Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Direct and Indirect Speech: You Tomorrow ."
Direct and Indirect Speech: You Tomorrow ."
Uploaded by
Deviana AnggrainiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Radio Jockeying and News Reading Unit-3: Voice Personality and Presentation TechniquesDocument6 pagesRadio Jockeying and News Reading Unit-3: Voice Personality and Presentation TechniquesDhruv S100% (1)
- Puluhan Contoh Kalimat Direct Dan Indirect Speech Beserta ArtinyaDocument106 pagesPuluhan Contoh Kalimat Direct Dan Indirect Speech Beserta ArtinyaDewi Purwanti20% (5)
- Coping With The Challenges of Intercultural Communication (Autosaved)Document27 pagesCoping With The Challenges of Intercultural Communication (Autosaved)ShailaMae Villegas100% (1)
- Indirect Speech: Reported StatementsDocument7 pagesIndirect Speech: Reported StatementsHamide Bahman PourNo ratings yet
- B 12 RDocument5 pagesB 12 RjoemacarraNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech 1Document22 pagesReported Speech 1gamzeNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument1 pageReported Speechhajar enneyahNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech Indirect Speech: I Like Chocolate. He Said He Liked Chocolate. He Told Me That He Liked ChocolateDocument2 pagesDirect Speech Indirect Speech: I Like Chocolate. He Said He Liked Chocolate. He Told Me That He Liked ChocolateLadyBlueRoNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported Speechfenix_miri00No ratings yet
- Reported Speech-1Document34 pagesReported Speech-1sanchisanchita9No ratings yet
- Direct Indirect SPHDocument17 pagesDirect Indirect SPHsafmaNo ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectDocument21 pagesDirect and Indirectgeetaryan01No ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported Speechmaggiesito1121No ratings yet
- TM Reported Speech Change ListDocument1 pageTM Reported Speech Change ListTeacher MonicaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Direct Speech: NAMA: Paris Nuratifah Nomor: 26 Kelas: Xii Ips 3Document3 pagesReported Speech Direct Speech: NAMA: Paris Nuratifah Nomor: 26 Kelas: Xii Ips 3ParisNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechDanielleOkNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument3 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechCarlos Alfonzo CalderónNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech Grade 9 NewDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech Grade 9 NewRumesh MadusankaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument20 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechChristian SiagianNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect Speech and Indirect SpeechAndreea PatrauteanuNo ratings yet
- Direct and Inderect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Inderect SpeechhyteddybearNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech For FCEDocument4 pagesReported Speech For FCEMarinaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect or Reported SpeechDocument17 pagesDirect and Indirect or Reported Speechолена когутNo ratings yet
- Materi Bulan April Minggu 1&2 A. Positive ImperativeDocument3 pagesMateri Bulan April Minggu 1&2 A. Positive ImperativeNk Yulia KireyNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesDirect and Reported SpeechadrianNo ratings yet
- Reported and Question Tags by Me 2021 Prep 1Document16 pagesReported and Question Tags by Me 2021 Prep 1Walid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect and Reported Speechkravecp698No ratings yet
- 2 Série - Recuperação Dia 2Document20 pages2 Série - Recuperação Dia 2luizjuniorNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Prośby (Requests) I Polecenia (Orders)Document4 pagesReported Speech: Prośby (Requests) I Polecenia (Orders)Klaudia KołodziejskaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ClassDocument4 pagesReported Speech ClassBeatrice 。No ratings yet
- Tenses FramesDocument3 pagesTenses FramesPrathap Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech-StatementsDocument11 pagesReported Speech-StatementsMiss Ale PellizaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect Speechnawa alafiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect MaterialDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect MaterialnuzulaNo ratings yet
- "I Often She Said (That) She OftenDocument5 pages"I Often She Said (That) She OftenKiberSalo322No ratings yet
- Y Formas Abstractas Trivia Juego Divertido PresentaciónDocument15 pagesY Formas Abstractas Trivia Juego Divertido PresentaciónSara Valentina Rivas SalasNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech TableDocument2 pagesReported Speech TableOrastean Andreea SimonaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Reported Sentences - MiceDocument14 pagesTopic 5 Reported Sentences - MiceadityafransiscolubisNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect NarrationDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect Narrationrizwan afzalNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech IntroductionDocument2 pagesReported Speech IntroductionDu PhamNo ratings yet
- Prefix Reported SpeechDocument9 pagesPrefix Reported Speechpazarmando0909No ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect & Indirect SpeechSilviNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech in EnglishDocument2 pagesIndirect Speech in EnglishOlga KukhtinaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech ExplanationDocument28 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech ExplanationImam AzharNo ratings yet
- 1317 Indirect SpeechDocument2 pages1317 Indirect SpeechVelika KaradjovaNo ratings yet
- 1317 Indirect SpeechDocument2 pages1317 Indirect SpeechVelika KaradjovaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument34 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJimin MochiNo ratings yet
- Indirect SpeechDocument29 pagesIndirect SpeechGabriel Antonio Macavilca AlmanzaNo ratings yet
- Tense Changes When Using Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesTense Changes When Using Reported SpeechVictoria Lipcean100% (1)
- Wonder, Want To Know: Stilo NdirectoDocument2 pagesWonder, Want To Know: Stilo NdirectoTD ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument14 pagesReported SpeechDiana PadillaNo ratings yet
- Direct An Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect An Indirect SpeechIvan RFCNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechMarcia TrellesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 35 Reported Speech PDFDocument11 pagesLesson 35 Reported Speech PDFArianneNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech 1Document24 pagesReported Speech 1avghvg123No ratings yet
- 6 - Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pages6 - Direct and Indirect SpeechBharathiNo ratings yet
- Use: "Report Speech": World English 4Document3 pagesUse: "Report Speech": World English 4osvvaldoNo ratings yet
- Lista Aula 27 - Discurso Direto e IndiretoDocument4 pagesLista Aula 27 - Discurso Direto e IndiretoEmerson ASNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledAsad RzayevNo ratings yet
- 12 B1b Reported SpeechDocument2 pages12 B1b Reported SpeechtworiversNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechANDREA VERONICA SALAZAR GARCIANo ratings yet
- The Planners by Boey KimDocument5 pagesThe Planners by Boey KimRadhika RuiaNo ratings yet
- Control Work "Being A Student". V - 1 Task #1. Match The WordsDocument3 pagesControl Work "Being A Student". V - 1 Task #1. Match The WordsСветлана ТрощиловаNo ratings yet
- Guía Virtual 5 Inglés Grado 10° Gladis Ramírez R.Document3 pagesGuía Virtual 5 Inglés Grado 10° Gladis Ramírez R.Chacho RamirezNo ratings yet
- Pedia 1.3 - Development Part 2 (Dany Targ) PDFDocument2 pagesPedia 1.3 - Development Part 2 (Dany Targ) PDFKaren ValdezNo ratings yet
- (89320) Grammar - All LevelsDocument19 pages(89320) Grammar - All LevelsAndreea MarinaNo ratings yet
- Middle EnglishDocument6 pagesMiddle EnglishAzhar Khan100% (1)
- Principles of Writing Good EnglishDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Writing Good EnglishTooba shafiqNo ratings yet
- Higher-Level and Lower-Level Text Processing Skills in Advanced ESL Reading ComprehensionDocument16 pagesHigher-Level and Lower-Level Text Processing Skills in Advanced ESL Reading ComprehensionDewi MaryamNo ratings yet
- Basic English Grammar 12 TensesDocument16 pagesBasic English Grammar 12 Tensesaa100% (1)
- CommunicationDocument5 pagesCommunicationRyan TomeldenNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Present Continuous. KENIA LAINEZDocument3 pagesSimple Present and Present Continuous. KENIA LAINEZKenia Lainez100% (1)
- Group 4Document2 pagesGroup 4Meg BabatinganNo ratings yet
- Grammar Summary Unit 1Document4 pagesGrammar Summary Unit 1Alison SanchoNo ratings yet
- ELE16 CONTENT AND PEDAGOGY IN THE - Google FormsDocument3 pagesELE16 CONTENT AND PEDAGOGY IN THE - Google FormsHeshell EllagaNo ratings yet
- Irregular and Regular Verbs TPCDocument3 pagesIrregular and Regular Verbs TPCLeandro MaioNo ratings yet
- IMT213 - 2022-2023 Course MaterialDocument104 pagesIMT213 - 2022-2023 Course MaterialMerveNo ratings yet
- SO 2nd Ed S UnitTest 10Document2 pagesSO 2nd Ed S UnitTest 10Juan Lopez - ESLNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-Grammar Past Irregular VerbsDocument1 pageLesson Plan-Grammar Past Irregular Verbsay1325819No ratings yet
- Athenaze 1 Chapter 7aDocument2 pagesAthenaze 1 Chapter 7amaverickpussNo ratings yet
- Year 1 Activity Book SampleDocument21 pagesYear 1 Activity Book SampleShenaya MalaikaNo ratings yet
- Possessive Adjectives With The Verb To BeDocument3 pagesPossessive Adjectives With The Verb To BeOmar Sanchez BecerraNo ratings yet
- Possession (John's Car, A Friend of Mine)Document10 pagesPossession (John's Car, A Friend of Mine)CarlosAbelFuentesRiveraNo ratings yet
- A Year Etc. Ago A Year Before/the Previous YearDocument2 pagesA Year Etc. Ago A Year Before/the Previous YearLiseth CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument2 pagesPast SimpleManu TámaraNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR 8 - Reflexive Verbs and PronounsDocument2 pagesGRAMMAR 8 - Reflexive Verbs and PronounsGonzalo Díaz-LetelierNo ratings yet
- Course Structure - Sem 1 and 2Document1 pageCourse Structure - Sem 1 and 2Nikita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exercises GRAMMAR 1st Unit Better Together V UTM-ILDocument4 pagesExercises GRAMMAR 1st Unit Better Together V UTM-ILStalin MSanNo ratings yet
- Meeting 1Document13 pagesMeeting 1ilhamNo ratings yet
Direct and Indirect Speech: You Tomorrow ."
Direct and Indirect Speech: You Tomorrow ."
Uploaded by
Deviana AnggrainiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Direct and Indirect Speech: You Tomorrow ."
Direct and Indirect Speech: You Tomorrow ."
Uploaded by
Deviana AnggrainiCopyright:
Available Formats
Yuli Choirul
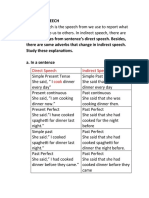
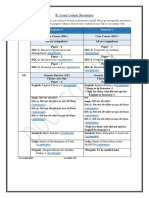
DIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH
DIRECT (Kalimat langsung): The sentence that is still original from the speaker without making any
changes.
He said to her, “I will visit you.”
Main Clause Sub Clause
David said, “I love you.”
Nadia says, “I am hungry.”
INDIRECT (Kalimat tidak langsung): The sentence that is used to rereport what the speaker said by making
some changes.
He said to her that he would visit her.
MC C SC
David said that he loved me.
Nadia says that she is hungry.
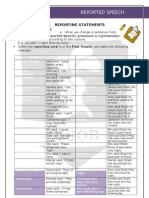
The rules of direct-indirect:
If the Main Clause is in Simple Present Tense/Present Perfect/Simple Future Tense, the tense of Sub
Clause is constant.
Direct: He says to her, “I will visit you tomorrow.”
Present Tense Simple Future Tense
INDIRECT: He says to her that he will visit her tomorrow.
Simple Future Tense
DIRECT: Yusuf has said, “I am coming.”
Present Perfect Present Tense
INDIRECT: Yusuf has said that he is coming.
Present Tense
DIRECT: Hafiza will say, “You are right.”
Simple Future Tense Present Tense
INDIRECT: Hafiza will tell you that you are right.
Present Tense
If the Main Clause is in Simple Past Tense/Past Perfect Tense, the tense of Sub Clause is usually
changes.
SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE ==> SIMPLE PAST TENSE
DIRECT: David said, “I love you.”
Simple Past T Simple Present T
INDIRECT: David said that he loved me.
Simple Past Tense
DIRECT: She explained, “I never do it.”
INDIRECT: She explained that she never did it
PRESENT CONTINUOUS/PROGRESSIVE TENSE ==> PAST CONTINUOUS/PROGRESSIVE TENSE
DIRECT: She said, “The boy is sleeping.”
Present Continuous Tense
INDIRECT: She said that the boy was sleeping.
Past Continuous Tense
DIRECT: Zidan said, “I am having lunch.”
INDIRECT: Zidan said that he was having lunch.
PRESENT PERFECT TENSE ==> PAST PERFECT TENSE
DIRECT: Rani said, “I have met him.”
Present Perfect Tense
INDIRECT: Rani said that she had met him.
Past Perfect Tense
Yuli Choirul
DIRECT: They explained, “We have done it.”
INDIRECT: They explained that they had done it.
PRESENT FUTURE TENSE ==> PAST FUTURE TENSE
DIRECT: Lidya said, “Rio will do it.”
Present Future T
INDIRECT: Lidya said that Rio would do it.
Past Future Tense
DIRECT: He said to her, “I will visit you tomorrow.”
INDIRECT: He said to her that he would visit her the following day.
SIMPLE PAST TENSE ==> PAST PERFECT TENSE
DIRECT: He said, “I ate apple.”
Simple Past T Simple Past T
INDIRECT: He said that he had eaten apple.
Past Perfect Tense
DIRECT: She explained, “I did it yesterday.”
INDIRECT: She explained that she had done it the day before .
If the content of Sub Clause is the general truth, the tense of Sub Clause doesn’t change although the
Main Clause is in Past Tense.
DIRECT: He says/said to him, “The world is round.”
General Truth
INDIRECT: He says/said to him that The world is round.
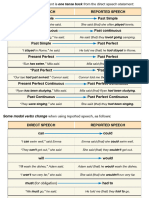
The changes of auxiliary verbs:
DIRECT INDIRECT
Do/Does Did
Have/Has Had
Am/Are/Is Was/Were
Was/Were Had been
Will/Shall Would/Should
Can Could
May Might
Must/Have to/Has to ..… Had to ..…
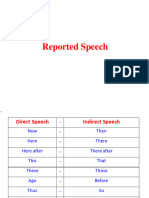
The changes of adverbs:
DIRECT INDIRECT
Now Then
This That
These Those
Here There
Yesterday The day before
Tomorrow The day after
Today That day
Tonight That night
Last night The night before
Last week/month The week/month before
Next Sunday The Sunday after
Two days ago The two days before
Two days later The following two days
The day after tomorrow ….. In two days’ time ..…
He said, “I met him yesterday.” He said that he had met him the day
She said, “I will do it tomorrow.” before.
She said that she would do it the next day.
PRONOUNS (Kata Ganti)
Yuli Choirul
Subject Pronoun : I, You, They, We, She, He, It.
Object Pronoun : Me, You, Them, Us, Her, Him, It.
You might also like
- Radio Jockeying and News Reading Unit-3: Voice Personality and Presentation TechniquesDocument6 pagesRadio Jockeying and News Reading Unit-3: Voice Personality and Presentation TechniquesDhruv S100% (1)
- Puluhan Contoh Kalimat Direct Dan Indirect Speech Beserta ArtinyaDocument106 pagesPuluhan Contoh Kalimat Direct Dan Indirect Speech Beserta ArtinyaDewi Purwanti20% (5)
- Coping With The Challenges of Intercultural Communication (Autosaved)Document27 pagesCoping With The Challenges of Intercultural Communication (Autosaved)ShailaMae Villegas100% (1)
- Indirect Speech: Reported StatementsDocument7 pagesIndirect Speech: Reported StatementsHamide Bahman PourNo ratings yet
- B 12 RDocument5 pagesB 12 RjoemacarraNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech 1Document22 pagesReported Speech 1gamzeNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument1 pageReported Speechhajar enneyahNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech Indirect Speech: I Like Chocolate. He Said He Liked Chocolate. He Told Me That He Liked ChocolateDocument2 pagesDirect Speech Indirect Speech: I Like Chocolate. He Said He Liked Chocolate. He Told Me That He Liked ChocolateLadyBlueRoNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported Speechfenix_miri00No ratings yet
- Reported Speech-1Document34 pagesReported Speech-1sanchisanchita9No ratings yet
- Direct Indirect SPHDocument17 pagesDirect Indirect SPHsafmaNo ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectDocument21 pagesDirect and Indirectgeetaryan01No ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported Speechmaggiesito1121No ratings yet
- TM Reported Speech Change ListDocument1 pageTM Reported Speech Change ListTeacher MonicaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Direct Speech: NAMA: Paris Nuratifah Nomor: 26 Kelas: Xii Ips 3Document3 pagesReported Speech Direct Speech: NAMA: Paris Nuratifah Nomor: 26 Kelas: Xii Ips 3ParisNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechDanielleOkNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument3 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechCarlos Alfonzo CalderónNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech Grade 9 NewDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech Grade 9 NewRumesh MadusankaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument20 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechChristian SiagianNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect Speech and Indirect SpeechAndreea PatrauteanuNo ratings yet
- Direct and Inderect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Inderect SpeechhyteddybearNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech For FCEDocument4 pagesReported Speech For FCEMarinaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect or Reported SpeechDocument17 pagesDirect and Indirect or Reported Speechолена когутNo ratings yet
- Materi Bulan April Minggu 1&2 A. Positive ImperativeDocument3 pagesMateri Bulan April Minggu 1&2 A. Positive ImperativeNk Yulia KireyNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesDirect and Reported SpeechadrianNo ratings yet
- Reported and Question Tags by Me 2021 Prep 1Document16 pagesReported and Question Tags by Me 2021 Prep 1Walid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect and Reported Speechkravecp698No ratings yet
- 2 Série - Recuperação Dia 2Document20 pages2 Série - Recuperação Dia 2luizjuniorNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Prośby (Requests) I Polecenia (Orders)Document4 pagesReported Speech: Prośby (Requests) I Polecenia (Orders)Klaudia KołodziejskaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ClassDocument4 pagesReported Speech ClassBeatrice 。No ratings yet
- Tenses FramesDocument3 pagesTenses FramesPrathap Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech-StatementsDocument11 pagesReported Speech-StatementsMiss Ale PellizaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect Speechnawa alafiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect MaterialDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect MaterialnuzulaNo ratings yet
- "I Often She Said (That) She OftenDocument5 pages"I Often She Said (That) She OftenKiberSalo322No ratings yet
- Y Formas Abstractas Trivia Juego Divertido PresentaciónDocument15 pagesY Formas Abstractas Trivia Juego Divertido PresentaciónSara Valentina Rivas SalasNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech TableDocument2 pagesReported Speech TableOrastean Andreea SimonaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Reported Sentences - MiceDocument14 pagesTopic 5 Reported Sentences - MiceadityafransiscolubisNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect NarrationDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect Narrationrizwan afzalNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech IntroductionDocument2 pagesReported Speech IntroductionDu PhamNo ratings yet
- Prefix Reported SpeechDocument9 pagesPrefix Reported Speechpazarmando0909No ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect & Indirect SpeechSilviNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech in EnglishDocument2 pagesIndirect Speech in EnglishOlga KukhtinaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech ExplanationDocument28 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech ExplanationImam AzharNo ratings yet
- 1317 Indirect SpeechDocument2 pages1317 Indirect SpeechVelika KaradjovaNo ratings yet
- 1317 Indirect SpeechDocument2 pages1317 Indirect SpeechVelika KaradjovaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument34 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJimin MochiNo ratings yet
- Indirect SpeechDocument29 pagesIndirect SpeechGabriel Antonio Macavilca AlmanzaNo ratings yet
- Tense Changes When Using Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesTense Changes When Using Reported SpeechVictoria Lipcean100% (1)
- Wonder, Want To Know: Stilo NdirectoDocument2 pagesWonder, Want To Know: Stilo NdirectoTD ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument14 pagesReported SpeechDiana PadillaNo ratings yet
- Direct An Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect An Indirect SpeechIvan RFCNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechMarcia TrellesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 35 Reported Speech PDFDocument11 pagesLesson 35 Reported Speech PDFArianneNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech 1Document24 pagesReported Speech 1avghvg123No ratings yet
- 6 - Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pages6 - Direct and Indirect SpeechBharathiNo ratings yet
- Use: "Report Speech": World English 4Document3 pagesUse: "Report Speech": World English 4osvvaldoNo ratings yet
- Lista Aula 27 - Discurso Direto e IndiretoDocument4 pagesLista Aula 27 - Discurso Direto e IndiretoEmerson ASNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledAsad RzayevNo ratings yet
- 12 B1b Reported SpeechDocument2 pages12 B1b Reported SpeechtworiversNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechANDREA VERONICA SALAZAR GARCIANo ratings yet
- The Planners by Boey KimDocument5 pagesThe Planners by Boey KimRadhika RuiaNo ratings yet
- Control Work "Being A Student". V - 1 Task #1. Match The WordsDocument3 pagesControl Work "Being A Student". V - 1 Task #1. Match The WordsСветлана ТрощиловаNo ratings yet
- Guía Virtual 5 Inglés Grado 10° Gladis Ramírez R.Document3 pagesGuía Virtual 5 Inglés Grado 10° Gladis Ramírez R.Chacho RamirezNo ratings yet
- Pedia 1.3 - Development Part 2 (Dany Targ) PDFDocument2 pagesPedia 1.3 - Development Part 2 (Dany Targ) PDFKaren ValdezNo ratings yet
- (89320) Grammar - All LevelsDocument19 pages(89320) Grammar - All LevelsAndreea MarinaNo ratings yet
- Middle EnglishDocument6 pagesMiddle EnglishAzhar Khan100% (1)
- Principles of Writing Good EnglishDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Writing Good EnglishTooba shafiqNo ratings yet
- Higher-Level and Lower-Level Text Processing Skills in Advanced ESL Reading ComprehensionDocument16 pagesHigher-Level and Lower-Level Text Processing Skills in Advanced ESL Reading ComprehensionDewi MaryamNo ratings yet
- Basic English Grammar 12 TensesDocument16 pagesBasic English Grammar 12 Tensesaa100% (1)
- CommunicationDocument5 pagesCommunicationRyan TomeldenNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Present Continuous. KENIA LAINEZDocument3 pagesSimple Present and Present Continuous. KENIA LAINEZKenia Lainez100% (1)
- Group 4Document2 pagesGroup 4Meg BabatinganNo ratings yet
- Grammar Summary Unit 1Document4 pagesGrammar Summary Unit 1Alison SanchoNo ratings yet
- ELE16 CONTENT AND PEDAGOGY IN THE - Google FormsDocument3 pagesELE16 CONTENT AND PEDAGOGY IN THE - Google FormsHeshell EllagaNo ratings yet
- Irregular and Regular Verbs TPCDocument3 pagesIrregular and Regular Verbs TPCLeandro MaioNo ratings yet
- IMT213 - 2022-2023 Course MaterialDocument104 pagesIMT213 - 2022-2023 Course MaterialMerveNo ratings yet
- SO 2nd Ed S UnitTest 10Document2 pagesSO 2nd Ed S UnitTest 10Juan Lopez - ESLNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-Grammar Past Irregular VerbsDocument1 pageLesson Plan-Grammar Past Irregular Verbsay1325819No ratings yet
- Athenaze 1 Chapter 7aDocument2 pagesAthenaze 1 Chapter 7amaverickpussNo ratings yet
- Year 1 Activity Book SampleDocument21 pagesYear 1 Activity Book SampleShenaya MalaikaNo ratings yet
- Possessive Adjectives With The Verb To BeDocument3 pagesPossessive Adjectives With The Verb To BeOmar Sanchez BecerraNo ratings yet
- Possession (John's Car, A Friend of Mine)Document10 pagesPossession (John's Car, A Friend of Mine)CarlosAbelFuentesRiveraNo ratings yet
- A Year Etc. Ago A Year Before/the Previous YearDocument2 pagesA Year Etc. Ago A Year Before/the Previous YearLiseth CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument2 pagesPast SimpleManu TámaraNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR 8 - Reflexive Verbs and PronounsDocument2 pagesGRAMMAR 8 - Reflexive Verbs and PronounsGonzalo Díaz-LetelierNo ratings yet
- Course Structure - Sem 1 and 2Document1 pageCourse Structure - Sem 1 and 2Nikita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exercises GRAMMAR 1st Unit Better Together V UTM-ILDocument4 pagesExercises GRAMMAR 1st Unit Better Together V UTM-ILStalin MSanNo ratings yet
- Meeting 1Document13 pagesMeeting 1ilhamNo ratings yet