 mark)
c. Conclusion: Fewer illegitimate users will be allowed access (More security), but more
legitimate users will be denied access (less convenience). (2 marks)
Problem 5: (10 marks)
Use the Vigenère cipher with the keyword ‘tablet’ to encrypt the following sentence: “Welcome
to ITC Program”. Show your work in details in the form of table.
Table below help you to find the code equivalent to each letter.
c ≡ p + K mod 26 (0.5 mark)
Plaintext w e l c o m e t o i t c p r o g r a m
Code 22 4 11 2 14 12 4 19 14 8 19 2 15 17 14 6 17 0 12
Key t a b l e t t a b l e t t a b l e t t
Code 19 0 1 11 4 19 19 0 1 11 4 19 19 0 1 11 4 19 19
Result 15 4 12 13 18 5 23 19 15 19 23 21 8 17 15 17 21 19 5
Cipher P E M N S F X T P T X V I R P R V T F
text
(0.5 for each correct column mark; Total marks= 19x0.5+0.5=10 marks)
(Deduct 1 mark if student write the ciphertext in small letters)
T215B_ Final_Exam_Key_Spring_2016/2017 Page 10 of 10
You might also like
- CSE3482 Final Winter2016Document20 pagesCSE3482 Final Winter2016Joseph Wu100% (1)
- IT Revision QuestionsDocument5 pagesIT Revision QuestionsPatricia Ĉutie-Lil Princesŝ Green100% (2)
- Inside Reading Unit 9 UpDocument35 pagesInside Reading Unit 9 UpChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Economics Boom and BustDocument50 pagesUnit 6 Economics Boom and BustChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Business Searching For SuccessDocument48 pagesUnit 8 Business Searching For SuccessChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Sociology Decisions, DecisionsDocument47 pagesUnit 7 Sociology Decisions, DecisionsChristina Fington0% (1)
- Astone AP-300 Media PlayerDocument3 pagesAstone AP-300 Media Playerevodata5217No ratings yet
- Manual Camera IP AltecDocument50 pagesManual Camera IP AltecNoel Silva CostaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam-KEY: Faculty of Computer StudiesDocument9 pagesFinal Exam-KEY: Faculty of Computer StudiesChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- COA511S TEST2 MemoDocument6 pagesCOA511S TEST2 MemoLavinia DongwiNo ratings yet
- T215B FINAL 2015-2016 FallDocument8 pagesT215B FINAL 2015-2016 FallChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- T215B - MTA - Spring 2014-2015 AKDocument7 pagesT215B - MTA - Spring 2014-2015 AKChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Lebanon Branch Faculty of Computer StudiesDocument9 pagesLebanon Branch Faculty of Computer StudiesDima TahaNo ratings yet
- T325-Final Exam-MockDocument5 pagesT325-Final Exam-MockDima TahaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Document7 pagesMidterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Christina FingtonNo ratings yet
- FIT1047 S1 2019 Sample Exam SolutionsDocument18 pagesFIT1047 S1 2019 Sample Exam Solutionstwist mcgeeNo ratings yet
- T215B FINAL 2016-2017 FallDocument8 pagesT215B FINAL 2016-2017 FallChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- T324 200810Document8 pagesT324 200810marki-555No ratings yet
- 12 January 2011Document9 pages12 January 2011shaniahNo ratings yet
- Technology in Action Complete 12th Edition Evans Test BankDocument15 pagesTechnology in Action Complete 12th Edition Evans Test BankMrsKellyHammondqrejw100% (16)
- Introduction To Computing and Information Technology 2 Final ExaminationDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Computing and Information Technology 2 Final ExaminationKhalidNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Cardiff Cardiff University Examination PaperDocument15 pagesSolutions: Cardiff Cardiff University Examination PaperKhan Muhammad ZaidNo ratings yet
- Computer StudiesDocument7 pagesComputer Studiesanees shahidNo ratings yet
- Comp 7thDocument3 pagesComp 7thMohib AbbasiNo ratings yet
- CS - QP - XI - Set 2Document7 pagesCS - QP - XI - Set 2shauryamittal11acsNo ratings yet
- EXAMDec2012 SolutionDocument8 pagesEXAMDec2012 Solutionخالد ناهض نايف نجمNo ratings yet
- T215B - MTA Make Up - Spring 2014 - 2015 AKDocument8 pagesT215B - MTA Make Up - Spring 2014 - 2015 AKChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- عماد فاينلDocument17 pagesعماد فاينلChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Mid Seg3155 Ceg3185 2013w SolutionsDocument8 pagesMid Seg3155 Ceg3185 2013w SolutionsMoe Shanti100% (1)
- EECS 485, Fall 2013 Midterm ExamDocument11 pagesEECS 485, Fall 2013 Midterm Examkakazzz2No ratings yet
- Midterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Document7 pagesMidterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Christina FingtonNo ratings yet
- CSEC Info Tech 1993-2003 SolutionsDocument68 pagesCSEC Info Tech 1993-2003 SolutionsVernon WhiteNo ratings yet
- Midterm Solution - COSC 3213 - Computer Networks 1Document13 pagesMidterm Solution - COSC 3213 - Computer Networks 1faesalhasanNo ratings yet
- 2000-1653190315242-CT6054ES - NPS - Exam (1) NewwwwDocument24 pages2000-1653190315242-CT6054ES - NPS - Exam (1) Newwwwdinudee27No ratings yet
- Test 1: LKC Fes UEET2523 October 2016 Digital CommunicationDocument4 pagesTest 1: LKC Fes UEET2523 October 2016 Digital CommunicationYenlyn TanNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 8 SolutionDocument5 pagesAssignment - 8 SolutionGnaneswar reddyNo ratings yet
- PracticeExam 2016Document6 pagesPracticeExam 2016Ahmed Mahmoud YassinNo ratings yet
- Ecomms s07 MidtermDocument6 pagesEcomms s07 MidtermJos2No ratings yet
- Quiz2 Answers Rev3.3Document6 pagesQuiz2 Answers Rev3.3qiaochuma2No ratings yet
- MT0031 Basics of IT Model Question PaperDocument13 pagesMT0031 Basics of IT Model Question Papertiyara124No ratings yet
- CGR Map W22Document26 pagesCGR Map W22arya.murudkar22No ratings yet
- ToDocument14 pagesToyetsedawNo ratings yet
- 2000-1653191490997-NPS QPDocument13 pages2000-1653191490997-NPS QPdinudee27No ratings yet
- SIT202 Problem Solving Report 1Document5 pagesSIT202 Problem Solving Report 1Rakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing and Information Technology 2 Final ExaminationDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Computing and Information Technology 2 Final ExaminationKhalidNo ratings yet
- Keselamatan Teknologi Maklumat Information Technology SecurityDocument9 pagesKeselamatan Teknologi Maklumat Information Technology SecurityKiera ShakiraNo ratings yet
- Exam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1Document4 pagesExam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1svahidsNo ratings yet
- Insem 2017 18 30 Marks CNDocument9 pagesInsem 2017 18 30 Marks CNMUHAMMAD ABU ZAR TAMIMINo ratings yet
- 13imagecompression 120321055027 Phpapp02Document54 pages13imagecompression 120321055027 Phpapp02Tripathi VinaNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning Week 12Document3 pagesDeep Learning Week 1221atharvaghodekarNo ratings yet
- EC360 - Computer CommunicationDocument9 pagesEC360 - Computer CommunicationTtfcfgbbNo ratings yet
- Su 2011 Final SolDocument19 pagesSu 2011 Final SolmissionchocolateNo ratings yet
- Mount Kenya UniversityDocument4 pagesMount Kenya UniversitymosesNo ratings yet
- CSC 340 - Assignment 1Document10 pagesCSC 340 - Assignment 1Daniel sNo ratings yet
- Screening Test Dec 2023Document5 pagesScreening Test Dec 2023adeel hussainNo ratings yet
- Midterm: F B KeyDocument13 pagesMidterm: F B Keyapi-26050323No ratings yet
- Computer Science 2210 XI Worksheet - Mock 2015 Mark Scheme PDFDocument18 pagesComputer Science 2210 XI Worksheet - Mock 2015 Mark Scheme PDFsofia_baloch09No ratings yet
- Networking Mid-Semester Exam Marking Scheme - 2004-5 Semester 1Document7 pagesNetworking Mid-Semester Exam Marking Scheme - 2004-5 Semester 1abraha gebruNo ratings yet
- ADC Ousetion Solutions (BT17ECE067)Document6 pagesADC Ousetion Solutions (BT17ECE067)Ashok YadavNo ratings yet
- Ist 2010 Computer Organization and Programming MidsemexnmsDocument5 pagesIst 2010 Computer Organization and Programming MidsemexnmsAbbNo ratings yet
- Thapar Institute of Engineering & Technology, Patiala: End Semester Examination (May 2019)Document4 pagesThapar Institute of Engineering & Technology, Patiala: End Semester Examination (May 2019)Forza HorizonNo ratings yet
- Csi 3131 Midterm 2015Document10 pagesCsi 3131 Midterm 2015Carlos MorenoNo ratings yet
- Ece-Vii-dsp Algorithms & Architecture (10ec751) - SolutionDocument79 pagesEce-Vii-dsp Algorithms & Architecture (10ec751) - Solutionsanjay prasadNo ratings yet
- Standard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerFrom EverandStandard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerNo ratings yet
- C Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemFrom EverandC Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemNo ratings yet
- Ledger Posting and Trial Balance: Date Particulars JF Amount Date Particulars JF AmountDocument4 pagesLedger Posting and Trial Balance: Date Particulars JF Amount Date Particulars JF AmountChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- The Portrait of A LadyDocument2 pagesThe Portrait of A LadyChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Psychology Your Attention, PleaseDocument65 pagesUnit 2 Psychology Your Attention, PleaseChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Physiology Movie MagicDocument44 pagesUnit 3 Physiology Movie MagicChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Anthropology The Mystery of Easter IslandDocument47 pagesUnit 10 Anthropology The Mystery of Easter IslandChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Music The Power of MusicDocument51 pagesUnit 4 Music The Power of MusicChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Neuroscience Sensory PerceptionDocument61 pagesUnit 5 Neuroscience Sensory PerceptionChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- ترجمة الدَّرْسُ السَّادسDocument8 pagesترجمة الدَّرْسُ السَّادسChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- session تعاريف + كلمات + رسماتDocument49 pagessession تعاريف + كلمات + رسماتChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Eat Right, Exercise and Get Plenty of RestDocument9 pagesEat Right, Exercise and Get Plenty of RestChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- ترجمة الدَّرْسُ السَّابعDocument7 pagesترجمة الدَّرْسُ السَّابعChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Midterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Document7 pagesMidterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Christina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Course Calendar: Week Course Book Reading Skills Homework and Self StudyDocument2 pagesCourse Calendar: Week Course Book Reading Skills Homework and Self StudyChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- ترجمة الدَّرْسُ الأوّلDocument12 pagesترجمة الدَّرْسُ الأوّلChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- ترجمة الدَّرْسُ الخامسDocument13 pagesترجمة الدَّرْسُ الخامسChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Revision On Session 1 & 2 MCQ: E-CountingDocument3 pagesRevision On Session 1 & 2 MCQ: E-CountingChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Approved KSA OU MTA Schedule 2018 2019 First 01-10-2018 v2Document1 pageApproved KSA OU MTA Schedule 2018 2019 First 01-10-2018 v2Christina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Midterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Document7 pagesMidterm Assessment - Answer Key: Faculty of Computer Studies T215B Communication and Information Technologies (II)Christina FingtonNo ratings yet
- MTA Makeup Spring 2014 PDFDocument8 pagesMTA Makeup Spring 2014 PDFChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Indigo DVR Quick Start GuideDocument28 pagesIndigo DVR Quick Start GuideSub ZeroNo ratings yet
- KNX Solutions enDocument32 pagesKNX Solutions enalexwongks6118No ratings yet
- AEO Light 2.2 Beta ManualDocument19 pagesAEO Light 2.2 Beta ManualzlovitchNo ratings yet
- Liveu Lu2000 Server User Guide: Part Number: Doc00076Document34 pagesLiveu Lu2000 Server User Guide: Part Number: Doc00076Javier Sanchez SanchezNo ratings yet
- List of MoviesDocument3 pagesList of MoviesTejaswi VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Lawo Compact ENDocument15 pagesLawo Compact ENEdilsn CruzNo ratings yet
- Skyworth 43 Inch Full HD Led TV - Led-43e3000, Price, Review and Buy in Dubai, ADocument8 pagesSkyworth 43 Inch Full HD Led TV - Led-43e3000, Price, Review and Buy in Dubai, AHer RiosNo ratings yet
- Stream Bitrate CalculatorDocument9 pagesStream Bitrate CalculatorRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Samsung TV UN-J6500Document62 pagesSamsung TV UN-J6500WilfredoRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lista ExtDocument3 pagesLista ExtAlekso GjakovskiNo ratings yet
- Extron MVX 1616 PDFDocument1 pageExtron MVX 1616 PDFBrianNo ratings yet
- Beko 28c723idw IbDocument37 pagesBeko 28c723idw Ibboki7777No ratings yet
- PeliculasasasDocument41 pagesPeliculasasasJose Armando SupoNo ratings yet
- DVB-T2: Digital Terrestrial Receiver WD-822T2Document21 pagesDVB-T2: Digital Terrestrial Receiver WD-822T2reza sajatNo ratings yet
- EC100 User ManualDocument43 pagesEC100 User Manualcristhian7cz356100% (1)
- Fourier - Traductori Si Stocare DateDocument113 pagesFourier - Traductori Si Stocare DateHanganu MariusNo ratings yet
- Specsheet XMR-X5Document2 pagesSpecsheet XMR-X5eduardoNo ratings yet
- Cine Tal MenusDocument18 pagesCine Tal MenusAbdelwahad LabiadNo ratings yet
- Lista Canale OROC TV Prin Cablu 24 Iunie 2022Document5 pagesLista Canale OROC TV Prin Cablu 24 Iunie 2022kukori143No ratings yet
- DM 50 Manual For Canon MicrophoneDocument2 pagesDM 50 Manual For Canon MicrophoneAnonymous 5EVS9avNo ratings yet
- Zoom Q4 ManualDocument32 pagesZoom Q4 ManualcoreymastNo ratings yet
- Comparison CCTV and IP CamerasDocument23 pagesComparison CCTV and IP Camerascommunicates100% (1)
- Audiovox Vme-9120tsDocument32 pagesAudiovox Vme-9120tsadrianNo ratings yet
- TP8 User Manual V009 1-25Document25 pagesTP8 User Manual V009 1-25William Orozco LópezNo ratings yet
- Kenwood DVF 3530 PDFDocument40 pagesKenwood DVF 3530 PDFEmil BlumeNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Pcam Wi2 Quick Install GuideDocument2 pagesHoneywell Pcam Wi2 Quick Install GuideAlarm Grid Home Security and Alarm MonitoringNo ratings yet
- Z7 TG N-Log (En) 01Document14 pagesZ7 TG N-Log (En) 01Zlatko OžanićNo ratings yet
- Philips Bds4241v Service ManualDocument204 pagesPhilips Bds4241v Service ManualopeninfNo ratings yet