Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Danabar Facm42l Elep08 Activity1
Danabar Facm42l Elep08 Activity1
Uploaded by
Aldrin Jesril BascoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Danabar Facm42l Elep08 Activity1
Danabar Facm42l Elep08 Activity1
Uploaded by
Aldrin Jesril BascoCopyright:
Available Formats
DANABAR, DEMIE JAY V.
FACM42L – ELEP08
T/F – 9:00AM – 11:00AM
04/16/2021
INTRODUCTION
Polarity means the direction of the induced voltages in the primary and the
secondary winding of the transformer. If the two transformers are connected in parallel,
then the polarity should be known for the proper connection of the transformer. There
are two types of polarity one is Additive, and another is Subtractive.
Current flows from high voltage point to low voltage point due to the potential
difference between them. Here, electrical polarity comes into the picture. Electrical
polarity simply describes the direction of the current flow. When we look into DC
system, we find that one pole is always positive and the other one is always negative
that imply that the current flows in one direction only. But when we look into an AC
system, the terminals are changing their polarity periodically, and the direction of the
current also changes accordingly.
When we look into the operations of the distribution transformers, we find that
they need to work all the time and also need to supply at high demand at peak times.
So, to cope up with these situations, we connect the transformers in parallel.
Paralleling is done by connecting same polarity terminals of the primary winding
together. A similar procedure is done for the secondary winding. Paralleling will increase
the power supplying capacity and also the reliability of the system.
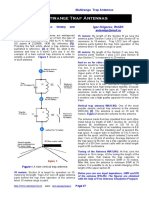
Procedures of Polarity Test of Transformer:
1. Connect the circuit as shown above with a voltmeter (Va) across primary winding
and another voltmeter (Vb) across the secondary winding.
2. If available, take down the ratings of the transformer and the turn ratio.
3. We connect a voltmeter (Vc) between primary and secondary windings.
4. We apply some voltage to the primary side.
5. By checking the value in the voltmeter (Vc), we can find whether it is additive or
subtractive polarity.
a.) What safety procedure must be observed in checking the polarity of transformer?
Use the lowest AC voltage level possible to excite the winding and reduce
potential hazards. An adjustable ac voltage source is recommended to keep the
test voltage low.
b.) Solve this:
I. The polarity test is performed upon a transformer. If the voltmeter
are 121.8 volts and 110.2 volts , calculate the turns ratio.
Using the given voltage on the voltmeter we can get the turns ration and the
answer is 11:10
II. If the transformer is actually rated 480/120 volts the transformer ratio is
4:1. In applying a test voltage of 120 on the primary, what is the
voltmeter reading if the polarity is
a.) Subtractive
= (120 – 30)
= 90v is the voltmeter reading
b.) Additive
= (120 + 30)
= 150v is the voltmeter reading
C.) State the purpose of having checked the polarity of the transformer.
We do polarity test on parallel transformers to ensure that we connect the
same polarity windings and not the opposite ones. If we accidentally connect
the opposite polarities of the windings, it will result in a short-circuit and
eventually damage the machine.
You might also like
- Board Exam1Document103 pagesBoard Exam1MJ Pineda59% (17)
- Lab Report On Single Phase TransformerDocument22 pagesLab Report On Single Phase TransformerSamuel Ogeda Otieno60% (5)
- ZEST-ZQ310 Series CatalogDocument7 pagesZEST-ZQ310 Series CatalogSofiyan HadyNo ratings yet
- Open Ended LAB: Object ApparatusDocument10 pagesOpen Ended LAB: Object ApparatusJawad QaimkhaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 02Document2 pagesExperiment 02micuNo ratings yet
- AREVA The Testing of TransformerDocument49 pagesAREVA The Testing of TransformerMahmoud Moez92% (12)
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2EmtiazEmonNo ratings yet
- BS 7639 Short Circuit Current Calculation in 3phase AC SysteDocument92 pagesBS 7639 Short Circuit Current Calculation in 3phase AC SysteAimee Rachel Dean Rabe100% (2)
- FORMER Testing Manual2003Document126 pagesFORMER Testing Manual2003Anonymous EKVfZYQiegNo ratings yet
- Zaragoza - Dominic - Ee07l-Experiment-4-Transformer - Polarity TestDocument5 pagesZaragoza - Dominic - Ee07l-Experiment-4-Transformer - Polarity TestDominic ZaragozaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Polarity Test - Simple Guide - LinquipDocument9 pagesWhat Is The Polarity Test - Simple Guide - Linquipbiju mrNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.3Document6 pagesExperiment No.3justinepunzalan250% (1)
- Electrical Machines I29012020Document73 pagesElectrical Machines I29012020fake1542002No ratings yet
- Experiment No: 1: Aim: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesExperiment No: 1: Aim: ObjectivesRushikesh WankhadeNo ratings yet
- Vincoy, John Lloyd Single Phase TransformerDocument19 pagesVincoy, John Lloyd Single Phase TransformerVincoy JohnlloydNo ratings yet
- Transformer PolarityDocument2 pagesTransformer PolaritysohailkhanzNo ratings yet
- Transformer TestingDocument33 pagesTransformer Testingiamketul6340No ratings yet
- SrabanDocument10 pagesSrabanTenz WastonNo ratings yet
- Polarity Test TransformerDocument7 pagesPolarity Test TransformerPINEDA CRISTIAN PAUL C.No ratings yet
- Exp4. CTDocument8 pagesExp4. CTMohammed Abu Al HaijaNo ratings yet
- Various Routine Test of Power Transformer - (Part-2)Document7 pagesVarious Routine Test of Power Transformer - (Part-2)supermannonNo ratings yet
- Figure 49: AC Method For Testing Transformer Polarities: POL H X 1 2 POL H X 1 2Document5 pagesFigure 49: AC Method For Testing Transformer Polarities: POL H X 1 2 POL H X 1 2senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Polarity Test On Single Phase Transformers and Three Phase Transformer ConnectionsDocument14 pagesPolarity Test On Single Phase Transformers and Three Phase Transformer ConnectionsPavan DakoreNo ratings yet
- EEE101 Ch8Document22 pagesEEE101 Ch8SERHAT YILDIRIMNo ratings yet
- Transformer: Disediakan Oleh: Siti Fatimah Binti Mohd JamilDocument39 pagesTransformer: Disediakan Oleh: Siti Fatimah Binti Mohd JamilSiti Fatimah Mohd Jamil100% (1)
- Experiment No. 03 Polarity and Ratio Tests of Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 03 Polarity and Ratio Tests of Single Phase TransformerAwais ChohanNo ratings yet
- Nbsbulletinv10n3p419 A2b PDFDocument10 pagesNbsbulletinv10n3p419 A2b PDFIlham HendratamaNo ratings yet
- EEP 2301 Notes22Document37 pagesEEP 2301 Notes22dennisnyala02No ratings yet
- EES612 Lab2Document19 pagesEES612 Lab2kombat13_708353334No ratings yet
- Transformer Testing Using MatlabDocument6 pagesTransformer Testing Using MatlabPramodTeliNo ratings yet
- Lecture Power System RepresentationDocument8 pagesLecture Power System RepresentationRaniel Rey CantorNo ratings yet
- Assignment Transformer SizesDocument7 pagesAssignment Transformer SizesAC CuetoNo ratings yet
- Machine Lab 3Document5 pagesMachine Lab 3Khurram HussainNo ratings yet
- Potentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDocument26 pagesPotentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDIVYA PRASOONA CNo ratings yet
- Six Units of MDocument21 pagesSix Units of MMayank Singh KushwahNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic InstrumentationDocument26 pagesElectrical & Electronic InstrumentationKamal PhyNo ratings yet
- Open Ended LabsDocument13 pagesOpen Ended LabsMuhammad ImadNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1.: Aim: Determination of Transformer Equivalent Circuit From Open Circuit TheoryDocument7 pagesExperiment 1.: Aim: Determination of Transformer Equivalent Circuit From Open Circuit TheorySur ShriNo ratings yet
- Exp5. VTDocument10 pagesExp5. VTMohammed Abu Al HaijaNo ratings yet
- NTDC-merged DataDocument123 pagesNTDC-merged DataShahzaib ElahiNo ratings yet
- Lectures 3&4Document47 pagesLectures 3&4Yong Jian RongNo ratings yet
- Transformer Basics and Transformer Principles of OperationDocument14 pagesTransformer Basics and Transformer Principles of Operationengsamir296No ratings yet
- Module 2 For IaDocument8 pagesModule 2 For IaRakshithNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Experiment-3Document6 pagesLab Report: Experiment-3ayash mohantyNo ratings yet
- Em Lab 3 091Document7 pagesEm Lab 3 091Mian Talha TalhaNo ratings yet
- Cha:4 Potentiometers: Principal of D.C. Potentiometer Crompton's Potentiometer Application of DC PotentiometerDocument16 pagesCha:4 Potentiometers: Principal of D.C. Potentiometer Crompton's Potentiometer Application of DC PotentiometerNirav ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Transformer Basics A Typical Voltage TraDocument13 pagesTransformer Basics A Typical Voltage Trarotimi olalekan fataiNo ratings yet
- Observation of Polarity Test of A Single Phase TransformerDocument3 pagesObservation of Polarity Test of A Single Phase TransformerAbdul Mubin100% (2)
- Method No: 2 (Current Voltage Method of Measurement of Winding Resistance)Document6 pagesMethod No: 2 (Current Voltage Method of Measurement of Winding Resistance)Hassan AbdoNo ratings yet
- 03 Electrical NotesDocument27 pages03 Electrical NotesizzazackNo ratings yet
- Testing of TransformerDocument19 pagesTesting of Transformerrecviswanathan100% (1)
- Nbsbulletinv10n3p419 A2bDocument10 pagesNbsbulletinv10n3p419 A2bmanikandaprabhuNo ratings yet
- Test On TransformerDocument13 pagesTest On TransformerGurvinder Singh Virdi100% (2)
- Polarity / Vector Group TestDocument6 pagesPolarity / Vector Group TestHassan AbdoNo ratings yet
- IEEE 62 (Guide ForField Testing of Oil Filled Transformers) (003) ...Document3 pagesIEEE 62 (Guide ForField Testing of Oil Filled Transformers) (003) ...Faheem PP13No ratings yet
- Percentage Impedance of Transformer & Its CalculationDocument6 pagesPercentage Impedance of Transformer & Its CalculationTran Quoc Thinh - M&ENo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report #04 Testing TransformersDocument5 pagesLaboratory Report #04 Testing TransformersCristian Camilo Díaz Piñeros0% (1)
- Chapter 4 AssignmentDocument2 pagesChapter 4 AssignmentAldrin Jesril BascoNo ratings yet
- LEC ThermoI 2 ConservationMassEnergy1Document16 pagesLEC ThermoI 2 ConservationMassEnergy1Aldrin Jesril BascoNo ratings yet
- National University: WAC 2: ZENATIX: Discovering Market FitDocument8 pagesNational University: WAC 2: ZENATIX: Discovering Market FitAldrin Jesril BascoNo ratings yet
- Transient Voltage Surge SupressorDocument2 pagesTransient Voltage Surge SupressorAldrin Jesril BascoNo ratings yet
- IEEE STD C37.34-1994 IEEE Standard Test Code For High-Voltage Air SwitchesDocument38 pagesIEEE STD C37.34-1994 IEEE Standard Test Code For High-Voltage Air SwitchesFranklin AntezanaNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet 3RH1911-2GA22Document4 pagesProduct Data Sheet 3RH1911-2GA22Franisco Daniel SanchezNo ratings yet
- U18EE706 - Power Systems Lab Manual & Record - PNRDocument125 pagesU18EE706 - Power Systems Lab Manual & Record - PNRChinni ManthruthaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 at UUDocument18 pagesUnit 2 at UUSolomon AsefaNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: AmplifierDocument12 pagesOperating Manual: AmplifiermigfrayaNo ratings yet
- Stereo Power Amplifier Amplificador: Operating Instructions Mode D'emploi Manual de InstruccionesDocument2 pagesStereo Power Amplifier Amplificador: Operating Instructions Mode D'emploi Manual de InstruccioneshidraulicNo ratings yet
- CW1128 - 1179 (From 2P To 600P)Document2 pagesCW1128 - 1179 (From 2P To 600P)Jason SecretNo ratings yet
- BS en 1 - 2016 - 2013Document28 pagesBS en 1 - 2016 - 2013Abey VettoorNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Learning Kit PDFDocument95 pagesPower Supply Learning Kit PDFrootNo ratings yet
- 53Document5 pages53djahid abdullohNo ratings yet
- SLD 3500kvaDocument1 pageSLD 3500kvaRashedul IslamNo ratings yet
- Rear Panel Layout: Description ItemDocument4 pagesRear Panel Layout: Description ItemHector CabreraNo ratings yet
- Linear Actuator LA33 Data Sheet EngDocument36 pagesLinear Actuator LA33 Data Sheet EngMirko VeckiardoNo ratings yet
- Fluidic State of The Art Symposium PDFDocument406 pagesFluidic State of The Art Symposium PDFbaja2014No ratings yet
- HT73XX Low Power Consumption LDO: FeaturesDocument12 pagesHT73XX Low Power Consumption LDO: FeatureslenavalentinNo ratings yet
- IEEE STD 1653.2™-2009Document60 pagesIEEE STD 1653.2™-2009GustavoAdolfoJimenezGomezNo ratings yet
- Siemens Nxplus Ha 35 41 enDocument60 pagesSiemens Nxplus Ha 35 41 enst_calvo100% (1)
- Coatings: A Review On Anodizing of Aerospace Aluminum Alloys For Corrosion ProtectionDocument30 pagesCoatings: A Review On Anodizing of Aerospace Aluminum Alloys For Corrosion ProtectionChristopher ServantNo ratings yet
- IEEE 14 Bus Test SystemDocument3 pagesIEEE 14 Bus Test SystemAsty HatiNo ratings yet
- SMPS Di-124Document2 pagesSMPS Di-124venkatreachNo ratings yet
- Hrrs 5Kv and 10Kv Series High Resistance, 5kV and 10kV Decade Substituter User and Service ManualDocument18 pagesHrrs 5Kv and 10Kv Series High Resistance, 5kV and 10kV Decade Substituter User and Service Manualb4tipibeNo ratings yet
- Acudc Power Energy Meter d1 PDFDocument4 pagesAcudc Power Energy Meter d1 PDFManthan TilvaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements Syllabus EE203Document2 pagesElectrical Measurements Syllabus EE203Reeta DuttaNo ratings yet
- 1hsm 9543 12-00 Surge Arresters Buyers Guide Edition 8 2010-12 - English - Section Excount-IiDocument5 pages1hsm 9543 12-00 Surge Arresters Buyers Guide Edition 8 2010-12 - English - Section Excount-IilalitbickNo ratings yet
- Homework 6 Induction Motor 1 - de La CruzDocument3 pagesHomework 6 Induction Motor 1 - de La CruzAlvaro De La CruzNo ratings yet
- ANTENTOP-02 - 2004, # 006: 15 MetersDocument15 pagesANTENTOP-02 - 2004, # 006: 15 MetersfixitdazNo ratings yet
- B6 ProblemsDocument18 pagesB6 ProblemsMohit SahuNo ratings yet